Mindful Eating: A Path to a Healthy Body Class 6 Extra Questions and Answers Science Chapter 3
Mindful Eating: A Path to a Healthy Body Class 6 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Do all meals consist of the same food items?
Answer:
No, all meals do not have the same food items.
Question 2.
Why should a meal have different food items?
Answer:
A meal should have different food items because our body needs different kinds of nutrients for proper functioning.
Question 3.
Do all foods contain all the reQuestion uired nutrients?
Answer:
No, all foods do not contain all the nutrients required by our body.
Question 4.
Name two main types of carbohydrates found in our food.
Answer:
- Starch
- Sugar .
Question 5.
What are carbohydrates?
Answer:
A component of food which acts as primary source of energy in our body is called carbohydrate.
Question 6.
What happens when two or mote drops of iodine solution fall on starch substanoe?
Answer:
The colour of the substance becomes blue- black.
Question 7.
If any food item gives blue-black colour with iodine then which nutrient is present in the food?
Answer:
Starch.
Question 8.
Name two substances which provide carbohydrates.
Answer:
- Potato
- Rice/wheat/maize/sugar
Question 9.
Name the food nutrient indicated by an oily patch on paper.
Answer:
An oily patch on paper shows the presence of fat.
Question 10.
Name two energy-providing nutrients.
Answer:
- Carbohydrates
- Fats
Question 11.
Name a nutrient which helps in repairing the damaged body cells.
Answer:
Proteins.
Question 12.
Name two nutrients which protect the body from diseases.
Answer:
- Vitamins
- Minerals
Question 13.
Name two plant food items which provide proteins.
Answer:
- Dal (pulses)
- Soya bean
![]()
Question 14.
Name two sources of proteins provided by animals.
Answer:
- Milk
- Eggs
Question 15.
Which type of food is called body-building food?
Answer:
The food containing proteins is called body-building food.
Question 16.
Name two food items which provide fats.
Answer:
- Oils
- Ghee
Question 17.
Name various types of vitamins.
Answer:
Various types of vitamins are:
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin B1
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin D
Question 18.
Name the chemicals reQuestion uired to test proteins in a food sample.
Answer:
Copper sulphate solution and caustic soda solution.
Question 19.
Name two sources of Vitamin A.
Answer:
- Carrot
- Milk
Question 20.
Write two sources of Vitamin B1
Answer:
- Paneer
- Flax seeds
Question 21.
Write two sources of Vitamin C.
Answer:
- Orange/lime
- Amla
Question 22.
Write two sources of Vitamin D.
Answer:
- Fish
- Butter
Question 23.
What is roughage?
Answer:
The food containing plant fibres which are also known as dietaiy fibres is called roughage.
Question 24.
What is the main function of roughage?
Answer:
The main function of roughage is to help our body get rid of undigested food.
![]()
Question 25.
Name some food items which provide roughage.
Answer:
Wholegrains, fresh fruits and vegetables are the main sources of roughage.
Question 26.
Which vitamin can be prepared by our body in presence of sunlight?
Answer:
Vitamin D.
Question 27.
Which mineral help in building bones and teeth?
Answer:
Calcium.
Question 28.
Name the mineral found in Blood.
Answer:
Iron.
Question 29.
Which disease occurs due to lack of Iron?
Answer:
Anaemia.
Question 30.
Which vitamin gets destroyed on heating?
Answer:
Vitamin C.
Question 31.
What is another name of millets?
Answer:
Nutricereals
Mindful Eating: A Path to a Healthy Body Class 6 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are nutrients? Name major nutrients.
Answer:
The components of food which are needed by our body for growth and development are called nutrients. The major nutrients are:
- Carbohydrates
- Fats
- Proteins
- Vitamins
- Minerals
Question 2.
What are the junctions of carbohydrates?
Answer:
They complete the energy requirements of the body so they are called energy-providing foods.
Question 3.
Write test for detecting the presence of starch
Answer:
Take a piece of the food item. Put 2-3 drops of dilute iodine solution on it. If the colour of the food item becomes blue-black, then it indicates the presence of starch in the food item.
- Food + Iodine → Blue-black colour (starch present)
- Food + Iodine → No blue-black colour (no starch present)
Question 4.
What are the functions of proteins?
Answer:
Proteins are the most important nutrient. They are called body-building foods. They help in the growth and repair of damaged cells and tissues of the body. They make our nails, hair and muscles.
![]()
Question 5.
How can you test presence of proteins in a given food item?
Answer:
Take a small quantity of the food item. If the sample is solid, grind it. Put some part of this in a clean test tube, add 10 drops, of water to it and shake the test tube. Now, with the help of a dropper, add 2 drops of solution of copper sulphate and 10 drops of solution of caustic soda to the test tube. Shake well and place the test tube in test tube stand for a few minutes.
Observe colour of the contents of test tube. If colour of the contents turns violet, the food item contains protein.
Note: Copper sulphate and caustic soda solutions are harmful. Handle them with care.
Food + Water + Copper sulphate + Caustic soda → Violet colour → Protein is present.
Question 6.
What are fats? Name some fat-containing substances.
Answer:
The energy rich sources of food are called fats. They provide energy to the body. All types of nuts, mustard seeds, milk and butter are the major sources of fat.
Question 7.
Write test for detecting presence of fat.
Answer:
Take small quantity of the food item (groundnut). Crush it and rub on a piece of white paper. Observe carefully, you will find that the piece of white paper shows an oily patch. Presence of this patch indicates that the food item contains fat.
Question 8.
What are vitamins? Give a brief description of various kinds of vitamins.
Answer:
Vitamins are protective nutrients with no energy value. They help in proper body-functioning and are reQuestion uired by the body in very small Question uantities. Various kinds of vitamins are—Vitamin A, Vitamin B1, Vitamin C and Vitamin D.
Question 9.
People who eat sea-food do not suffer from Goitre. Explain.
Answer:
It is so because sea-food is a rich source of Iodine and Goitre is a deficiency disease caused due to lack of Iodine.
Question 10.
Excess intake of fats is harmful for the body because it causes obesity. Would it be harmful for the body to take too much of proteins or vitamins in the diet?
Answer:
Yes, excess intake of proteins and vitamins in the diet is harmful and may lead to other diseases.
Question 11.
Name the vitamin found in these food items.
(i) Papaya, Carrot, Fish oil, Milk
(ii) Orange, Guava, Lemon, Tomato, Chilli
(iii) Fishes, Butter, Egg, Milk, Liver
(iv) Legumes, Nuts, Whole grains, Milk products
Answer:
(i) Vitajhin ‘A’
(ii) Vitamin ‘C’
(iii) Vitamin D’
(iv) Vitamin B1
Question 12.
Write the name of minerals found in following items.
(i) Fish, Seaweed, Salt
(ii) Green leafy vegetables, Beetroot, Pomegranate
(iii) Milk, Cheese, Egg
Answer:
(i) Iodine
(ii) Iron
(iii) Calcium
![]()
Question 13.
What are the functions of minerals?
Answer:
Minerals are protective nutrients occurring naturally and are needed by our body in small amount. Minerals are essential for proper growth of the body and to maintain good health. They do not provide energy. Milk, salt, eggs and green leafy vegetables are the main sources of minerals.
Question 14.
Write the functions of water in our body.
Answer:
Water helps our body to absorb nutrients from the food. It also helps in removing the waste from the body in the form of urine and sweat. We get water from various types of liquids, fruits and vegetables.
Question 15.
What is obesity?
Answer:
When a person eats too much fat-containing foods, then the fat gets deposited in his body and he may end up suffering from a condition called obesity.
Question 16.
What are deficiency diseases?
Answer:
When a person eats such a food continuously for a long time which may not contain a particular nutrient, then this condition is called deficiency of that nutrient. Deficiency of one or more nutrients can cause diseases or disorders in our body. Such type of diseases are known as deficiency diseases.
Question 17.
Write the name of disease caused by lack of following:
(i) Vitamin D
(ii) Iron
Answer:
(i) Rickets
(ii) Anaemia
Question 18.
Why food should not be overcooked?
Answer:
If we cook food at high temperature or we overcook it, essential nutrients present in food get destroyed.
Question 19.
What are junk foods?
Answer:
Some foods have high calories due to high sugar and fat content. Moreover, they contain very low amounts of proteins, minerals, vitamins and dietary fibres. These foods are called junk foods. These foods include potato wafers, candy bars and carbonated drinks.
Question 20.
What do you understand by the term food miles?
Answer:
The entire distance travelled by a bag of wheat or any other food item, from the producer to the consumer, is known as its food miles.
Mindful Eating: A Path to a Healthy Body Class 6 Long Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
List various types of nutrients and write the functions of each
Answer:
The various types of nutrients are:
- Carbohydrates: They are mainly energy-providing nutrients.
- Fats: They provide energy for the body. They give much more energy than carbohydrates if consumed in same amount.
- Proteins: They are called body-building foods. Proteins help in the formation and repairing of body parts. Skin, hair, muscles, enzymes are made up of proteins.
- Vitamins: Vitamins help in protecting our body against diseases. They also protect eyes, bones, teeth and gums.
- Minerals: Minerals are essential for proper growth of body and to maintain good health.
Question 2.
What is a balanced diet? Write the components of balanced diet.
Answer:
A diet which provides the right proportion of all the nutrients that our body needs along with roughage and water is called balanced diet. The various components of balanced diet are carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, roughage and water.
Question 3.
Prepare a chart to show various vitamins and minerals and the disorders caused by their deficiency.
Answer:
| Vitamin/mineral | Deficiencydisease/disorder | Symptoms |
| Vitamin A | Loss of vision | Poor vision, loss of vision in darkness, sometimes complete loss of vision. |
| Vitamin B1 | Beriberi | Swelling, tingling or burning sensation in feet and hands. |
| Vitamin C | Scurvy (See figure below) | Bleeding gums, wounds take longer time to heal. |
| Vitamin D | Rickets (See figure below) | Bones become soft and bend easily. |
| Calcium | Bone and tooth decay | Weak bones, tooth decay. |
| Iodine | Goitre | Glands in the neck appear swollen, mental disability in children. |
| Iron | Anaemia | Weakness |
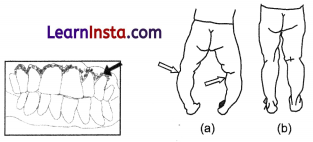
Arrow-head indicates swollen and spongy gums and loose teeth
(a) Infantile rickets indicated by arrow head before treatment
(b) two years and later after vitamin • D therapy.
Question 4.
What are the different functions of following vitamins and minerals?
(i) Vitamin A
(ii) Vitamin C
(iii) Vitamin D
(iv) Calcium
(v) Iodine
Answer:
(i) Vitamin A : It keeps our eyes and skin healthy.
(ii) Vitamin C : It helps body to fight against diseases.
(iii) Vitamin D : It helps our body to use calcium for bones and teeth.
(iv) Calcium: It keeps our bones and teeth healthy.
(v) Iodine: It helps to perform physical and mental activities.
![]()
Question 5.
With the help of a flow-chart explain how food from the farm reaches to our plates.
Answer:
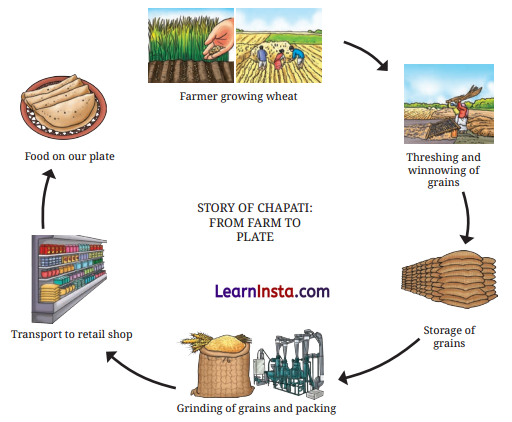
Mindful Eating: A Path to a Healthy Body Class 6 Skill-Based Questions
Question 1.
Draw a diagram to show some sources of carbohydrates.
Answer:
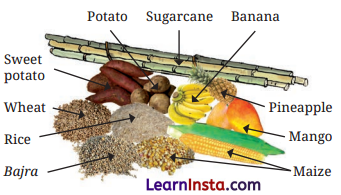
Question 2.
Observe the given figure and answer the following Questions:

(i) Which nutrient is mainly provided by these items?
(ii) Name the sources of these food items.
Answer:
(i) They provide mainly fats.
(ii) The sources of these food items are plants.
Question 3.
Observe the given figure and answer the following Questions:
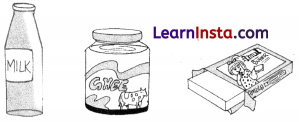
(i) Which nutrient is mainly provided by these items?
(ii) Name the sources of these food items.
Answer:
(i) They provide mainly fats.
(ii) The sources of these food items are animals.
Question 4.
Draw diagrams for three food items of plants and animals which are rich sources of proteins.
Answer:
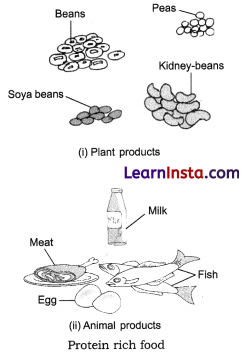
Note: You may draw any three items from (i) and (ii)
Question 5.
Observe the given diagram of food items and answer the following Questions:

(i) What should be the caption of the diagram?
(ii) They are rich sources of which Vitamin?
Answer:
(i) Caption should be “Some Sources of Vitamin C”.
(ii) They are rich sources of Vitamin C.
Question 6.
Observe the diagrams (a) and (b), and answer the following Question uestions:

(i) Provide appropriate captions for (a) and (b).
(ii) Write roles of the minerals they provide to us.
Answer:
(i) Captions for these diagrams may be:
(a) Some Plant Sources of Iron, and
(b) Some Animal Sources of Calcium.
(ii) Iron: Deficiency of iron causes hindrance in the formation of blood (red blood cells). This leads to a deficiency disease called Anaemia that causes weakness. Calcium: Calcium is an essential component of bone and teeth. Deficiency of calcium causes weak bones and teeth.
![]()
Mindful Eating: A Path to a Healthy Body Class 6 Case-Based Questions
Question 1.
We all know that each eatable dish is usually made up of one or more ingredients, which we get from plants or animals. These ingredients contain some components that are must for our body. These components are termed as nutrients. The major nutrients in our food are proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, fats and minerals. In addition to them, food contains dietary fibres and water too which are eQuestion ually needed by our body. There are many types of carbohydrates. The main carbohydrates found in our food are starch and sugars.
With the help of some simple methods we can test whether cooked food or a raw ingredient contains one or more of these nutrients. For conducting these tests, we will need solutions of iodine, copper sulphate and caustic soda. We can try these tests on cooked food items as well as raw materials.
I. Name the two carbohydrates mainly present in our food.
II. Write the names of three reagents reQuestion uired to test the presence of nutrients in food.
III. What are nutrients? Give one example.
IV. Name all the components present in our food.
Answer:
I. Starch and Sugars.
II. (a) Caustic soda solution
(b) Copper sulphate solution
(c) Iodine solution
III. Our food is made up of one or more ingredients. These ingredients contain components that are needed by our body. These components are called nutrients. For example: proteins.
IV. The major nutrients in our food are carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins and minerals. Food also contains dietary fibres and water.
Question 2.
The tests for presence of carbohydrates, proteins and fats are simpler to do as compared to the tests for other nutrients. Let us begin by testing different food items to see if they contain carbohydrates. Take a small Question quantity v of a food item or a raw ingredient. Put 2-3 drops of dilute Iodine solution on it. Observe if there is any change in the colour of the food item. A blue-black colour indicates that it contains starch. To test the presence of proteins in food we need to take a small Question uantity of a food item for testing. If the food you want to test is a solid, you first need to make a paste or powder of it. Grind or mash a small Question uantity of the food item. Put some of this in a clean test tube, add 10 drops of water to it and shake the test tube. Now, using a dropper, add 2 drops of solution of copper sulphate and 10 drops of solution of caustic soda to the test tube. Shake well and let the test tube stand for a few minutes. You will see that the contents of the test tube will turn violet. A violet colour indicates presence of proteins in the food item.
For fats, take a small Question uantity of a food item. Wrap it in a piece of paper and crush it. Take care that the paper does not tear. Now, straighten the paper and observe it carefully. If you see an oily patch on paper, then it shows that the food item contains fat. Absence of oily patch shows that the food item does not contain any fat. The food items may sometimes contain a little water. Therefore, after you have rubbed an item on paper, let the paper dry for a while. If there were any water that may have come from food, it would dry up after some time. .
I. Which colour indicates the presence of proteins in the food items?
II. What we use to test the presence of starch?
III. How can we test the presence of fats in food items?
IV. Solutions of copper sulphate and caustic soda are used to test the presence of which nutrient?
Answer:
I. Violet.
II. We put drops of dilute Iodine solution to test the presence of starch.
III. Wrap the food item in a piece of paper and crush it. Next, straighten the paper and observe it carefully. If you see an oily patch on paper, then it shows that the food item contains fat.
IV. Both are used to detect the presence of proteins in food items.
![]()
Question 3.
Foods containing fats and carbohydrates are also called ‘energy-giving foods’. Proteins are needed for the growth and repair of our body. Foods rich in proteins are often called ‘body-building foods’. Vitamins help in protecting our body against diseases. Vitamins are of different kinds. Our body needs all types of vitamins in small Quantities. Vitamin A keeps our skin and eyes healthy. Vitamin C helps our body to fight against diseases. Vitamin D helps our body to use calcium for bones and teeth.
However, in a given raw material, one particular nutrient may be present in much larger Quantity than in others. For example, rice has more carbohydrates than other nutrients. Thus, we say that rice is a “carbohydrate rich” food.
Besides these nutrients, our body needs dietary fibres and water. Dietary fibres are also known as roughage. Roughage is mainly provided by plant products in our foods. Whole grains, pulses, potatoes, fresh fruits and vegetables are main sources of roughage.
I. Which vitamin keeps our skin and eyes healthy?
II. Which foods are known as “energy-giving foods”?
III. Name the nutrient needed for the growth and repair of the body?
IV. What is roughage?
Answer:
I. Vitamin A
II. Foods containing carbohydrates and fats
III. Proteins
IV. Dietary fibres are known as roughage. It is mainly provided by plant products in our foods. Whole grains, pulses, potatoes, fresh fruits and vegetables are sources of roughage.