Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have Provided Work and Energy Class 9 Science MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
Class 9 Science Physics Chapter 11 MCQ With Answers
You can refer to NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy to revise the concepts in the syllabus effectively and improve your chances of securing high marks in your board exams.
Physics Class 9 Chapter 11 MCQs on Work and Energy
Question 1.
When a body falls freely towards the earth, then its total energy
(a) increases
(b) decreases
(c) remains constant
(d) first increases and then decreases
Answer
Answer: (c) remains constant
Calculate Potential Energy (PE) for the given mass (m), acceleration of gravity (g) and height (h) through gravitational potential energy Calculator.
Question 2.
A car is accelerated on a levelled road and attains a velocity 4 times of its initial velocity. In this process the potential energy of the car
(a) does not change
(b) becomes twice to that of initial
(c) becomes 4 times that of initial
(d) becomes 16 times that of initial
Answer
Answer: (a) does not change
Question 3.
In case of negative work the angle between the force and displacement is (NCERT Exemplar)
(a) 0°
(b) 45°
(c) 90°
(d) 180°
Answer
Answer: (d) 180°
Kinetic Energy Calculator is a handy tool that solves the kinetic energy problems easily & quickly.
Question 4.
An iron sphere of mass 10 kg has the same diameter as an aluminium sphere of mass is 3.5 kg. Both spheres are dropped simultaneously from a tower. When they are lo m above the ground, they have the same.
(a) acceleration
(b) momenta
(c) potential energy
(d) kinetic energy
Answer
Answer: (a) acceleration
Question 5.
A girl is carrying a school bag of 3 kg mass on her back and moves 200 m on a levelled road. The work done against the gravitational force will be (g = 10 ms²)
(a) 6 × 10³ J
(b) 6 J
(c) 0.6 J
(d) zero
Answer
Answer: (d) zero
Question 6.
Which one of the following is not the unit of energy?
(a) joule
(b) newton metre
(c) kilowatt
(d) kilowatt hour
Answer
Answer: (c) kilowatt
Question 7.
The work done on an object does not depend upon the
(a) displacement
(b) force applied
(c) angle between force and displacement
(d) initial velocity of the object
Answer
Answer: (d) initial velocity of the object
Question 8.
Water stored in a dam possesses
(a) no energy
(b) electrical energy
(c) kinetic energy
(d) potential energy
Answer
Answer: (d) potential energy
Question 9.
A body is falling from a height h. After it has fallen a height \(\frac{h}{2}\), it will possess
(a) only potential energy
(b) only kinetic energy
(c) half potential and half kinetic energy
(d) more kinetic and less potential energy
Answer
Answer: (c) half potential and half kinetic energy
Question 10.
The number of joules contained in 1 kWh is
(a) 36 × 105 J
(b) 3.6 × 107 J
(c) 36 × 108 J
(d) 3.7 × 107 J
Answer
Answer: (a) 36 × 105 J
Question 11.
Two army persons A and B each of weight of 500 N climb up a rope through a height of 10 m. A takes 20 s while B takes 40 s to achieve this task. What is ratio of the powers of person A and B?
(a) 1 : 2
(b) 1 : 4
(c) 2 : 1
(d) 14 : 1
Answer
Answer: (c) 2 : 1
Question 12.
Which of the following graphs best represents graphical relation between momentum P and kinetic energy K for a body in motion?
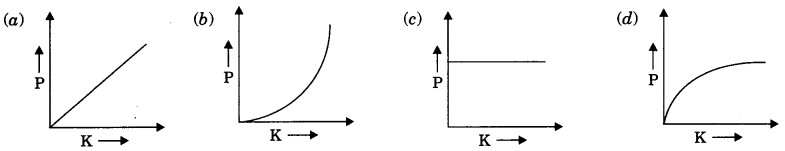
Answer
Answer: (d)
Question 13.
If speed of a car becomes 2 times, its kinetic energy becomes
(a) 4 times
(b) 8 times
(c) 16 times
(d) 12 times
Answer
Answer: (a) 4 times
Question 14.
Work done by friction
(a) increases kinetic energy of body
(b) decreases kinetic energy of body
(c) increases potential energy of body
(d) decreases potential energy of body.
Answer
Answer: (b) decreases kinetic energy of body
Question 15.
When a coil spring is compressed, the work is done on the spring. The elastic potential energy
(a) increases
(b) decreases
(c) disappears
(d) remains unchanged
Answer
Answer: (a) increases
Question 16.
One joule work is said to be done when
(a) a force of 1 N displaces a body by 1 cm
(b) a force of 1 N displaces a body by 1 m
(c) a force of 1 dyne displaces a body by 1 m
(d) a force of 1 dyne displaces a body by 1 cm.
Answer
Answer: (b) a force of 1 N displaces a body by 1 m
Question 17.
SI unit of power is
(a) watt
(b) joule
(c) newton
(d) metre
Answer
Answer: (a) watt
Question 18.
Mechanical energy of a body includes
(a) kinetic energy only
(b) potential energy only
(c) kinetic energy and potential energy
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: (c) kinetic energy and potential energy
Question 19.
Commercial unit of energy is
(a) joule
(b) kWh
(c) watt
(d) newton
Answer
Answer: (b) kWh
Question 20.
Potential energy of a body depends on its
(a) position
(b) configuration
(c) position and configuration
(d) mass and velocity
Answer
Answer: (c) position and configuration
Fill in the blanks
1. Work done is product of ………….. and distance moved the direction of the force.
Answer
Answer: force
2. If the angle between force and displacement is …………. then work done is said to be zero.
Answer
Answer: 90°
3. Energy of a body is defined as the capacity or …………. to do work.
Answer
Answer: ability
4. Mechanical energy includes ………….. and ……………
Answer
Answer: kinetic energy, potential energy
5. Energy can neither be ………….. nor ………….. it can only transformed from one form to another.
Answer
Answer: created, destroyed
6. ………….. is defined as the rate of doing work.
Answer
Answer: Power
7. Commercial unit of energy is ………………
Answer
Answer: kilowatt hour
Match the following columns
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) SI unit of power | (i) 1/2 mv2 |
| (b) Kinetic energy | (ii) The change of one form of energy into another |
| (c) Potential energy | (iii) watt |
| (d) SI unit of work | (iv) If applied force on an object and displacement is in opposite direction. |
| (e) Negative work | (v) Energy possessed by a body due to its position or configuration. |
| (f) Power | (vi) Joule |
| (g) Expression of kinetic energy | (vii) Energy possessed by a body due to its motion. |
| (h) Transformation of energy | (viii) Rate of doing work |
Answer
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) SI unit of power | (iii) watt |
| (b) Kinetic energy | (vii) Energy possessed by a body due to its motion. |
| (c) Potential energy | (v) Energy possessed by a body due to its position or configuration. |
| (d) SI unit of work | (vi) Joule |
| (e) Negative work | (iv) If applied force on an object and displacement is in opposite direction. |
| (f) Power | (viii) Rate of doing work |
| (g) Expression of kinetic energy | (i) 1/2 mv2 |
| (h) Transformation of energy | (ii) The change of one form of energy into another |
Crossword Puzzle:
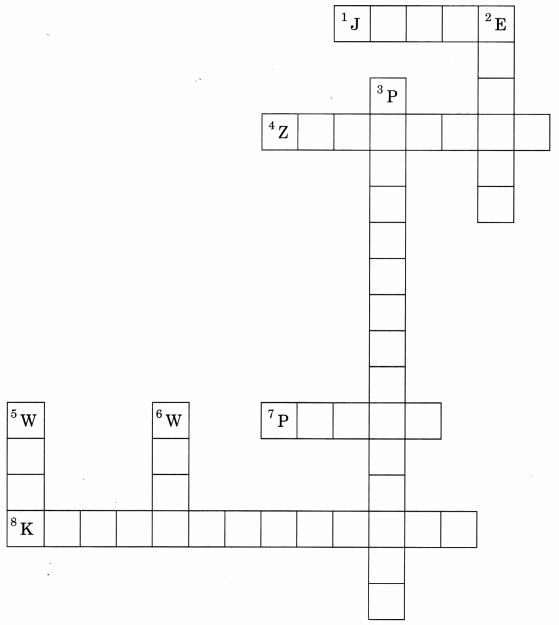
Across:
1. SI unit of work
4. Work done if force is perpendicular to displacement
7. Rate of doing work
8. Energy possessed by a body due to virtue of its motion
Down:
2. Ability to do work
3. Energy possessed by a body due to virtue of its position or configuration
5. Product of force and displacement
6. SI unit of power
Answer
Answer:
Across:
1. Joule
4. Zerowork
7. Power
8. Kinetic energy
Down:
2. Energy
3. Potential energy
5. Work
6. Watt
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding Work and Energy CBSE Class 9 Science MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.
Class 9 Science Physics MCQ With Answers
- Motion Class 9 MCQ
- Force and Laws of Motion Class 9 MCQ
- Gravitation Class 9 MCQ
- Work and Energy Class 9 MCQ
- Sound Class 9 MCQ