In this page, we are providing Light Shadows and Reflection Class 6 Extra Questions and Answers Science Chapter 11 pdf download. NCERT Extra Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflection with Answers will help to score more marks in your CBSE Board Exams.
Class 6 Science Chapter 11 Extra Questions and Answers Light Shadows and Reflection
Extra Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflection with Answers Solutions
Light Shadows and Reflection of Distances Class 6 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
What is light?
Answer:
Light is a form of energy which enables us to see.
Question 2.
What is a luminous object?
Answer:
An object having its own light is called a luminous object, e.g., torch, sun, etc.
Question 3.
What is a non-luminous body?
Answer:
An object which does not have its own light is called a non-luminous object, e.g., chair, moon, etc.
Question 4.
Name some luminous objects.
Answer:
Torch, bulb, sun, firefly and a burning candle.
Question 5.
Give four examples of non-luminous objects.
Answer:
Table, chair, blackboard and notebook.
Question 6.
Name four natural luminous bodies.
Answer:
The sun, firefly, stars and fire.
Question 7.
Name some artificial source of light.
Answer:
Candle, bulb, kerosene oil, lamp and torch.
Question 8.
What is a transparent object?
Answer:
An object which allow light to pass through it, is called transparent object, e.g., clear glass, water, etc.
Question 9.
What is a translucent object?
Answer:
An object which allows only a small part of light through it, is called translucent object, e.g., wax paper, fog, etc.
Question 10.
What is an opaque object?
Answer:
An object which does not allow light at all to pass through it, is called opaque object, e.g., wooden sheet, wall, etc.
Question 11.
Give four examples of transparent objects.
Answer:
Clear glass, clean water, cellophane paper and air.
Question 12.
Give four examples of translucent object.
Answer:
Frosted glass, wax paper, greased paper and butter paper.
Question 13.
Give four examples of opaque objects.
Answer:
Wood, metals, clay and black paper.
Question 14.
What is a shadow?
Answer:
The dark patch formed due to obstruction of light rays by an opaque object is called a shadow.
Question 15.
What information does a shadow give about an object?
Answer:
A shadow gives information about the shape of the object.
Question 16.
Does the colour of the object affect the colour of the shadow?
Answer:
No, the colour of the object does not affect the colour of the shadow.
Question 17.
When is a shadow formed?
Answer:
A shadow is formed when an opaque object is placed in the path of light.
Question 18.
Define a pinhole camera.
Answer:
A pinhole camera is a device which forms a photograph like image of a bright object on a screen.
Question 19.
On which property of light a pinhole camera does work?
Answer:
Rectilinear propagation of light.
Question 20.
How does light travel?
Answer:
Light travels in a straight line.
Question 21.
What type of images are formed by a pinhole camera?
Answer:
The images formed by a pinhole camera are upside down, i.e., inverted image.
Question 22.
What is mirror?
Answer:
A smooth, polished reflecting surface is called a mirror.
Question 23.
What type of image is formed by a plane mirror?
Answer:
Erect and laterally inverted image is formed by a plane mirror.
Question 24.
What is the size of the image formed by a plane mirror?
Answer:
The size of the image formed by a plane mirror is same as that of the object.
Question 25.
What is the colour of the image formed by a plane mirror?
Answer:
The colour of the image formed by a plane mirror is same as that of the object.
Question 26.
What is an eclipse?
Answer:
The phenomenon of formation of shadows of celestial bodies on one another is called an eclipse.
Question 27.
What is rectilinear propagation of light?
Answer:
The property due to which light travels in a straight line is called rectilinear propagation of light.
Question 28.
What is reflection?
Answer:
the phenomenon of bouncing back of light by a highly polished surface is called reflection.
Question 29.
What is an incident ray?
Answer:
The ray of light falling on the surface of the mirror is called an incident ray.
Question 30.
What is reflected ray?
Answer:
The ray of light returning back from the mirror is called a reflected ray.
Light Shadows and Reflection of Distances Class 6 Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
What is light?
Answer:
Light is a form of energy which when falls on the object enables us to see them. It helps us to see the objects from which it comes or from which it is reflected.
Question 2.
Distinguish between luminous and non-luminous objects?
Answer:
The objects which have light of their own are called luminous objects such as torch, bulb, burning candle, etc., whereas non-luminous objects does not have light of their own and can be seen only when light falls on them such as table, wall, book, etc.
Question 3.
What is a shadow? How is it formed?
Answer:
The dark patch formed behind an opaque object is called a shadow. It is formed when light ray falling on the surface of the mirror (say an opaque object) is blocked by it.
Question 4.
What are the essential conditions for formation of shadows?
Answer:
A shadow is formed when
- there is a source of light.
- there is an opaque object in the way of light.
- the light ray falling on the opaque object is blocked by it.
Question 5.
Moon is a non-luminous body though it glows. Justify.
Answer:
Moon does not emit light of its own. So it is a non-luminous body. It glows due to reflection of sunlight by it.
Question 6.
What is a pinhole camera? What type of images is formed by it?
Answer:
A pinhole camera is a device which forms a photographic image of a bright object on a screen. The images formed by a pinhole camera are upside down (inverted images).
Question 7.
What is mirror? What type of images is formed by it?
Answer:
The glass sheet having a polished, shiny, smooth and reflective surface on the other side is called a mirror. The images formed by a mirror are erect and laterally inverted.
Question 8.
Why should we not look at the sun directly?
Answer:
The sun radiates ultraviolet radiations that could be extremely harmful for our eyes. This is why we should never see the sun with naked eyes.
Question 9.
What is natural pinhole camera? What type of images is formed by it?
Answer:
When sunlight falls in the leaves of a tree, the gaps between the leaves act as a natural pinhole camera. Afterwards rounded shaped images are formed on the earth. These are pinhole images of the sun.
Question 10.
What is lateral inversion?
Answer:
Lateral inversion means the apparent reversal of the mirror images when compared with the object. For example, right side of the object appear as left side in the image.
Question 11.
Write two differences between a shadow and an image.
Answer:
Images are formed by intersection of reflected rays whereas a shadows are formed when light does not reach behind the object. Images gives more information about the objects such as colour, structure, etc., whereas shadows do not provide such information.
Question 12.
Why is a silvered glass used as a mirror?
Answer:
A silvered glass has a smooth surface which helps in forming clear image. Silverness makes the surface shiny which helps in reducing the absorption of light falling on the mirror surface.
Question 13.
What is an eclipse? What are the two types of eclipse?
Answer:
The formation of shadows by celestial bodies on one another is called an eclipse. There are two types of eclipse.
- When the moon comes in between the sun and the earth, the shadow of the moon falls on the earth. This is called solar eclipse.
- When the earth comes in between the sun and the moon, the shadow of the earth falls on the moon. This is called lunar eclipse.
Question 14.
What are incident ray and reflected ray?
Answer:
(a) A light ray falling on a smooth, shiny and polished surface (say a plane mirror) is called the incident ray.
(b) The light ray returning back in the same medium after striking a smooth, shiny and highly polished surface (say a plane mirror) is called reflected ray.
Light Shadows and Reflection of Distances Class 6 Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
What are the different types of object based on their ability to pass the light? Give suitable examples of each objects.
Answer:
On the basis of ability to pass light through an object, objects are classified into three main groups, i.e.,
(a) transparent
(b) translucent and
(c) opaque.
(a) Transparent objects: Objects through which light can pass easily are called transparent objects, e.g., clean glass, clean water, clean air, etc.
(b) Translucent objects: Objects through which light can pass partially and through which we cannot see clearly are called translucent objects, e.g., greased paper, wax paper, butter paper, etc.
(c) Opaque objects: Objects through which light cannot pass at all and through which we cannot see are called opaque objects. Only opaque objects can make shadows, e.g., wall, blackboard, stone, etc.
Question 2.
What is a pinhole camera? How does it works? Explain its construction and image formation.
Answer:
A pinhole camera is a device which casts a photographic image of a bright object on a screen. It works on the principle that light travels in a straight line.
A pinhole camera can be made with simple materials and can be used to obtain the image of sun and brightly lit objects. It consists of a box made of metal or a cardboard that has a fine hole in one face. A plate or any translucent sheet on the side opposite to the face containing the pinhole serves as a screen.
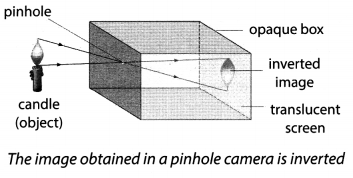
Images formed by a pinhole camera are upside down, i.e., inverted images.
Question 3.
With the help of diagrams show solar and lunar eclipses.
Answer:
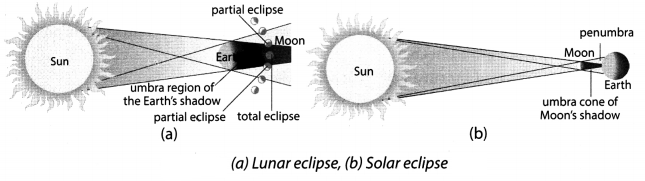
Question 4.
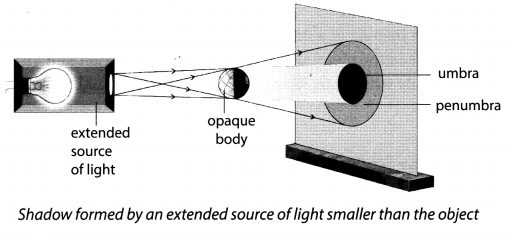
What is umbra and penumbra? With the help of a suitable diagram, show their formation.
Answer:
The inner region of a shadow which is completely dark is called umbra and the outer region surrounding the umbra which is a partially dark region is called penumbra. These two regions in shadows are formed when an opaque body is placed in front of an extended or slit source.
Light Shadows and Reflection of Distances Class 6 Extra Questions HOTS
Question 1.
Why shadows are black in colour?
Answer:
Shadow is formed by an object by obstructing light so that it doesn’t reach a surface. The area in shadow appears black because there is no light falling on it.
Question 2.
Why we do not obtain upside-down image of the Sun through a pinhole camera?
Answer:
Shape of the Sun is round, so when we see the sun from any angle we get a circle only.
Question 3.
We consider moon as non-luminous body but still we can see things on a full moon night. Why?
Answer:
Moon does not have light of its own. Moon reflects the light of sun in the night. On dark nights a little illumination by moon enables us to see things around us.
Question 4.
Why lunar eclipse not occur every month?
Answer:
It do not occur every month because the Earth’s orbit around the sun is not in the same plane as the moon’s orbit around the earth.
Light Shadows and Reflection of Distances Class 6 Extra Questions Value Based (VBQs)
Question 1.
Parthiv’s grandmother looked a little worried today. She asked everybody to have their lunch after 3 p.m. When Parthiv asked the reason she said, “today is solar eclipse at 2:15 p.m.” Parthiv made her relaxed and said this is a natural phenomenon and nothing bad or unpleasant things are related to this. His grandmother listen him carefully.
(a) What is solar eclipse?
(b) Why do you think that some people believe that these eclipses will have some bad effect on them?
(c) Do you experienced such superstition in your life?
(d) What value of Parthiv is shown here?
Answer:
(a) When the earth, moon and sun are in a straight line, with moon in between, the shadow of moon falls on the earth and this is known as solar eclipse.
(b) Because these type of people are superstitious and doesn’t know the scientific reason behind this.
(c) Yes, many a times by my grandmother.
(d) Parthiv is an intelligent and mature boy with scientific aptitude.
Question 2.
Soumen’s teacher asked their class to make a pinhole camera by themselves. Soumen read the activity 5 given in his textbook on how to make a pinhole camera. But he was unable to get the image of a well lit object. He was very upset. His elder brother on observing his pinhole camera found that the hole made by him was quite large. He rectified Soumen’s mistake and helped him making another pinhole camera. Now, Soumen can see the image of the object.
(a) On which principle of light does a pinhole camera works?
(b) Why was Soumen unable to get the image of a well lit object?
(c) How does the formation of the image by a pinhole camera is affected by size of the hole?
(d) What values of Soumen is shown here?
Answer:
(a) Rectilinear propagation of light
(b) He made a larger hole instead of a fine hole.
(c) The finer will be the hole the sharper will be the image formation and vice versa.
(d) Soumen got upset easily without looking and inspecting the actual cause, he is bit careless in doing his activity.