Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have Provided Human Eye and Colourful World Class 10 Science MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
Class 10 Science Physics Chapter 11 MCQ With Answers
You can refer to NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World to revise the concepts in the syllabus effectively and improve your chances of securing high marks in your board exams.
Physics Class 10 Chapter 11 MCQs on Human Eye and Colourful World
Question 1.
A person cannot see distinctly objects kept beyond 2 m. This defect can be corrected by using lens of power
(a) +0.5 D
(b) -0.5 D
(c) +0.2 D
(d) -0.2 D
Answer
Answer: (b) -0.5 D
Question 2.
A student sitting on the last bench can read the letters written on the blackboard but is not able to read / the letters written in his textbook. Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) The near point of his eyes has receded away.
(b) The near point of his eyes has come closer to him.
(c) The far point of his eyes has come closer to him.
(d) The far point of his eyes has receded away.
Answer
Answer: (a) The near point of his eyes has receded away.
Question 3.
A prism ABC (with BC as base) is placed in different orientations. A narrow beam of white light is incident on the prism as shown in the Figures given below. In which of the following cases, after dispersion, the third colour from the top corresponds to the colour of the sky?
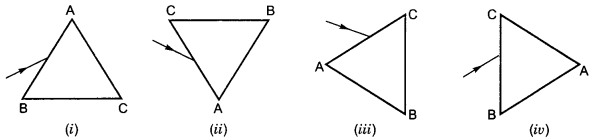
(a) (i)
(b) (ii)
(c) (iii)
(d) (iv)
Answer
Answer: (b) (ii)
Question 4.
At noon the sun appears white as
(a) light is least scattered.
(b) all the colours of the white light are scattered away.
(c) blue colour is scattered the most.
(d) red colour is scattered the most.
Answer
Answer: (a) light is least scattered.
Question 5.
Which of the following phenomena of light are involved in the formation of a rainbow?
(a) Reflection, refraction and dispersion
(b) Refraction, dispersion and total internal reflection
(c) Refraction, dispersion and internal reflection
(d) Dispersion, scattering and total internal reflection
Answer
Answer: (c) Refraction, dispersion and internal reflection
Question 6.
Twinkling of stars is due to atmospheric
(a) dispersion of light by water droplets
(b) refraction of light by different layers of varying refractive indices
(c) scattering of light by dust particles
(d) internal reflection of light by clouds
Answer
Answer: (b) refraction of light by different layers of varying refractive indices
Question 7.
The clear sky appears blue because
(а) blue light gets absorbed in the atmosphere.
(b) ultraviolet radiations are absorbed in the atmosphere.
(c) violet and blue lights get scattered more than lights of all other colours by the atmosphere.
(d) light of all other colours is scattered more than the violet and blue colour lights by the atmosphere.
Answer
Answer: (c) violet and blue lights get scattered more than lights of all other colours by the atmosphere.
Question 8.
Which of the following statements is correct regarding the propagation of light of different colours of white light in air?
(a) Red light moves fastest.
(b) Blue light moves faster than green light.
(c) All the colours of the white light move with the same speed.
(d) Yellow light moves with the mean speed as that of the red and the violet light.
Answer
Answer: (c) All the colours of the white light move with the same speed.
Question 9.
The danger signals installed at the top of tall buildings are red in colour. These can be easily seen from a distance because among all other colours, the red light
(a) is scattered the most by smoke or fog.
(b) is scattered the least by smoke or fog.
(c) is absorbed the most by smoke or fog.
(d) moves fastest in air.
Answer
Answer: (b) is scattered the least by smoke or fog.
Question 10.
Which of the following phenomena contributes significantly to the reddish appearance of the sun at sunrise or sunset?
(a) Dispersion of light
(b) Scattering of light
(c) Total internal reflection of light
(d) Reflection of light from the earth
Answer
Answer: (b) Scattering of light
Question 11.
The bluish colour of water in deep sea is due to
(a) the presence of algae and other plants found in water
(b) reflection of sky in water
(c) scattering of light
(d) absorption of light by the sea
Answer
Answer: (c) scattering of light
Question 12.
When light rays enter the eye, most of the refraction occurs at the
(a) crystalline lens
(b) outer surface of the cornea
(c) iris
(d) pupil
Answer
Answer: (b) outer surface of the cornea
Question 13.
The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye muscles
(a) are relaxed and lens becomes thinner
(b) contract and lens becomes thicker
(c) are relaxed and lens becomes thicker
(d) contract and lens becomes thinner
Answer
Answer: (a) are relaxed and lens becomes thinner
Question 14.
Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) A person with myopia can see distant objects clearly.
(b) A person with hypermetropia can see nearby objects clearly.
(c) A person with myopia can see nearby objects clearly.
(d) A person with hypermetropia cannot see distant objects clearly.
Answer
Answer: (c) A person with myopia can see nearby objects clearly.
Question 15.
A student traces the path of a ray through a glass prism for four different values of angle of incidence. On analysing the diagrams he is likely to conclude that the emergent ray
(a) is always parallel to the incident ray.
(b) is always perpendicular to the incident ray.
(c) is always parallel to the refracted ray.
(d) always bends at an angle to the direction of incident ray.
Answer
Answer: (d) always bends at an angle to the direction of incident ray.
Question 16.
A student is observing the diagram showing the path of a ray of light passing through a glass prism. He would find that for all angles of incidence the ray of light bends:
(а) towards the normal while entering into the prism and away from the normal while emerging out of the prism
(b) away from the normal while entering into the prism and towards the normal while emerging out of the prism.
(c) away from the normal while entering as well as while emerging out of the prism.
(d) towards the normal while entering as well as while emerging out of the prism.
Answer
Answer: (а) towards the normal while entering into the prism and away from the normal while emerging out of the prism
Question 17.
In the following diagram, the path of a ray of light passing through a glass prism is shown:
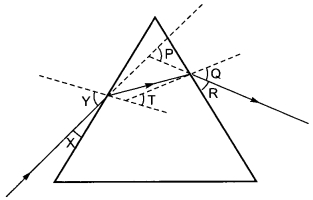
In this diagram the angle of incidence, the angle of emergence and the angle of deviation respectively are (select the correct option):
(a) X, R and T
(b) Y, Q and T
(c) X, Q and P
(d) Y, Q and P
Answer
Answer: (d) Y, Q and P
Question 18.
After tracing the path of a ray of light through a glass prism a student marked the angle of incidence (∠i), angle of refraction (∠r), angle of emergence (∠e) and the angle of deviation (∠D) as shown in the diagram. The correctly marked angles are:
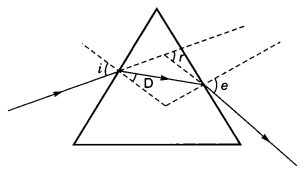
(a) ∠i and ∠r
(b) ∠i and ∠e
(c) ∠i, ∠e and ∠D
(d) ∠i, ∠r and ∠e
Answer
Answer: (b) ∠i and ∠e
Question 19.
The splitting of white light into its component colours is called
(a) refraction
(b) reflation
(c) dispersion
(d) tyndall effect
Answer
Answer: (c) dispersion
Question 20.
Reason behind advance sunrise and delayed sunset
(a) atmospheric refraction
(b) total internal reflection
(c) dispersion
(d) reflection
Answer
Answer: (a) atmospheric refraction
Question 21.
Type of lens used in correction of myopia
(a) convex lens
(b) concave lens
(c) reflecting lens
(d) bifocal lens
Answer
Answer: (b) concave lens
Question 22.
Type of lens used in correction of hypermetropia
(a) concave lens
(b) reflecting lens
(c) bifocal lens
(d) convex lens
Answer
Answer: (d) convex lens
Question 23.
Myopia may arise due to
(a) excessive curvature of the eye lens
(b) elongation of the eyeball
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: (c) both (a) and (b)
Question 24.
In an experiment to trace the path of a ray of light through a glass prism for different values of angle of incidence a student would find that the emergent ray:
(a) is parallel to the incident ray
(b) is perpendicular to the incident ray
(c) is parallel to the refracted ray
(d) bends at an angle to the direction of incident ray
Answer
Answer: (d) bends at an angle to the direction of incident ray
Question 25.
While performing the experiment to trace the path of a ray of light passing through a glass prism, four students marked the incident ray and the emergent ray in their diagrams in the manner shown below.
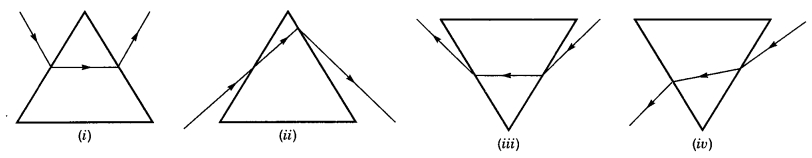
The correct path of the rays has been shown by:
(a) I
(b) II
(c) III
(d) IV
Answer
Answer: (c) III
Question 26.
A dark muscular membrane which controls size of pupil
(a) eye
(b) iris
(c) cornea
(d) retina
Answer
Answer: (b) iris
Question 27.
Least distance of distinct vision for normal eye is
(a) 25 cm
(b) 50 cm
(c) 75 cm
(d) infinity
Answer
Answer: (a) 25 cm
Question 28.
Farthest point of a normal eye is
(a) 25 cm
(b) 50 cm
(c) 75 cm
(d) infinity
Answer
Answer: (d) infinity
Question 29.
Crystalline lens of people at old age becomes milky and cloudy. This condition is called
(a) myopia
(b) lever
(c) cataract
(d) presbyopia
Answer
Answer: (c) cataract
Question 30.
The splitting of light into its component colours is called
(a) Spectrum
(b) Dispersion
(c) Tyndall effect
(d) Refraction
Answer
Answer: (b) Dispersion
Question 31.
Bifocal lens is used in
(a) myopia
(b) lever
(c) Cataract
(d) Presbyopia
Answer
Answer: (d) Presbyopia
Question 32.
Stars appears to be twinkling because of
(a) atmospheric refraction
(b) reflection
(c) Tyndall effect
(d) spectrum
Answer
Answer: (a) atmospheric refraction
Fill in the blanks
1. ………….. regulates and controls the amount of light entering the eye.
Answer
Answer: Pupil
2. The ability of the eye lens to adjust its focal length is called …………..
Answer
Answer: Accomodation
3. A person with ………….. can see nearby objects clearly but cannot see distant objects clearly.
Answer
Answer: Myopia
4. The splitting of light into its component colours is called …………..
Answer
Answer: Dispersion
5. The phenomenon of scattering of light by colloidal particles gives rise to …………..
Answer
Answer: Tyndall effect
Match the following columns
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Rainbow formation | (i) A person cannot see nearby objects clearly |
| (b) Twinkling of stars | (ii) Regulates and controls amount of light entering the eye |
| (c) Blue colour of sky | (iii) Scattering of light |
| (d) Myopia | (iv) Dispersion |
| (e) Hypermetropia | (v) Infinity |
| (f) Least distance of distinct vision | (vi) Membrane which controls the size of pupil |
| (g) Far point of eye | (vii) Atmospheric refraction |
| (h) Iris | (viii) Twenty five centimeters |
| (i) Pupil | (ix) A person cannot see distant objects distinctly |
Answer
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Rainbow formation | (iv) Dispersion |
| (b) Twinkling of stars | (vii) Atmospheric refraction |
| (c) Blue colour of sky | (iii) Scattering of light |
| (d) Myopia | (ix) A person cannot see distant objects distinctly |
| (e) Hypermetropia | (i) A person cannot see nearby objects clearly |
| (f) Least distance of distinct vision | (viii) Twenty five centimeters |
| (g) Far point of eye | (v) Infinity |
| (h) Iris | (vi) Membrane which controls the size of pupil |
| (i) Pupil | (ii) Regulates and controls amount of light entering the eye |
Complete the crossword below:
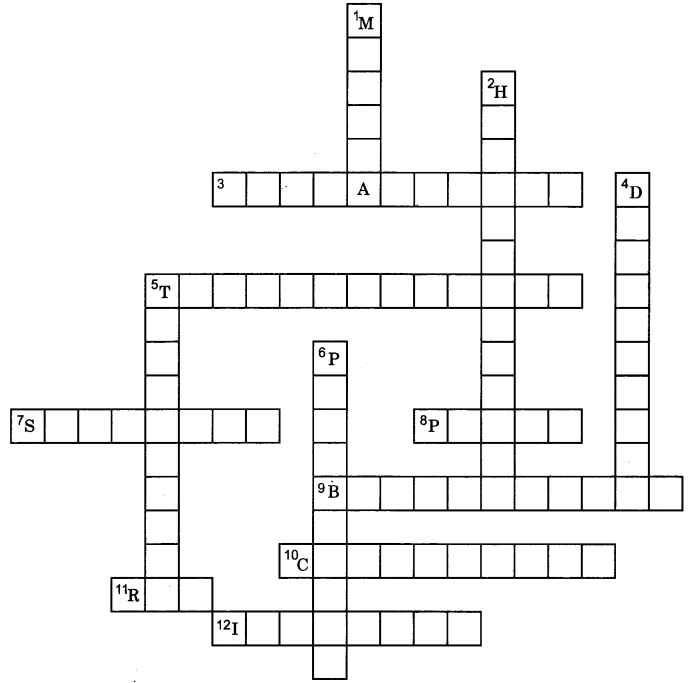
Across
3. Lens used for correction of myopia
5. The phenomenon of scattering of light by colloidal particles .
7. The band of coloured components of a light beam
8. Part of eye which regulates and controls the amount of light entering the eye
9. Lens used in correction of presbyopia
10. Lens used in correction of hypermetropia
11. Colour used for danger signal
12. Farthest point for a normal eye
Down
1. Eye defect in which a person cannot see distant objects distinctly
2. Eye defect in which a person cannot be nearby objects clearly
4. Splitting of light into its component colours
5. Least distance of distinct vision (in cm)
6. The eye defect which is caused by weakening of ciliary muscles
Answer
Answer:
Across:
3. Concave lens
5. Tyndall effect
7. Spectrum
8. Pupil
9. Bifocal lens
10. Convex lens
11. Red
12. Infinity
Down:
1. Myopia
2. Hypermetropia
4. Dispersion
5. Twenty five
6. Presbyopia
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding Human Eye and Colourful World CBSE Class 10 Science MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.
Class 10 Science Physics MCQ With Answers
- Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 MCQ
- Human Eye and Colourful World Class 10 MCQ
- Electricity Class 10 MCQ
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Class 10 MCQ