These Solutions are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption.
Class 11 Biology Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption NCERT Solutions
Digestion and Absorption NCERT Solutions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer among the following:
(a) Gastric juice contains
(i) pepsin, lipase, and rennin
(ii) trypsin, lipase, and rennin
(iii) trypsin, pepsin, and lipase
(iv) trypsin, pepsin, and rennin
(b) Succuss enterics is the name given to:
(i) a junction between the ileum and large intestine
(ii) intestinal juice
(iii) swelling in the gut
Solution:
(a) (i) Pepsin, lipase, and rennin
(b) (ii) Intestinal juice
Question 2.
Match column I with column II
Column I Column II
(a) Bilirubin and biliverdin (i) Parotid
(b) Hydrolysis of starch (ii) Bile
(c) Digestion of fat (iii) Lipases
(d) Salivary gland (iv) Amylases
Solution:
Column I Column II
(a) Bilirubin and biliverdin (ii) Bile
(b) Hydrolysis of starch (iv) Amylases
(c) Digestion of fat (iii) Lipases
(d) Salivary gland (i) Parotid
Question 3.
Answer briefly:
(a) Why are villi present in the intestine and not in the stomach?
(b) How does pepsinogen change into its active form?
(c) What are the basic layers of the wall of the alimentary canal?
(d) How does bile help in the digestion of fats
Solution:
(a) Villi increases surface area for absorption and maximum absorption takes place in the intestine.
(b) Coming in contact with hydrochloric acid in stomach proenzyme pepsinogen convert to its active form pepsin, the proteolytic enzyme of the stomach.
(c) There are four basic layers in the wall of alimentary canal i.e. serosa, muscularis, submucosa and mucosa.
(d) Bile helps in the emulsification of fats i.e. breakdown the fats into very small micelles. Bile also activates lipases.
Question 4.
State the role of pancreatic juice in the digestion of proteins.
Solution:
Pancreatic juice contains inactive enzymes like trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, procarboxypeptidases. Trypsinogen is activated by an enzyme enterokinase secreted by the intestinal mucosa into active trypsin which in turn activates other enzymes in the pancreatic juice. Proteins, proteases, and peptones in the chyme are digested by the proteolytic enzymes of pancreatic juice.
Question 5.
Describe the process of digestion of protein in the stomach.
Solution:
The mucosa of the stomach has gastric glands that secrete mucus, proenzyme pepsinogen, HCl, and intrinsic factor. Intrinsic factor is essential for the absorption of vitamin B12. The food mixes thoroughly with acidic gastric juice of the stomach and called the chyme. The proenzyme pepsinogen on exposure to HC1 gets converted to active enzyme pepsin. Pepsin converts proteins into proteases and peptones. Renin found in the gastric juice of infants also helps in the digestion of milk protein.
Question 6.
Give the dental formula of human beings.
Solution:
Dental formula of human beings is 2123/2123.
Question 7.
Bile juice contains no digestive enzymes, yet it is important for digestion. Why?
Solution:
The bile juice released into the duodenum contains bile pigments (bilirubin and biliverdin), bile salts, cholesterol, and phospholipids but no enzymes. Bile helps in the emulsification of fats i.e. break down the fats into very small micelles. Bile also activates lipases. Bile is alkaline (pH about 8). Bile pigments are excreted in faeces. In absence of HCl, the above-mentioned functions will not occur and digestion of food will be affected.
HCl of the gastric juice may cause gastric or duodenal ulcers and damage, the underlying blood vessels. These cause hemorrhage inside. Strong HCl is produced in stress conditions also. Parental or oxyntic cells which secrete HCl and intrinsic factor (Intrinsic factor is essential for the absorption of vitamin B2)
Some NCLEX RN Practice Questions involve analyzing data from laboratory reports, diagnostic tests, and client assessments.
Question 8.
Describe the digestive role of chymotrypsin. Which two other digestive enzymes of the same category are secreted by their source gland?
Solution:
Chymotrypsin changes proteins into peptides and also milk protein, changes into paracasein (curd). The pancreatic juice contains inactive enzymes, trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, procarboxypeptidases, amylases, lipases and nucleases. Trypsinogen is activated by an enzyme, enterokinase, secreted by the intestinal mucosa into active trypsin, which in turn activates the other enzymes in the pancreatic juice.
Trypsin changes proteases and peptones into peptides and amino acids. Procarboxypetidases change peptides into small peptides and amino acids. Amylases change starch into maltose. Lipases change emulsified fat into fatty acids and glycerol. Nucleases changes nucleotides into phosphate, sugar and nitrogen bases.
Question 9.
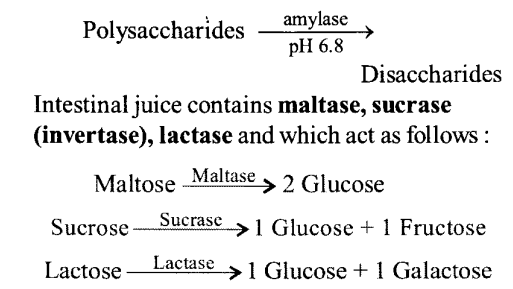
How are polysaccharides and disaccharides digested?
Solution:
(a) Digestion of carbohydrates starts in the mouth cavity with the help of enzymes salivary amylase.
Question 10.
What would happen if HCl were not secreted in the stomach?
Solution:
HCl is secreted by oxyntic cells in the stomach wall and performs five functions:
- Kill bacteria and germs
- Loosens fibrous material of food.
- Activates proenzyme pepsinogen to its active form pepsin.
- Gives an acidic medium for action by pepsin.
- Curdles milk. Pepsin changes proteins into proteases and peptones.
Question 11.
How does butter in your food get digested and absorbed in the body?
Solution:
Butter is a kind of fat. Fats are broken down by lipases with the help of bile into di- and monoglycerides:
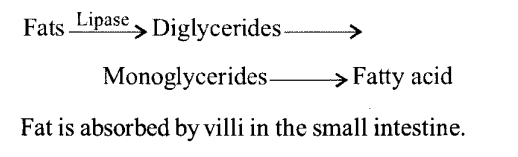
Question 12.
Discuss the main steps in the digestion of proteins as the food passes through different parts of the alimentary canal.
Solution:
(a) In the stomach the proenzyme pepsinogen, on exposure to HC1 converted into active pepsin that converts proteins into proteases and peptones.
![]()
(b) Proteins, proteases and peptides in the chyme reaching the intestine are acted upon by proteolytic enzymes of pancreatic juice and converted to dipeptides.
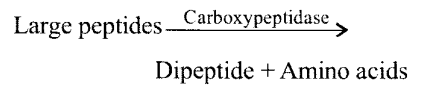
(c) The enzymes in succuss entericus act on the end product to form amino acids.
![]()
Question 13.
Explain the terms thecodont and diphyodont.
Solution:
Thecodont: In human beings, teeth are
embedded in pits, the sockets of the jawbones. Such teeth are called the thecodont.
Diphyodont: The teeth that appear in two sets, i. e., milk-teeth which are later replaced by permanent teeth. This condition is called diphyodont.
Question 14.
Name different types of teeth and their number in an adult human.
Solution:
Incisors – 8
Canines – 4
Premolars – 8
Molars – 12
Question 15.
What are the functions of the liver?
Solution:
- Secretion of bile
- Synthesis of blood clotting factors
- Regulating carbohydrate, protein, and lipid metabolism.
- Synthesis of amino acids, plasma proteins, cholesterol, etc.
- Stores glycogen, fats, fat-soluble vitamins, etc.
- Detoxifies toxic substances
- Elimination of foreign bodies
- Produces heat through metabolism
- Produces anticoagulant heparin
- Synthesis of urea from ammonia.
VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question 1.
What is digestion?
Solution:
Digestion is the mechanical, enzymatic, and biochemical transformation of complex (polymers) food molecules into simple molecules (monomers) which are suitable for absorption.
Question 2.
Which is the food constituent that bile helps to digest and absorb?
Solution:
Fats.
Question 3.
What is the function of enterokinase?
Solution:
Enterokinase of intestinal juice activates the inactive trypsinogen into trypsin which digests protein in the duodenum.
Question 4.
Which is a nondigestive activating enzyme?
Solution:
Enterokinase.
Question 5.
Mention the role of bile salt in the digestion of fats.
Solution:
Bile salts emulsify fat particles and reduce the surface tension of fat droplets to increase the action of enzyme lipase.5. Bile salts emulsify fat particles and reduce the surface tension of fat droplets to increase the action of the enzyme lipase.
Question 6.
What is the role of HCl in protein digestion?
Solution:
Role of HCl:
- It activates pepsinogen into active pepsin.
- It provides a suitable acidic medium for the action of proteases in the stomach.
Question 7.
Name the hardest substance in the body.
Solution:
Enamel.
Question 8.
What is a cystic duct?
Solution:
Duct of gall bladder.
Question 9.
Mention two functions of mucus.
Solution:
Role of mucus:
(a) Acts as a lubricant.
(b) Protects the epithelial surface of the stomach from the corrosive effect of hydrochloric acid and digestion by pepsin.
Question 10.
Name the secretion of goblet cells in the human stomach.
Solution:
Goblet cells secrete mucus.
Question 11.
Where the taste buds located?
Solution:
Taste buds are located in the papillae on the upper surface of the tongue.
Question 12.
What is the ‘Pancreatic Enzyme’ which acts on starch? (Oct. 83, 01)
Solution:
The pancreatic amylase(Amylopsin).
Question 13.
What is the function of epiglottis?
Solution:
Epiglottis prevents the entry of food into the trachea, by closing its opening called the glottis.
Question 14.
Which part of the stomach continues into the duodenum?
Solution:
Pyloric region
Question 15.
What name is given to the major lymph vessel present in the intestinal villi?
Solution:
Lacteal
Question 16.
Where are the crypts of Leiberkuhn located?
Solution:
Crypts of Lieberkuhn are located in between the bases of the villi in the intestine.
Question 17.
Name the structural and functional unit of the liver.
Solution:
Hepatic lobules
Question 18.
Mention the secretion of Goblet cells.
Solution:
Mucin (Mucus) (April 93)
Question 19.
What is a bolus?
Solution:
When the thoroughly masticated food mixes with the saliva, the food particles become adhered together by the mucus known as bolus.
Question 20.
What is chyme?
Solution:
After partial digestion in the stomach, the form of food is called chyme.
Question 21.
What is the meaning of deglutition?
Solution:
The act of swallowing is called deglutition.
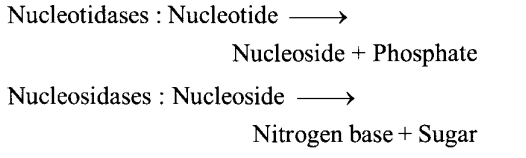
Question 22.
Name the enzyme involved in the breakdown of nucleotides into sugars and bases.
Solution:
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question 1.
Mention the juice secreted by the liver. State its function indigestion. (April 1985)
Solution:
The liver cells secrete a juice called the ‘Bile juice’. ‘Bile salts’ are one of the components of Bile juice. These are very important in digesting lipids or fats. Specifically ‘Bile salts’ aid in digestion than bringing about digestion of fat by emulsifying fats and making the fat molecules accessible to the action of the pancreatic Lipase (or Lipid digesting) enzyme. Apart from this the bile juice also creates an alkaline medium in the intestine so that food particles can be actively acted upon by the pancreatic enzymes.
Question 2.
Name the organs which secret carboxypeptidases and aminopeptidases respectively. Give the function performed by these enzymes
Solution:
Carboxypeptidases are secreted by the pancreas. Aminopeptidases are secreted by the intestine. Both the enzymes act on the terminal peptide bonds and release the terminal/last amino acids of the peptide chain.
Question 3.
State the Role of HCI indigestion. (Oct. 88, April 93, 98)
Solution:
The main role of HCI is to convert the inactive enzyme pepsinogen to pepsin which in turn helps in the digestion of proteins. It also creates an acidic medium in the stomach for the activity of pepsin.
Question 4.
What is succus entericus? Mention any two carbohydrate digesting enzymes present in it? (April 2006)
Solution:
Succus entericus intestinal juice is the secretion of intestinal glands in the ileum of the small intestine. The carbohydrate digesting enzymes are maltase, lactase, and sucrase.
Question 5.
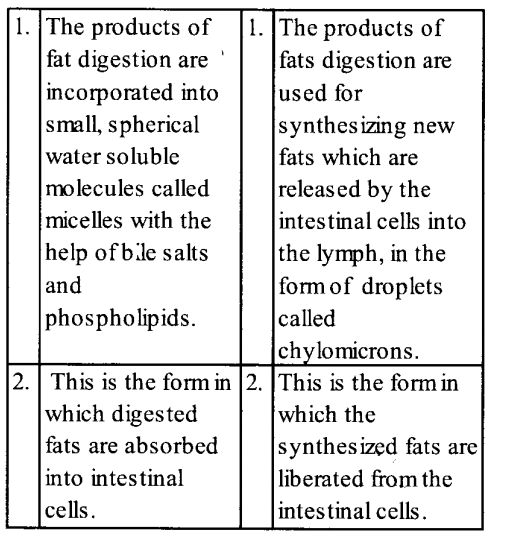
Differentiate between micelles and chylomicrons.
Solution:
The differences between micelles and chylomicrons are
Question 6.
How is our gut lining protected from its own secretion of proteases?
Solution:
(i) Protease is secreted in an inactive form and poses no threat to the gut lining.
(ii) The mucus provides protection to the epithelial lining.
Question 7.
Name the organs which secrete carboxypeptidases and aminopeptidases respectively. Give the functions performed by these enzymes.
Solution:
Carboxypeptidases are secreted by the exocrine part of the pancreas. Aminopeptidases are secreted by the intestinal mucosa. These enzymes act on the terminal peptide bonds and release the last amino acid from the polypeptide chain, thereby progressively shortening the peptide chain.
Question 8.
Where is the ileocaecal valve present? What is its function?
Solution:
The ileo-caecal valve is present at the junction of the ileum of the small intestine and the caecum of the large intestine.
It prevents the backflow of the matter from the caecum into the ileum.
Question 9.
How does the nervous system control the activities of the gastro-intestinal tract?
Solution:
The sight, smell and presence of food in the oral cavity can stimulate the secretion of saliva. Gastric and intestinal secretions are also stimulated by similar neural signals. Muscular activities of the alimentary canal are coordinated by both local and CNS neural mechanisms. Hormonal control of secretion of digestive enzymes is carried out by local hormones.
Question 10.
Name the final products of the digestion of proteins. How and where are they absorbed from the alimentary canal?
Solution:
The final products of digestion of proteins are amino acids They are absorbed by an active process utilising energy against the concentration gradient in the ileum.
Question 11.
What is the pancreas? Mention the major secretions of the pancreas that are helpful in digestion.
Solution:
The pancreas is a carrot-shaped soft greyish pink gland that lies transversely below the stomach between the duodenum and spleen, which secretes digestive enzymes from its exocrine parts and hormones from its endocrine parts.
The pancreas secretes three enzymes in inactive proenzyme or zymogen state and three in active enzyme state.
Proenzymes. Trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, and procarboxypeptidases.
Active Enzymes. Amylase, lipase, and nucleases.
LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question 1.
What is meant by vernalization? Explain the significance of vernalization.
Solution:
Question 2.
Write short notes on
(a) Liver
(b) Layers of the alimentary canal
Solution:
(a) Liver: The liver is the largest gland of the body. It is situated in the abdominal cavity, just below the diaphragm and has two lobes. The hepatic lobules are the structural and functional units of the liver containing hepatic cells arranged in the form of cords. Each lobule is covered by a thin connective tissue sheath called the Glisson’s capsule. The bile secreted by the hepatic cells passes through the hepatic ducts and is stored and concentrated in a thin muscular sac called the gall bladder. The duct of gall bladder (Cystic duct) along with the peptic duct from the liver forms the common bile duct. The bile contains pigments like bilirubin and biliverdin, bile salts, cholesterol and phospholipids but no enzymes. Bile helps in the emulsification of fats and activates lipases.
(b) Layers of the alimentary canal:
The wall of the alimentary canal possesses four layers namely serosa, muscularis, sub-mucosa, and mucosa. The serosa is the outermost layer and is made up of a thin mesothelium with some connective tissues. Muscularis is formed by smooth muscles usually arranged into an inner circular and an outer longitudinal layer. An oblique muscle layer may be present in some regions.
The sub-mucosal layer is formed of loose connective tissues containing nerves, blood, and lymph vessels. In the duodenum, glands are also present in the sub-mucosa. The innermost layer lining the lumen of the alimentary canal is the mucosa. This layer forms irregular folds in the stomach and small finger-like foldings called villi in the small intestine. The cells lining the villi produce numerous microscopic projections called microvilli giving a brush border appearance.
Villi are supplied with a network of capillaries and a large lymph vessel called the lacteal. The mucosal epithelium has goblet cells which secrete mucus that help in lubrication. Mucosa also forms glands in the stomach and crypts in between the bases of villi in the intestine (crypts of lieberkuhn).
Question 3.
Describe the major disorders of the human digestive system.
Solution:
Disorders of the digestive system:
(i) Indigestion:
- It is the condition in which the food is not properly digested leading to a feeling of fullness.
- It is caused by inadequate secretion of digestive enzymes, food poisoning, overeating or spicy food.
(ii) Constipation
- It refers to the condition where the faeces are retained in the rectum for longer periods as the bowel movements occur irregularly.
(iii) Diarrhoea:
- It refers to the abnormal frequency of bowel movement and increased liquidity of the faecal discharge; absorption of food is impaired.
(iv) Vomiting:
- It is the ejection of stomach contents through the mouth; this reflex action is controlled by the vomit centre in the medulla.
- It is due to viral infection, where liver is affected and digestion of fats is impaired.
- The eyes and skin turn yellow due to the deposit of bile pigments.
Question 4.
How is the DNA content in our diet digested in the body?
Solution:
DNA content is digested in the intestinal part of our alimentary canal by the enzymes present in pancreatic juice and succus entericus.
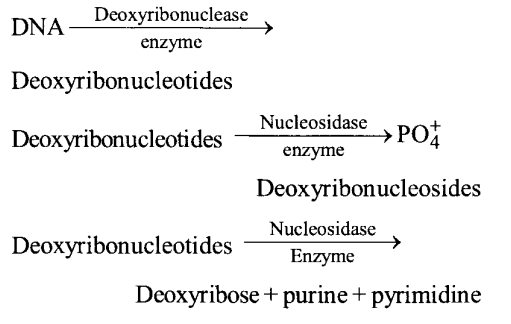
DNAase is found in pancreatic juice while nucleotidase and nucleosidase occur in succus entericus and hydrolyse the DNA content in our diet.
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology at Work Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption, help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology at Work Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
Class 11 Biology NCERT Solutions
- Mineral Nutrition Class 11 Question Answer
- Photosynthesis Class 11 Question Answer
- Respiration in Plants Class 11 Question Answer
- Plant Growth and Development Class 11 Question Answer
- Digestion and Absorption Class 11 Question Answer
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases Class 11 Question Answer
- Body Fluids and Circulation Class 11 Question Answer
- Excretory Products and their Elimination Class 11 Question Answer
- Locomotion and Movement Class 11 Question Answer
- Neural control and co-ordination Class 11 Question Answer
- Chemical Coordination and Integration Class 11 Question Answer