Find free online Chemistry Topics covering a broad range of concepts from research institutes around the world.
Structure of Carbonyl Group
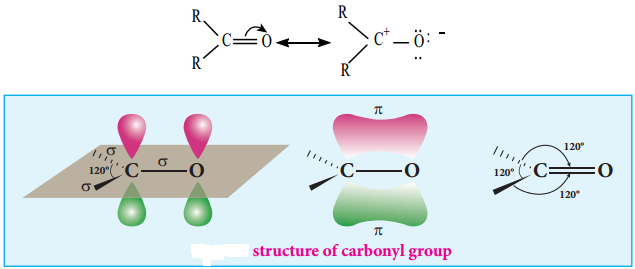
The carbonyl carbon 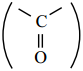 is sp2 hybridised and the carbon – oxygen bond is similar to carbon – carbon double bond in alkenes. The carbonyl carbon forms three σ bonds using their three sp2 hybridised orbital. One of the sigma bond is formed with oxygen and the other two with hydrogen and carbon (in aldehydes) or with two carbons (in ketones).
is sp2 hybridised and the carbon – oxygen bond is similar to carbon – carbon double bond in alkenes. The carbonyl carbon forms three σ bonds using their three sp2 hybridised orbital. One of the sigma bond is formed with oxygen and the other two with hydrogen and carbon (in aldehydes) or with two carbons (in ketones).
All the three ‘σ’ bonded atoms are lying on the same plane as shown in the fig (12.1). The fourth valence electron of carbon remains in its unhybridised ‘2p’ orbital which lies perpendicular to the plane and it overlaps with 2p orbital of oxygen to form a carbon – oxygen π bond. The oxygen atom has two nonbonding pairs of electrons, which occupy its remaining two p-orbitals.
Oxygen, the second most electro negative atom attracts the shaired pair of electron between the carbon and oxygen towards itself and hence the bond is polar. This polarisation contributes to the reactivity of aldehydes and ketones.
A carbonyl group is a chemically organic functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom → [C=O]. The simplest carbonyl groups are aldehydes and ketones usually attached to another carbon compound. These structures can be found in many aromatic compounds contributing to smell and taste.
Properties of Carbonyl Compounds:
- These are to be polar in nature. They exhibit both positive and negative charge in slight form.
- These compounds are reported to be insoluble in water but sometimes they dissolve other forms of polar molecules.
- These are known to be as chemically reactive compounds.
Carbonyl group, in organic chemistry, a divalent chemical unit consisting of a carbon (C) and an oxygen (O) atom connected by a double bond.
Formula of Carbonyl Group
Both organic families have the general formula CnH2nO. The carbonyl functional group (C = O) consists of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom. The position of the C=O. functional group in the carbon chain marks the difference between aldehydes and ketones.
Examples:
Examples of inorganic carbonyl compounds are carbon dioxide and carbonyl sulphide. A special group of carbonyl compounds are 1, 3-dicarbonyl compounds that have acidic protons in the central methylene unit. Examples are Meldrum’s acid, diethyl malonate and acetylacetone.