Find free online Chemistry Topics covering a broad range of concepts from research institutes around the world.
Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
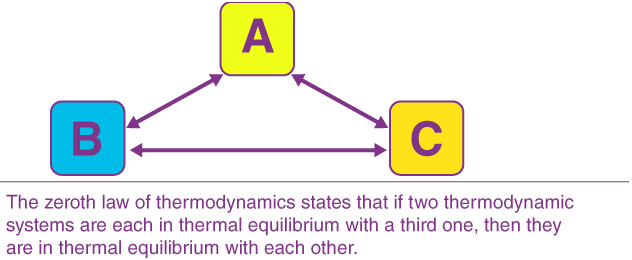
The law states that ‘If two systems are separately in thermal equilibrium with a third one, then they tend to be in thermal equilibrium with themselves’. According to this law, if systems B and C separately are in thermal equilibrium with another system A, then systems B and C will also be in thermal equilibrium with each other. This is also the principle by which thermometers are used.
The zeroth law of thermodynamics states that if two bodies are each in thermal equilibrium with some third body, then they are also in equilibrium with each other. This says in essence that the three bodies are all the same temperature.
Why is it called the zeroth law of thermodynamics? Answer: There were three law of thermodynamics originally established and named. Since the law is the fundamental one, the scientist Raplh H Fowler came with an alternative and numbered the new law as a lower number zero and the law is called the “Zeroth law.”
Similarly, another example of the zeroth law of thermodynamics is when you have two glasses of water. One glass will have hot water and the other will contain cold water. Now if we leave them in the table for a few hours they will attain thermal equilibrium with the temperature of the room.
Zeroth law of thermodynamics states that when two systems are in thermal equilibrium through a third system separately then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other also. Heat flow happens between systems A and C, and between B and C, due to which all 3 systems attain thermal equilibrium.
The zeroth law is incredibly important as it allows us to define the concept of a temperature scale. If two systems are each in thermal equilibrium with a third, they are also in thermal equilibrium with each other. The thermometer is therefore also in thermal equilibrium with the second cup of water.
Zeroth law of Thermodynamics:
If two thermodynamic systems are each in thermal equilibrium with a third, then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other. First law of thermodynamics – Energy can neither be created nor destroyed. In any process, the total energy of the universe remains the same.