
When to use Active Voice:
When the focus is on an agent, the sentence is used in active mode.
This grammar section explains English Grammar in a clear and simple way. There are example sentences to show how the language is used. You can also visit the most accurate and elaborate NCERT Solutions for Class 8 English. Every question of the textbook has been answered here.
Active And Passive Voice Exercises for Class 8 With Answers CBSE Pdf
‘Voice’ is a grammatical category that applies to sentences. Voice in English expresses the relationship of the subject to the action.
Voice has two values:
- Active: the subject does the action
- Passive: the subject receives the action
| Active | Shakespeare | wrote | Hamlet. | |||
| Passive | Hamlet | was written | by | Shakespeare |
The active voice is the ‘normal’ voice – the one that we use most of the time. In the active voice, the object receives the action stated by the verb.
| active | subject | verb | object |
| Cats | eat | mice. |
The passive voice is less common. In passive voice, the subject receives the action stated by the verb.
| passive | subject | verb | object |
| Mice | are eaten | by cats |
See how the object of the active voice becomes the subject of the passive voice.
| subject | verb | object | |
| active | Everybody | drinks | water. |
| passive | Water | is drunk | by everybody |
Active Voice
Cats eat mice:
The active voice is the “normal” voice of an English sentence. Intransitive verbs (verbs with no direct object) are always in active voice. Transitive verbs are usually in active voice.
| subject | verb | |
| Johnny | laughed | |
| Amit | got up | late. |
| People | drink | water |
In active voice, the subject is the person or thing responsible for the action described by the verb.
All tenses are possible in the active voice, as well as all sentence types, positive, negative or interrogative.
Use of Active
The active voice is the “default” voice in English. All intransitive verbs can only be in the active voice, and all transitive verbs usually are active voice – unless we deliberately make them passive.
The active voice is:
- direct and specific
- uses fewer words – which is usually good thing
- dynamic
Except on occasions when passive voice is more useful, active voice is the voice of choice.
Passive Voice
Mice are eaten by cats:
Although passive voice is less common than active voice, there are several good reasons to sometimes use passive voice. On the next page we look at how to construct sentences in passive voice and when and why to use it.
How do we make a sentence in passive voice?
The basic structure of a passive clause is very simple:
| Subject | + | Auxiliary verb be | + | Main verb past participle | + | by | + | Agent |
| optional |
The auxiliary be is conjugated in all tenses. The main verb is always the past participle. The agent is the original “doer” of the action.
Look at some examples.
| subject | the auxiliary verb be past participle | main verb | by | |
| I | am | employed | by | Apple. |
| You | will be | woken up | at 6. | |
| It | will have been | finished | by then. | |
| We | have been | notified | by | Head Office. |
| You | are being | transferred | next week. | |
| They | will be | paid. |
Note that:
- auxiliary be can be conjugated for all persons and tenses.
- main verb is invariable: past participle
- if there is an agent {Apple, Head Office), it is introduced by ‘by’.
Agentless passive
The subject of an active sentence ‘does’ the action. In a passive sentence, we express the doer (or agent) through a ‘by’ phrase (the long passive) or, very often, we remove the agent completely (the short passive). In the following example, the agent is ‘the Allies’:
| active | The Allies firebombed the fort. | |
| passive | long | The fort was firebombed by the Allies. |
| short | Fort was firebombed. | |
The short passive is also known as the “agentless passive”. Soon you will see how useful it can be.
Negatives and questions
The table below shows examples of passive voice in negative sentences, question sentences and negative-question sentences:
| subject | auxiliary verb be | main verb past participle |
|||||
| You | are | not | paid | to watch YouTube. | |||
| They | will | never | be | employed | by us. | ||
| Are | they | cleaned | regularly? | ||||
| Has | your wallet | been | stolen? | ||||
| Is | he | not | notified | immediately? | |||
| Will | they | not | be | dismissed? | |||
| Haven’t | they | been | forgotten? |
Note that:
- position of auxiliary be or first auxiliary for questions
- possible positions of not, n’t, never to create negation
Use of the passive
When and why do we use passive voice?
There are several times when passive voice is useful, and usually the decision has to do with the “doer” (agent) or the “receiver” of the action. For example, we use passive when:
1. We want to emphasise the receiver of the action.
- President Kennedy was killed by Lee Harvey Oswald,
- cf: Lee Harvey Oswald killed President Kennedy.
2. We don’t know who did the action (the agent):
- My wallet has been stolen.
- cf: Somebody has stolen my wallet.
3. We think the agent is not important or interesting:
- Our house is being painted.
- cf: XYZ Company is painting our house.
4. The agent is obvious.
- I am paid weekly.
- cf: My company pays me weekly.
5. We are making general statements or announcements.
- Passengers are reminded to fasten their seatbelts.
- cf: The captain reminds passengers to fasten their seatbelts.
6. The agent is everyone.
- The emergency services can be called by dialing 999.
- cf: The public can call the emergency services by dialing 999.
7. When writing formal or scientific texts.
- Potassium was added and mixed in. The solution was heated to 80°C and then allowed to cool.
- cf: The observer added potassium and mixed it in. The observer heated the solution to 80°C and then allowed it to cool.
8. We want to avoid responsibility for our own actions (typically found in government reports):
- Mistakes were made and unfortunately never rectified.
- cf: The Prime Minister made mistakes and unfortunately never rectified them.
Look at this sentence.
He was killed with a gun:
Normally we use by to introduce the agent. But the gun is not the original doer of the action. The gun did not kill him. He was killed by somebody with a gun. In the active voice, it would be: Somebody killed him with a gun. Somebody is the agent. The gun is the instrument.
The get-passive
Although we normally construct the passive with be + past participle, it is also possible (in informal language) to use get + past participle. So if France beat England at football, we could turn this to passive and say “England were beaten by France” (de-passive) or “England got beaten by France” {get-passive). And we might also add: “But France will get thrashed by Russia.”
For formal English and exams you should use the be-passive, but in informal language people sometimes use the gef-passive.
Forms of passive
The passive voice is not a tense itself. But for transitive verbs each tense, as well as other verb forms such as infinitives and participles, can be produced in the passive voice. Some of the more complicated tenses (mostly perfect continuous) are rarely used in the passive, but they are possible.
Here are some examples of passive voice with many of the possible forms using the verb sing:
| infinitive | to be sung | ||
| perfect infinitive | to have been sung | ||
| participle | sung | ||
| perfect participle | having been sung | ||
| gerund | being sung | ||
| Simple | Continuous | Perfect | |
| Present | am, are, is sung | am, are, is being sung | have, has been sung |
| Past | was, were sung | was, were being sung | had been sung |
| Future | will be sung | will be being sung | will have been sung |
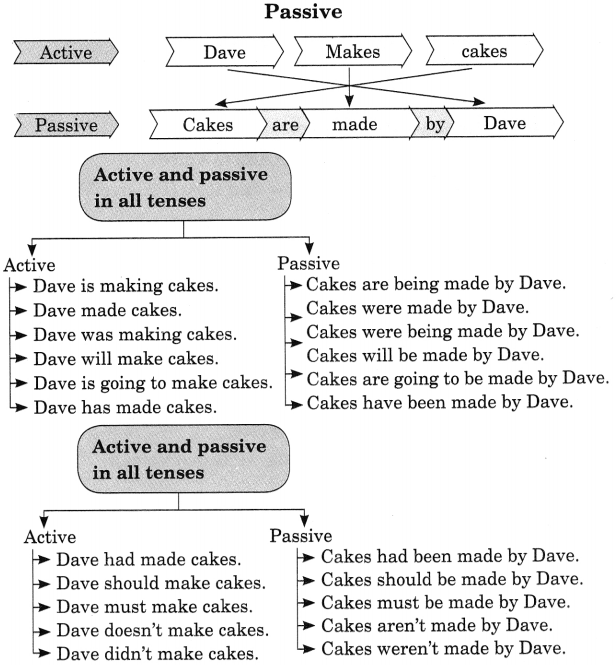
Active and Passive Examples
The table below shows example of sentences in active and passive voice for the basic tenses as well as various other verb forms, including infinitives and participles.
| Active | Passive | |
| Present Simple | How does one pronounce his name? | How is his name pronounced? |
| Present Continuous | Ati’s helping Tara. | Tara’s being helped by Ati. |
| Present Perfect | The kid has served dinner. | Dinner has been served. |
| Past Simple | They did n’t fix my phone yesterday. | My phone wasn’t fixed yesterday. |
| Past Continuous | They were interrogating him when I called. | He was being interrogated when I called. |
| Past Perfect | I wondered why they hadn’t invited me. | I wondered why I hadn’t been invited. |
| Future Simple | They will hang him at dawn. | He will be hanged at dawn. |
| Future Continuous | They won’t be questioning him when you get there. | He won’t be being questioned when you get there. |
| Future Perfect | They will have repaired your car by 7pm. | Your car will have been repaired by 7pm. |
| Infinitive | I don’t want anyone to disturb me. | I don’t want to be disturbed. |
| Perfect infinitive | They seem to have taken it. | It seems to have been taken. |
| Participle | I saw the cat eating it. | I saw it being eaten by the cat. |
| Perfect participle | Having finished my work, I went home. | My work having been finished, I went home. |
| Gerund | I insisted on them paying me. | I insisted on being paid. |
| Going to | Is he going to sing Thriller at the party? | Is Thriller going to be sung at the party? |
| Used to | Ram used to take care of everything. | Everything used to be taken care of by Ram. |
| Can | They can question him for six hours. | He can be questioned for six hours. |
| Could | It could have badly hurt you. | You could have been badly hurt. |
| Way | The papers say they may release him. | The papers say he may be released. |
| Might | Somebody might buy it. | It might be bought. |
| Must | Passengers must wear seat belts. | Seat belts must be worn. |
| Should | You should have told me. | I should have been told. |
| Ought to | They ought to forgive him. | He ought to be forgiven. |
Passive Voice in Interrogative Sentences
- The question words when, why, where, how and what do not change their position at the beginning of the sentence when the active voice is changed into the passive voice.
- Note that who changes to by whom and whom into who.
Examples
- What did he say? (Active Voice)
What was said by him? (Passive Voice) - Whom did you invite? (Active Voice)
Who was invited by you? (Passive Voice) - Who wrote this book? (Active Voice)
By whom was this book written? (Passive Voice)
Passive Voice in Imperative Sentences
- These are the sentences in which we express commands, order, advice and requests.
- Passive Imperative Sentence Formation:-
- Lets + object + be/not be +past participle or 3rd form.
- For sentences containing requests advice and orders, we use you are requested to, advised to and ordered to.
- Always remove ‘please’ and ‘kindly’ if they are given in the sentence.
Examples
| Active Voice | Passive Voice |
| Shut the door. | Let the door be shut. |
| Post the letter at once. | Let the letter be posted at once. |
| Always speak the truth. | Let the truth always be spoken. |
| Do not starve the cow. | Let the cow not be starved. |
| Let him help his brother. | Let his brother be helped by him. |
| Clean your room. | Let your room be cleaned. |
| Learn your lesson. | Let your lesson be learnt. |
| Please do me a favour tonight. | You are requested to do me a favour tonight. |
| Get out of my house. | You are ordered to get out of my house. |
| Kindly do not smoke in public place. | You are requested not to smoke in public place. |
To make passive voice, we use the following rules.
1. Change the object into subject. If as an object, we have a pronoun than we convert it as follows:
| Active | Passive |
| Me | I |
| You | You |
| Her | She |
| Them | They |
| Us | We |
| Him | He |
| It | It |
| Whom | Who |
2. Change the subject into object. And use ‘by’ before the object. If as a subject, we have a pronoun of nominative then we convert it as follows:
| Active | Passive |
| I | by me |
| You | by you |
| She | by her |
| They | by them |
| We | by us |
| He | by him |
| It | by it |
| Who | by whom |
An imperative sentence is changed from active to passive voice according to the message contained in the sentence. For this purpose words used are as follows:
If ¡t contains an order or a command: – You are ordered to or You are commanded to
If it contains a request: – You are requested to
If it contains advice: – You are advised to
If it contains a negative order: – You are forbidden to
If it contains ‘Let us’: – It is suggested that we should or It is proposed that we should
It is time to (verb first form) – It is time for (object) to be (verb third form)
Active And Passive Voice Exercises Solved Examples for Class 8 CBSE
Question 1.
Change the following sentences into passive voice.
(i) The principal has forbidden smoking on the campus.
(ii) The principal has forbidden students to smoke on the campus.
(iii) I advise consulting a good doctor.
(iv) I advise you to consult a good doctor.
(v) They don’t allow parking in front of their gate.
(vi) They don’t allow people to park in front of their gate.
(vii) We advise early booking.
(viii) We advise passengers to book their tickets early.
(ix) They made her repeat the whole story.
(x) We don’t advise pregnant women to go on a diet.
Answer:
(i) Smoking has been forbidden on the campus.
(ii) Students have been forbidden to smoke on the campus.
(iii) Consulting a good doctor is advised.
(iv) You are advised to consult a good doctor.
(v) Parking in front of their gate is not allowed.
(vi) People are not allowed to park in front of their gate.
(vii) Early booking is advised.
(viii) Passengers are advised to book their tickets early.
(ix) She was made to repeat the whole story
(x) Pregnant women are not advised to go on a diet.
Question 2,
Change the voice.
(i) Ms. Sullivan teaches us grammar.
(ii) The teacher praised him.
(iii) The firemen took the injured to the hospital.
(iv) An earthquake destroyed the town.
(v) The boy’s work pleased the teacher.
(vi) The fire damaged the building.
(vii) Who taught you French?
(viii) The manager will give you a ticket.
(ix) Spectators thronged the streets.
(x) Everyone will blame us.
(xi) The wind blew down the trees.
(xii) The police caught the thieves.
(xiii) Alice posted the letter.
(xiv) The hostess received us.
(XV) They/somebody killed the snake with a stick.
(xvi) The people welcomed the minister.
(xvii) They found him guilty of murder.
(xviii) John Mathews built this house in 1991.
Answer:
(i) We are taught grammar by Ms Sullivan.
(ii) He was praised by the teacher.
(iii) The injured were taken to the hospital by the fireman.
(iv) The town was destroyed by an earthquake.
(v) The teacher was pleased with the boy’s work.
(vi) The building was damaged by the fire.
(vii) By whom were you taught French?
(viii) You will be given a ticket by the manager.
(ix) The streets were thronged with spectators.
(x) We will be blamed by everyone.
(xi) The trees were blown down by the wind.
(xii) The thieves were caught by the police.
(xiii) The letter was posted by Alice.
(xiv) We were received by the hostess.
(xv) The snake was killed with a stick.
(xvi) The minister was welcomed by the people.
(xvii) He was found guilty of murder. See
(xviii) This house was built by John Mathews in 1991.
Question 3.
Test your knowledge of active and passive voice with this grammar exercise. Each sentence given below is in the active voice. Change it into a passive voice.
(i) He sings a song.
_______________________________________________
(ii) The boy killed the spider.
________________________
(iii) Help him.
________________________
(iv) Farmers sow maize in the rainy season.
________________________
(v) Are you writing a letter?
________________________
Answer:
(i) A song is sung by him. (Active verb – sings; passive verb – is sung)
(ii) The spider was killed by the boy. (Active verb – killed; passive verb – was killed)
(iii) Let him he helped. (imperative sentences in the passive voice begin with let.)
(iv) Maize is sown in the rainy season. (Active verb – sow; passive verb – is/are sown)
(v) Is a letter being written by you? (Active verb – is/are writing; passive verb – is/are being written)
Active And Passive Voice Exercises Practice Examples for Class 8 CBSE
Question 1.
Change into passive voice
1. Lata sings lovely songs.
2. We did not grow rice.
3. What do you want?
4. They will run a race.
5. Tom is building a house.
6. I was writing a letter.
7. Someone has stolen my purse.
8. She had finished her work.
9. People will admire him.
10. Did no one help you?
11. Will she deliver the message?
12. Respect your elders.
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks using the most suitable passive form of the verbs given in brackets. The first one has been done for you.
1. There’s somebody behind us. I think we are being followed (follow).
2. A mystery is something that ____________ (can’t/explain).
3. We didn’t play football yesterday. The match ____________ (cancel).
4. The television ____________ (repair). It’s working again now.
5. The church tower ____________ (restore). The work is almost finished.
6. ‘How old is the tower?’ ‘It ____________ (believe) to be over 600 years old.’
7. If I didn’t do my job properly, I ____________ (would/sack).
8. A: I left some papers on the desk last night and I can’t find them now.
B: They ____________ (might/throw) away.
9. I learnt to swim when I was very young. I ____________ (teach) by my mother.
10. After ____________ (arrest), I was taken to the police station.
11. ____________ (you/ever/arrest) ?’ ‘No, never.’
12. Two people ____________ (report) to ____________ (injure) in an explosion at a factory in Surat early this morning.
Question 3.
Change the following sentences into passive voice. The first one has been done for you.
1. I am sure they will take care of the child properly
I am sure that the child will be taken care of properly.
2. Someone is conducting research into the private life of that great sculptor.
______________________________________________________
3. People consider him to be the richest man in the country.
______________________________________________________
4. They say that these herbs are good for rheumatism.
______________________________________________________
5. We think that she is the most understanding and patient teacher in the school.
______________________________________________________
6. We shall have to deal with these problems one at a time.
______________________________________________________
7. They took down the old notice, but they put up another one in its place.
______________________________________________________
8. The teacher ordered Suresh out of the classroom because he was making too much noise.
______________________________________________________
9. We understand that his invention is of the greatest importance and secrecy.
______________________________________________________
10. The family left the hall lights on in case they decided to come back that night.
______________________________________________________
CBSE Class 8 English Grammar
- Noun Exercises for Class 8
- Pronoun Exercise for Class 8
- Adjectives Exercises for Class 8
- Subject Verb Agreement Exercises for Class 8
- Adverb Exercises for Class 8
- Preposition Exercise for Class 8
- Conjunction Exercise for Class 8
- Interjections Exercises for Class 8
- Tenses Exercise for Class 8
- Active And Passive Voice Exercises for Class 8
- Reported Speech Exercises for Class 8
- Sentences Exercises for Class 8
- Modals Exercises for Class 8
- Integrated Exercises