Find free online Chemistry Topics covering a broad range of concepts from research institutes around the world.
Gram Equivalent Mass | Formula, Definition, Diagrams
Similar to mole concept gram equivalent concept is also widely used in chemistry especially in analytical chemistry. In the previous section, we have understood that mole concept is based on molecular mass. Similarly gram equivalent concept is based on equivalent mass.
Definition:
Gram equivalent mass is defined as the mass of an element (compound or ion) that combines or displaces 1.008 g hydrogen or 8 g oxygen or 35.5 g chlorine.
Consider the following reaction:
Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2
In this reaction 1 mole of zinc (i.e. 65.38 g) displaces one mole of hydrogen molecule (2.016 g).
Mass of zinc required to displace 1.008 g hydrogen is
= \(\frac{65.38}{2.016}\) × 1.008
= \(\frac{65.38}{2}\)
The equivalent mass of zinc = 32.69
The gram equivalent mass of zinc = 32.69 g eq-1
Equivalent mass has no unit but gram equivalent mass has the unit g eq-1
It is not always possible to apply the above mentioned definition which is based on three references namely hydrogen, oxygen and chlorine, because we can not conceive of reactions involving only with those three references. Therefore, a more useful expression used to calculate gram equivalent mass is given below.
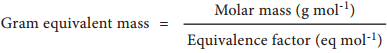
On the basis of the above expression, let us classify chemical entities and find out the formula for calculating equivalent mass in the table below.
Equivalent Mass of Acids, Bases, Salts, Oxidising Agents and Reducing Agents
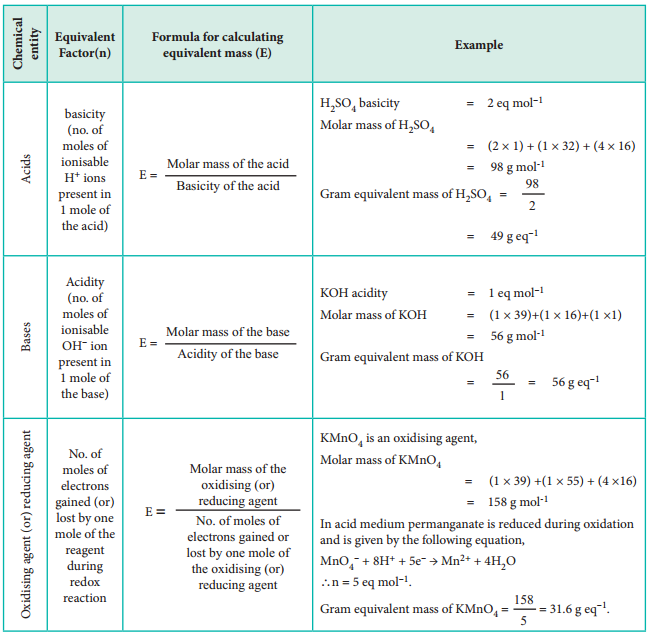
Mole concept requires a balanced chemical reaction to find out the amount of reactants involved in the chemical reaction while gram equivalent concept does not require the same. We prefer to use mole concept for non-redox reactions and gram equivalent concept for redox reactions.
For example,
If we know the equivalent mass of KMnO4 and anhydrous ferrous sulphate, without writing balanced chemical reaction we can straightaway say that 31.6 g of KMnO4 reacts with 152 g of FeSO4 using gram equivalent concept.
The same can also be explained on the basis of mole concept. The balanced chemical equation for the above mentioned reaction is
10FeSO4 + 2KMnO4 + 8H2SO4
↓
K2SO4 + 2 MnSO4 + 5Fe2(SO4)3 + 8H2O
i.e. 2 moles (2 × 158 = 316 g) of potassium permanganate reacts with 10 moles (10 × 152 = 1520 g) of anhydrous ferrous sulphate.
∴ 31.6 g KMnO4 reacts with
\(\frac{1520}{316}\) × 31.6 = 152 g of FeSO4