Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 4 Basic Geometrical Ideas with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 6 Maths with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided Basic Geometrical Ideas Class 6 Maths MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
Students can also refer to NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 4 Basic Geometrical Ideas for better exam preparation and score more marks.
Basic Geometrical Ideas Class 6 MCQs Questions with Answers
Question 1.
How many points are enough to fix a line?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
Answer: (b)
Question 2.
Two intersecting lines intersect in
(a) 1 point
(b) 2 points
(c) 3 points
(d) 4 points
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 3.
How many lines can pass through one given point?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) Countless
Answer
Answer: (d)
Question 4.
How many lines can pass through two given points?
(a) Only one
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) Countless
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 5.
How many vertices are there in the following figure?
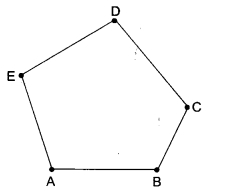
(a) 5
(b) 3
(c) 2
(d) 4
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 6.
How many sides are there in the following figure?
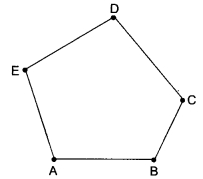
(a) 5
(b) 4
(c) 2
(d) 3
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 7.
How many diagonals are there in the follow-ing figure?
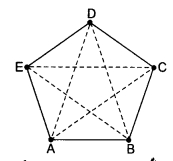
(a) 4
(b) 5
(c) 2
(d) 3
Answer
Answer: (b)
Question 8.
How many vertices are there in a triangle?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
Answer: (c)
Question 9.
How many sides are there in a triangle?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
Answer: (c)
Question 10.
How many angles are there in a triangle?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
Answer: (c)
Question 11.
How many vertices are there in a quadrilat¬eral?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
Answer: (d)
Question 12.
How many sides are there in a quadrilateral?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
Answer: (d)
Question 13.
How many angles are there in a quadrilateral?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
Answer: (d)
Question 14.
How many pairs of adjacent sides are there in a quadrilateral?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
Answer: (d)
Question 15.
How many pairs of opposite angles are there in a quadrilateral?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
Answer: (b)
Question 16.
How many pairs of opposite sides are there in a quadrilateral?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
Answer: (b)
Question 17.
How many pairs of adjacent angles are there in a quadrilateral?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
Answer: (d)
Question 18.
Which of the following statements is false?
(a) Two diameters of a circle will necessarily intersect.
(b) The centre of a circle is always in its interior.
(c) Every diameter of a circle is also a chord.
(d) Every chord of a circle is also a diameter.
Answer
Answer: (d)
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 4 Basic Geometrical Ideas with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding Basic Geometrical Ideas CBSE Class 6 Maths MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.