Experts have designed these Class 10 AI Important Questions Chapter 2 AI Project Cycle Class 10 Important Questions and Answers NCERT Solutions Pdf for effective learning.
AI Project Cycle Class 10 Important Questions
Class 10 AI Project Cycle Important Questions
Important Questions of AI Project Cycle Class 10 – Class 10 AI Project Cycle Important Questions
Very Short Answer Type Questions (1 mark each)
Question 1.
At which stage of the AI Project Cycle, do we look at various parameters which affect the problem we wish to solve so that the picture becomes clearer?
Answer:
- Problem Scoping
- Explanation: In Problem Scoping you scope the problem by which, you set the goal for your Al project by stating the problem which you wish to solve with it.
- Under problem scoping, we look at various parameters which affect the problem we wish to solve so that the picture becomes clearer.
Question 2.
How many SDGs have been announced by the United Nations?
Answer:
There are 17 SDGs have been announced by the United Nations
Question 3.
By which term the people who face the stated problem and would be benefitted from the solution are described as
Answer:
Stakeholders
Question 4.
Which W of 4 Ws canvas problem helps in analysing the affected people directly or indirectly?
Answer:
Who
Explanation: Who-“Who” part helps us in comprehending and categorising that who are affected directly and indirectly by the problem and who are called the stakeholders.
![]()
Question 5.
Name the data which is available as soon as an event takes place.
Answer:
Real-time data is available as soon as the data event occurs.
Question 6.
What is the name of the data which is available freely for everyone to use and which is not restricted through copyrights, patents, control, etc.?
Answer:
The data which is available freely for everyone to use and is not restricted through copyrights, patents, control, etc., are known as Open Source Data.
Question 7.
The combination of structured and unstructured data is known as which data?
Answer:
The combination of structured and unstructured data is known as Semi-Structured data.
Question 8.
Name the second stage of the AI project cycle.
Answer:
Data Acquisition
Question 9.
Which approach is based on rules and data fed into the machine?
Answer:
Rule-based approach
Short Answer Type Questions (3 marks each)
Question 1.
Name any 2 methods for collecting data.
Answer:
Surveys and Interviews.
Explanation:
Question 2.
What stages of an AI project cycle are there?
Answer:
There are five different stages of the AI Project. Problem Scoping $\gg$ Data Acquisition > > Data Exploration > > Modelling > > Evaluation
Question 3.
What is problem Scoping?
Answer:
The process through which student designers “figure out” the problem they need to solve is called problem scoping. It is the procedure used to identify the issue.
![]()
Question 4.
Who are the stakeholders?
Answer:
Stakeholders are people who are either actively involved in the project or who have interests that the project’s results might influence. Project managers, project sponsors, executives, clients, or users are typically included in this group.
Question 5.
What do you mean by Problem Statement Template?
Answer:
Stakeholders can define and describe a problem by writing a summarised report called a problem statement. Its objective is to offer a comprehensive plan of action to address the issue and include suggestions for how those responsible can stop it from happening again in the future.
Question 6.
What is data Acquisition?
Answer:
The process of gathering correct and trustworthy data to work with is known as data acquisition. The second stage of the project cycle is data acquisition, and for successful decision-making, we must make sure the data is gathered from genuine and trustworthy sources.
Question 7.
What is the difference between Training Data & Testing Data?
Answer:
The datasets are divided into two groups in machine learning. The first subset, referred to as the training data, is a section of our actual dataset that is used to train a machine learning model. The second subset, referred to as testing data, Once your machine learning model is built, you need unseen data to test your model. This data is called testing data.
Training data use 80% of the whole data and testing data use 20%.
Question 8.
What is data exploration?
Answer:
Data exploration is the process of displaying and detecting unique patterns and trends in data using tools and procedures. Data visualisation and other complex statistical techniques can be used to do this.
Question 9.
What is data modelling?
Answer:
Data modelling is the process of developing a visual representation of an entire information system or certain components of it. for example, the development, training, and application of machine learning algorithms that simulate logical decisionmaking based on accessible facts are known as AI modelling.
![]()
Question 10.
What are the types of AI Modelling?
Answer:
AI Models are classified into two types –
(a) Learning Based
(b) Rule Based
Question 11.
What is Rule-Based Approach?
Answer:
When the developer sets’ the rules. The machine executes its duty in accordance with the rules or instructions specified by the developer.
A rule-based Al system is one that aims to develop AI systems by using a model that is exclusively based on predetermined rules.
Question 12.
What is Learning Based Approach?
Answer:
AI modelling where the computer learns on its own. The Al model is trained on the data provided to it under the learning based technique, and after that, it is able to create a model that is flexible to the change in data.
Long Answer Type Questions (6 marks each)
Question 1.
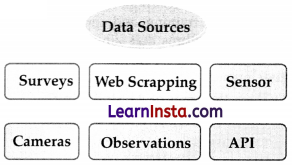
What are the various ways to collect data?
Answer:
Various ways to collect the data is –
(a) Surveys
(b) Web Scraping
(c) Sensors
(d) Cameras
(e) Observations
(f) Application Program Interface (API)
Question 2.
What is 4 Ws Problem Canvas?
Answer:
Who, What, Where, and Why are, the 4 Ws of problem scoping. These Ws aid in more accurate and effective problem identification and comprehension.
(a) who: who is facing for problem who are the stakeholders of problem.
(b) what: what is refer to a asking question.
(c) where: where is refer to asking about the place where the person was going.
(d) why: why is refer to asking about the person like why are you asking questions.
Question 3.
What are the different types of Learning based approaches?
Answer:
The learning-based approach can be divided into three types-
(a) Supervised Learning: In order for a computer to learn from data, it must have external supervision. This is known as supervised learning. We use the labelled dataset to train the supervised learning models. Supervised machine learning is a method for addressing two major issues: regression and classification.
(b) Unsupervised Learning: This term refers to a sort of machine learning in which the machine can learn from the data on its own without any external supervision. The unlabelled dataset can be used to train the unsupervised models. These are employed in order to address the Association and Clustering issues.
(c) Reinforcement Learning: Reinforcement learning is a learning process where an agent interacts with its environment by taking actions and learns through feedback. The agent receives feedback in the form of rewards; for example, he receives a positive reward for each good activity and a negative reward for each bad action. The agent is not under any oversight. Reinforcement learning makes use of the Q-Learning algorithm.
![]()
Question 4.
Who many types of Supervised Learning models in AI?
Answer:
There are two types of Supervised Learning models
(a) Classification: When the data is labelled-based categorised. For instance, under the grading system, students are categorised based on the grades they receive in relation to their exam marks.
(b) Regression: Such models work on continuous data. For example, if you wish to predict your next salary, then you would put in the data of your previous salary, any increments, etc., and would train the model.
Question 5.
How many types of Unsupervised Learning model in AI?
Answer:
There are two type of Unsupervised learning models in Al
(a) Clustering: Refers to the unsupervised learning technique that can cluster the unknown data according to patterns or trends found in it. The developer may already be aware of the patterns noticed, or it may even generate some original patterns as a result.
(b) Dimensionality Reduction: If you have a large number of features, it could be beneficial to minimise them using an unsupervised step before moving on to supervised steps. Numerous unsupervised learning techniques include a transform technique that can be used to lessen the dimensionality.
Case Based Subjective Questions :
I. Read the following text and answer the following questions based on the same:
In recent years, there has been increasing concern about the impacts of climate change and other environmental issues on global ecosystems, economies, and societies. As we delve into the complexities of addressing these challenges, it’s essential to thoroughly examine the various dimensions and implications involved.
(A) Create ‘What’ canvas of 4 Ws problem.
(B) Create ‘Why’ canvas of 4 Ws problem.
(C) Create ‘Who’ canvas of 4 Ws problem.
(D) Create ‘Where’ canvas of 4 Ws problem.
Answer:
What:
(A) What specific environmental issues or aspects. of climate change are most pressing?
Identifying the key environmental challenges such as rising temperatures, extreme weather events, loss of biodiversity, deforestation, ocean acidification, and pollution.
What are the primary causes and drivers behind these environmental issues?
Understanding the root causes including greenhouse gas emissions from human activities, deforestation, industrialisation, agricultural practices, and unsustainable consumption patterns.
![]()
Why:
(B) Why is it important to address these environmental , challenges urgently?
Exploring the urgency due to the severe impacts on ecosystems, biodiversity loss, threats to human health, economic instability, social inequality, and risks to future generations.
Why should individuals, communities, governments, and businesses prioritise efforts to mitigate climate change and environmental degradation?
Understanding the interconnectedness of environmental health with economic prosperity, public health, social justice, and global stability, as well as the ethical responsibility to preserve the planet’s resources.
Who:
(C) Who are the key stakeholders involved in addressing climate change and environmental issues?
Identifying stakeholders such as governments, policymakers, scientists, NGOs, businesses, communities, indigenous groups, and individuals, each with unique roles and responsibilities.
Who are the most vulnerable populations and ecosystems affected by climate change and environmental degradation?
Highlighting vulnerable communities including low-income groups, indigenous peoples, coastal regions, small island nations, arctic ecosystems, and wildlife species, disproportionately impacted by environmental changes.
When:
(D) When should action be taken to mitigate the impacts of climate change and environmental,degradation?
Determining the urgency for immediate action considering the accelerating pace of environmental degradation and the limited window to mitigate irreversible consequences.
When can we expect to see tangible progress in addressing these environmental challenges?
Setting timelines and milestones for achieving goals such as reducing emissions, transitioning to renewable energy, conserving biodiversity, and promoting sustainable development, while recognising the ongoing nature of environmental stewardship.
By addressing the “what,” “why,” “who,” and “when” aspects of climate change and environmental issues within this 4 W canvas, we can develop a comprehensive understanding of the complexities and implications involved, guiding efforts towards effective solutions and sustainable practices.