In this page, we are providing Carbon and its Compounds Class 10 Extra Questions and Answers Science Chapter 4 pdf download. NCERT Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds with Answers will help to score more marks in your CBSE Board Exams.
Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Extra Questions and Answers Carbon and its Compounds
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds with Answers Solutions
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Draw the electron dot notation of O2 molecule.
Answer:
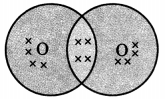
Question 2.
Name a molecule that has triple bond.
Answer:
Nitrogen (N2).
Question 3.
Name the hardest substance which is an allotrope of carbon.
Answer:
Diamond.
Question 4.
Name the allotrope of carbon which have the structure of C-60.
Answer:
Fullerenes.
5. Name the unique ability of carbon to form bonds with other atoms of carbon.
Answer:
Catenation.
Question 6.
Mention the two characteristic features seen in carbon.
Answer:
Tetravalency and catenation.
Question 7.
Name the first organic compound synthesised by Wohler.
Answer:
Urea.
Question 8.
Write the general molecular formula of alkane series.
Answer:
CnH2n+2
Question 9.
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound:
CH3CH2CH2CH2—C ≡ C—H
Answer:
Hex-1-yne.
Hex adder calculator is an effcient tool for adding two hex values. Similarly, Hex calculator can easily calculate two given values.
Question 10.
Identify the functional group present in the following compound:
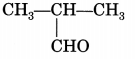
Answer:
Aldehyde.
Question 11.
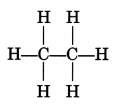
How many covalent bonds are there in a molecule of ethane, C2H6?
Answer:
Seven (7)
Question 12.
Draw the structure of the hexanal molecule, C5H11CHO.
Answer:
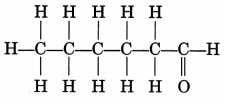
Question 13.
Write the name and formula of the 2nd member of homologous series having general formula CnH2n. [CBSE 2015]
Answer:
CnH2n : Alkene
2nd member = C3H6 (propene)
Question 14.
Write the molecular formula of an alkyne containing 10 atoms of hydrogen.
Answer:
C6H10.
Question 15.
Why is ethanoic acid known as glacial acetic acid?
Answer:
Acetic acid freezes at 290 K to form crystals which look like glaciers, so pure ethanoic acid is known as glacial acetic acid.
Question 16.
Which property of ethanol makes it suitable for preparing medicines such as tincture iodine, cough syrup and other tonics?
Answer:
Ethanol is a good solvent.
Question 17.
What is the function of cone. H2SO4 in the formation of ethene from ethanol?
Answer:
Dehydrating agent
Question 18.
Name the alcohol which is an active ingredient of all alcoholic drinks.
Answer:
Ethanol or ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH)
Question 19.
Which two of the following compounds could belong to the same homologous series?
C2H6O2, C2H6O, C3H28, CH4O
Answer:
CH4O and C2H6O (General formula CnH2n+1. OH)
Question 20.
Which of the following molecule is called buckminsterfullerene?
C90, C60, C70, C120
Answer:
C60.
Question 21.
Name the gas evolved when sodium carbonate and bicarbonate is added to ethanoic acid.
Answer:
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Question 22.
Among CH4, C2H6 and C4H10 which is expected to show isomerism?
Answer:
C4H10.
Question 23.
Write the structural formula of a saturated hydrocarbon whose molecule contains three atoms of carbon.
Answer:
C3H8.
Question 24.
A neutral organic compound is warmed with some ethanoic acid and a little cone. H2SO4. Vapours having sweet smell or fruity smell are observed. Identify the functional group present in the organic compound.
Answer:
Question 25.
Name the oxidising agent which can oxidise ethanol to ethanoic acid.
Answer:
Alkaline potassium permanganate (KMnO4/KOH) or acidified potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7/H2SO4).
Question 26.
Write the formula and name of next homologue of CH3COCH3.
Answer:
CH3CH2COCH3, Butanone.
Question 27.
Why do alkanes burn with a blue flame?
Answer:
Alkanes generally burn with a blue flame or clean flame because the combustion is complete and no unbumt carbon particles are released.
Question 28.
Draw the structure of an unsaturated cyclic compound having six carbon atoms. Also draw its electron dot structure. (Cyclohexene)
Answer:
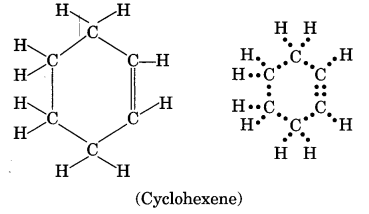
Question 29.
How do the melting and boiling points of the hydrocarbons change with increase in molar mass?
Answer:
Intermolecular forces of attraction increases due to increase in molar mass, hence the melting and boiling points increase.
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Short Answer Type I
Question 1.
Draw the electron dot structure of ethyne and also draw its structural formula. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Ethyne, C2H2
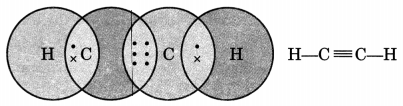
Question 2.
Name the functional groups present in the following compounds:
(a) CH3 CO CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3
(b) CH3 CH2 CH2 COOH
(c) CH3 CH2 OH (NCERT Exemplar)
Answer:
(a) Ketone
(b) Carboxylic acid
(c) Aldehyde
(d) Alcohol
Question 3.
Which of the following hydrocarbons can undergo addition reactions:
C2H6, C4H10, C3H6, C3H4, CH4, C2H2, C4H8
Answer:
C3H6, C3H4, C2H2 and C4H8 because these compounds are unsaturated organic compounds and hence can undergo addition reactions.
Question 4.
Draw the electron dot structure of O2 and N2 molecules.
Answer:
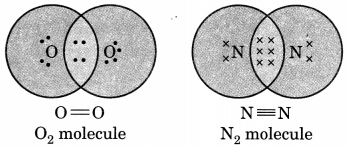
Question 5.
Give the general formula of alkanes. Write the name, structural formula and physical state of the compound containing:
(i) 3-carbon atoms
(ii) 8-carbon atoms.
Answer:
(a) General formula of alkanes is CnH2n+2
n = 1, 2, 3…
(i) Propane, CH3—CH2—CH3
or
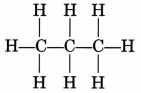
Propane is a gas.
(ii) CH3—CH2—CH2—CH2—CH2—CH2—CH2—CH3
or
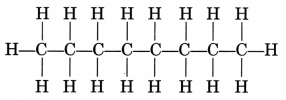
Octane is a liquid
Question 6.
Why does carbon form compounds mainly by covalent bonding?
Answer:
Carbon atoms have 4 valence electrons in their valence shell, it needs to gain or lose 4 electrons to attain the noble gas configuration.
(i) It could gain four electrons forming C4- anion. But it would be difficult for the nucleus with six protons to hold on to ten electrons.
(ii) It could lose four electrons forming C4+ cation. But it would require a large amount of energy to remove four electrons from its outermost shell.
Therefore, carbon shares its valence electrons to complete its octet with other atoms to form covalent bonds.
Question 7.
List the common physical properties of carbon compounds.
Answer:
- They have covalent bonds between their atoms therefore they do not form ions. So they are poor conductors of electric current.
- These compounds have low melting and low boiling points.
- They are generally insoluble in water but soluble in the organic solvents like ether, carbon- tetrachloride, etc.
Question 8.
Draw the structures of diamond and graphite.
Answer:
In diamond, each carbon atom is bonded to four other carbon atoms forming a rigid three dimensional structure.
In graphite, each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms in the same plane giving a hexagonal array. One of these bonds is a double bond.
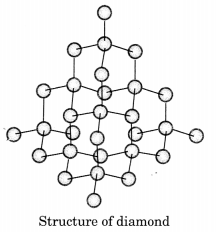
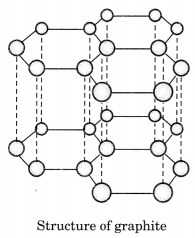
Question 9.
Write the general IUPAC names of alcohol, carboxylic acid, aldehyde and ketone.
Answer:
| Compound | General IUPAC name |
| Alcohol | Alkanol |
| Carboxylic acid | Alkanoic acid |
| Aldetjyde | Alkanal |
| Ketone | Alkanone |
Question 10.
Ethane , Ethene, Ethanoic acid, Ethyne, Ethanol
From the box given above, name:
(i) The compound with —OH as a part of its structure.
(ii) The compound with —COOH as a part of its structure.
(iii) Gas used in welding.
(iv) Homologue of the homologous series with general formula CnH2n+2.
Answer:
(i) Ethanol
(ii) Ethanoic acid
(iii) Ethyne
(iv) Ethane
Question 11.
Give two uses each of methyl alcohol and ethyl alcohol.
Answer:
Uses of ethyl alcohol:
- It is used in the manufacture of dyes, perfumes, antiseptics, etc.
- It is used in alcoholic drinks.
Uses of methyl alcohol:
- It is used as a solvent
- It is used as an antifreeze
Question 12.
List two main points of difference between organic and inorganic compound.
Answer:
Organic compounds:
- They are made up of few elements (C, H, O, N, S) through covalent bonds.
- They are combustible.
Inorganic compounds:
- They are made up of all the known elements, which involve ionic bond.
- They are generally non-combustible.
Question 13.
What are substitution reactions? Justify your answer with a suitable example.
Answer:
A chemical reaction in which atom(s) or group of atoms of an organic compound is/are replaced by other atom(s) or group of atoms without any change in the rest of the molecule is called a substitution reaction.
For example,
CH4 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + HCl
In this chemical reaction Cl atom substitutes one hydrogen atom from methane.
Question 14.
Give any four uses of ethanoic acid.
Answer:
- Ethanoic acid is used in making synthetic vinegar.
- Ethanoic acid is used as a reagent in chemistry laboratory.
- Ethanoic acid is used for making dyes, perfumes and esters.
- Ehanoic acid is used for coagulating rubber from latex and casein from milk.
Question 15.
List four differences between soaps and detergents.
Answer:
Soaps:
- Soaps are sodium salts of higher fatty acids.
- Biodegradable.
- Soaps cannot be used in acidic medium.
- Soaps cannot be used in hard water.
Synthetic Detergents:
- Detergents are sodium alkyl sulphates or sodium alkyl benzene sulphonates with alkyl group having more than ten carbon atoms.
- Non-biodegradable.
- They can be used in acidic medium.
- Detergents can be used even in hard water.
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Short Answer Type II
Question 1.
What is the role of metal or reagents written on arrow’s in the given chemical reactions?
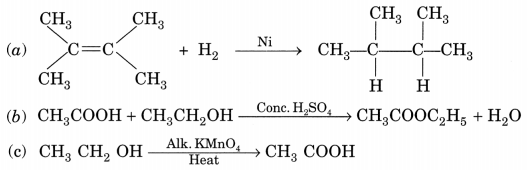
[NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
(a) Ni acts as a catalyst.
(b) Concentrated H2SO4 acts as a catalyst.
(c) Alkaline KMnO4 acts as an oxidising agent.
Question 2.
The molecular formula of an organic compound X is C2H4O2 which has vinegar like smell.
(i) Identify the compound.
(ii) Write its chemical formula and name.
(iii) What happens when sodium bicarbonate is added into it?
Answer:
(i) The organic compound X is acetic acid.
(ii) Chemical formula: CH3COOH
IUPAC name: Ethanoic acid
(iii) Ethanoic acid produces effervescence with sodium bicarbonate liberating carbon dioxide gas.
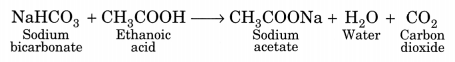
Question 3.
Write one chemical equation to represent each of the following types of reactions of organic substances.
(a) Esterification
(b) Saponification
(c) Substitution [CBSE 2011]
Answer:
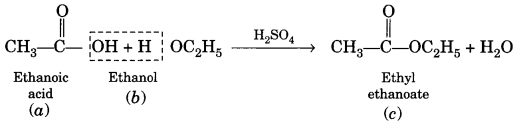
(a) Esterification. Ethanol reacts with ethanoic acid on warming in presence of a few drops of conc. H2SO4 to form a sweet smelling ester, ethyl ethanoate.
![]()
(b) Saponification. The alkaline hydrolysis of esters is known as saponification as this reaction is used for the preparation of soaps.

(c) Substitution. The reaction, in which one (or more) hydrogen atoms of a hydrocarbon are replaced by some other atoms, is called substitution reaction.
![]()
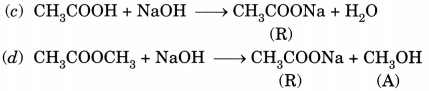
4. Write chemical equations for what happens when
(a) Sodium metal is added to ethanoic acid
(b) Solid sodium carbonate is added to ethanoic acid
(c) Ethanoic acid reacts with a dilute solution of sodium hydroxide.
Answer:
(a) 2Na + 2CH3COOH → 2CH3COONa + H2(g)
(b) Na2CO3 + 2CH3COOH → 2CH3COONa + CO2 (g)+ H2O
(c) CH3COOH + NaOH → CH3COONa + H2O
Question 5.
Name the oxidising agent used for the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid. Distinguish between ethanol and ethanoic acid on the basis of (i) litmus test, (ii) reaction with sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Answer:
Alkaline KMnO4 or acidified potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) are used for the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid.
Ethanol:
- Ethanol has no effect on red or blue litmus solution.
- No gas evolved when ethanol is treated with sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Ethanoic acid:
- Ethanoic acid turns blue litmus solution red.
- Ethanoic acid reacts with sodium hydrogen carbonate to evolve carbon dioxide along with the formation of salt and water.
CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COONa + CO2 + H2O
Question 6.
(a) Differentiate between alkanes and alkenes. Name and draw the structure of one member of each. [CBSE 2013]
(b) Alkanes generally burn with clean flame. Why?
Answer:
Alkanes:
- An alkane is a hydrocarbon in which the carbon atoms are connected by only single covalent bond.
- General formula of alkane is CnH2n+2.
- The simplest alkane is methane (CH4).
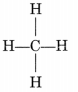
- Alkanes generally burn in air with a blue and non-sooty flame.
- Alkanes undergo substitution reactions.
- Alkanes do not decolourise red brown colour of bromine water.
alkenes:
- An alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon in which the two carbon atoms are connected by a double bond.
- General formula of alkene is CnH2n.
- The simplest alkene is ethene (C2H4).
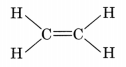
- Alkenes burn in air with a yellow and sooty flame.
- Alkenes undergo addition reactions.
- Alkenes decolourise bromine water.
(b) Alkanes burn in air with a blue and non-sooty flame because the percentage of carbon in the alkane is comparatively low which gets oxidised completely by oxygen present in air.
Question 7.
What happens when
(а) ethanol is burnt in air?
(b) ethanol is heated with excess cone. H2SO4 at 443 K?
(c) a piece of sodium is dropped into ethanol? [CBSE 2013]
Answer:
(a) C2H5OH + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O + Heat + Light
![]()
(c) 2C2H5OH + 2Na → 2C2H5ONa + H2(g)
Question 8.
What is meant by homologous series of carbon compounds? Write the general formula of
(i) alkenes, and
(ii) alkynes. Draw the structures of the first member of each series to show the bonding between the two carbon atoms. [CBSE 2014]
Answer:
Homologous series:
A series of carbon compounds in which the same functional group substitutes for hydrogen on a carbon chain is called a homologous series. There is a difference of –CH2 in the molecular formulae of two nearest compounds of a homologous series. Each such series has same general molecular formula and has a general scientific name. There is a difference of 14 u (unified mass) in the molecular masses of two nearest compounds of a series.
Members of homologous series of aldehydes:
H – CHO Methanal
CH3 – CHO Ethanal
C2H5 – CHO Propanal
General formula:
(i) Alkenes, CnH2n
(ii) Alkynes, CnH2n-2
Structure:
- The first member of alkenes is ethene and its structure is
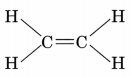
- The first member of alkynes is ethyne and its structure is H—C ≡ C—H
Question 9.
With the help of an example, explain the process of hydrogenation.
Mention the essential conditions for the reaction and state the change in physical property with the formation of the product. [CBSE 2015]
Answer:
Process of hydrogenation:
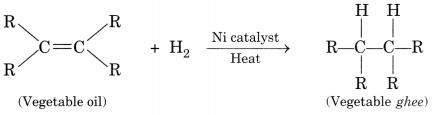
The addition of hydrogen to an unsaturated hydrocarbon to obtain a saturated hydrocarbon is called hydrogenation.
Essential conditions for the reaction are:
- Presence of an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
- Presence of a catalyst such as nickel (Ni) or palladium.
Changes observed:
- Change observed in the physical property is the change of unsaturated compound from the liquid state to saturated compound in the solid state.
- The boiling or melting points of a product is increased.
Question 10.
The list of some organic compounds is given below:
Ethanol, ethane, methanol, methane, ethyne, ethene
From the above list, name a compound:
(i) formed by the dehydration of ethanol by conc. H2SO4.
(ii) which will give red precipitate with ammoniacal cuprous chloride solutions,
(iii) which forms ethanoic acid on oxidation with KMnO4.
(iv ) which has vapour density 14 and decolourises pink alkaline potassium permanganate.
(v) which forms chloroform on halogenation in the presence of sunlight.
(vi) which decolourises bromine solution in carbon tetrachloride.
Answer:
(i) Ethene
(ii) Ethyne
(iii) Ethanol
(iv) Ethene
(v) Methane
(vi) Ethene
Question 11.
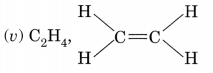
The molecule of alkene family are represented by a general formula CnH2n. Now answer the following:
(i) What do n and 2n signify?
(ii) What is the name of alkene when n = 4?
(iii) What is the molecular formula of alkene when n = 6?
(iv) What is the molecular formula of the alkene if there are six H-atoms in it?
(v) What is the molecular formula and structural formula of the first member of the alkene family?
(vi) Write the molecular formulae of lower and higher homologues of an alkene which contains four carbon atoms.
Answer:
(i) n indicates number of carbon atoms and 2n indicates number of hydrogen atoms.
(ii) Butene
(iii) C6H12
(iv) C3H6
(vi) Lower homologue —C3H16, Higher homologue – C5H10
Question 12.
Copy and complete the following table which relates to three homologous series of hydrocarbons:
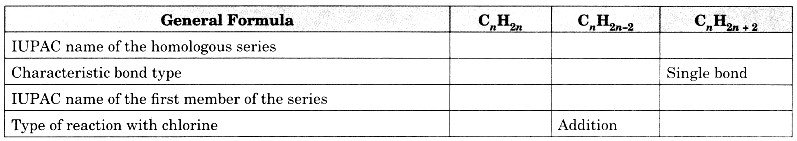
Answer:
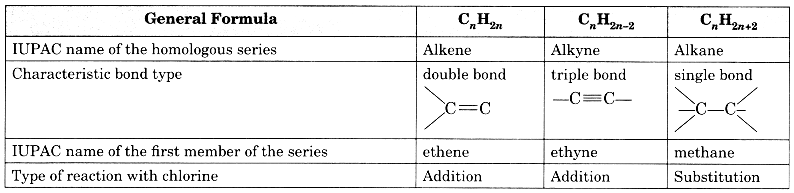
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Long Answer Type
Question 1.
Write the names of the following compounds:(a) Pentanoic acid (c) Heptanal (e) Methyl ethanoate
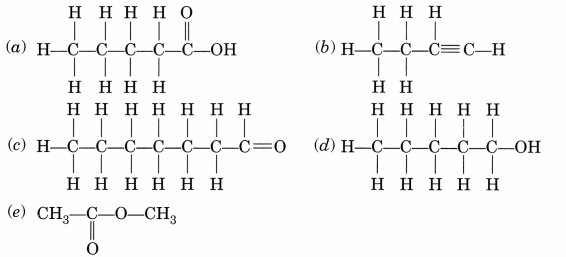
Answer:
(a) Pentanoic acid
(b) But-l-yne or Butyne
(c) Heptanal
(d) Pentanol
(e) Methyl ethanoate
Question 2.
(а) What are hydrocarbons? Give examples.
(b) Give the structural differences between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons with two examples
(c) What is a functional group? Give examples of four different functional groups. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
(a) Hydrocarbons are compounds of carbon and hydrogen. For example, ethane, ethene, benzene, etc.
(b) Saturated compounds are saturated by means of number of bonds or they contains only single bonds. For example,
CH3—CH3 (ethane), CH3CH2CH3 (propane)
Unsaturated hydrocarbon contains multiple bonds (C=C or C≡C)
For example, CH≡CH (ethyne) and CH2=CH2 (ethene).
(c) Functional group is an atom or group of atoms which imparts certain characteristic properties to the organic compound.
Question 3.
(a) Distinguish between esterification and saponification reactions of organic compounds.
(b) With a labelled diagram describe an activity to show the formation of an ester.
Answer:
(a) Esterification:
When carboxylic acid reacts with alcohol in the presence of a little concentrated sulphuric acid to form ester, the reaction is called esterification.
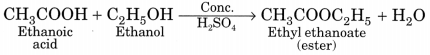
Saponification:
When an ester is heated with sodium hydroxide solution then the esters get hydrolysed to form alcohol and sodium salt of carboxylic acid. This alkaline hydrolysis of esters is known as saponification as it is used in the preparation of soap.

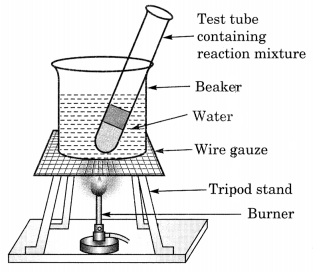
(b) Activity to show the formation of an ester:
- 1 ml ethanol and 1 mL glacial acetic acid along with a few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid are taken in a test tube.
- The mixture is allowed to warm in a water-bath for at least five minutes.
- The hot mixture of the test tube is poured into a beaker containing 20-50 ml of water.
- A sweet smelling substance called ester is formed.
Question 4.
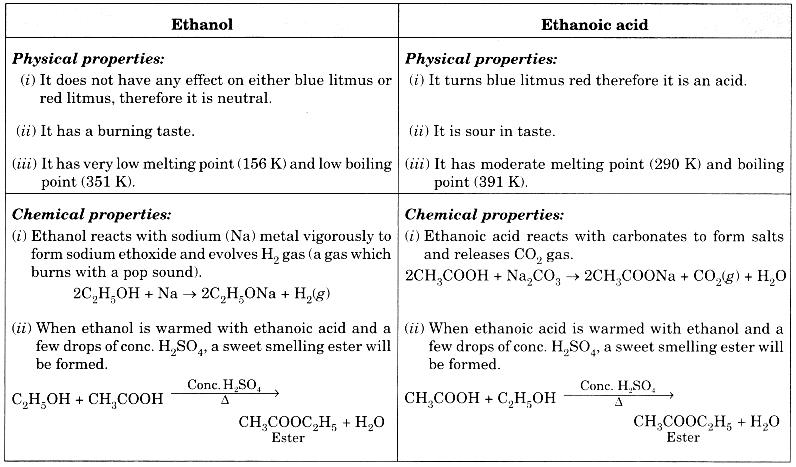
List in tabular form three physical and two chemical properties on the basis of which ethanol and ethanoic acid can be differentiated. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
Question 5.
Give one example each of:
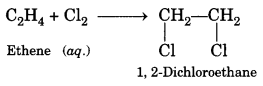
1. Cracking
2. Hydrogenation
3. Dehydration
4. Substitution reaction
5. Addition reaction.
Answer:
1. Cracking
![]()
2. Hydrogenation
![]()
3. Dehydration
![]()
4. Substitution reaction
![]()
5. Addition reaction
Carbon and its Compounds HOTS Questions With Answers
Question 1.
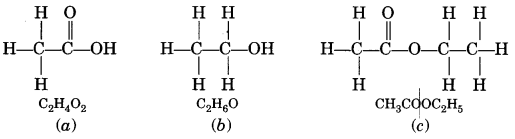
A compound X is formed by the reaction of a carboxylic acid C2H4O2 and an alcohol in presence of a few drops of H2SO4. The alcohol on oxidation with alkaline KMnO4 followed by acidification gives the same carboxylic acid as used in this reaction. Give the names and structures of (a) carboxylic acid, (b) alcohol and (c) the compound X. Also write the reaction. (NCERT Exemplar)
Answer:
The available information suggests that the alcohol which gives the same carboxylic acid upon oxidation has two carbon atoms. It is therefore ethanol (C2H5OH). The structures of the different compounds are:
Question 2.
Carbon, Group (14) element in the Periodic Table, is known to form compounds with many elements.
Write an example of a compound formed with
(a) chlorine (Group 17 of Periodic Table)
(b) oxygen (Group 16 of Periodic Table) (NCERT Exemplar)
Answer:
(a) Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)
(b) Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Question 3.
A salt X is formed and a gas is evolved when ethanoic acid reacts with sodium hydrogen carbonate. Name the salt X and the gas evolved. Describe an activity and draw the diagram of the apparatus to prove that the evolved gas is the one which you have named. Also, write chemical equation of the reaction involved. (NCERT Exemplar)
Answer:
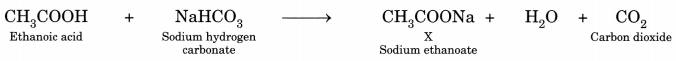
X is sodium ethanoate. Gas evolved is carbon dioxide (CO2).
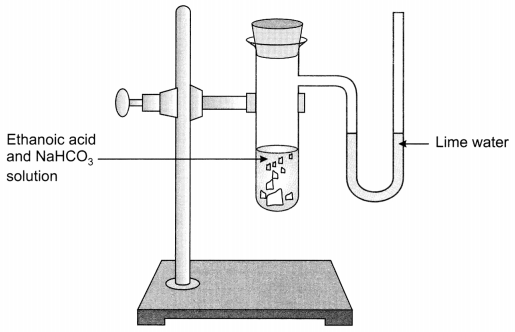
Activity:
- Take sodium hydrogen carbonate in a test tube and add 2 ml ethanoic acid in it.
- Carbon dioxide gas is evolved with brisk effervescence.
- Pass the gas through lime water, it will turn milky. This shows that the gas evolved is carbon dioxide (CO2).
Question 4.
A compound C (molecular formula, C2H4O2) reacts with Na metal to form a compound R and evolves a gas which bums with a pop up sound. Compound C on treatment with an alcohol A in presence of an acid forms a sweet smelling compound S (molecular formula, C3H6O2). On addition of NaOH to C, it also gives R and water. S on treatment with NaOH solution gives back R and A.
Identify C, R, A, S and write down the reactions involved. (NCERT Exemplar)
Answer:
C – Ethanoic acid
R – Sodium salt of ethanoic acid (sodium acetate) and gas evolved is hydrogen
A – Methanol
S – Ester (Methyl acetate)
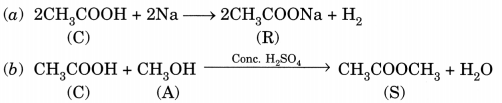
Question 5.
Look at figure given on the next page and answer the following questions:
(a) What change would you observe in calcium hydroxide solution taken in test tube B?
(b) Write the reaction involved in test tubes A and B respectively.
(c) If ethanol is given instead of ethanoic acid, would you expect the same change?
(d) How can a solution of lime water be prepared in the laboratory? (NCERT Exemplar)
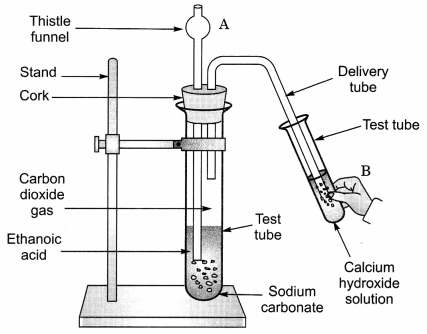
Answer:
(a) It will become milky.
(b) In test tube A, ethanoic acid react with sodium carbonate to form sodium ethanoate along with carbon dioxide. The gas is evolved accompanied by brisk effervescence.
CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → CH3COONa + CO2 + H2O
In test tube B, calcium hydroxide reacts with carbon dioxide to form a milky solution of calcium carbonate.
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
(c) No, it would be different. No chemical reaction is possible between ethanol and sodium carbonate.
(d) Lime water is prepared by keeping a suspension of calcium hydroxide overnight in a beaker. The solution is decanted and is transferred to another beaker. It contains traces of calcium hydroxide and is called lime water.
Question 6.
An organic compound A on heating with concentrated H2SO4 forms a compound B which on addition of one mole of hydrogen in presence of Ni forms a compound C. One mole of compound C on combustion forms two moles of CO2 and 3 moles of H2O. Identify the compounds A, B and C and write the chemical equations of the reactions involved. (NCERT Exemplar)
Answer:
Since compound C gives 2 moles of CO2 and 3 moles of H2O, it shows that it has the molecular formula C2H6 (ethane). C is obtained by the addition of one mole of hydrogen to compound B, so the molecular formula of B should be C2H4 (ethene). Compound B is obtained by heating compound A with concentrated H2SO4 which shows it to be an alcohol. So compound A could be C2H5OH (Ethanol).
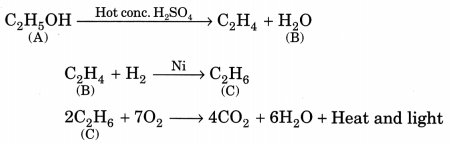
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Value Based Questions
Question 1.
Ethanol is one of the most important industrial chemicals. It is used in medicine, to synthesise many important compounds and as an excellent solvent.
However, inspite of its benefits it causes many social problems. If a person drinks alcohol regularly, he becomes an alcoholic. Alcohol is non-toxic but it produces physiological effects disturbing brain activity. These persons are also a threat to the lives of others.
(a) Give three reasons in favour and three reasons against ‘alcohol-free world’.
(b) ‘Alcohol drinking should not be portrayed on media’. Give valid reasons to justify.
(c) As a student what initiative would you take in the concern of “We should condemn drinking alcohol”,
Answer:
(a) In favour of‘Alcohol-free world’:
- Alcohol drinking lowers inhibitions which leads to increased violence and crime in the society.
- A liver disease ‘cirrhosis’ caused by alcohol can lead to death.
- Drunken driving leads to increased road accidents.
Against ‘Alcohol-free world’:
- Alcohol is used for making some medicines like cough syrups, tincture iodine, some tonics, etc.
- Mixed with petrol, it is now being used as a fuel for light vehicles.
- It is used for making antifreeze material for cooling engines of vehicles.
(b) ‘Alcohol drinking should not be portrayed on media’ because young people and children are greatly influenced by the media.
(c) Initiatives taken by a student to create awareness about drinking alcohol could be:
- By writing slogan
- Through debates
- By writing articles
- By role plays/skits
Question 2.
Intake of small quantity of methanol can be lethal. Comment. (NCERT Exemplar)
Answer:
Methanol is oxidised to methanal in the liver. Methanal reacts with the component of the cells. It causes the protoplasm to coagulate. It also affect the optic nerve, due to which it causes blindness.