In this page, we are providing Heredity and Evolution Class 10 Extra Questions and Answers Science Chapter 9 pdf download. NCERT Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution with Answers will help to score more marks in your CBSE Board Exams.
Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Extra Questions and Answers Heredity and Evolution
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution with Answers Solutions
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Define heredity. [CBSE 2012]
Answer:
Transmission of characters/traits from parents to their offspring is called heredity.
Question 2.
Write the sex of the baby that inherits Y-chromosome from the father. [CBSE 2013]
Answer:
The baby that inherits the Y-chromosome from the father will be a male.
Question 3.
Name the scientist who gave the theory of evolution. [CBSE 2013]
Answer:
Charles Darwin.
Question 4.
Define species. [CBSE 2013]
Answer:
Species is a group of organisms which can interbreed among themselves to produce fertile offsprings.
Question 5.
Define natural selection. [CBSE 2012]
Answer:
The process of evolution of species where the characteristics of the organisms which enable them to survive and reproduce are passed on to their progeny is called natural selection.
Question 6.
Identify the analogous and homologous organs amongst the following – wings of an insect, wings of a bat, forelimbs of lizard, and forelimbs of bird. [CBSE 2012]
Answer:
Analogous organs: Wings of an insect and wings of a bat.
Homologous organs: Forelimbs of lizard and forelimbs of bird.
Question 7.
Give an example where sex is determined by the environmental factors. [CBSE 2012]
Answer:
In some snails and turtles, sex is determined by environmental factors.
Question 8.
Write one word for the formation of new species due to gradual change over long period of time. [CBSE 2013]
Answer:
Speciation.
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Short Answer Type I
Question 1.
How can we say that change in genes can be brought about by change in DNA? [CBSE 2013]
Answer:
Segment of DNA on a chromosome which carries information for the appearance of a particular character is called a gene. It helps in the inheritance of the character from one generation to another. So, we can say that changes in gene can be brought about by change in DNA.
Question 2.
In pea plant, round seed is dominant over wrinkled. If a cross is carried between these two plants, give answer to the following questions.
(a) Mention the genes for the traits of parents.
(b) State the trait of F1 hybrids.
(c) Write the ratio of F2 progeny obtained from this cross. What is the name of the cross?[CBSE 2011]
Answer:
(a) RR/rr
(b) The F1 hybrid will be Round (Rr).
(c) Phenotypic ratio = 3 : 1; Genotypic ratio = 1 : 2 : 1; The cross will be called as Monohybrid cross.
Question 3.
What do you understand by reproductive isolation? [CBSE 2012]
Answer:
If the members of the two species are unable to reproduce themselves due to physical, behavioural, ecological, and temporal or development reasons, then the process is called as reproductive isolation.
Question 4.
Explain with the help of a suitable example where the colour change gives no survival advantage to a species. [CBSE 2013]
Answer:
In the illustration shown the colour of the red coloured beetles living in the green coloured bushes changes to blue colour, but still, it offers no advantage in the green colour bushes because the predators can easily spot the beetles. An elephant stumps on the bushes and kills most of the red beetles. The blue beetles survive merely by chance and not due to their body colour.
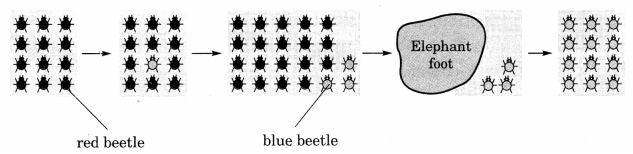
Question 5.
Distinguish between acquired and inherited traits with example of each.
Answer:
Inherited traits:
- The traits which are passed on from the parents to their progeny by transfer of genes.
- For example, Eye colour
Acquired traits:
- The traits acquired by individual during its lifetime.
- For example, Riding a bicycle, playing cricket, etc.
Question 6.
How can it be said that birds are closely related to reptiles? [CBSE 2013]
Answer:
Reptiles like Dinosaurs had feathers to maintain their body temperature. The birds have adapted the feathers for flight. So, it can be said that the birds have evolved from the reptiles. Archaeopteryx is a fossil which forms a link between the birds and the reptiles.
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Short Answer Type II
Question 1.
Can you justify the statement that “Human males are responsible for determining the sex of the baby and not females”? [CBSE 2012, 2013]
Answer:
The sex in human beings or the sex of the individual is largely genetically determined. A male cell has two types of sex chromosomes i.e., X – chromosome and Y – chromosome because of which male produces two types of sperms with genotype A + X and A + Y. Female cells have two X – chromosomes so the genotype of eggs produced by her is A + X. During fertilisation the chances are:
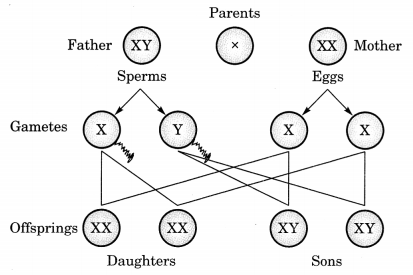
- If a sperm carrying Y – chromosome fertilises the egg, then the child born will be a male i.e., AA + XY.
- If a sperm carrying X – chromosome fertilises the egg then the child born will be a female i.e., AA + XX.
Thus we can infer that the sperm of the male determines the sex of the child.
Question 2.
“Red beetles live in a bush with green beetles. Eventually, the number of green beetles increases as compared to red beetles”.
(a) Give a reason for the increased number of green beetles.
(b) State two advantages of variations. [CBSE 2012]
Answer:
(a) The crows are unable to spot the green coloured beetles in the green coloured bushes, so the number of green coloured beetles increases.
(b) Variations are advantageous as they:
- Enable the survival of the organism under adverse conditions.
- Leads to evolution.
Question 3.
Name the scientist who gave the ‘Theory of Natural Selection’. State and explain the theory briefly. [CBSE 2013]
Answer:
The theory of evolution by natural selection, first formulated in Darwin’s book “On the Origin of Species” in 1859, is the process by which organisms change over time as a result of changes in heritable physical or behavioural traits. Changes that allow an organism to better adapt to its environment will help it survive and have more offspring.
The four steps in the process can be summarised as:
- Large numbers: The parent produces more offspring than that can survive.
- Competition: There is a limited amount of resources, so competition occurs among the offsprings and also with the other members of the population.
- Survival of the fittest: Only the members who have favourable variations survive the competition.
- Natural selection: The surviving members reproduce and pass on the variations to their progeny.
Question 4.
Define the term ‘Evolution’. “Evolution cannot be equated with progress”. Justify. [CBSE 2013]
Answer:
The process by which the new types of organisms are formed from the pre-existing organisms through variations and modifications is called evolution.
Natural selection and genetic drift cause evolution but that does not mean that
- One species is eliminated to form the new one, or
- The new species is better than the older one. So, evolution should not be equated with progress as multiple branches are possible at each and every stage of evolution.
Example: Human beings have not evolved from chimpanzees. Both have evolved in their own separate ways from a common ancestor a long time ago.
Question 5.
“Our teeth and elephant’s tusks are homologous organs”. Justify this statement. What do the analogous organs indicate? [CBSE 2012]
Answer:
Our teeth and elephant’s tusks are homologous organs because they have the same basic structure and origin but perform different functions.
Analogous organs are those organs which perform the same function but have different structure.
Question 6.
How and why did human race spread from Africa to other parts of the world? [CBSE 2013]
Answer:
Earliest members of human species (Homo sapiens) came from Africa. Some of our ancestors stayed back in Africa while others moved and spread across to West Asia, Central Asia, Eurasia, South Asia, and East Asia.
They moved from the islands of Indonesia and the Philippines to Australia, and some crossed the Bering land bridge to reach America. They did not go in a single line but went forwards and backwards, with groups sometimes separating from each other, sometimes coming back to mix with each other, even moving in and out of Africa.
Question 7.
Give reasons why acquired characters are not inherited.
Answer:
No change in the DNA of germ cells is produced by the acquired characters, so they cannot be inherited. Only those characters are inherited which have a gene for them.
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Long Answer Type
Question 1.
Demonstrate with an example that traits may be dominant or recessive. Write down Mendel’s law related to it. [CBSE 2013]
Answer:
The cross shown below demonstrates that the traits may be dominant or recessive.
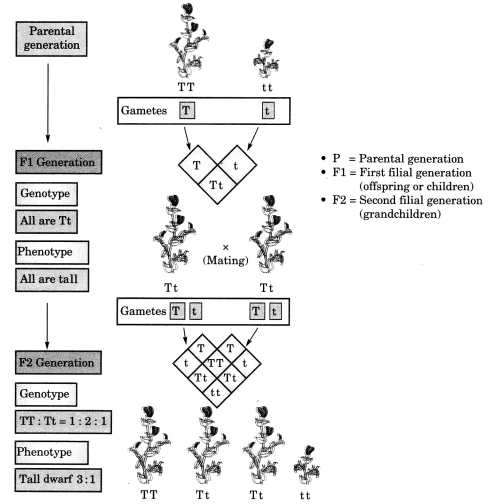
The law related to it is the Mendel’s first law of inheritance i.e., Law of dominance, which states that:
- Characters are controlled by discrete units called factors.
- Factors occur in pairs.
- In a dissimilar pair of factors one member of the pair dominates (dominant) the other (recessive).
Question 2.
In a monohybrid cross between tall pea plants denoted by TT and short pea plants denoted by tt, Preeti obtained only tall plants denoted by Tt in the F1 generation. However, in F2 generation she obtained both tall and short pea plants. Using the above information, explain the law of dominance. [CBSE 2011]
Answer:
The cross shown below demonstrates that the traits may be dominant or recessive.
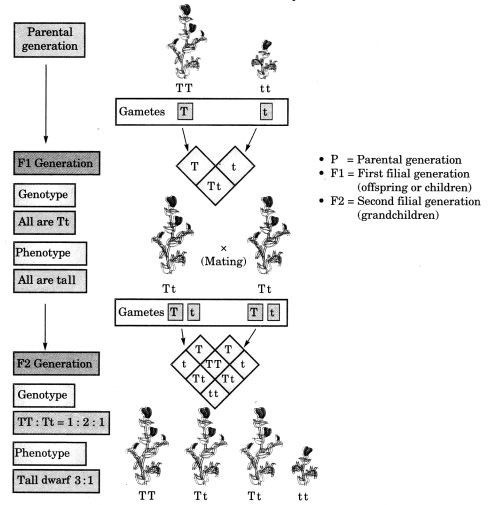
The law related to it is the Mendel’s first law of inheritance i.e., Law of dominance, which states that:
- Characters are controlled by discrete units called factors.
- Factors occur in pairs.
- In a dissimilar pair of factors one member of the pair dominates (dominant) the other (recessive).
Question 3.
Define speciation. What are the factors which lead to speciation? [CBSE 2013]
Answer:
The process of formation of new species from the existing species is called speciation.
The factors which lead to the formation of new species are:
(i) Reproductive Isolation:
(a) Allopatric speciation: Caused by the various types of barriers like mountain ranges, rivers, seas, etc. It leads to reproductive isolation between members of the species and this is also called geographical isolation.
(b) Sympatric speciation: It occurs when populations of a species that share the same habitat become reproductively isolated from each other.
(ii) Genetic Drift: It is caused by change in the frequency of a particular genes by accident or by chance alone.
(iii) Natural Selection: The process by which a group of organisms adopts to fit their environment in a better way.
(iv) Migration: When movement of a section of population to another place and population occurs.
(v) Mutation: Sudden changes in the sequence of DNA.
Question 4.
In a cross between plants with purple flowers and plants with white flowers, the FI had all white flowers. When F1 generation was self bred, the F2 generation gave rise to 100 individuals, 75 of which had white flowers. Make a cross and answer.
(а) What are the genotypes of F2 individual?
(b) What is the ratio of purple flowered plants in F2 generation? [CBSE 2012]
Answer:
W = White.
w – Purple.
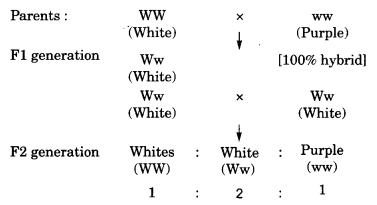
(a) Genotypes of F2 individuals are 1(WW) : 2(Ww) : 1(ww)
(b) Ratio of white to purple flowers = 3 : 1, i.e., 3 white : 1 purple
Question 5.
Does geographical isolation of individuals of a species lead to formation of a new species? Provide a suitable explanation.
Answer:
Yes, geographical isolation gradually leads to genetic drift. It leads to productive isolation between members of the species as it imposes limitations to sexual reproduction of the separated population.
Slowly new variations arise as the separated individuals reproduce among themselves. Accumulation of the variations which arise through a few generations may ultimately lead to the formation of a new species.
Question 6.
Bacteria have a similar body plan when compared with human beings. Does it mean that human beings are more evolved than bacteria. provide a suitable explanation.
Answer:
It depends on the perspective which we consider while assessing whether humans are more evolved than the bacteria because, if appearance of complexity is concurrent with evolution, then human beings are certainly more evolved than bacteria.
But if we take the toataliy of life characteristics into account, then it is hard to lable either organisms are evolved.
Question 7.
Give the basic features of the mechanism of inheritance.
Answer:
The basic features of the mechanism of inheritance are:
- Characters are controlled by genes.
- Genes are present on the chromosomes.
- Each gene controls one character.
- There may be two or more forms of the same gene.
- One form of the gene may be dominant over the other.
- Two forms of the gene whether similar or dissimilar are present in an individual.
- The two forms of the gene separate at the time of gamete formation.
- The two forms of the gene are brought together in the zygote.
Heredity and Evolution HOTS Questions With Answers
Question 1.
In a cross between plants with purple flowers and plants with white flowers, the F1 had all purple flowers. When F1 generation was self bred, the F2 generation gave rise to 100 individuals, 75 of which had purple flowers. Make a cross and answer.
(a) What are the genotypes of F2 individual?
(b) What is the ratio of purple flowered plants in F2 generation? [CBSE 2012]
Answer;
The cross is depicted as under:
W = White, w = purple
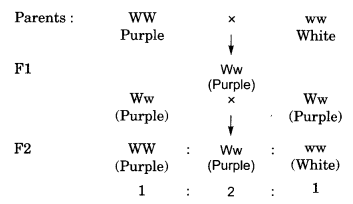
(a) The genotype of F2 individuals is
![]()
(b) Ratio of purple flowered plants in F2 generation is:
![]()
Question 2.
An elephant learns a trick at the circus. Will his offsprings also know the trick by birth? Support your answer with reasons. [CBSE 2013]
Answer:
Learning a trick at the circus is not an inherited trait. It is an acquired trait which cannot be transferred into the progeny. So, his offsprings will not know the trick by birth.
Question 3.
Do genetic combination of mother’s play a significant role in determining the sex of a new born?
Answer:
No, because mothers have a pair of X-chromosomes. All children will inherit an “X’ chromosome from their mother regardless of whether they are boys or girls.
Question 4.
Mention three important features of fossils which help in the study of evolution.
Answer:
The features of fossils which help in the study of evolution are:
- They are modes of preservation of ancient species.
- They help in establishing evolutionary relationships among organisms and their ancestors.
- They help in establishing the time period in which organisms lived.
Question 5.
In human beings, the statistical probability of getting either a male or female child is 50 : 50. Give a suitable explanation.
Answer:
The type of sex chromosome contributed by the male gamete determines the sex of an infant. Since the ratio of male gametes containing X chromosome and those containing Y chromosome is 50 : 50, the statistical probability of male or a female infant is also 50 : 50.
Question 6.
A very small population of a species faces a greater threat of extinction than a larger population. Provide a suitable genetic explanation.
Answer:
Extensive inbreeding is imposed by fewer individuals in a species. This limits the appearance of variations and the species is put at a disadvantage if there are changes in the environment. Such individuals fail to cope up with the environmental changes and may become extinct.
Question 7.
A man who has four sons and one daughter believes that he produces more of sperms with Y as a chromosome. With suitable reasons, justify whether he is right or wrong in thinking this way.
Answer:
A man produces 50% sperms with Y chromosome and 50% with X chromosome whereas a female produces 100% ovum with X chromosome. So, it’s just a matter of chance which sperm fertilises the ovum. If sperm with Y chromosome fertilises the ovum the progeny will be son and if sperm with X chromosome fertilises the egg, then the progeny will be daughter. So, the man is not right in his thinking that he is producing more sperms having Y chromosome.
Question 8.
Akshat and his wife have attached earlobe (recessive trait) and are professional dancers. They told their colleagues that their offspring would also have attached earlobe and will be a good dancer. Is their notion right? Support your answer with suitable reasons.
Answer:
Attached earlobe or free earlobe is an inherited trait. Also, both parents have attached earlobe which is a recessive trait, so the progeny produced will have attached earlobe. But, the ability to dance or being a good dancer is an acquired trait which an individual acquires during its lifetime. So, there is no certainty that the offspring produced will be a good dancer or not. Therefore, the notion they perceive is not right.
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Value Based Questions
Question 1.
Ashima saw a female being blamed by the family members for producing a girl child. She approached them and told that the genetic basis of sex determination of human beings clearly indicates that only the female should not be blamed for producing a girl child. The family members agreed to her argument and felt sorry for their act.
Based on the above answer the following questions:
(а) What is the basis of sex determination in human beings?
(b) What are the chances of the birth of a boy or a girl during sexual reproduction in human beings?
(c) What values were shown by Ashima in dealing with the situation?
Answer:
(a) Sex in human beings is genetically determined by the sperm of the father. A male cell has two types of sex chromosomes i.e., X-chromosome and Y-chromosome because of which male produces two types of sperms with genotype A + X and A + Y. Female cells have two X-chromosomes so the genotype of eggs produced by her is A + X.
(b) During fertilisation the chances are:
- If a sperm carrying Y-chromosome fertilises the egg, then the child born will be a male i.e., AA + XY.
- If a sperm carrying X-chromosome fertilises the egg, then the child born will be a female i.e., AA + XX.
(c) Care for Others, Knowledge, Intelligent, Responsibility, scientific temperament.
Question 2.
Rohit’s father is a wrestler and has a robust body. He was also awarded as Mr. India when he was young. Rohit is the only child. As Rohit grew older, everyone expected him to have the same body built as his father. But he is thin. His friends tease him and he feels depressed by it.
(а) Is it true that a wrestler’s son should also have heavy muscles?
(b) What type of character is it: acquired or inherited?
(c) What are the values shown by Rohit’s friends? [CBSE 2013]
Answer:
(a) No, it is not true that a wrestler’s son should also have heavy muscles.
(b) It is an acquired character.
(c) Rohit’s friend are careless and ignorant. They lack scientific attitude in relation to the above situation.