Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have Provided Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Class 10 Science MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
You can refer to NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current to revise the concepts in the syllabus effectively and improve your chances of securing high marks in your board exams.
Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Class 10 MCQs Questions with Answers
Question 1.
Choose the incorrect statements from the following regarding magnetic lines of field.
(a) the direction of magnetic field at a point is taken to be the direction in which the north pole of a magnetic compass needle points
(b) magnetic field lines are closed curves
(c) if magnetic field lines are parallel and equidistant, they represent zero field strength
(d) relative strength of magnetic field is shown by the degree of closeness of the field lines.
Answer
Answer: (c) if magnetic field lines are parallel and equidistant, they represent zero field strength
Question 2.
If the key in the arrangement figure given below is taken out (the circuit is made open) and magnetic . field lines are drawn over the horizontal plane ABCD, the lines are
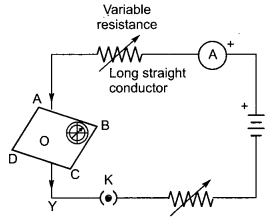
(a) concentric circles
(b) elliptical in shape
(c) straight lines parallel to each other (Due to earth’s magnetic field)
(d) concentric circles near the point O but of elliptical shapes as we go away from it.
Answer
Answer: (c) straight lines parallel to each other (Due to earth’s magnetic field)
Question 3.
A circular loop placed in a plane perpendicular to the plane of paper carries a current when the keys is ON. The current as seen from points A and B (in the plane of paper and on the axis of the coil) is anticlockwise and clockwise respectively. The magnetic field lines point from B to A. The N-pole of the resultant magnet is on the faces close to
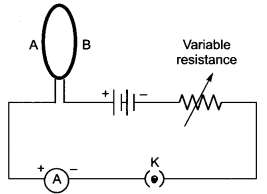
(a) A
(b) B
(c) A if the current is small, and B if the current is large
(d) B if the current is small and A if the current is large.
Answer
Answer: (a) A
Question 4.
For a current in a long straight solenoid, N- and S-poles are created at the two ends. Among the following statements, the incorrect statement is
(a) the field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of straight lines which indicates that the magnetic field is the same at all points inside the solenoid
(b) the strong magnetic field produced inside the solenoid can be used to magnetise a piece of magnetic material like soft iron, when placed inside the coil
(c) the pattern of the magnetic field associated with the solenoid is different from the pattern of the magnetic field around a bar magnet
(d) the N- and S-poles exchange position when the direction of current through the solenoid is reversed.
Answer
Answer: (c) the pattern of the magnetic field associated with the solenoid is different from the pattern of the magnetic field around a bar magnet
Question 5.
In the arrangement shown in the figure there are two coils wound on a non-conducting cylindrical rod. Initially the key is not inserted. Then the key is inserted and later removed. Then
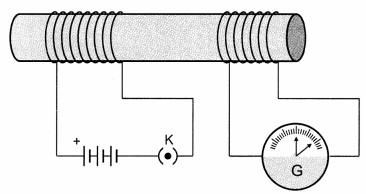
(a) the deflection in the galvanometer remains zero throughout.
(b) there is a momentary deflection in the galvanometer but it dies out shortly and there is no effect when the keys is removed.
(c) there are momentary galvanometer deflections that die out shortly; the deflections are in the same direction.
(d) there are momentary galvanometer deflections that die out shortly; the deflection are in opposite directions.
Answer
Answer: (d) there are momentary galvanometer deflections that die out shortly; the deflection are in opposite directions.
Question 6.
Choose the incorrect statement
(a) Fleming’s right-hand rule is a simple rule to know the direction of induced current.
(b) The right-hand thumb rule is used to find the direction of magnetic fields due to current carrying conductors.
(c) The difference between the direct and alternating currents is that the current always flows in one direction, whereas the alternating current reverses its direction periodically.
(d) In India, the AC changes direction after every \(\frac{1}{50}\) second.
Answer
Answer: (d) In India, the AC changes direction after every \(\frac{1}{50}\) second.
Question 7.
A constant current flows in a horizontal wire in the plane of the paper from east to west as shown in the figure. The direction of magnetic field at a point will be North to South
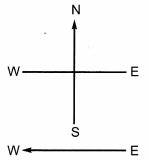
(a) directly above the wire
(b) directly below the wire
(c) at a point located in the plane of the paper, on the north side of the wire
(d) at a point located in the plane of the paper, on the south side of the wire.
Answer
Answer: (b) directly below the wire
Question 8.
The strength of magnetic field inside a long current carrying straight solenoid is
(a) more at the ends than at the centre
(b) minimum in the middle
(c) same at all points
(d) found to increase from one end to the other
Answer
Answer: (c) same at all points
Question 9.
The most important safety method used for protecting home appliances from short circuiting or overloading is by
(a) earthing
(b) use of fuse
(c) use of stabilizers
(d) use of electric meter.
Answer
Answer: (b) use of fuse
Question 10.
Select the incorrect statement
(а) Magnetic field lines are closed curves
(b) No two field lines can cross each other
(c) Field lines can cross each other
(d) The relative strength of the magnetic field is shown by degree of closness of the field lines.
Answer
Answer: (c) Field lines can cross each other
Question 11.
Magnetic field lines around a straight conductor forms a pattern of
(a) concentric circles
(b) concentric ellipse
(c) straight line
(d) square shape.
Answer
Answer: (a) concentric circles
Question 12.
Electric motor is a device which converts
(a) mechanical energy to electrical energy
(b) electrical energy to mechanical energy
(c) chemical energy to mechanical energy
(d) mechanical energy to light energy.
Answer
Answer: (b) electrical energy to mechanical energy
Question 13.
The direction of induced current is given by
(a) Fleming’s right hand rule
(b) Fleming’s left hand rule
(c) Right hand thumb rule
(d) Left hand thumb rule.
Answer
Answer: (a) Fleming’s right hand rule
Question 14.
The insulation colour of earth wire is
(a) blue
(b) red
(c) green
(d) white.
Answer
Answer: (c) green
Question 15.
In India the potential difference between live wire and neutral wire is
(a) 240 V
(b) 250 V
(c) 280 V
(d) 220 V.
Answer
Answer: (d) 220 V.
Fill in the blanks
1. By convention the magnetic field lines emerge from …………… pole and merge at …………… pole.
Answer
Answer: north, south
2. A coil of many circular turns of insulated copper wire wrapped closely in shape of a cylinder is called a ……………
Answer
Answer: solenoid
3. An electric motor is rotating device that converts …………… energy to …………… energy.
Answer
Answer: electrical, mechanical
4. AC generator converts …………… energy into …………… energy.
Answer
Answer: mechanical, electrical
5. The difference between the direct current and alternating current is that the direct current flows in …………… direction, whereas the alternating current …………… its direction periodically.
Answer
Answer: one, reverses
6. At the centre of current carrying loop the magnetic field appears to be a ……………
Answer
Answer: straight line
Match the following columns
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Right hand thumb rule | (а) converts electrical energy into mechanical energy |
| 2. Fleming’s left hand rule | (b) gives the direction of magnetic field around a conductor |
| 3. Fleming’s right hand rule | (c) converts mechanical energy into electrical energy |
| 4. Alternating current | (d) gives the direction of force on current carrying conductor placed in magnetic field |
| 5. Direct current | (e) the direction of current changes periodically |
| 6. Electric motor | (f) gives the direction of induced current |
| 7. Generator | (g) current always flows in one direction. |
Answer
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Right hand thumb rule | (b) gives the direction of magnetic field around a conductor |
| 2. Fleming’s left hand rule | (d) gives the direction of force on current carrying conductor placed in magnetic field |
| 3. Fleming’s right hand rule | (f) gives the direction of induced current |
| 4. Alternating current | (e) the direction of current changes periodically |
| 5. Direct current | (g) current always flows in one direction. |
| 6. Electric motor | (а) converts electrical energy into mechanical energy |
| 7. Generator | (c) converts mechanical energy into electrical energy |
Complete the crossword below.
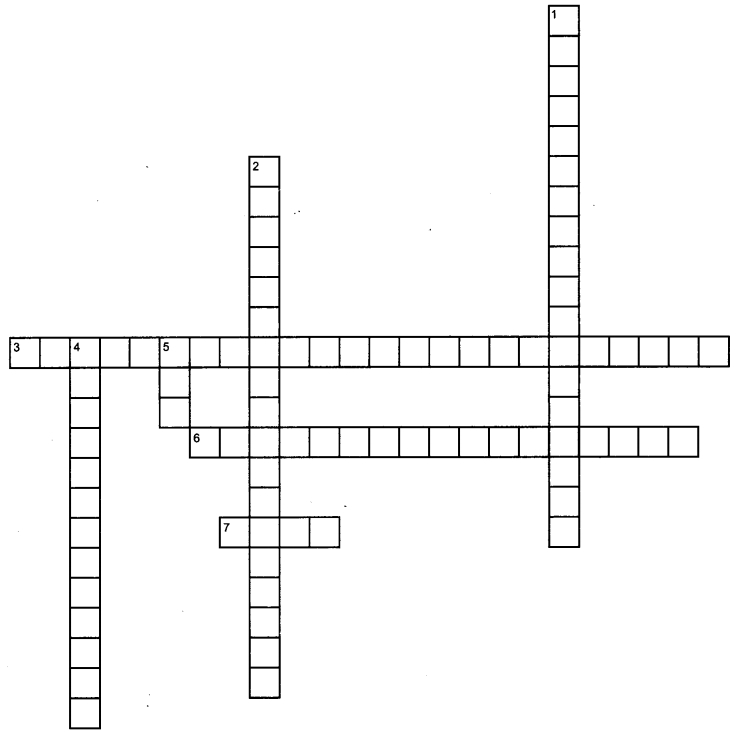
Across
3. Principle of electric generator
6. Magnetic field around a straight conductor
7. The safety device which is used to protect the circuit from short circuiting and overloading
Down
1. The direction of magnetic field produced by a current carrying conductor can be found out by using
2. The current which reverses its direction periodically
4. The device which convert electrical energy into mechanical energy
5. Colour of insulation of live wire
Answer
Answer:
Across:
3. Electromagnetic induction
6. Concentric circles
7. Fuse
Down:
1. Right hand thumb rule
2. Alternating current
4. Electric motor
5. Red
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding Magnetic Effects of Electric Current CBSE Class 10 Science MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.