Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have Provided Management of Natural Resources Class 10 Science MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
Class 10 Science Biology Chapter 16 MCQ With Answers
You can refer to NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources to revise the concepts in the syllabus effectively and improve your chances of securing high marks in your board exams.
Biology Class 10 Chapter 16 MCQs on Management of Natural Resources
Question 1.
The better way to assess the pollution level of a water body is to calculate the:
(a) Nutrient level
(b) Number of organisms
(c) Coliform count
(d) Pesticide level.
Answer
Answer: (c) Coliform count
Question 2.
The purpose of rainwater harvesting is to:
(a) use it for irrigation
(b) culture fishes
(c) use it for washing ears
(d) recharge ground water
Answer
Answer: (d) recharge ground water
Question 3.
‘Kulhs’ the ancient water harvesting structure were made in
(a) Manipur
(b) Bihar
(c) Himachal Pradesh
(d) Uttar Pradesh
Answer
Answer: (c) Himachal Pradesh
Question 4.
The three R’s that will help us to conserve natural resources for long term use are
(a) recycle, regenerate, reuse
(b) reduce, regenerate, reuse
(c) reduce, reuse, redistribute
(d) reduce, recycle, reuse
Answer
Answer: (d) reduce, recycle, reuse
Question 5.
Amrita Devi Bishnoi sacrificed her life to protect the
(a) Palm trees
(b) Khejri trees
(c) Sal trees
(d) Teakwood trees.
Answer
Answer: (b) Khejri trees
Question 6.
Khadins, bundhis, ahars and kattas are ancient structures built for the purpose of:
(a) store grains
(b) conserve soil
(c) water harvesting
(d) conserve wildlife.
Answer
Answer: (c) water harvesting
Question 7.
The Tehri Dam is constructed on River
(a) Yamuna
(b) Bhagirathi
(c) Ravi
(d) Sutlej
Answer
Answer: (b) Bhagirathi
Question 8.
The degraded Arabari forests were revived by the efforts of
(a) A.K. Chatterjee
(b) A.K. Baneijee
(c) Sunder Lai Bahuguna
(d) Amrita Devi
Answer
Answer: (b) A.K. Baneijee
Question 9.
Which plan has been started by government to control pollution of Ganga?
(a) Ganga Action Plan
(b) Ganga Revival Plan
(c) Swachh Jal Abhiyan
(d) Ganga Restoration Plan
Answer
Answer: (a) Ganga Action Plan
Question 10.
Which pH range is most suitable for life of fresh water plants and animals?
(a) 6.5 – 7.5
(b) 2.0 – 3.5
(c) 3.5 – 7.0
(d) 9.0 – 10.5
Answer
Answer: (a) 6.5 – 7.5
Question 11.
The most appropriate definition of a natural resource is that it is a substance/commodity that is
(a) present only on land
(b) a gift of nature which is very useful to mankind
(c) a man-made substance placed in nature
(d) available only in the forest
Answer
Answer: (b) a gift of nature which is very useful to mankind
Question 12.
The main cause for abundant coliform bacteria in the river Ganga is
(a) disposal of unbumt corpses into water
(b) discharge of effluents from electroplating industries
(c) washing of clothes
(d) immersion of ashes
Answer
Answer: (a) disposal of unbumt corpses into water
Question 13.
Among the statements given below select the ones that correctly describe the concept of sustainable development
(i) Planned growth with minimum damage to the environment
(ii) Growth irrespective of the extent of damage caused to the environment
(iii) Stopping all developmental work to conserve the environment
(iv) Growth that is acceptable to all the stakeholders
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (iii) only
Answer
Answer: (a) (i) and (iv)
Question 14.
In our country, there are attempts to increase the height of several existing dams like Tehri and Almati, dams across Narmada. Choose the correct statements among the following that are a consequence of raising the height of dams
(i) Terrestrial flora and fauna of the area is destroyed completely
(ii) Dislocation of people and domestic animals living in the area
(iii) Valuable agricultural land may be permanently lost
(iv) It will generate permanent employment for people
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Answer
Answer: (b) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Question 15.
Select the incorrect statement.
(a) Economic development is linked to environmental conservation
(b) Sustainable development encourages development for current generation and conservation of resources for future generations
(c) Sustainable development does not consider the view points of stakeholders
(d) Sustainable development is a long planned and persistent development
Answer
Answer: (c) Sustainable development does not consider the view points of stakeholders
Question 16.
Pick the right combination of terms which has no fossil fuel.
(a) Wind, ocean and coal
(b) Kerosene, wind and tide
(c) Wind, wood, sun
(d) Petroleum, wood, sun
Answer
Answer: (c) Wind, wood, sun
Question 17.
Select the eco-friendly activity among the following:
(a) Using car for transportation
(b) Using polybags for shopping
(c) Using dyes for colouring clothes
(d) Using windmills to generate power for irrigation
Answer
Answer: (d) Using windmills to generate power for irrigation
Question 18.
A successful forest conservation strategy should involve
(a) protection of animals at the highest trophic level
(b) protection of only consumers
(c) protection of only herbivores
(d) comprehensive programme to protect all the physical and biological components
Answer
Answer: (d) comprehensive programme to protect all the physical and biological components
Question 19.
Arabari forests of Bengal is dominated by
(a) Teak
(b) Sal
(c) Bamboo
(d) Mangrove
Answer
Answer: (b) Sal
Fill in the blanks
1. Loss of diversity may lead to a loss of ………….. stability.
Answer
Answer: Ecological
2. ………….. are ‘biodiversity hot spots’.
Answer
Answer: Forests
3. Surangams in ………….. and ………….. in Karnataka are some of the ancient water harvesting methods.
Answer
Answer: Kerala, Kattas
4. The ………….. of water can be checked using universal indicator.
Answer
Answer: pH
5. The concept of ………….. encourages judicious use of resources for current basic human needs, while preserving them for the needs of future generations.
Answer
Answer: sustainable development
6. The management of natural resources requires a ………….. perspective so that they cater to the needs of the generations to come.
Answer
Answer: long-term
7. Pollution due to mining is caused by the large amount of ………….. which is discarded for every tonne of metal extracted.
Answer
Answer: slag
8. Amrita Devi Bishnoi sacrificed her life for protection of ………….. trees in Khejarli village.
Answer
Answer: Khejri
9. The movement called ………….. originated from a remote village called Rani in Garhwal for conservation of forests.
Answer
Answer: Chipko Andolan
10. Due to the efforts of forest officer ………….. villagers were involved in the protection of 1, 272 hectares of badly degraded ………….. forest in the Arabari forest range.
Answer
Answer: A.K. Baneijee, Sal
Answer the one word
1. Name the three R’s which help to conserve natural resources.
Answer
Answer: Reduce, Recycle, Reuse
2. Name the movement started in Garhwal Himalayas to conserve forests.
Answer
Answer: Chipko movement
3. What is the practice of growing and cultivation of trees called?
Answer
Answer: Silviculture
4. Name the traditional water harvesting systems of Himachal Pradesh and Tamilnadu.
Answer
Answer: Kulhs, Eris
5. Which trees were replenished by efforts of local people of Arabari forest range?
Answer
Answer: Sal
6. Which indicator is used to test pH levels of all kinds of water?
Answer
Answer: Universal indicator
7. Which places are called as the “biodiversity hot spots’?
Answer
Answer: Forests
8. What is the use of tendu leaves?
Answer
Answer: Making bidis
9. Give the term which denotes the variety of life forms present on Earth.
Answer
Answer: Biodiversity
10. Name the trees for whose protection Amrita Devi Bishnoi sacrificed her life.
Answer
Answer: Khejri
Match the following columns
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Khadins | (a) Fossil fuel |
| (ii) Cow dung | (b) Bihar |
| (iii) Universal Indicator | (c) Biomass |
| (iv) Ahars | (d) pH |
| (v) Coal | (e) Rajasthan |
| (vi) Flooded gullies | (f) Bhagirathi |
| (vii) Tehri dam | (g) Check dams |
| (viii) Coliform | (h) Pine, teak |
| (ix) Salts for huts | (i) Water contamination |
| (x) Monoculture | (j) Bamboo |
Answer
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Khadins | (e) Rajasthan |
| (ii) Cow dung | (c) Biomass |
| (iii) Universal Indicator | (d) pH |
| (iv) Ahars | (b) Bihar |
| (v) Coal | (a) Fossil fuel |
| (vi) Flooded gullies | (g) Check dams |
| (vii) Tehri dam | (f) Bhagirathi |
| (viii) Coliform | (i) Water contamination |
| (ix) Salts for huts | (j) Bamboo |
| (x) Monoculture | (h) Pine, teak |
Crossword
Across:
3. Water harvesting system of Maharashtra [4]
5. A kind of water harvesting system [5]
6. Coal and petroleum are this type of fuel [6]
7. A water harvesting system in Tamilnadu [4]
8. Wood used as building material [6]
Down:
1. They help to generate electricity [4]
2. A water harvesting system Used in Bihar [4]
3. A dam on river Bhagirathi [5]
4. Forests revived in Arabari range [3]
6. They are the biodiversity hot spots [6]
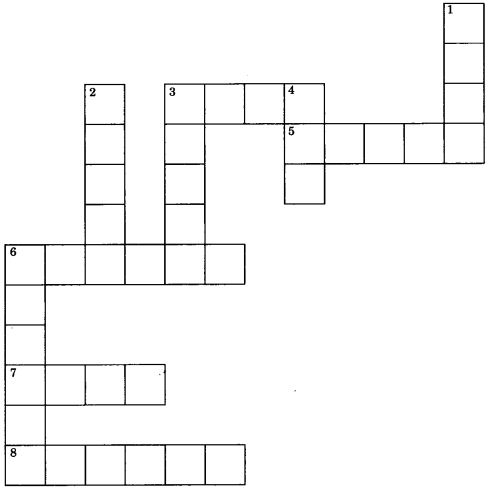
Answer
Answer:
Across:
3. Tals
5. Ahar
6. Fossil
7. Erssal
8. Timber
Down:
1. Dams
2. Pynes
3. Tehri
4. Sal
6. Forest
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding Management of Natural Resources CBSE Class 10 Science MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.
Class 10 Science Biology MCQ With Answers
- Life Processes Class 10 MCQ
- Control and Coordination Class 10 MCQ
- How do Organisms Reproduce? Class 10 MCQ
- Heredity and Evolution Class 10 MCQ
- Sources of Energy Class 10 MCQ
- Our Environment Class 10 MCQ
- Management of Natural Resources Class 10 MCQ