Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 4 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Term 2 Set 4 with Solutions
Time : 2 Hours
Max. Marks : 40
General Instructions :
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has three sections and 15 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Section-A has 7 questions of 2 marks each; Section-B has 6 questions of 3 marks each; and Section-C has 2 case based questions of 4 marks each.
- Internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
Section – A
Question 1.
Why are carbon and its compounds used as fuels for most applications? (2)
OR
Catenation is the ability of an atom to form bonds with other atoms of the same element. It is exhibited by both carbon and silicon. Compare the ability of catenation of the two elements. Give reasons.
Answer:
Carbon and its compounds are used as fuels for most applications because they give large amount of heat on combustion due to high percentage of carbon and hydrogen. Carbon compounds used as fuel have optimum ignition temperature with high calorific values and are easy to handle. Apart from that, their combustion can be controlled. Therefore, carbon and its compounds are used as fuels.
OR
Catenation can be defined as the self-linking of atoms of an element to form chains and rings. It is shown by both Silicon and Carbon. However, carbon has the maximum capacity of catenation. The reason for this is the smaller size of carbon which makes the C-C bonds strong. On the other hand, the size of sulphur is greater than carbon which makes Si-Si bonds comparatively weaker than C-C bond. Thus, silicon bonds are less stable and reactive whereas bonds formed by carbon are very strong hence carbon shows better catenation than silicon.
Question 2.
Two pink coloured flowers on crossing resulted in 1 red, 2 pink and 1 white flower progeny. What will be the nature of the cross? (2)
Answer:
The nature of cross will be formed by the self-pollination. In incomplete dominance, the cross between plants with pure red and white flowers results in Fa generation plants with all pink flowers. The self-pollination or fertilisation of these plants results in progenies (F2 generation) with red, pink and white flowers in a ratio of 1 : 2 : 1 respectively.
Question 3.
List two sexually transmitted diseases in each of the following cases: (2)
(a) Bacterial infections
(b) Viral infections
Answer:
(a) Gonorrhoea and syphilis are bacterial infections.
(b) AIDS, warts are viral infections.
Question 4.
What is an electric motor? Name five main parts of a D.C. motor. (2)
Answer:
An electric motor is a device which converts the electrical energy into mechanical energy.
The five main parts of a D.C. motor are:
1. Strong field magnet
2. Armature coil
3. Split ring or commutator
4. Carbon brushes
5. Battery
Question 5.
Answer the following questions: (2)
(a) Name the group of chemical compounds which adversely affects the ozone layer?
(b) In the following food chain, 100 j of energy is available to the lion. How much energy was available to the producer?
Plants → Deer → Lion
OR
(a) What limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain?
(b) Why forest is considered a natural ecosystem?
Answer:
(a) Chlorofluorocarbons [CFCs] are the group of chemical compounds which adversely affect the ozone • layer.
(b) Plants are able to capture only 1% of the energy of sunlight. 10% of energy is present at each step and reaches the next level of consumers. So, if 100 J of energy is available to the lion, then the energy available to the producer is 10,000 J.
![]()
OR
(a) The flow of energy in each trophic level follows 10% rule i.e., only 10% of the energy is available to the next higher trophic level hence, the amount of energy goes on decreasing at each trophic level which limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain.
(b) Forests are considered as natural ecosystem because of the following reasons:
1. They have species of plants and animals that grow without human intervention.
2. All these species interact with each other and are interdependent on each other.
3. These are naturally sustainable.
Question 6.
Answer the following questions: (2)
(a) What property do all elements in the same column of the periodic table as boron have in common?
(b) What property do all elements in the same column of the periodic table as fluorine have in common?
OR
Define atomic size. Give its unit of measurement. In the modern periodic table what trend is observed in the atomic radius in a group and a period and why is it so?
Answer:
(a) All the elements in the same column as boron have the same number of valence electrons i.e., 3. Hence, they all have valency equal to 3.
(b) All the elements in the same column as fluorine have the same number of valence electrons i.e., 7. Hence, they all have valency equal to 1.
OR
The term atomic size refers to the radius of an atom. It is the distance between the centre of the nucleus and the outermost shell of an isolated atom. Atomic size is measured in picometer (pm). Atomic radius decreases on moving from left to right along a period. This is due to an increase in nuclear charge which tends to pull the electrons closer to the nucleus and reduces the size of the atom. While atomic size increases down the group. This is because new shells are being added as we go down the group. This increases the distance between the outermost electrons and the nucleus so that the atomic size increases inspite of the increase in nuclear charge.
Question 7.
At which trophic level is maximum energy available in the figure given below for the various tropic levels in a food chain? (2)
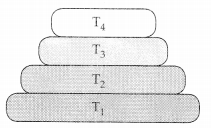
Answer:
All ecosystems are characterised by a unidirectional flow of energy. At each trophic level, most of the energy available is utilised for respiration and excretion and only ten percent of the available energy is passed on to the next level because only ten percent of the available energy can be passed on to the next trophic level, higher trophic levels have substantially less energy content and the number of trophic levels in a food chain is limited. The lower the trophic level higher will be energy content. Hence, the greatest amount of energy is expected to be in trophic level T1.
Section – B
Question 8.
Answer the following questions: (3)
(a) Name the different types of asexual reproduction seen in living organisms. Give examples for each.
(b)
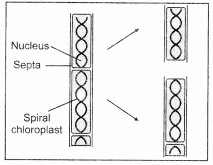
Identify the process occurring in the above figure. Briefly describe the process.
Answer:
(a) The different types of asexual reproduction seen in living organisms are:
1. Fission: It is the process in which a unicellular organism splits into two or more daughter cells. They are mainly of two types- Binary fission which is seen in Amoeba, Leshmania, Paramecium and Multiple fission seen in Plasmodium.
2. Fragmentation: It is seen in Spirogyra.
3. Regeneration: It is seen in Hydra, Planaria.
4. Budding: It is seen in Yeast, Hydra.
5. Spore formation: Here reproduction occurs through formation of spores. Spores under favourable conditions give rise to new individuals. It is seen in Rhizopus, Mucor etc.
6. Vegetative propagation: It is mainly seen in plants.
(b) The figure depicts fragmentation process in Spirogyra. In the process of fragmentation, organism after maturation breaks into smaller fragments and each fragment grows into a new individual. This process is called fragmentation.
Question 9.
State the reason why carbon can neither form \(C^{4+}\) cations nor \(C^{4-}\) anions, but forms covalent compounds. Also state reasons to explain why covalent compounds: (3)
(a) Are bad conductors of electricity?
(b) Have low melting and boiling point?
OR
A colourless organic liquid X of molecular formula C2H4O2 turns blue litmus to red. Another colourless organic liquid Y of molecular formula C3H6O has no action on any litmus but it is used as a nail polish remover. A yet another colourless organic liquid Z of molecular formula C2H6O has also no action on litmus but it is used in tincture of iodine.
(a) Name the liquid X. To which homologous series does it belong? Give the name of another member of this homologous series.
(b) Name the liquid Y. To which homologous series does it belong? Write the name of another member of this homologous series.
(c) Can you name an organic compound having the same molecular formula as liquid Y but which belongs to a different homologous series? What is this homologous series?
Answer:
Carbon has 4 electrons in its valence shell and it needs 4 electrons to complete its octet. Thus, carbon can either gain or lose 4 electrons. But due to energy consideration, it is not possible. Therefore, in place of gaining or losing 4 electrons, carbon does sharing of these 4 electrons to form covalent bonds. Therefore, carbon can neither form C4+ cations nor C4- anions but forms covalent compounds only by sharing of electrons.
(a) Covalent compounds are bad conductors of electricity because they do not contain ions.
(b) Covalent compounds have usually low melting and boiling point because the force of attraction between the molecules of covalent bond is very weak.
OR
(a) Liquid X is ethanoic acid; it belongs to homologous series of carboxylic acids. Methanoic acid is another member of this homologous series.
(b) Liquid Y is Propanone; it belongs to homologous series of ketones. Butanone is another member of this homologous series.
(c) Propanal; it belongs to homologous series of aldehydes and has same molecular formula as liquid Y.
Question 10.
Answer the following questions: (3)
(a) List any three observations which posed a challenge to Mendeleev’s Periodic law.
(b) How does the metallic character of elements vary on moving from?
(i) Left to right in a period,
(ii) From top to bottom in a group of the Modern Periodic Table?
Give reason for your answer
Answer:
Three observations which posed a challenge to Mendeleev’s Periodic law are:
1. The position of isotopes could not be explained.
2. Wrong order of atomic masses of some elements could not be explained.
3. A correct position could not be assigned to hydrogen in the periodic table.
(i) On moving from left to right in a period, the metallic character of elements increases because electropositive character decreases.
(ii) On going down in a group of the periodic table, the metallic character of elements increases because electropositive character of elements increases.
Question 11.
How will you infer with the help of an experiment that the same current flows through every part of a circuit containing three resistors in series connected to a battery? (3)
Answer:
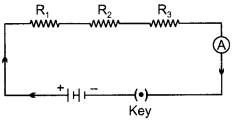
Let three resistors R1, R2 and R3 are connected in series which are also connected with a battery, an ammeter and a key as shown in figure.
When key is closed, the current starts flowing through the circuit. Take the reading of ammeter. Now change the position of ammeter to anywhere in between the resistors and take its reading. We will observe that in both the cases reading of ammeter will be same showing same current flows through every part of the circuit above.
Question 12.
Answer the following questions: (3)
(a) Explain the role of UV radiation in producing ozone layer.
(b) Mention the reactions involved.
(c) Why is excessive use of CFCs a cause of concern?
Answer:
(a) Ozone at the higher levels of the atmosphere is a product of UV radiation acting on oxygen (O2)
molecule. The higher energy UV radiations split apart some molecular oxygen (O2) into free oxygen (O) atoms. These atoms then combine with the molecular oxygen to form ozone.
(b)
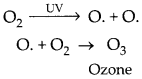
(c) The excessive use of the chemicals such as CFCs damages the ozone layer and leads to its depletion. At the higher levels of the atmosphere, ozone performs an essential function, it shields the surface of the earth from ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun. This radiation is highly damaging to organisms, since it is known to cause skin cancer in human beings.
Question 13.
Answer the following questions: (3)
(a) What do you mean by ‘magnetic field’ of a magnet?
(b) What are magnetic field lines? List two characteristic properties of these lines.
OR
Answer the following questions:
(a) State Ampere’s swimming rule.
(b) Name and state the rule to determine the direction of magnetic field produced by a straight wire carrying current.
Answer:
(a) The space or region around a magnet in which the force of attraction or repulsion due to the magnet can be detected is called the magnetic field.
(b) The lines drawn in a magnetic field along which north magnetic pole moves, are called magnetic field lines.
The characteristic properties of magnetic field lines are:
1. The magnetic lines originate from north pole and ends at south pole.
2. The magnetic lines do not intersect each other.
OR
(a) If a swimmer swims in the direction of current, facing the magnetic needle, then the north pole of the magnetic needle deflects towards his left hand i.e., west and the south pole towards his right hand i.e., east.
(b) Maxwell’s right hand thumb rule is used to determine the direction. According to this rule, when you hold a current carrying conductor in your right hand in such a way that your thumb points in the direction of the current then the direction in which your fingers encircle the conductor will give the direction of magnetic field around it.
Section – C
This section has 02 case-based questions (14 and 15). Each case is followed by 03 sub-questions (a, b and c). Parts a and b are compulsory. However, an internal choice has been provided in part c.
Question 14.
What is a solenoid? Draw the pattern of magnetic field lines of: (4)
(a) a current carrying solenoid and
(b) a bar magnet. List two distinguishing features between the two fields.
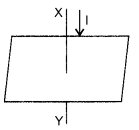
(c) In the diagram XY is a straight conductor carrying current in the direction marked by the arrow. The conductor is held vertically by passing it through a horizontal cardboard sheet. Draw three magnetic lines of force on the board and mark the direction of magnetic field in your diagram. State two factors on which magnitude of magnetic field at a point, depends.
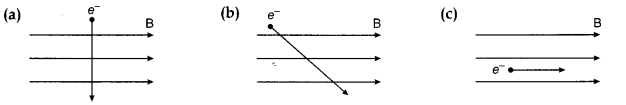
Given below are three diagrams showing entry of an electron in a magnetic field. Identify the case in which the force on electron will be maximum and minimum respectively. Give reason for your answer. Find the direction of maximum force acting on electron.
Answer:
Solenoid is a long cylindrical coil of wire consisting of a large number of turns bound together very tightly.
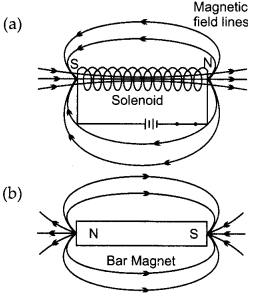
Distinguishing features are as follows :
1. Magnetic field outside the solenoid is negligible as compared to the bar magnet.
2. Magnetic field of solenoid can be varied as per our requirement just by changing current or core of solenoid but in bar magnet it is fixed.
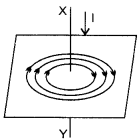
(c) The magnetic lines of force due to current in the straight conductor XY are shown in figure given alongside. The arrows on the magnetic lines of force show the direction of magnetic field.
The magnitude of magnetic field at a point depends on :
1. The strength of current in the conductor, and
2. The distance of point from the conductor.
OR
Force on electron is maximum in fig. (a) because here direction of motion of electron is at right angles to that of magnetic field ‘B’. The force is minimum (or zero) in fig. (c) because here electron is moving along the direction of magnetic field B.
The direction of maximum force acting on electron is perpendicular to the plane of paper and directed into it.
Question 15.
Acquiring characteristics or traits from one generation to the other is nothing but inheritance. Here, both the parents contribute equally to the inheritance of traits. It was Gregor Mendel, known as the Father of Genetics, who conducted immense research and studied this inheritance of traits. It was with his research on plant breeding that he came up with the laws of inheritance in living organisms. He conducted his experiments on pea plants to show the inheritance of traits in living organisms. He observed the pattern of inheritance from one generation to the other in these plants. (4)
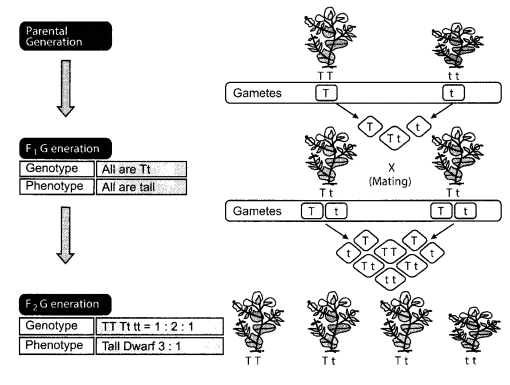
(a) Name which Mendel’s experiments shows that traits are inherited independently?
(b) What is observed by Mendel in his experiment about the phenotype and genotype?
(c) Define the term Genotype.
OR
Given below is the experiment carried out by Mendel to study inheritance of two traits in garden pea.
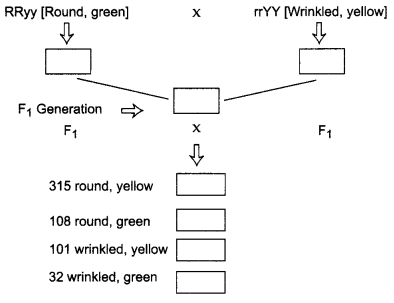
Why did Mendel carry experiment with two traits? What were his finding with respect to inheritance of traits in F1 and F2 generations?
Answer:
(a) The Dihybrid cross experiment that Mendel performed with the pea plants, shows that traits are inherited independently. In a cross between two plants with two pairs of contrasting characters, the expression of traits occurs independently.
(b) In F2, the phenotype ratio is 9 : 3 : 3 : 1. The genotype ratio is a very complex one.
(c) Genotype: It is the complete heritable genetic identity of an organism. It is the actual set of alleles that are carried by the organism.
OR
Mendel carried out experiment with two traits to study the independent assortment of characters during inheritance. In generation though both the traits were inherited but only dominant traits [i.e., round, yellow characters] are expressed, the recessive traits, [wrinkled, green] were not expressed. But in F2 generation both dominant and recessive traits were expressed in the ratio 9 : 3 : 3 : 1.