In this page, we are providing Winds, Storms and Cyclones Class 7 Extra Questions and Answers Science Chapter 8 pdf download. NCERT Extra Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 8 Winds, Storms and Cyclones with Answers will help to score more marks in your CBSE Board Exams.
Class 7 Science Chapter 8 Extra Questions and Answers Winds, Storms and Cyclones
Extra Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 8 Winds, Storms and Cyclones with Answers Solutions
Winds, Storms and Cyclones Class 7 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
What is called the wind?
Answer:
The moving air is called the wind.
Question 2.
What was the speed of wind of cyclone hit in Odisha on 18 October 1999?
Answer:
200 km/hr
Question 3.
What is called the eye of the storm?
Answer:
The centre of a cyclone.
Question 4.
From which wind is the word monsoon derived?
Answer:
The Arabic word ‘mausam’.
Question 5.
What does the word ‘mausam’ mean?
Answer:
Season
Question 6.
What do the wind, from the oceans carry?
Answer:
Water
Question 7.
What bring rain?
Answer:
The winds from the oceans carry water and brings rain.
Question 8.
What are monsoon winds?
Answer:
The winds from the oceans carry water and bring rain. These winds are called monsoon winds.
Question 9.
What is natural disaster?
Answer:
Natural disaster are extreme, sudden events caused by environmental factors that injure people and damage property.
Question 10.
Name two natural disasters.
Answer:
Thunderstorms and cyclones.
Question 11.
Why does the can with hot water get distorted?
Answer:
Due to air pressure.
Question 12.
What is the direction of winds in summer?
Answer:
From the ocean towards the land
Question 13.
What is the direction of winds in winter?
Answer:
From the land to the ocean.
Question 14.
In what type of climate do thunderstorms develop?
Answer:
Hot, humid tropical areas.
Question 15.
Define pressure.
Answer:
The force applied per unit area is called pressure.
Question 16.
Which instrument is used to measure the air pressure at any place?
Answer:
Barometer
Question 17.
Which instrument does measure the wind speed?
Answer:
Anemometer
Question 18.
In which direction does the warm air rise?
Answer:
The warm air rises up.
Question 19.
Name two devices that forecast a cyclone.
Answer:
- Satellites
- Radars
Question 20.
Which instrument is used to measure the direction of the wind?
Answer:
Wind vane
Winds, Storms and Cyclones Class 7 Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Describe the two cyclones that hit Odisha in 1999.
Answer:
Odisha was hit by two cyclones, first on 18 October 1999. The wind speed of this cyclone was 200 km/h. It smashed 45000 houses making 7,00,000 people homeless. On 29 October 1999, another cyclone with wind speed of 260 km/h hit Odisha the second time.
It was accompanied by water waves about 9 m high. It was very destructive. Thousands of people lost their lives. Property worth crores of rupees was destroyed. The cyclone affected agriculture, transport, communication and electricity supply.
Question 2.
When we pour cold water over the can half-filled with hot water, the can slowly gets crumpled, why?
or
Show with the help of an activity that air exerts pressure.
Answer:
Take a tin can. Fill it half with water. Boil the water. After the water gets boiled, remove the can from the flame and immediately close the mouth of the can tightly. Place it in a sink and pour cold water over it. The tin can slowly gets crumpled.
This is due to the fact that when we cover the can and pour water over it, the steam condenses to form water reducing the amount of air inside. The air pressure outside the can is more than that inside the can. That is why the can gets distorted. This shows that the air exerts pressure.
Question 3.
Why does the warm air move upwards?
or
The warm air is lighter than the cold air. Explain.
Answer:
When the air is heated, it expands and occupies large space. When the same thing occupies more space, it becomes lighter. The warm air is, thus, lighter than the cold air and rises upwards.
Question 4.
What causes the winds to flow from the oceans towards the land?
Answer:
In summer, near the equator the land warms up faster and most of the time the temperature of the land is higher than that of water in the oceAnswer:The air over the land gets heated and rises. This causes the winds to flow from the oceans towards the land.
Question 5.
What is thunderstorm?
Answer:
The rising temperatures produce strong upward rising winds. These winds carry water droplets upwards, where they freeze, and fall down again. The swift movement of the falling water droplets along with the rising air create lightning and sound. It is this event that is called thunderstorm. It develops in hot, humid tropical areas like India very frequently.
Question 6.
What is a tornado? Describe.
Answer:
A tornado is a dark funnel-shaped cloud that reaches from the sky to the ground. Its diameter can be as small as a metre or even wider. The funnel of a tornado sucks dust, debris and everything near it at the base and throws them out near the top. Most of the tornadoes are weak. A violent tornado can travel at speed of about 300 km/h. Tornadoes may form within cyclones. In our country they are not very frequent.
Question 7.
What happens when high speed wind blow over the roofs of high buildings and why?
Answer:
When high speed wind blows over the roofs, a low pressure area is created above the roof. However, air pressure below the roof is high. This exerts a pressure on the roof and if the roofs are not firmly fixed, they could be lifted and blown away.
Winds, Storms and Cyclones Class 7 Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
Explain with the help of an activity that air expands on heating and contracts on cooling.
Answer:
See the ‘NCERT Intext Activity 8.5’.
Question 2.
Give an activity to show that warm air is lighter than cold air.
Answer:
See the ‘NCERT Intext Activity 8.6’.
Question 3.
Explain how are wind currents generated due to uneven heating between the equator and the poles.
Answer:
The areas close to the equator get maximum heat from the sun. As a result, the air in these regions gets warm. The warm air moves upwards and the cooler air from the regions in the 0-30° latitudes belt on either side of the equator moves in.
These winds blow from the north and south towards the equator. At the poles the air is colder than that at latitudes about 60 degrees. The warm air at these latitudes rises up and cold wind from the polar regions rushes in, to take its place. In this way, wind circulation is set up between these poles and the warmer latitudes as shown below (Fig. 8.10).

Question 4.
How do cyclones cause destruction?
Answer:
Cyclones cause destruction to our life and property. The water waves produced by the wind are so powerful that a person cannot overcome them. The rising water may be as high as 3-12 metres. It moves towards the shore. As a result, the sea-water enters the low-lying coastal areas, causing severe loss of life and property.
It also reduces the fertility of the soil. High-speed winds accompanying a cyclone can damage houses, telephones and other communication systems, trees, etc., causing tremendous loss of life and property. Continuous rainfall may further worsen the flood situation.
Question 5.
Explain the formation of a cyclone.
Answer:
The formation of a cyclone is a very complex process (Fig. 8.11). Before formation of the cloud, water takes up heat from the atmosphere to change into vapour. When water vapour changes back to liquid form as raindrops, this heat is released to the atmosphere. This warms the air around. The air tends to rise and causes a drop in pressure.
More air moves to the centre of the storm. This process is repeated. The chain of events ends with the formation of a very low-pressure system with very high-speed winds revolving around it. It is this weather condition that we call a cyclone. Various factors like wind speed, wind direction, temperature and humidity contribute to the development of a cyclone.
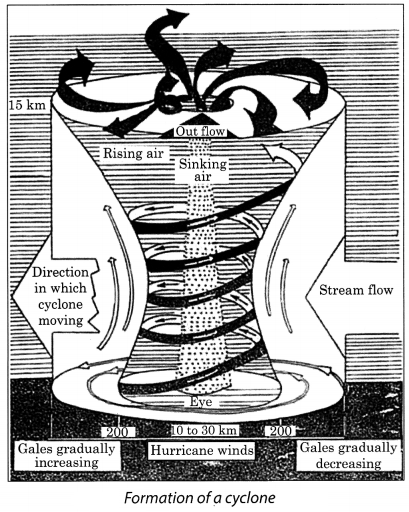
Question 6.
What are the precautions we must take if a storm is accompanied by lightning?
Answer:
We must take following precautions if a storm is accompanied by lightning:
- We should never take shelter under an isolated tree. If we are in a forest, we should take shelter under a small tree. We should never lie on the ground.
- We should not take shelter under an umbrella with a metallic rod.
- We should not sit near a window. Open garages, storage sheds, metal sheds are not safer places to take shelter. A car or a bus is a safe place for shelter.
- If in water, we should get out of water and go inside a building.
Question 7.
What are the effective safety measures to be adopted in case of a cyclone?
Answer:
Steps should be taken both on the government part and on the part of the people as safety measures to save from cyclonic dangers.
(a) On the part of the government:
- A cyclone forecast and warning service.
- Rapid communication of warnings to the Government agencies, the ports, fishermen, ships and to the general public.
- Construction of cyclone shelters in the cyclone-prone areas, and administrative arrangements for shifting people fast to safer places.
(b) Measures to be taken on the part of the public:
- People should follow the warnings issued by the Government agencies like meteorological department through TV, radio, or newspapers, etc.
- People should make suitable arrangements to shift the essential household goods, domestic animals and vehicles, etc., to safer places.
- People should avoid driving on roads through standing water, as floods may have damaged the roads, and keep ready the phone numbers of all emergency services like police, fire brigade and medical centres.
Some other precautions should be taken, if staying in a cyclone hit area as:
- Avoid drinking contaminated water. People should take water stored for emergencies.
- People should keep themselves away from wet switches and fallen power lines.
- People should not unnecessarily go out.
- People should cooperate and help their neighbours and other people who need any help.
Winds, Storms and Cyclones Class 7 Extra Questions HOTS
Question 1.
Paheli kept an empty bottle made of plastic inside a refrigerator. After few hours, when she opened the refrigerator she found the bottle had collapsed. Explain the possible reason.
Answer:
The air inside the bottle contracts due to low temperature. Hence pressure inside the bottle becomes less than the outside and the bottle collapsed.
Question 2.
Why an umbrella held upright, at times, gets upturned when high speed wind blows?
Answer:
High speed wind passing over the umbrella creates a low pressure. Thus, the umbrella upturns.
Question 3.
Why is it advisable not to shut all the doors and windows during a storm?
Answer:
Low pressure created by storm may blow away the roof. To avoid this condition, it is not advisable to shut all the doors and windows during a storm.
Question 4.
A house near coastal area has a flag on its roof. Towards which direction the flag will be blown in the afternoon? Explain.
Answer:
The flag will be blown towards the land in the afternoon. This is because land get heated up faster comparatively to the water in sea. So air flows from sea to land.
Question 5.
During lightning and thunderstorm, one should not take shelter under a tree or lie on the ground. Why?
Answer:
Tree may be the tallest object around, making it perfect target of lightning and one of the worst place to seek shelter. If we lie down, an electrical current passing through the ground from a nearby lightning strike can pass right through our body. So the above two positions may prove fatal in case lightning strike.
Question 6.
Suggest some precautions to be taken to prevent the roof of a tin sheet from flying away during a fierce wind storm.
Answer:
- Roof should be perfectly nailed with the house.
- Heavy objects should be kept on the roof.
Winds, Storms and Cyclones Class 7 Extra Questions Value Based (VBQs)
Question 1.
Ramaya while going to school found his bicycle’s tyres to be little deflated. He went to a cycle repairing shop and overfilled his bicycle tube. On seeing this, the shopkeeper adviced him that this is not good for his cycle tube. But Ramaya overlooked shopkeeper’s advice and went to his school. He kept his cycle in the cycle stand.
In afternoon when he came to take his cycle, he observed that its tyre has bursted. He got puzzled why his tyres bursted though they were new.
(a) What is air pressure?
(b) What will happen if we use our bicycle with deflated tyres?
(c) Ramaya went to his school with overfilled tyre tubes but nothing happened to his tyres then. Why did it burst when he was not riding and just kept it in cycle stand?
(d) What value of Ramaya is shown here?
Answer:
(a) Air pressure is the force exerted onto a surface by the weight of the air.
(b) Deflated tyres make moving the bicycle harder and also wear and tear of the tyres soon.
(c) The temperature is maximum in afternoon and the heat of the sun warm the air inside the tube, thus rising its pressure to such an extent which caused the tyre to burst.
(d) Ramaya is inexperienced, he overheard the advice of shopkeeper so he is disobedient also. He lacks scientific knowledge on expansion of air.
Question 2.
Saket and Ali, two friends, built a house for themselves. To expel hot air out of kitchen Saket fitted an exhaust fan on the window of his kitchen and Ali fitted a similar exhaust fan on the wall near the ceiling of his kitchen.
(a)Which of the exhaust fan will expel the hot air more effectively? Why?
(b)How a ventilator works in circulating fresh air in the room?
(c)What values of Saket and Ali are shown here?
Answer:
(a) Exhaust fan fitted by Ali will expel the hot air more effectively because hot air has tendency to move up.
(b) The hot and stale air being lighter rises up and get exhausted through the ventilators. The fresh and cold air being heavier than warm air takes its place. So by this way ventilators helps in circulating fresh air within a house.
(c) Saket is impractical whereas Ali is intelligent and practical in placing the exhaust fan at right place.