NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 is the best study material for all the students. It not only prepares them for the board exams but also strengthens their concepts for competitive exams such as NEET and JEE.
The solutions are provided by subject mater experts and are accurate. The diagrammatic representations make it even easier for the students to understand. The students appearing for UP board, MP board, Gujarat board, CBSE find the NCERT Solutions beneficial while preparing for the exams.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 12 |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Chapter | Chapter 16 |
| Chapter Name | Chemistry in Every Day Life |
| Number of Questions Solved | 37 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 Chemistry in Every Day Life NCERT Solutions
Chemistry in Every Day Life NCERT Solutions
This chapter deals with the principles of chemistry in everyday life. All the products such as soaps, detergents have an organic composition. All our daily activities are controlled by chemicals. This chapter gives some interesting facts about the products we use in our daily lives and how are they controlled by the chemicals.
The students are advised to go through the NCERT solutions for Class 12 Chemstry for better understanding of the concepts provided in the chapter.
NCERT INTEXT QUESTIONS
Question 1:
Sleeping pills are recommended by doctors to the patients suffering from sleeplessness but it is not advisable to take their doses without consultation with the doctor. Why?
Answer:
Sleeping pills contain drugs which may be tranquilizers or antidepressants. They affect the nervous system and induce sleep. However, if these doses are not properly controlled, they may create havoc. They even adversely affect the vital organs of the body. It is advisable to take these sleeping pills under the strict supervision of a doctor.
Question 2.
With refrence to which classification has the statement “ranitidine is an antacid”, been given?
Answer:
This statement refers to the classification of drugs according to pharmacological effect because any drug which will be used to neutralise the excess acid present in the stomach will be called an antacid.
Question 3.
Why do we require artificial sweetening agents?
Answer:
The commonly used sweetening agent i.e., sucrose is a carbohydrate with molecular formula C12H22O11. Since it has high calorific value, it is not recommended to the patients, diabetics in particular which require low calorie diet. Most of the artificial sweeteners are better than sucrose but hardly provide any calories to the body. These are being used as substitutes of sugar.
Question 4.
Write chemical equations for preparing sodium soap from glyceryl oleate and glyceryl palmitate. Structural formulas of these compounds are given:
(i) (C15H31COO)3C3H5 (Glyceryl palmitate)
(ii) (C17H33COO)3 C3H5 (Glyceryl oleate)
Answer:
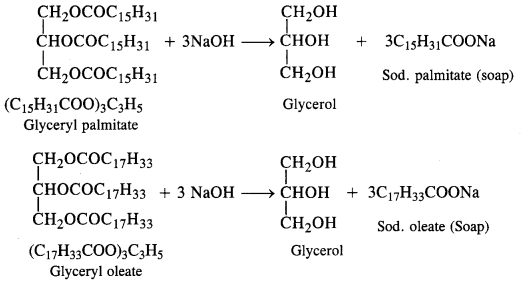
Question 5.
Label the hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts in the following molecule which is a detergent. Also identify the functional group(s) present.
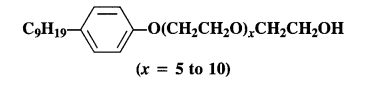
Answer:
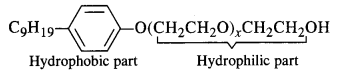
NCERT Exercise
Question 1.
Why do we need to classify the drugs in different ways?
Answer:
Drugs have been classified in different ways depending
- upon their pharmacological effect
- upon their action on a particular biochemical process
- on the basis of their chemical structure
- on the basis of molecular targets.
For example, the classification of the drugs based on pharmacological effect is useful for doctors. The classification of drugs based on molecular targets is the most useful classification for medicinal chemists. Thus, drugs are classified in different ways to serve different purposes.
Question 2.
Explain the term, target molecules or drug targets as used in medicinal chemistry.
Answer:
In medicinal chemistry, drug targets refer to the key molecules involve in certain metabolic pathways that result in specific diseases Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids are examples of drug targets.
Drugs are chemical agents designed to inhibit these target molecules by binding with the active sites of the key molecules.
Question 3.
Name the macromolecules that are chosen as drug targets.
Answer:
The different macromolecules or biomolecules which are used as drug targets are carbohydrates, proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids. Out of these, enzymes are the most significant because their deficiency leads to many disorders in the body.
Question 4.
Why should not medicines be taken without consulting doctors?
Answer:
A medicine can bind to more than one receptor site, thus a medicine may be toxic for some receptor site Further, in most cases, medicines cause harmful effects when taken in a higher dose than recommended As a result, medicines may be poisonous in such cases Hence, medicines should not be taken without consulting doctors.
Question 5.
Define the term chemotherapy. (C.B.S.E. Delhi 2008)
Answer:
The branch of chemistry which deals with the treatment of diseases using chemicals is called chemotherapy.
Question 6.
Which forces are involved in holding the drugs to the active sites of enzymes?
Answer:
These are different intermolecular forces like dipolar forces, hydrogen bonding, van der Waals’ forces etc. The receptor targets have specific roles to perform. They help in transferring message from messengers to the cell. The messengers are in fact chemical compounds which are received by the active sites of the receptor proteins that project out of the surface. In order to accommodate these, the receptors may undergo a change in shape. The receptors are held by the active sites also called binding sites. Once the message is transferred to the cells.
Question 7.
While antacids and antiallergic drugs interfere with the function of histamines, why do these not interfere with the function of each other?
Answer:
They do not interfere with the functioning of each other because they work on different receptors in the body. Secretion of histamine causes allergy and acidity while antacid removes only acidity.
Question 8.
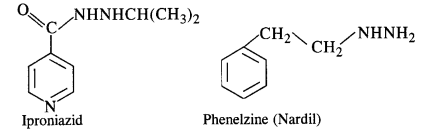
Low level of noradrenaline is the cause of depression. What type of drugs are needed to cure this problem ? Name two drugs (C.B.S.E. Outside Delhi 2008 Supp.)
Answer:
Low level of noradrenaline which acts as a neurotransmitter reduces the signal sending ability to the nerves and the patient suffers from depression. Antidepressants are needed to give relief from depression. These are also called tranquilizers or neurologically active drugs. The two specific drugs are iproniazid and phenelzine.
Question 9.
What is meant by the term ‘broad-spectrum antibiotic? Explain.
Answer:
Broad-spectrum antibiotics are the drugs which are effective against a large number of harmful micro-organisms causing diseases.
Chloramphenicol It is a broad-spectrum antibiotic, isolated in 1947. It is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and hence can be given orally. It is very effective against typhoid, dysentery, acute fever, certain form of urinary infections, meningitis and pneumonia.
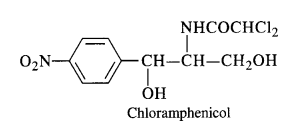
Chloramphenicol is quite easy to synthesise. Therefore, most of the chloramphenicol available in the market is synthetic.
Question 10.
How do antiseptics differ from disinfectants? Give one example of each.
Answer:
Antiseptics and disinfectants are effective against micro-organisms However antiseptics are applied to the living tissues such as wounds, cuts, ulcers, and diseased skin surfaces, while disinfectants are applied to inanimate objects such as floors, drainage system, instruments, etc Disinfectants are harmful to the living tissues.
Iodine is an example of a strong antiseptic Tincture of iodine (2-3 percent of the solution of iodine in the alcohol-water mixture) is applied to wounds 1 percent solution of phenol is used as a disinfectant.
Question 11.
Why are cimetidine and ranitidine better antacids than sodium bicarbonate or magnesium or aluminium hydroxides?
Answer:
Both sodium bicarbonate and hydroxides of magnesium or aluminium are very good antacids since they neutralise the acidity in the stomach. But their prolonged use can cause the secretion of excessive acid in the stomach. This may be quite harmful and may lead to the formation of ulcers. Both cimetidine and ranitidine are better salts without any side effects.
Question 12.
Name a substance which can be used as an antiseptic as well as a disinfectant.
Answer:
Phenol can be used as an antiseptic as well as a disinfectant 0.2 percent solution of phenol is used as an antiseptic, while 1 percent of its solution is used as a disinfectant.
Question 13.
What are the main constituents of Dettol?
Answer:
The main constituents of antiseptic Dettol are chloroxylenol and terpenol.
Question 14.
What is the tincture of iodine? What is its use?
Answer:
Tincture of iodine is a 2-3 percent solution of iodine in an alcohol-water mixture It is applied to wounds as an antiseptic.
Question 15.
What are food preservatives?
Answer:
Chemical substances which are used to protect food against bacteria, yeasts and moulds are called preservatives. For example, sodium benzoate and sodium metabisulphite.
Question 16.
Why is the use of aspartame restricted to cold foods and drinks?
Answer:
Aspartame becomes unstable at cooking temperature This is the reason why its use is limited to cold foods and drinks.
Question 17.
What are artificial sweetening agents? Give two examples.
Answer:
Carbohydrates in the form of sugar (sucrose) are the traditional sweeteners and are the essential constituents of our diet. In the present lifestyle, people lack physical activities and exercise and it becomes rather difficult to burn the extra calories that are produced by the carbohydrates. Chemists have provided certain chemicals known as artificial sweeteners which provide the desired sweet taste io the food articles but hardly affect the calorie intake by the body. The most popular among the artificial sweeteners is saccharin which is nearly 550 times more sweet than the cane sugar. It is a boon for diabetic patients who don’t want to take carbohydrates (sugar) which is likely to increase the calories. It is in fact, a life saviour for these patients and is in the form of sodium or calcium salt which is water-soluble. These days, a number of other sweeteners are also available, e.g.. Aspartame, Alitame, Sucrolose etc.
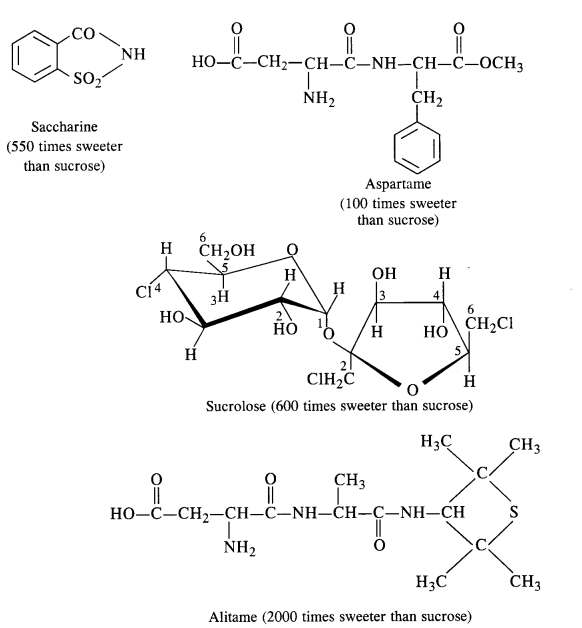
(a) Aspartame: It is a very successful and commonly used artificial sweetener. As stated above, it is nearly 100 times as
sweet as cane sugar. However, it can be used in soft drinks and cold foods only since it decomposes upon heating. Chemically
aspartame is the methyl ester of dipeptide formed by the action of aspartic acid with phenylalanine.
(b) Sucrolose: The artificial sweetener as the name suggests is a trichioroderivative of sucrose. It is better, than
aspartame in the sense that it can be used in hot food at the cooking temperature, since it does not decompose on heating.
Moreover, it does not provide calories.
Question 18.
Name the sweetening agent used in the preparation of sweets for a diabetic patient.
Answer:
Artificial sweetening agents such as saccharin, alitame, and aspartame can be used in preparing sweets for diabetic patients.
Question 19.
What problem arises by using alitame as an artificial sweetener?
Answer:
Alitame is no doubt, a very potent sweetener. Its sweetening capacity is more than 2000 times as compared to ordinary cane sugar or sucrose. But sometimes, it becomes quite difficult to control the sweetness level in the food which is actually desired.
Question 20.
Why are detergents called soapless soaps?
Answer:
Soaps work in soft water, they are not effective in hard water In contrast synthetic detergents work both in soft water and hard water Therefore, synthetic detergents are better than soaps.
Question 21.
Explain the following terms with suitable examples.
(a) Cationic detergents
(b) Anionic detergents
(c) Neutral detergents.
Answer:
1. Anionic Detergents: These detergents contain anionic hydrophilic groups. These are generally made from long-chain alcohols which are reacted with concentrated sulphuric acid to form alkyl hydrogen sulphates. These are then neutralised with alkali to give water-soluble salts.
A few examples are listed below :
Sodium Alkyl Sulphates: These are the sodium salts of sulphonic acid esters of long-chain aliphatic alcohols which normally contain 10 to 15 carbon atoms. The alcohols are formed from fats and oils as a result of hydrogenolysis.
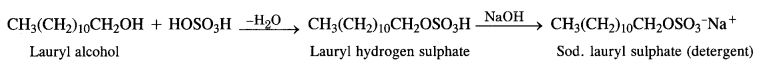
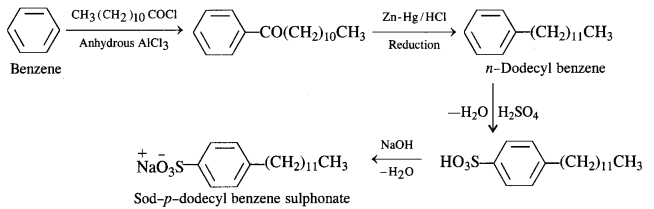
Sodium Alkyl Benzene Suiphonates: A common detergent belonging to this class is Sod – p – dodecyl benzene sulphonate. It is obtained from benzene by reacting with dodecyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 acting as a catalyst.
The different steps involved are as follows :
2. Cationic Detergents: In these detergents, the hydrophilic group is of cationic nature. These are generally acetates, chlorides or bromides of quaternary ammonium CH CH CH B salts. The cationic part enclosed in the bracket contains a long hydrocarbon chain. These detergents have germicidal qualities and are quite expensive as well, The cationic CH3 detergents are present in hair conditioners. Cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide
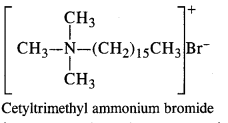
3. Non-ionic or neutral Detergent: These detergents are simply long-chain organic compounds and are esters in nature. For example, stearic acid and polyethylene glycol react to form a non-ionic detergent.
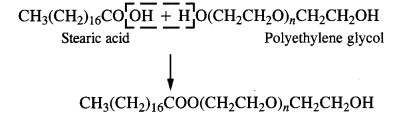
Non-ionic detergents contain polar groups and form hydrogen bonds with water. Some dishwashing liquids contain non-ionic detergents.
The field of detergents is very vast because of their immense utility. Companies engaged in their manufacture are spending huge amounts of money to bring products of better quality.
Question 22.
What are biodegradable and non-biodegradable detergents? Give an example of each. (C.B.S.E. Delhi 2008, 2009)
Answer:
Bio-degradable detergents are degraded by bacteria. In them, the hydrocarbon chain is unbranded. They do not cause water pollution and are bitter. Example: Sodium lauryl sulphate.
Non-biodegradable detergents possess highly branched hydrocarbon chain so bacteria cannot degrade them easily. They cause water pollution. Example: Sodium 4-(l, 3, 5, 7-tetramethyl-actyl) benzene sulphonate.
Question 23.
Why do soaps not work in hard water?
Answer:
Hard water contains calcium and magnesium salts. Therefore, in hard water soaps get precipitated as calcium and magnesium soaps which being insoluble stick to the clothes as gummy mass.
Question 24.
Can you use soaps and synthetic detergents to check the hardness of water?
Answer:
Soaps can be used to check hardness of water as they will form insoluble precipitates of calcium and magnesium salts on reacting with hard water. Since detergents do not form any precipitate, they cannot check hardness of water.
Question 25.
Explain the cleansing action of soaps.
Answer:
In order to understand the cleansing action of soaps let us try to analyse how the clothes become dirty. They first become oily because of the perspiration coming out of the skin and also from the organic matter dispersed in the atmosphere. Dust particles stick to oil drops and the clothes become dirty. In order to wash these, they are dipped in water and soap is applied.
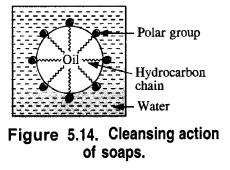
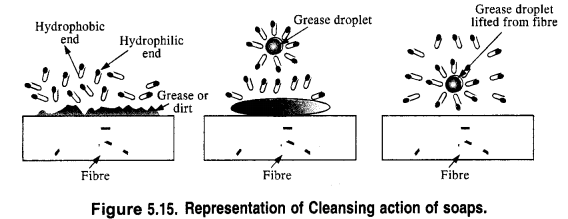
In solution, it dissociates to give carboxylate ions (RCOO–) and the cations (Na+). The alkyl portion which contains a long chain of hydrocarbons is a tail pointing towards the oil drops while the COO portion is the head directed towards water. This is quite evident from the figure where the solid circles (.) represent the polar groups and the wavy lines represent the alkyl portions. This formation is known as micelle and helps in forming a stable emulsion of oil and water by acting as a bridge between the two. The oil droplets along with the particles of the dirt get detached from the fibres of the clothes and pass into the emulsion. In this manner, the clothes become free from dust or dirt. The cleansing action of the soap is depicted in the Fig. 5.15.
Question 26.
If the water contains dissolved calcium bicarbonate, out of soaps and synthetic detergents, which one will you use for cleaning clothes?
Answer:
Synthetic detergents are preferred for cleaning clothes When soaps are dissolved in water containing calcium ions, these ions form insoluble salts that are of no further use, however when synthetic detergents are dissolved in water containing calcium ions, these ions form soluble salts that act as cleaning agents.
![]()
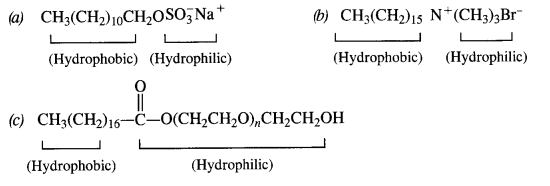
Question 27.
Label the hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts in the following compounds.
(a) CH3(CH2)10CH2OSO3Na+
(b) CH3(CH2)15-N+(CH3)3Br–
(c) CH3(CH2)16-COO(CH2CH2O)nCH2CH2OH
Answer:
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 Chemistry in Every Day Life help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 Chemistry in Every Day Life, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
Class 12 Chemistry NCERT Solutions
- The Solid State Class 12 NCERT Solutions
- Solutions Class 12 NCERT Solutions
- Electrochemistry Class 12 NCERT Solutions
- Chemical Kinetics Class 12 NCERT Solutions
- Surface Chemistry Class 12 NCERT Solutions
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements Class 12 NCERT Solutions
- The p-Block Elements Class 12 NCERT Solutions
- d-and f-Block Elements Class 12 NCERT Solutions
- Coordination Compounds Class 12 NCERT Solutions
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 NCERT Solutions
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Class 12 NCERT Solutions
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Class 12 NCERT Solutions
- Amines Class 12 NCERT Solutions
- Biomolecules Class 12 NCERT Solutions
- Polymers Class 12 NCERT Solutions
- Chemistry in Every Day Life Class 12 NCERT Solutions