Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science with Solutions and marking scheme Set 2 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set 2 with Solutions
Time Allowed: 3 hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- This question paper consists of 39 questions in 5 sections.
- All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions. A student is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
- Section A consists of 20 Objective type questions carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B consists of 6 Very Short questions carrying 02 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 30 to 50 words.
- Section C consists of 7 Short Answer type questions carrying 03 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 50 to 80 words.
- Section D consists of 3 Long Answer type questions carrying 05 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
- Section E consists of 3 source-based/case-based units of assessment of 04 marks each with sub-parts.
Section – A (20 Marks)
Select and write the most appropriate option out of the four options given for each of the questions 1 – 20. There is no negative mark for incorrect response.
Question 1.
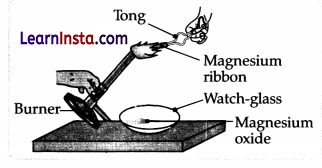
Which of the following is the correct observation of the reaction shown in the above setup?
(A) Brown powder of Magnesium oxide is formed.
(B) Colourless gas which turns lime water milky is evolved.
(C) Magnesium ribbon burns with brilliant white light.
(D) Reddish brown gas with a smell of burning Sulphur has evolved.
Answer:
(C) Magnesium ribbon burns with brilliant white light.
Explanation: When a piece of magnesium ribbon is ignited, light and heat are produced. Magnesium ribbon on burning in the air is an exothermic reaction
![]()
Question 2.
The following reaction is an example of (1)
CaO (s) + H2O (l) → Ca(OH)2 (aq)
(a) Displacement and combination reaction
(b) Decomposition and exothermic reaction
(c) Combination and exothermic reaction
(d) Combination and endothermic reaction
Answer:
(c) Combination and exothermic reaction
The given reaction is an example of both a combination and exothermic reaction because calcium oxide and water are combined to form a single product, i.e. calcium hydroxide, and produce heat during the reaction.
Question 3.
Acid present in tomato is:
(A) Methanoic acid
(B) Acetic acid
(C) Lactic acid
(D) Oxalic acid
Answer:
(D) Oxalic acid
Explanation: The acid present in tomatoes is oxalic acid.
Question 4.
The composition of aqua-regia is (1)
(a) dil.HCI : conc. HNO3 (3 : 1)
(b) conc. HCl : dil. HNO3 (3 : 1)
(c) conc. HCl : conc. HNO3 (3 : 1)
(d) dil. HCl : dil. HNO3 (3 : 1)
Answer:
(c) conc. HCl : conc. HNO3 (3 : 1)
conc. HCl and conc. HNO3 in 3 : 1 ratio form aqua-regia. It is a highly corrosive, fuming liquid. It can dissolve all metals even gold and platinum also.
Question 5.
The electron dot structure of chlorine molecule is:
(A) 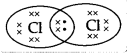
(B) 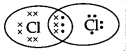
(C) 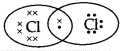
(D) ![]()
Answer:
(C) 
Explanation: The atomic number of chlorine is 17 so the electronic configuration of chlorine is 2,8,7. Since the outermost shell contains 7 valence electrons; hence, chlorine needs 1 more electron to complete its outermost shell. It combines with another chlorine atom by sharing 1 electron each to complete their outermost shells.
The number of shared electrons is 2. Hence, the correct presentation of a chlorine molecule is:

Question 6.
Pritam added hydrochloric acid in a first test tube containing small pieces of marble and then in a second test tube containing zinc granules. He observed gas evolved from both the test tubes. The gases evolved are (1)
(a) H2 in first test tube, O2 in second test tube
(b) CO2 in the first test tube, H2 in the second test tube
(c) O2 in first test tube, Cl2 in second test tube
(d) Cl2 in the first test tube, CO2 in the second test tube
Answer:
(b) CO2 in the first test tube, H2 in the second test tube
In the first test tube, the following reaction takes place.
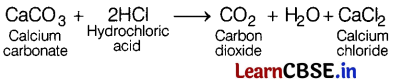
CO2 gas has evolved here.
In a second test tube, the following reaction takes place.
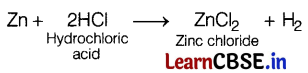
Here, H2 gas is evolved.
![]()
Question 7.
What is X in the reaction?
2AI + 3H2O → AI2O3 + X
(A) AI
(B) H2
(C) O3
(D) AIH3
Answer:
(B) H2
Explanation: X is hydrogen gas. The reaction is:
2AI(s) + 3H2O(g) → AI2O3(s) + 3H2(g)
Question 8.
The diagram given below shows a section through an alveolus and a blood capillary.
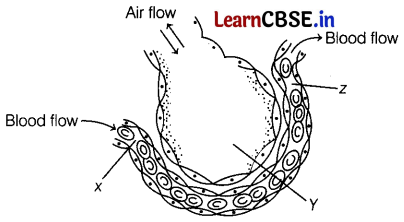
What is the oxygen concentration in X, Y, and Z? (1)
| X | Y | Z | |
| (a) | High | Low | High |
| (b) | High | Low | Low |
| (c) | Low | High | High |
| (d) | Low | High | Low |
Answer:
(c) X – Low, Y – High, Z – High
A high concentration of oxygen in the alveolar air and a low concentration in the blood create a higher diffusion gradient. Blood leaving the alveolus contains a higher concentration of oxygen.
Question 9.
The cerebellum in the brain controls the voluntary actions of the body. Which of these actions is controlled by the cerebellum?
(A) Beating of the heart
(B) Blinking of the eyes
(C) Watering of the mouth
(D) Jumping from a height
Answer:
(D) Jumping from a height
Explanation: The cerebellum controls voluntary movements such as walking, posture, balance coordination, eye movements and speech. This control results in smooth and balanced muscular activity.
Question 10.
When a new plant is formed as a result of cross-pollination from different varieties of a plant, the newly formed plant is (1)
(a) dominant plant
(b) mutant plant
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) hybrid plant
Answer:
(d) hybrid plant
When a new plant is formed as a result of cross-pollination from different varieties of plants, the newly formed plant is hybrid as it contains alleles from two different plants. So, it exhibits the characteristics of both plants.
Question 11.
A cross between pea plant with white flowers (vv) and pea plant with violet flowers (VV) resulted in F2 progeny in which the ratio of violet (VV) and white (vv) flowers will be:
(A) 1:1
(B) 2:1
(C) 3:1
(D) 1:3
Answer:
(A) 1:1
Explanation: A cross between pea plants with white flowers (vv) and pea plants with violet flowers (VV) resulted in F, progeny of violet flowers (Vv). On self pollinating the F, progeny, the ratio of violet (VV) and white (vv) flowers in F2 is 1:1.
Question 12.
Choose the mode of asexual reproduction exhibited by Bryophyllum and Plasmodium. (1)
(a) Bryophyllum, Vegetative propagation Plasmodium, Multiple fission
(b) Plasmodium, Multiple fission Bryophyllum, Vegetative propagation
(c) Planaria, Budding Plasmodium, Binary fission
(d) Hydra, Budding Rhizopus, Spore formation
Answer:
(a) Bryophyllum, Vegetative propagation Plasmodium, Multiple fission
Bryophyllum reproduces by vegetative propagation. Plasmodium reproduces by multiple fission.
![]()
Question 13.
The phenomena of light involved in the formation of a rainbow are:
(A) Refraction, dispersion and scattering.
(B) Refraction, reflection and dispersion.
(C) Refraction, dispersion and internal reflection.
(D) Reflection, dispersion and total internal reflection.
Answer:
(C) Refraction, dispersion and internal reflection.
Explanation: The formation of a rainbow involves all three phenomena: Refraction, dispersion and total internal reflection. The sunlight shines on a water droplet. As the light passes into the raindrop, the light bends or refracts. Due to slow down of light, white light gets dispersed into seven colours. Then total internal reflection happens on the other end of the drop.
Question 14.
Where is the magnetism of a bar magnet maximum? (1)
(a) At the centre of a bar magnet
(b) Near the poles of a bar magnet
(c) Far away from the poles of a bar magnet
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Near the poles of a bar magnet
The magnetism of a bar magnet is maximum near the poles and minimum at the centre of a magnet.
Question 15.
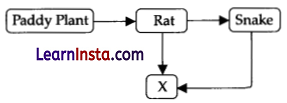
“X” in the given food chain is :
(A) Primary consumer
(B) Secondary consumer
(C) Tertiary consumer
(D) Producer
Answer:
(C) Tertiary consumer
Explanation: ‘X’ is represented by tertiary consumers. Tertiary consumers (X) feed on secondary consumer (snake), which feed on primary consumers (rat), which in turn feed on producers (paddy plant).
Question 16.
Which of the following structures is involved in gaseous exchange in the woody stem of a plant? (1)
(a) Stomata
(b) Lenticels
(c) Guard cell
(d) Epidermis
Answer:
(b) In the stems of woody plants, the exchange of respiratory gases takes place through lenticels. These are small openings in the pits of the bark.
![]()
Questions Nos. 17 to 20 consist of two statements- Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true but R is false.
(D) A is false but R is true.
Question 17.
Assertion (A): Reaction of quicklime with water is an exothermic reaction.
Reason (R): Quicklime reacts vigorously with water releasing a large amount of heat.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: Exothermic reactions are those reactions in which heat is released along with the formation of products. Quicklime reacts vigorously with water releasing a large amount of heat along with the formation of calcium hydroxide.
Therefore, it is an exothermic reaction.
CaO (s) + H2O (l) → Ca(OH)2 (aq) + Heat
Question 18.
Assertion (A): The rate of breathing in aquatic organisms is much slower than that seen in terrestrial organisms. (1)
Reason (R): The amount of oxygen dissolved in water is very low compared to the amount of oxygen in air.
Answer:
(d) A is false but R is true.
Assertion is false but Reason is true and Assertion can be corrected as The rate of breathing in aquatic organisms is much faster than that seen in terrestrial animals this is due to the lesser amount of dissolved oxygen in water.
Question 19.
Assertion (A): A current-carrying straight conductor experiences a force when placed perpendicular to the direction of a magnetic field.
Reason (R): The net charge on a current-carrying conductor is always zero.
Answer:
(B) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: A current-carrying conductor experiences a force when placed perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field. The current-carrying conductor has only electrons flowing through it which experience force, not the stationary protons. Hence, the net charge on it is zero. Hence, the statements are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for the assertion.
Question 20.
Assertion (A): When a charged particle enters in the direction of a uniform magnetic field, then it moves on a straight path without deviation. (1)
Reason (R): Magnetic force on a charged particle is zero, when it moves in the direction of magnetic field.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
When a charged particle enters in the direction of the magnetic field, then no magnetic force acts on the charged particle, hence it moves on a straight path without deviation in a uniform magnetic field.
Section – B (12 Marks)
(Q. no. 21 to 26 are very short answer questions.)
Question 21.
Trupti mixes an aqueous solution of sodium sulphate (Na2SO4) and an aqueous solution of copper chloride (CuCl2). Will this lead to a double displacement reaction? Justify your answer.
Answer:
Yes, this will lead to a double displacement reaction. A double displacement reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which the reactant ions exchange places to form new products. Sodium ions in the sodium sulphate bond with the chlorine ions in copper chloride and the copper ion bonds with the sulphate ion to form sodium chloride and copper sulphate.
Na2SO4 + CuCl2 → 2NaCl + CuSO4
Question 22.
What is a feedback mechanism? Explain this mechanism with the help of a suitable example.
Answer:
The feedback mechanism is the mechanism of the body to maintain the levels of hormones in the body to the desired limit. (1)
For example, if the sugar level in the blood rises, cells of the pancreas detect this change and respond by producing more insulin in the blood. As the sugar level falls, insulin secretion is reduced. (1)
Question 23.
Give two reasons why bile juice is considered to be an important secretion of the liver in the process of digestion.
Answer:
(i) Bile juice has bile salts such as bilirubin and biliverdin. These break down large fat globules into smaller globules so that the pancreatic enzymes can easily act on them. This process is known as emulsification of fats.
(ii) Bile juice also makes the medium alkaline and activates lipase.
OR
What is the other name of ’tissue fluid’? Write its two functions.
Answer:
Another name for tissue fluid is interstitial fluid.
Functions:
(i) Tissue fluid acts as a middleman. It hands over food materials and oxygen from the blood to the tissue cells and receives C02, nitrogenous wastes, hormones and other synthetic substances from the tissue cells and discharges them into blood.
(ii) It also keeps the tissue cells moist.
![]()
Question 24.
The value of current (I) flowing through a given resistor of resistance (R). The corresponding values of potential difference (V) across the resistor are given below.
| V (Volts) | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 |
| I (Ampere) | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.0 |
Plot a graph between current (I) and potential difference (V) and determine the resistance (R) of the resistor. (2)
Answer:
From the scale, At the X-axis, 1 div (1 cm) = 0.1 A
At Y-axis, 1 div (1 cm) = 0.5 V
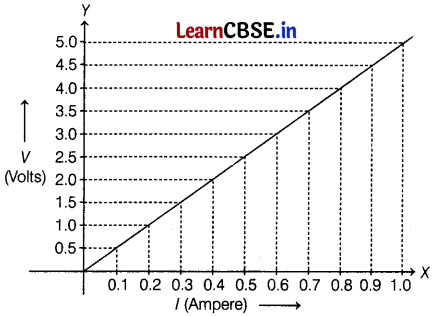
∴ Slope of graph resistance, (R) = \(\frac{V}{I}\)
∴ R = \(\frac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1}\)
= \(\frac{1.5-1.0}{0.3-0.2}\)
= \(\frac{0.5}{0.1}\)
= 5 Ω
Question 25.
Priya has a copper wire and an aluminium wire of the same length. Can the electrical resistance of the two wires be the same? Justify your answer.
Answer:
Yes, the electrical resistance of the two wires can be the same.
If the area of the cross-section of the two wires is different/ if the thickness of the two wires is different.
OR
(a) Name the poles P, Q, R, and S of the magnets in the following figures ‘a’ and ‘b’:

Answer:
In Figure (a)- P is the north pole and Q is the south pole.
In Figure (b)- R is the north pole and S is the south pole.
(b) State the inference drawn about the direction of the magnetic field lines based on these diagrams.
Answer:
In the given diagrams, the direction of the magnetic field shows that outside the magnet, the magnetic field lines emerge from the North Pole of a magnet and merge at the South Pole of the magnet
Question 26.
How does the study of the food chain in an area or habitat help us? Give an example of a food chain operating in a large lake.
Answer:
The study of the food chain in an area or habitat helps in
- understanding the energy transfer through organisms.
- understanding harmful human activities and disruption of ecological balance, if any.
An example of the four steps of the food chain operating in a large lake is as follows:
Algae → Protozoan → Small fish → Big fish. (2)
![]()
Section – C (21 Marks)
(Q.no. 27 to 33 are short answer questions.)
Question 27.
(a) Suggest a safe procedure of diluting a strong concentrated add.
(b) Name the salt formed when sulphuric add is added to sodium hydroxide and write its pH.
(c) Dry HCL gas does not change the colour of dry blue litmus paper. Why?
Answer:
(a) The acid is always diluted by adding the acid to water slowly and with constant stirring. In addition to it, it is advised to wear gloves and
goggles and maintain safe distance.
(b) The salt formed when sulphuric acid is added to sodium hydroxide is sodium sulphate.
The balanced equation is:
2NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
Its pH is approximately equal to 7.
(c) The colour of litmus paper changes only in the presence of ions like hydrogen (H+) or hydronium (H2O+) ions.
HCl can produce these ions only in the form of aqueous solution.
Hence, dry HCl gas does not change the colour of dry litmus paper.
Question 28.
Baking soda is used in small amounts for making bread and cake. It helps to make these soft and spongy. An aqueous solution of baking soda turns red litmus blue. It is also used in soda acid fire extinguishers. Use this information to answer the following questions: (3)
(a) How does it help in extinguishing fire?
(b) What is the reaction involved when it is heated?
(c) Is the pH value of baking soda solution lower than or higher than 7?
Answer:
(a) 2NaHCO3 (Baking Soda) (s) + H2SO4 (Acid) (aq) → Na2SO4 (s) + 2H2O (l) + 2CO2 (g)
The CO2 gas produced by the reaction of baking soda and acid in the soda-acid fire extinguisher helps in extinguishing fire. (1)
(b) When sodium bicarbonate is heated, it disintegrates into sodium carbonate, water and carbon dioxide.
2NaHCO3 \(\stackrel{\text { Heat }}{\longrightarrow}\) Na2CO3 (s) +H2O (l) + CO2 (g) ↑ (1)
(c) pH value of baking soda solution is higher than 7, i.e. it is alkaline. (1)
Question 29.
Name the gland and the hormone secreted by it in scary situations in human beings. List any two responses shown by our body when this hormone is secreted into the blood.
Answer:
Hormone: Adrenaline
Functions:
(i) Increases the heart rate.
(ii) Increases blood pressure.
(iii) Expands the air passages of the lungs.
(iv) Enlarges the pupil in the eye.
Question 30.
Shyam wants to experiment to show angle of incidence (i) is equal to the angle of refraction (r) through a transparent slab. (3)
(a) Specify the value of i at which angle of i incidence (i) and refraction (r) are equal in the transparent slab.
(b) What is the angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray through the glass slab?
(c) If the refractive index of the glass slab is 1.5, then find the speed of light in the glass slab.
(Take, the speed of light in air = 3 × 108 m/s)
Answer:
(a) When the incident ray falls normally on the glass slab, it will refract without deviation, i.e. along the normal in the glass slab, ∠i = ∠r = 0. (1)
(b) When the refraction through a glass slab takes place, then the emergent ray becomes parallel to the incident ray. So, the angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray will be zero. (1)
(c) Given, the refractive index of the glass slab = 1.5
We know that,
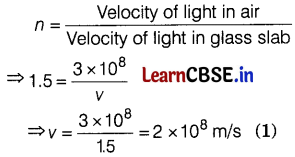
![]()
Question 31.
The diagram given shows object O and its image I. Without actually drawing the ray diagram state the following:
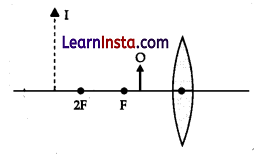
(a) Type of lens (Converging/Diverging)
Answer:
Converging lens
(b) Name two optical instruments where such an image is obtained.
Answer:
Microscope and Telescope
(c) List three characteristics of the image formed if this lens is replaced by a concave mirror of focal length F and an object is placed at a distance F/2 in front of the mirror.
Answer:
Characteristics of the image formed by the concave mirror are:
(i) Virtual image
(ii) Magnified image
(iii) Image behind the mirror
Question 32.
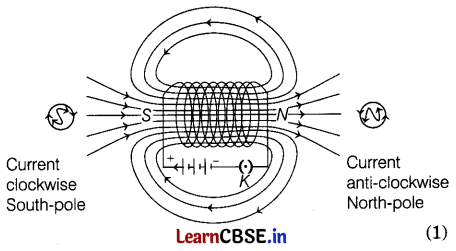
A student performs an activity in which a current is passed through a solenoid. Then, he observes magnetic field patterns inside and outside the solenoid.
(a) Explain the pole formation at the ends of the solenoid.
(b) Draw magnetic field lines due to current carrying solenoid.
Answer:
(a) Pole formation at the ends of the solenoid can be explained by looking at one face of the coil. If the direction of current through the coil is clockwise, then that face has South polarity and if the direction of current is anti-clockwise, then that face has North polarity. (1)
(b) Magnetic field lines force due to a current-carrying solenoid are as shown in the figure.
Question 33.
(a) Why is an alternating current (A.C.) considered to be advantageous over direct current (D.C.) for the long distance transmission of electric power?
Answer:
Alternating current can be transmitted over long distances at very high voltages to ensure that the current value is very low and as a result very low amount of energy is lost during transmission. When it reaches near the household, the voltage can be stepped down to restore the required value of current whereas the voltage of direct current cannot be stepped up and down.
(b) How is the type of current used in household supply different from the one given by a battery of dry cells?
Answer:
The type of current used in domestic household supply is alternating while a battery of dry cells supplies direct current.
(c) How does an electric fuse prevent the electric circuit and the appliances from possible damage due to short-circuiting or overloading?
Answer:
An electric fuse is made of wires of very low melting point. If there is a current larger than the specified value, the temperature of a fuse wire increases, and it melts to break the electric circuit and stop the flow of unduly high electric current. This saves appliances from possible damage.
![]()
Section – D (15 Marks)
(Q.no. 34 to 36 are long answer questions.)
Question 34.
A compound C (molecular formula, C2H4O2) reacts with Na metal to form a compound R and evolves a gas that burns with a pop sound. Compound C on treatment with alcohol A in the presence of an acid forms a sweet-smelling compound S (molecular formula = C3H6O2). In addition to NaOH to C, it also gives R and water. S on treatment with NaOH solution gives back R and A. Identify C, R, A, S and write down the reactions involved. (5)
Or
(a) Name the type of carbon compounds that can be hydrogenated. With the help of a suitable example explain the process of hydrogenation.
(b) Explain any three methods to prevent rancidity.
Answer:
Since, compound C (Molecular formula C2H4O2) contains two oxygen atoms, therefore most probably it may be a carboxylic acid, i.e. ethanoic acid (CH3COOH).
Ethanoic acid reacts with a metal (Na), to evolve a gas that burns with a pop sound alongwith the formation of compound R, therefore, R must be salt, i.e. sodium ethanoate and the gas that burns with a pop sound must be H2 gas. (1)
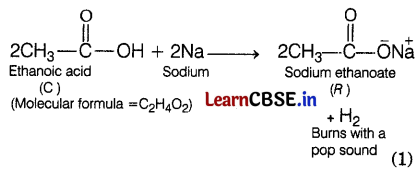
Compound R is sodium ethanoate. This is also supported by the observation that when ethanoic acid reacts with NaOH, it gives R, (sodium ethanoate) and water.
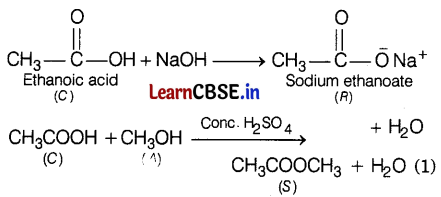
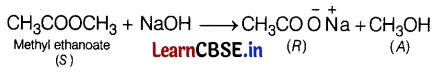
Since compound C on treatment with alcohol A in the presence of acid forms a sweet-smelling compound S (Molecular formula C3H6O2), therefore, S is methyl ethanoate (ester). Since ester S has three carbon atoms and the acid C has two carbon atoms, alcohol A must contain one C atom, i.e. A is methanol.
Thus, C = CH3COOH (ethanoic acid)
R = \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COO}^{-} \stackrel{+}{\mathrm{Na}}\) (sodium ethanoate)
A = CH3OH (methanol)
S = CH3COOCH3 (methyl ethanoate) (2)
Or
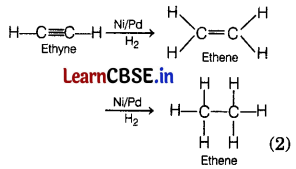
(a) Only unsaturated hydrocarbons, i.e. alkenes, and alkynes can be hydrogenated.
e.g. In the presence of a catalyst Ni/Pd, ethyne is hydrogenated into ethare.
(b) Methods by which rancidity can be prevented are as follows.
- Keeping the food materials in air-tight containers.
- Refrigeration of cooked food at low temperature.
- Packing of food like wafers, and potato chips in packets containing nitrogen gas instead of air. (3)
Question 35.
Give a reason for the following:
(a) During reproduction, inheritance of different proteins will lead to altered body designs.
Answer:
During reproduction, the information for the inheritance of characteristics is passed on from the parents to the offspring in the form of DNA. DNA in the cell nucleus carries the genetic information. Hence DNA copying is the basic event in reproduction. If the information dining the DNA copying is changed, different proteins will be made. Different proteins will eventually lead to altered body designs.
(b) Fertilisation cannot take place in flowers if pollination does not occur.
Answer:
The process of fertilization is the fusion of both male and female gametes. If pollination does not occur it means that the male gamete is not available, hence fertilisation cannot take place.
(c) All multicellular organisms cannot give rise to new individuals through fragmentation or regeneration.
Answer:
Regeneration and fragmentation are only possible when the entire body part is made up of similar kinds of cells. All multicellular organisms cannot give rise to new individuals through fragmentation or regeneration because the complex multicellular organisms have organ system level organisation. The tissues in these organisms are highly differentiated to perform specialised functions and cannot regenerate a new individual.
(d) Vegetative propagation is practised for growing only some types of plants.
Answer:
Vegetative propagation is practised for growing some types of plants because of the following advantages:
- It is used to grow a plant in which viable seeds are not formed or very few seeds are produced such as orange, banana, pineapple.
- It helps to introduce plants in new areas where the seed germination fails to produce mature plant due to change in environmental factors and the soil.
- It is more rapid, easier and cheaper method.
- By this method a good quality of a race or variety can be preserved.
(e) The parents and off-springs of organisms reproducing sexually have the same number of chromosomes.
Answer:
Gametes of sexually-reproducing animals have half the number of chromosomes as that of the parents. During fertilisation, when two gametes i.e. male and female gametes fuse, the offspring produced will have the same amount of DNA or the same number of chromosomes as that of the parent.
OR
(a) Why is the use of iodised salt advisable? Name the disease caused due to deficiency of iodine in our diet and state its one symptom.
Answer:
- Iodine is essential for the functioning of thyroid/formation of thyroxine hormone.
- Disease is Goitre.
- Swollen neck
(b) How do nerve impulses travel in the body? Explain.
Answer:
Impulse travels from dendrite to cell body, then along the axon to its end. At the end, some chemicals are released which fill the gap of synapse, and start a similar electrical impulse to another neuron and the impulse further travel in the body.
Detailed(b) Answer:
The information received at the end of the dendritic tip, sets off a chemical reaction that creates an electrical impulse. This impulse travels from the dendrite to the cell body and then along the axon to it send. Here, the electrical impulse sets off the release of some chemicals which cross synapse, inducing a similar impulse in a dendrite of the next neuron.
![]()
Question 36.
(a) Three incandescent bulbs of 100 W each are connected in series in an electric circuit. In another circuit, another set of 3 bulbs of the same wattage are connected in parallel to the same source. Will the 2 bulbs in the circuits glow with the same brightness? Justify your answer.
(b) If R1 and R2 are the resistances of the filament of 40W and 60W respectively, operating at 220V. Out of R1 and R2, which one is greater?
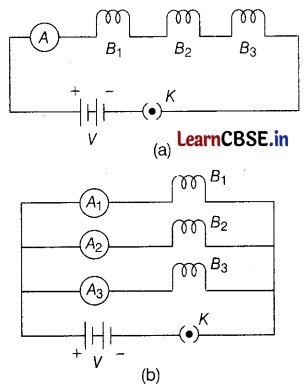
(c) How much energy does a 100W bulb transfer in 1 minute? (5)
Or
(a) A letter ‘A’ consists of a uniform wire of resistance 1 ohm per cm. The side of the letter is 20 cm long and the cross piece in the middle is 2 cm long while the apex angle is 60°. Find the resistance of the letter between the two ends of the legs.
(b) Calculate the amount of charge flowing in 2 min in a wire of resistance 10Ω when a potential difference of 20V is applied between the ends.
(c) In the circuit, determine the current flowing through 10Ω resistance.
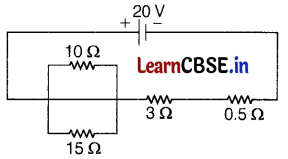
Answer:
(a) In series circuit (a)
Equivalent resistance in series combination,
Rs = R + R + R = 3R, Voltage = V
Let current through each bulb in series combination be I.
(∵ Current remains same in series combination)
By Ohm’s law,
V = I × 3R ⇒ I = \(\frac{V}{3 R}\)
∴ Power consumption of each bulb in series combination,
P1 = I2 (3R)
P1 = \(\left(\frac{V}{3 R}\right)^2\) × 3R
P1 = \(\frac{V^2}{3 R}\) …….(i)
In parallel circuit (b)
The resistance of each bulb = R
The voltage across each bulb = V
(∵ voltage remains same in parallel combination)
∴ Power consumption of each bulb in parallel combination,
P2 = \(\frac{V^2}{R}\) …….(ii)
Hence, from Eqs. (i) and (ii), we get
P2/P1 = \(\frac{V^2}{R} \times \frac{3 R}{V^2}\)
P2 = 3P1
Therefore, each bulb in a parallel combination glows 3 times brighter to that of each bulb in a series combination. (3)
(b) As, power, P = \(\frac{V^2}{R}\) or R = \(\frac{V^2}{P}\)
For same voltage, R ∝ \(\frac{1}{P}\)
i.e., More the power, the lesser will be the resistance.
∴ R2 < R1 (1)
(c) Given, P = 100 W and t = 1 min = 60 s
P = \(\frac{\text { Work done }}{\text { Time }}=\frac{\text { Energy spent }}{t}\)
∴ Energy spent = P × t = 100 × 60 = 6000 J (1)
Or
(a) Clearly, AB = BC = CD = DE = BD = \(\frac{20}{2}\) = 10 cm
and R1 = R2 = R3 = R4 = R5 = 10Ω and R5 = 2Ω
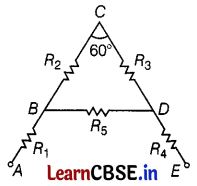
As R2 and R3 are in series, their combined resistance = 10 + 10 = 20Ω
The combination is in parallel with R5 = 2Ω
Hence, Resistance between points B and D
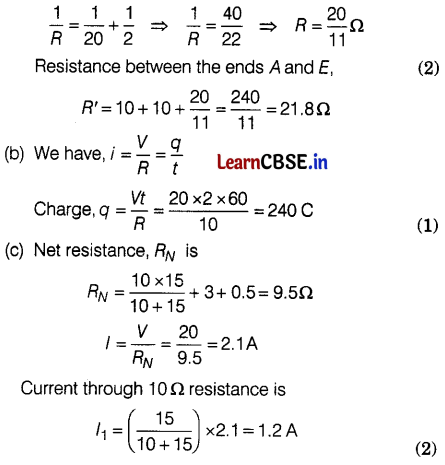
Section – E (12 Marks)
(Q.no. 37 to 39 are case-based/data-based questions with 2 to 3 short sub-parts.)
(Internal choice is provided in one of these sub-parts.)
Question 37.
Read the given passage and answer the questions that follow:
The pictures show the bonds formed by the sharing of electrons by the atoms of four different molecules.

(a) Out of these molecules- Hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen and oxygen, which has the strongest bond between its atoms? What is this type of bond between atoms known as?
Answer:
Carbon can gain four electrons and form C4- anion or lose four electrons to form the C4+ cation. It forms four covalent bonds by sharing its valence electrons with other atoms.
This type of bond between atoms is known as covalent bond covalent, carbon compounds are those where there is a carbon-carbon bond.
![]()
(b) Which of these statements is true about carbon compounds? Write ‘Yes’ or ‘No’ for the correct response.
| Is this true about carbon compounds? | Yes or No |
| (i) They are good conductors of electricity? | |
| (ii) They exist in either saturated or unsaturated form. | |
| (iii) They have lower boiling points than ionic compounds |
Answer:
| Is this true about carbon compounds? | Yes or No |
| (i) They are good conductors of electricity? | No |
| (ii) They exist in either saturated or unsaturated form. | Yes |
| (iii) They have lower boiling points than ionic compounds | Yes |
OR
(b) Which element exhibits the property of catenation to the maximum extent and why?
Answer:
Carbon, due to strong C-C bond.
Question 38.
Mohan in his kitchen garden crossed pure-breed tall pea plants with pure-breed dwarf pea plants and obtained pea plants of F1-generation. Then he performed two types of experiments. In the first, he self-crossed the plants of F1-generation (experiment A) and in the second, he crossed the plants of F1-generation with the pure-breed dwarf parent plants (experiment B). (4)
(a) What would be the phenotypic ratio of plants in the Frgeneration?
(b) How would the genotypic ratio differ in experiment ‘B’?
(c) What would be the phenotypic and genotypic ratio of F2-generation in experiment ‘A’?
Or
How do we describe the phenotypic character that is expressed in the F1 generation? What is the term given to the contrasting character?
Answer:
(a) The phenotype of all the plants in the F1 generation would be tall.
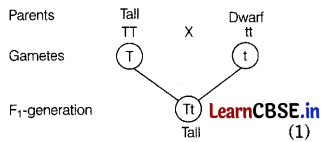
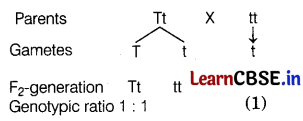
(b) When crossed with homozygous recessive parent the genotypic ratio would be Tt : tt; 1 : 1.
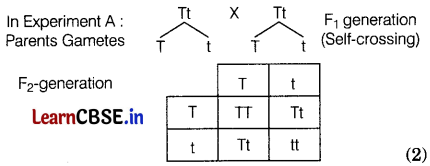
(c) In experiment ‘A’, the phenotypic ratio of tall and dwarf plants would be Tall : Dwarf :: 3 : 1, whereas the genotypic ratio would be, TT : Tt : tt : 1 : 2 : 1
Or
The phenotypic character that is capable of expressing in the F1 generation is described as ‘dominant’. The contrasting character, i.e. dwarfness is the recessive character. (2)
Question 39.
Study the circuit shown in which three identical bulbs B1, B2 and B3 are connected in parallel with a battery of 4.5 V and answer the following questions.
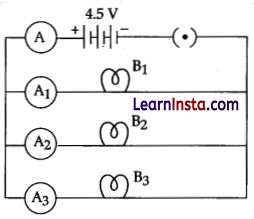
(a) What will happen to the glow of the other two bulbs if the bulb B3 gets fused?
(b) If the wattage of each bulb is 1.5 W how much readings will the ammeter A show when all the three bulbs glow simultaneously.
(c) Find the total resistance of the circuit.
Answer:
(a) Other bulbs will glow with the same brightness.
(b) When the bulbs are in parallel, wattage will be added (4.5 W) and the ammeter reading would be,
I = P/V
= 4.5W / 4.5V
= 1.0 Ampere
(c) Since, the ammeter reading is 1.0 ampere, the resistance of the combination is 4.5 V/ 1.0 A = 4.5 Ω
![]()
OR
How many resistors of 88 Ω are connected in parallel to carry 10 A current on a 220 V line?
Answer:
Let n number of resistances is connected in
parallel.
Equivalent resistance, 1/ Rp = n/88
Rp = 88/n …. (i)
Since, V = IR …. (ii)
Now from equations (i) and (ii):
n = I × 88/220
= 10 × 88/220
Or, n = 88/22 = 4 resistors.