Class 6 Science Chapter 6 Notes Materials Around Us
→ Material: The matter from which something is or can be made is called material.
→ Classification: The method of arranging objects into groups is called classification.
→ Materials are grouped together on the basis of similarities and dissimilarities in their properties. For example, hard or soft, soluble or insoluble in water, lustrous or non-lustrous, transparent, translucent or opaque.
→ Appearance: The materials look different from each other. For example, Gold appears different from the Iron.
→ Lustrous Materials: Materials that are shiny, or have freshly cut surfaces are shiny are called lustrous materials and their shine is called lustre. Materials that have lustre are usually metals.
![]()
→ Non-lustrous materials: Those materials which do not have a shiny surface are called non- lustrous materials. For examples, paper, wood, rubber, jute, non-metals, etc.
→ Metal: It is a hard, shiny, solid material.
→ Non-metals: They are commonly soft and broken into pieces on being beaten. For example, carbon, sulphur, oxygen, etc.
→ Rough: An object having an uneven or irregular surface, not smooth or levelled or polished is said to be rough.
→ Hard: A material which is difficult to compress or scratch is said to be hard.
→ Soft: A material which can be compressed or scratched easily is called soft.
→ Materials can be grouped on the basis of whether they are opaque, transparent or translucent. This can be tested by looking through them.
→ Transparent: The materials through which things can be seen clearly and light can pass completely through them are said to be transparent.
→ Translucent: The materials through which objects can be seen but not clearly and light can pass partially through them are said to be translucent.
→ Opaque: The materials through which we are not able to see and light cannot pass through them are said to be opaque.
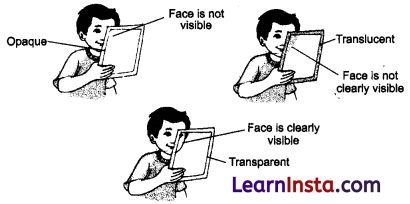
Looking through opaque, transparent and translucent material
→ Insoluble: Substances which do not mix with water or do not disappear in water even after stirring for a long time are called insoluble in water.
![]()
→ We can also group materials on the basis of whether they float or sink in water.
→ Mass: The amount or weight of substance is called mass. The mass gives the quantity of matter present in an object. The units to measure mass are gram (g), kilogram (kg), etc.
→ Weight: Weight is the amount of substance which is determined by weighing.
→ Volume: The space occupied by matter is its volume. The units to measure volume are litre (L), millilitre (mL), etc.
→ Matter: Anything that occupies space and has mass is called matter.
→ Classification : The method of arraning objects into groups is called classification.
→ Non-lustrous : These materials which have dull appearance are called nonlustrous.
![]()
→ Classify : Grouping.
→ Hard : Those materials which cannot be easily cut, bent or scratched, are called hard.
→ Opaque : Those materials through which was cannot see at all, are called opaque.
→ Explore : Travel through in order to learn about it.
→ Insoluble : The materials that do not dissolve in water are called insoluble.
→ Soft : Those materials which can be easily compressed, cut, bent, or scratched are called soft.
→ Identify : Who or what is
→ Mass : It is the amount of matter present in an object.
→ Translucent : The materials through which objects can be seen but not clearly are said to be translucent.
![]()
→ Record : To write down facts and events.
→ Matter : Anything that occupies space and has mass is called matter.
→ Volume : The measure of space occupied by a solid body is called its volume.
→ Objects are made from a large variety of materials. An object can be made up of a single material or a combination of different materials.
→ We can use different materials to make objects with similar functions.
→ The method of arranging objects into groups is called classification.
→ Materials possess different properties which determine their use.
→ Materials are grouped or classified based on their similarities or differences in their properties.
→ Materials can be grouped on appearance, such as lustrous or non-lustrous and based on the feel, such as hard or soft.
→ Materials are grouped as transparent, translucent or opaque depending on how much we can see through them.
→ Some materials are soluble in water while others remain insoluble.
→ Materials are grouped as heavier or lighter.
![]()
→ Grouping things based on their properties is very useful.
→ Anything that occupies space and has mass is called matter.
→ The space occupied by matter is its volume.
→ Mass quantifies the amount of matter present in an object.
→ Materials are types of matter used in the creation or making of objects.
→ Kilogram is the unit of mass in the International system of units (S.I.)
→ The S.I. unit for volume is cubic metre (m3).
Introduction
→ According to Rasaratnasamuchchaya, “The materials used to make the crucible are clay and iron.”
→ Observing Objects Around Us All things are made of some materials like paper, wood, cloth, glass, metal, plastic, clay and so on. An object can be made from different kinds of material. Any substance that is used to create an object is reffered to as material.
![]()
→ How To Group Materials : The method of arranging the objects into groups is called classification. We can classify materials based on certain properties. The objects with similar properties are put into one group. This kind of grouping helps us in many ways.
What Are The Different Properties Of Mateirals ?
1. Classification of Materials on the Basis of their Appearance: Some materials have a shiny appearance whereas other materials do not have a shiny appearance. So, on the basis of their appearance, all the materials are classified into two groups.
- Materials having lustre or shiny appearance.
- Materials having no lustre or dull appearance.
Materials often look different from each other. Freshly, cut wood, which is unpolished, has a distinct appearance, quite different from copper or aluminium. Materials that typically have shiny surfaces are said to have a lustrous appearance. Such materials with lustre are usually metals. Examples of metals include iron, copper, zinc, aluminium, gold etc. However, some metals may lose their lustre and start to look non-lustrous or due to the effect of air and moisture on them. As a result, we often notice the lustre only on their freshly cut surfaces.
Non-luminous materials are those that do not have a shiny surface. Some examples of nonlustrous materials are paper, wood, rubber, jute, chalks, sand etc. Not all the materials that shine are metals. Surfaces of some materials are made shiny by polishing or coating them with layer of plastic, wax or any other material which makes them look shiny. These materials may not be metals.
![]()
Which Materials are hard ?
Some materials are very hard whereas some others are soft. Those materials which cannot be easily compressed, cut, bent or scratched are called hard materials. Diamond is the hardest known materials. Diamond can cut glass.
Those materials which can be easily compressed, cut, bent or scratched, are called soft materials. Cotton is soft because it traps lot of air in it.
However, these properties are relative in nature. For example, rubber is harder than sponge but softer than iron.
→ Explore Materials through One can See or cannot See
The materials, through which things can be seen clearly are called transparent. Glass, water, air, cellophane paper etc. are some examples of transparent materials.
The materials through which we cannot see at all are called opaque materials. Wood cardboard and metals are examples of opaque materials.
The materials through which objects can be seen, but not clearly, are known as translucent. Butter paper and frosted glass are examples translucent materials.
→ What is Soluble in Water, What ¡s not?
Substances such as salt and sugar that are soluble in water are called soluble substances.
Substances such as sand and saw dust that do not mix with water even on stirring are called insoluble substances.
When a material dissolves in a liquid, it forms a solution. Salt dissolves in water and forms a salt solution liquids that dissolve in water are said to be miscible. Oils are not soluble in water.
They are immiscible in water. Petrol, kerosene, ground nut oil and coconut oil are immiscible in water.
Glass such as oxygen, carbondioxide and ammonia also dissolves in water easily. Aquatic animals and plants use oxygen dissolved in water to live.
→ Space and Volume
The space occupied by matter is its volume. The measure of the space occupied by a solid body is called its volume. Drinking water bottles of different sizes being sold in the market. 1L, 500mL, 200mL, etc. written as net quantity on the bottles. These indicate the volume of water in the bottles. The water in the first tumbler occupies less space, indicating that the volume of water in this tumbler is less than the water in the other tumbler. The space occupied by water represents
![]()
→ What is Matter ?
Any thing that occupies space and has mass is called matter. The mass gives the quantity of matter and the units to measure it are gram (g) and kilogram ( kg ). The space occupied by matter is the volume. The units to measure the volume are litre ( L ) and millilitre ( mL ).
Kilogram is the unit of mass in the international system of units (S.I.). Kilogram is abbreviated as kg . For example, we have mass of kilograms, it would be written as 9 kg and not as 9 kgs. Similarly, litre is abbreviated as capital L and millilitre as mL. For example, if you have 200 millilitres of water, it would be written as 200 mL . The S.I. unit for volume is cubic metre, abbreviated as m3. For example, if you have volume of 3 cubic metres, it would be written as 3m3. The unit 1m3=1000L.
