Find free online Chemistry Topics covering a broad range of concepts from research institutes around the world.
Arrhenius Equation – The Effect of Temperature on Reaction Rate
Generally, the rate of a reaction increase with increasing temperature. However, there are very few exceptions. The magnitude of this increase in rate is different for different reactions. As a rough rule, for many reactions near room temperature, reaction rate tends to double when the temperature is increased by 10°C.
A large number of reactions are known which do not take place at room temperature but occur readily at higher temperatures. Example: Reaction between H2 and O2 to form H2O takes place only when an electric spark is passed.
Arrhenius suggested that the rates of most reactions vary with temperature in such a way that the rate constant is directly proportional to e-(Ea/RT) and he proposed a relation between the rate constant and temperature.
k = Ae-(Ea/RT) …………. (1)
Where A the frequency factor,
R the gas constant,
Ea the activation energy of the reaction and,
T the absolute temperature (in K)
The frequency factor (A) is related to the frequency of collisions (number of collisions per second) between the reactant molecules. The factor A does not vary significantly with temperature and hence it may be taken as a constant.
Ea is the activation energy of the reaction, which Arrhenius considered as the minimum energy that a molecule must have to posses to react.
Taking logarithm on both side of the equation (1)
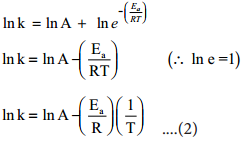
y = c + mx
The above equation is of the form of a straight line y = mx + c.
A plot of ln k Vs 1/T gives a straight line with a negative slope – \(\frac{\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{a}}}{\mathrm{R}}\) line with a negative slope –\(\frac{\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{a}}}{\mathrm{R}}\). If the rate constant for a reaction at two different temperatures is known, we can calculate the activation energy as follows.
At temperature T = T1; the rate constant k = k1
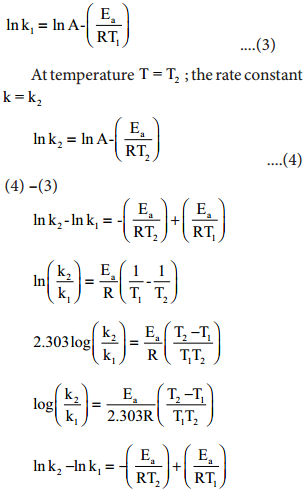
This equation can be used to caluculate Ea from rate constants K1 and k2 at temperatures
T1 and T2.
Example 1
The rate constant of a reaction at 400 and 200K are 0.04 and 0.02 s-1 respectively. Caluculate the value of activation energy.
Solution:
According to Arrhenius equation
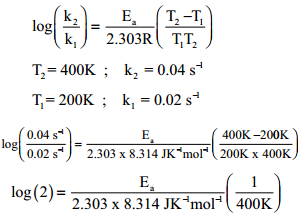
Ea = log(2) × 2.303 × 8.314 JK-1mol-1 × 400K
Ea = 2.305 J mol-1
Example 2
Rate constant k of a reaction varies with temperature T according to the following Arrhenius equation log k = log A – \(\frac{\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{a}}}{2.303 \mathrm{R}}\)(\(\frac{1}{T}\)) Where Ea is the activation energy. When a graph is plotted for log K Vs \(\frac{1}{T}\) a straight line with a slope of – 4000k is obtained. Caluculate the activation energy.
Solution:
log k = logA – \(\frac{\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{a}}}{2.303 \mathrm{R}}\)(\(\frac{1}{T}\))
y = c + mx
m = – \(\frac{\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{a}}}{2.303 \mathrm{R}}\)
Ea = – 2.303 R m
Ea = – 2.303 × 8.314 JK-1 mol-1 × (-4000K)
Ea = 76, 589 J mol-1
Ea = 76.589 kJ mol-1