ML Aggarwal Class 6 Solutions Chapter 11 Understanding Symmetrical Shapes Objective Type Questions for ICSE Understanding Mathematics acts as the best resource during your learning and helps you score well in your exams.
ML Aggarwal Class 6 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 11 Understanding Symmetrical Shapes Objective Type Questions
Mental Maths
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
(i) An angle whose measure is less than that of a right angle is …………
(ii) An angle whose measure is the sum of the measures of two right angles is …………
(iii) When the sum of measures of two angles is that of a right angle, then each on of them is …………
(iv) When the sum of measures of two angles is that of a straight angle and if one of them is acute then the other is …………
(v) A triangle having one of its angles as right angle and with lengths of two sides equal is called ………… triangle.
(vi) A cuboid has ………… faces, ………… edges and ………… vertices.
(vii) A rectangular pyramid has ………… faces, ………… edges and ………… vertices.
Solution:

Question 2.
State whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F):
(i) Each angle of an equilateral triangle is a right angle.
(ii) The adjacent sides of a rectangle are equal in length.
(iii) The diagonals of a rectangle are equal in length.
(iv) The diagonals of a rectangle are perpendicular to one another.
(v) The diagonals of a rhombus are equal in length.
(vi) Any three line segments make up a triangle.
(vii) All the faces of a triangular prism are triangles.
(viii)All the faces of a triangular pyramid are triangles.
Solution:

Question 3.
State whether the following statement is true or false. Justify your answer.
‘An angle whose measure is greater than that of a right angle is obtuse’.
Solution:
![]()
Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer from the given four options (4 to 15):
Question 4.
Comparison of lengths is possible in case of
(a) two lines
(b) two line segments
(c) two rays
(d) a ray and a line segment
Solution:
![]()
Question 5.
A reflex angle measures
(a) more than 90° but less than 180°
(b) more than 180° but less than 270°
(c) more than 180° but less than 360°
(d) none of these
Solution:
![]()
Question 6.
A scalene triangle cannot be
(a) an acute angled triangle
(b) an obtuse angled triangle
(c) a right angled triangle
(d) an equilateral triangle
Solution:
![]()
Question 7.
An obtuse angled triangle can be
(a) right angled
(b) isosceles
(c) equilateral
(d) none of these
Solution:
![]()
Question 8.
If you are facing north and turn through \(\frac{3}{4}\) of a turn in anti-clockwise direction, which direction will you face?
(a) east
(b) south
(c) west
(d) north
Solution:
![]()
Question 9.
Open any two adjacent fingers of your hand. What kind of angle you get?
(a) acute
(b) right
(c) obtuse
(d) straight
Solution:
![]()
Question 10.
In the given figure, the number of obtuse angles is
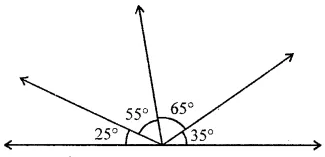
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Solution:
![]()
Question 11.
If the sum of two angles is an obtuse angle, then which of the following is not possible? one right angle and one acute angle one obtuse angle and one acute angle two acute angles two right angles
(a) two right angles
(b) one obtuse angle and one acute angle
(c) two acute angles
(d) two right angles
Solution:
![]()
Question 12.
If the sum of two angles is greater than 180°, then which of the following is not possible?
(a) two obtuse angles
(b) two right angles
(c) one obtuse and one acute angle
(d) one reflex and one acute angle
Solution:
![]()
Question 13.
Which of the following statements is false?
(a) Every quadrilateral triangle is an isosceles triangle.
(b) Every isosceles triangle is an equilateral triangle.
(c) Every parallelogram is a trapezium.
(d) Every trapezium is a quadrilateral.
Solution:
![]()
Question 14.
Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) Every rhombus is a square
(b) Every parallelogram is a rectangle
(c) Every square is a rhombus
(d) Every rectangle is a square
Solution:
![]()
Question 15
A quadrilateral whose each angle is a right angle is a
(a) trapezium
(b) parallelogram
(c) rhombus
(d) rectangle
Solution:
![]()
Higher Order Thinking Skills (Hots)
Question 1.
If the lengths of two sides of an isosceles triangle are 3 cm and 7 cm, then what is the lengths of the third side?
Solution:

Question 2.
If the lengths of three consecutive sides of an isosceles trapezium are 5 cm, 6 cm and 8 cm, then what is the length of the fourth side?
Solution:
![]()