These Solutions are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Thermodynamics.
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Thermodynamics NCERT Solutions
Thermodynamics NCERT Solutions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer.
A thermodynamic state function is a quantity
(i) used to determine heat changes
(ii) whose value is independent of path
(iii) used to determine pressure volume work
(iv) whose value depends on temperature only.
Answer:
(ii) whose value is independent of path
Question 2.
For the process to occur under adiabatic conditions, the correct condition is :
(i) ∆T = 0
(ii) ∆p = 0
(iii) q = 0
(iv) w = 0
Answer:
(iii) q = 0
Question 3.
The enthalpies of all elements in their standard states are :
(i) unity
(ii) zero
(iii) < 0
(iv) different for each element
Answer:
(ii) zero
Question 4.
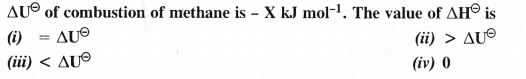
Answer:

Question 5.
The enthalpy of combustion of methane, graphite and dihydrogen at 298 K are – 890.3 kJ mol-1, -393.5 kJ mol-1 and – 285.8 kJ mol-1 respectively. Enthalpy of formation of CH4 (g) will be
(i) -74.8 kJ mol-1 (ii) -52.27 kJ mol-1
(iii) + 74.8 kJ mol-1 (iv) + 52.26 kJ mol-1
Answer:
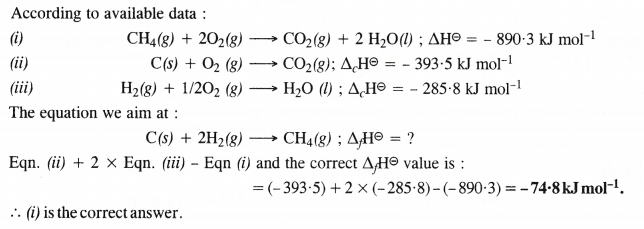
Question 6.
A reaction, A + B → C + D + q is found to have a positive entropy change. The reaction will be
(i) possible at high temperature
(ii) possible only at low temperature
(iii) not possible at any temperature
(iv) possible at any temperature
Answer:
(iv) possible at any temperature
Question 7.
In a process, 701 J of heat is absorbed by a system and 394 J of work is done by the system. What is the change in internal energy for the process ?
Answer:
Heat absorbed by the system, q = 701 J
Work done by the system = – 304 J
Change in internal energy (∆U) = q + w = 701 – 394 = 307 J.
Question 8.
The reaction of cyanamide, NH2CN(s) with oxygen was affected in a bomb calorimeter and ∆U was found to be – 742.7 kJ mol-1 of cyanamide at 298 K. Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction at 298 K.
NH2CN(y) + 3/2O2(g) → N2fe) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
Answer:
∆U = – 742.7 kJ mol-1 ; ∆ng = 2 – \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 } \) = + \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) mol.
R = 8.314 × 10-3 kJ K-1 mol-1 ; T = 298 K
According to the relation, ∆H = ∆U + ∆ng RT
AH = (- 742.7 kJ) + (\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) mol) × (8.314 × 10-3 kJ K-1 mol-1) × (298 K)
= -742.7 kJ + 1.239 kJ = -741.5 kJ.
Question 9.
Calculate the number of kJ necessary to raise the temperature of 60 g of aluminium from 35 to 55°C. Molar heat capacity of Al is 24 J mol-1 K-1.
Answer:
No. of moles of Al (m) = \(\frac { 60g }{ 27gmo{ l }^{ -1 } } \) = 2.22 mol
Molar heat capacity (C) = 24 J mol-1 K-1
Rise in temperature (∆T) = 55 – 35 = 20°C = 20 K
Heat evolved (q) = C × m × T = (24 J mol-1 K-1) × (2.22 mol) × (20 K)
= 1065.6 J = 1.067 kJ.
Question 10.
Calculate the enthalpy change on freezing of 1.0 mole of water at – 10.0°C to ice at – 10.0°C. ∆fusH = 6.03 kJ mol-1 at 0°C; Cp[H2O(l)] = 75.3 J mol-1 K-1 ; Cp[H2O(s)l = 36.8 J mol-1 K-1.
Answer:
Total change in enthalpy (AH) for the freezing process may be calculated as :
∆H = (1 male of water at 10°C → 1 mole of water at 0°C) + (1 mole of water at °C → 1 mole of ice at 0°C)
+ (1 mole of ice at °C → 1 mole of ice at – 10°C)
= Cp[H2O(l)] × ∆T + ∆Hfreezmg + Cp [H2O(s)] × ∆T.
= (75.3 Jk-1 mol-1) (0 – 10 K) + (-6.03 kJ mol-1) + (36.8Jk-1 mol-1) × (-10 K)
= (-753 J mol-1) – (6.03 kJ mol-1) – (368 J mol-1)
= (-0.753 kJ mol-1) – (6.03 kJ mol-1) – (0.368 kJ mol-1)
= – 7.151 kJ mol-1
Question 11.
Enthalpy of combustion of carbon to carbon dioxide is – 393.5 kJ mol-1. Calculate the heat released upon formation of 35.2 g of CO2 from carbon and oxygen gas.
Answer:
The combustion equation is :
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ; ∆cH = – 393.5 kJ mol-1 (44 g)
(44g)
Heat released in the formation of 44g of CO2 = 393.5 kJ
Heat released in the formation of 35.2 g of CO2 = \(\frac { (393.5kJ)\times (35.2g) }{ (44g) } \) = 314.8 kJ.
Question 12.
Calculate the enthalpy of the reaction :
N2O4(g) + 3CO(g) → N2O(g) + 3CO2(g)
Given that;
∆fH CO(g) = – 110 kJ mol-1 ;
∆fH CO2(g) = – 393 kJ mol-1
∆fH. N2O(g) = 81 kJ mol-1 ;
∆fH N2O4(g) = – 9.7 kJ mol-1.
Answer:
Enthalpy of reaction (∆rH) = [81 + 3(- 393)] – [9.7 + 3(- 110)]
= [81 – 1179] – [9.7 – 330] = – 778 kJ mol-1.
Question 13.
![]()
Answer:
![]()
Question 14.
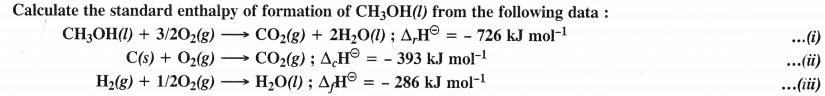
Answer:
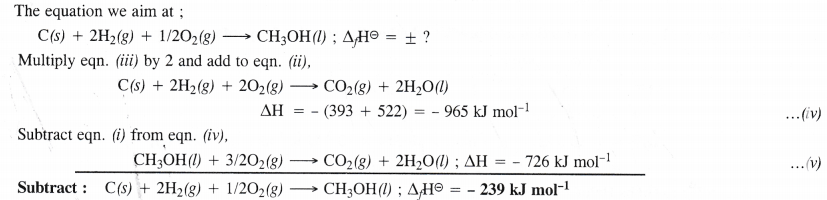
Question 15.
Calculate the enthalpy change for the process
CCl4 (g) → C (g) + 4 Cl (g) and calculate bond enthalpy of C—Cl in CC14 (g)
Given : ∆vap H° (CCl4) = 30.5 kJ mol-1 ; ∆fH°(CCl4) = – 135.5 kJ mol-1
∆aH° (C) = 715.0 kJ mol-1 where ∆a H° is enthalpy of atomisation
∆aH° (Cl2) = 242 kJ mol-1.
Answer:
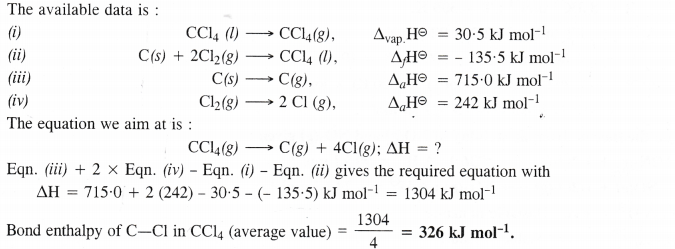
Question 16.
For an isolated system ∆U = 0 ; what will be ∆S ?
Answer:
Change in internal energy (∆U) for an isolated system is zero because it does not exchange any energy with the surroundings. But entropy tends to increase in case of spontaneous reaction. Therefore, ∆S > 0 or positive.
Question 17.
For a reaction at 298 K
2 A + B → C
∆H = 400 kJ mol-1 and ∆S = 0.2 kJ K’1 mol-1.
At what temperature will the reaction become spontaneous considering ∆H and ∆S to be constant over the temperature range ?
Answer:
According to Gibbs-Helmholtz equation :
∆G = ∆H – T∆S
For ∆G = 0; ∆H = T∆S or T : = \(\frac { \triangle H }{ \triangle s } \)
T = \(\frac { (400kJmo{ l }^{ -1 }) }{ (0.2kJ{ K }^{ -1 }mo{ l }^{ -1 }) } \)
Thus, reaction will be in a state of equilibrium at 2000 K and will be spontaneous above this temperature.
Question 18.
For the reaction ; 2Cl (g) → Cl2(g) ; what will be the signs of ∆H and ∆S ?
Answer:
∆H : negative (-ve) because energy is released in bond formation
∆S : negative (-ve) because entropy decreases when atoms combine to form molecules.
Question 19.
For a reaction ; 2A (g) + B (g) → 2D(g)
![]()
Calculate ∆U298 for the reaction and predict whether the reaction is spontaneous or not.
Answer:
Let the mass of H2 in the mixture = 20 g
The mass of O2 in the mixture will be = 80 g

Question 20.

Answer:

Question 21.

Answer:

Question 22.
![]()
Answer:
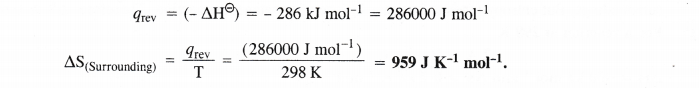
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry at Work Chapter 6 Thermodynamics, help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry at Work Chapter 6 Thermodynamics, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
Class 11 Chemistry NCERT Solutions
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Class 11 NCERT Solutions
- Structure of Atom Class 11 NCERT Solutions
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Class 11 NCERT Solutions
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Class 11 NCERT Solutions
- States of Matter Class 11 NCERT Solutions
- Thermodynamics Class 11 NCERT Solutions
- Equilibrium Class 11 NCERT Solutions
- Redox Reactions Class 11 NCERT Solutions
- Hydrogen Class 11 NCERT Solutions
- The s Block Elements Class 11 NCERT Solutions
- The p Block Elements Class 11 NCERT Solutions
- Organic Chemistry: Some Basic Principles and Techniques Class 11 NCERT Solutions
- Hydrocarbons Class 11 NCERT Solutions
- Environmental Chemistry Class 11 NCERT Solutions