Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 6 Linear Inequalities with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 11 Maths with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided Linear Inequalities Class 11 Maths MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
Class 11 Maths Chapter 6 MCQ With Answers
Maths Class 11 Chapter 6 MCQs On Linear Inequalities
Question 1.
Sum of two rational numbers is ______ number.
(a) rational
(b) irrational
(c) Integer
(d) Both 1, 2 and 3
Answer
Answer: (a) rational
Hint:
The sum of two rational numbers is a rational number.
Ex: Let two rational numbers are 1/2 and 1/3
Now, 1/2 + 1/3 = 5/6 which is a rational number.
Question 2.
If x² = -4 then the value of x is
(a) (-2, 2)
(b) (-2, ∞)
(c) (2, ∞)
(d) No solution
Answer
Answer: (d) No solution
Hint:
Given, x² = -4
Since LHS ≥ 0 and RHS < 0
So, No solution is possible.
Question 3.
Solve: (x + 1)² + (x² + 3x + 2)² = 0
(a) x = -1, -2
(b) x = -1
(c) x = -2
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) x = -1
Hint:
Given, (x + 1)² + (x² + 3x + 2)² = 0
This is true when each term is equal to zero simultaneously,
So, (x + 1)² = 0 and (x² + 3x + 2)² = 0
⇒ x + 1 = 0 and x² + 3x + 2 = 0
⇒ x = -1, and x = -1, -2
Now, the common solution is x = -1
So, solution of the equation is x = -1
Question 4.
If (x + 3)/(x – 2) > 1/2 then x lies in the interval
(a) (-8, ∞)
(b) (8, ∞)
(c) (∞, -8)
(d) (∞, 8)
Answer
Answer: (a) (-8, ∞)
Hint:
Given,
(x + 3)/(x – 2) > 1/2
⇒ 2(x + 3) > x – 2
⇒ 2x + 6 > x – 2
⇒ 2x – x > -2 – 6
⇒ x > -8
⇒ x ∈ (-8, ∞)
Question 5.
The region of the XOY-plane represented by the inequalities x ≥ 6, y ≥ 2, 2x + y ≤ 10 is
(a) unbounded
(b) a polygon
(c) none of these
(d) exterior of a triangle
Answer
Answer: (c) none of these
Hint:
Given inequalities x ≥ 6, y ≥ 2, 2x + y ≤ 10
Now take x = 6, y = 2 and 2x + y = 10
when x = 0, y = 10
when y = 0, x = 5
So, the points are A(6, 2), B(0, 10) and C(5, 0)
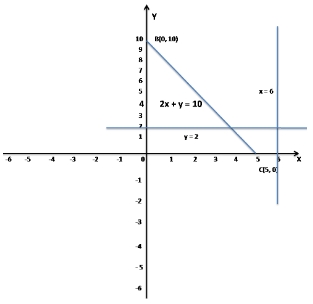
So, the region of the XOY-plane represented by the inequalities x ≥ 6, y ≥ 2, 2x + y ≤ 10 is not defined.
Question 6.
The interval in which f(x) = (x – 1) × (x – 2) × (x – 3) is negative is
(a) x > 2
(b) 2 < x and x < 1
(c) 2 < x < 1 and x < 3
(d) 2 < x < 3 and x < 1
Answer
Answer: (d) 2 < x < 3 and x < 1
Hint:
Given, f(x) = (x – 1) × (x – 2) × (x – 3) has all factors with odd powers.
So, put them zero
i.e. x – 1 = 0, x – 2 = 0, x – 3 = 0
⇒ x = 1, 2, 3
Now, f(x) < 0 when 2 < x < 3 and x < 1
Question 7.
If -2 < 2x – 1 < 2 then the value of x lies in the interval
(a) (1/2, 3/2)
(b) (-1/2, 3/2)
(c) (3/2, 1/2)
(d) (3/2, -1/2)
Answer
Answer: (b) (-1/2, 3/2)
Hint:
Given, -2 < 2x – 1 < 2
⇒ -2 + 1 < 2x < 2 + 1
⇒ -1 < 2x < 3
⇒ -1/2 < x < 3/2
⇒ x ∈(-1/2, 3/2)
Question 8.
The solution of the inequality |x – 1| < 2 is
(a) (1, ∞)
(b) (-1, 3)
(c) (1, -3)
(d) (∞, 1)
Answer
Answer: (b) (-1, 3)
Hint:
Given, |x – 1| < 2
⇒ -2 < x – 1 < 2
⇒ -2 + 1 < x < 2 + 1
⇒ -1 < x < 3
⇒ x ∈ (-1, 3)
Question 9.
If | x − 1| > 5, then
(a) x∈(−∞, −4)∪(6, ∞]
(b) x∈[6, ∞)
(c) x∈(6, ∞)
(d) x∈(−∞, −4)∪(6, ∞)
Answer
Answer: (d) x∈(−∞, −4)∪(6, ∞)
Hint:
Given |x−1| >5
Case 1:
(x – 1) > 5
⇒ x > 6
⇒ x ∈ (6,∞)
Case 2:
-(x – 1) > 5
⇒ -x + 1 > 5
⇒ -x > 4
⇒ x < -4
⇒ x ∈ (−∞, −4)
So the range of x is (−∞, −4)∪(6, ∞)
Question 10.
The solution of |2/(x – 4)| > 1 where x ≠ 4 is
(a) (2, 6)
(b) (2, 4) ∪ (4, 6)
(c) (2, 4) ∪ (4, ∞)
(d) (-∞, 4) ∪ (4, 6)
Answer
Answer: (b) (2, 4) ∪ (4, 6)
Hint:
Given, |2/(x – 4)| > 1
⇒ 2/|x – 4| > 1
⇒ 2 > |x – 4|
⇒ |x – 4| < 2
⇒ -2 < x – 4 < 2
⇒ -2 + 4 < x < 2 + 4
⇒ 2 < x < 6
⇒ x ∈ (2, 6) , where x ≠ 4
⇒ x ∈ (2, 4) ∪ (4, 6)
Question 11.
If (|x| – 1)/(|x| – 2) ≥ 0, x ∈ R, x ± 2 then the interval of x is
(a) (-∞, -2) ∪ [-1, 1]
(b) [-1, 1] ∪ (2, ∞)
(c) (-∞, -2) ∪ (2, ∞)
(d) (-∞, -2) ∪ [-1, 1] ∪ (2, ∞)
Answer
Answer: (d) (-∞, -2) ∪ [-1, 1] ∪ (2, ∞)
Hint:
Given, (|x| – 1)/(|x| – 2) ≥ 0
Let y = |x|
So, (y – 1)/(y – 2) ≥ 0
⇒ y ≤ 1 or y > 2
⇒ |x| ≤ 1 or |x| > 2
⇒ (-1 ≤ x ≤ 1) or (x < -2 or x > 2)
⇒ x ∈ [-1, 1] ∪ (-∞, -2) ∪ (2, ∞)
Hence the solution set is:
x ∈ (-∞, -2) ∪ [-1, 1] ∪ (2, ∞)
Question 12.
The solution of the -12 < (4 -3x)/(-5) < 2 is
(a) 56/3 < x < 14/3
(b) -56/3 < x < -14/3
(c) 56/3 < x < -14/3
(d) -56/3 < x < 14/3
Answer
Answer: (d) -56/3 < x < 14/3
Hint:
Given inequality is :
-12 < (4 -3x)/(-5) < 2
⇒ -2 < (4-3x)/5 < 12
⇒ -2 × 5 < 4 – 3x < 12 × 5
⇒ -10 < 4 – 3x < 60
⇒ -10 – 4 < -3x < 60-4
⇒ -14 < -3x < 56
⇒ -56 < 3x < 14
⇒ -56/3 < x < 14/3
Question 13.
If x² = -4 then the value of x is
(a) (-2, 2)
(b) (-2, ∞)
(c) (2, ∞)
(d) No solution
Answer
Answer: (d) No solution
Hint:
Given, x² = -4
Since LHS ≥ 0 and RHS < 0
So, No solution is possible.
Question 14.
Solve: |x – 3| < 5
(a) (2, 8)
(b) (-2, 8)
(c) (8, 2)
(d) (8, -2)
Answer
Answer: (b) (-2, 8)
Hint:
Given, |x – 3| < 5
⇒ -5 < (x – 3) < 5
⇒ -5 + 3 < x < 5 + 3
⇒ -2 < x < 8
⇒ x ∈ (-2, 8)
Question 15.
The graph of the inequations x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0, 3x + 4y ≤ 12 is
(a) none of these
(b) interior of a triangle including the points on the sides
(c) in the 2nd quadrant
(d) exterior of a triangle
Answer
Answer: (b) interior of a triangle including the points on the sides
Hint:
Given inequalities x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0, 3x + 4y ≤ 12
Now take x = 0, y = 0 and 3x + 4y = 12
when x = 0, y = 3
when y = 0, x = 4
So, the points are A(0, 0), B(0, 3) and C(4, 0)
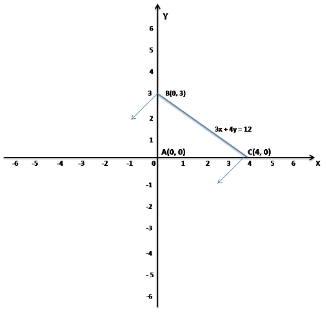
So, the graph of the inequations x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0, 3x + 4y ≤ 12 is interior of a triangle including the points on the sides.
Question 16.
If |x| < 5 then the value of x lies in the interval
(a) (-∞, -5)
(b) (∞, 5)
(c) (-5, ∞)
(d) (-5, 5)
Answer
Answer: (d) (-5, 5)
Hint:
Given, |x| < 5
It means that x is the number which is at distance less than 5 from 0
Hence, -5 < x < 5
⇒ x ∈ (-5, 5)
Question 17.
Solve: f(x) = {(x – 1)×(2 – x)}/(x – 3) ≥ 0
(a) (-∞, 1] ∪ (2, ∞)
(b) (-∞, 1] ∪ (2, 3)
(c) (-∞, 1] ∪ (3, ∞)
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) (-∞, 1] ∪ (2, 3)
Hint:
Given, f(x) = {(x – 1)×(2 – x)}/(x – 3) ≥ 0
or f(x) = -{(x – 1)×(2 – x)}/(x – 3)
which gives x – 3 ≠ 0
⇒ x ≠ 3
![]()
Using number line rule as shown in the figure,
which gives f(x) ≥ 0 when x ≤ 1 or 2 ≤ x < 3
i.e. x ∈ (-∞, 1] ∪ (2, 3)
Question 18.
If x² = 4 then the value of x is
(a) -2
(b) 2
(c) -2, 2
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) -2, 2
Hint:
Given, x² = 4
⇒ x² – 4 = 0
⇒ (x – 2)×(x + 2) = 0
⇒ x = -2, 2
Question 19.
The solution of the 15 < 3(x – 2)/5 < 0 is
(a) 27 < x < 2
(b) 27 < x < -2
(c) -27 < x < 2
(d) -27 < x < -2
Answer
Answer: (a) 27 < x < 2
Hint:
Given inequality is:
15 < 3(x-2)/5 < 0
⇒ 15 × 5 < 3(x-2) < 0 × 5
⇒ 75 < 3(x-2) < 0
⇒ 75/3 < x-2 < 0
⇒ 25 < x-2 < 0
⇒ 25 +2 < x <0+2
⇒ 27 < x < 2
Question 20.
Solve: 1 ≤ |x – 1| ≤ 3
(a) [-2, 0]
(b) [2, 4]
(c) [-2, 0] ∪ [2, 4]
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) [-2, 0] ∪ [2, 4]
Hint:
Given, 1 ≤ |x – 1| ≤ 3
⇒ -3 ≤ (x – 1) ≤ -1 or 1 ≤ (x – 1) ≤ 3
i.e. the distance covered is between 1 unit to 3 units
⇒ -2 ≤ x ≤ 0 or 2 ≤ x ≤ 4
Hence, the solution set of the given inequality is
x ∈ [-2, 0] ∪ [2, 4]
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 6 Linear Inequalities with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding CBSE Class 11 Maths Linear Inequalities MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.
Class 10 Maths MCQ:
- Sets Class 11 MCQ
- Relations and Functions Class 11 MCQ
- Trigonometric Functions Class 11 MCQ
- Principle of Mathematical Induction Class 11 MCQ
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations Class 11 MCQ
- Linear Inequalities Class 11 MCQ
- Permutations and Combinations Class 11 MCQ
- Binomial Theorem Class 11 MCQ
- Sequences and Series Class 11 MCQ
- Straight Lines Class 11 MCQ
- Conic Sections Class 11 MCQ
- Introduction to Three Dimensional Geometry Class 11 MCQ
- Limits and Derivatives Class 11 MCQ
- Mathematical Reasoning Class 11 MCQ
- Statistics Class 11 MCQ
- Probability Class 11 MCQ