Students can easily access the best AI Class 10 Notes Chapter 1 Introduction to AI Class 10 Notes for better learning.
Class 10 Introduction to AI Notes
Foundational concepts of AI Class 10 Notes
What is Artificial Intelligence?
According to the father of Artificial Intelligence, John McCarthy, it is “The science and engineering of making intelligent machines, especially intelligent computer programs”.
Artificial Intelligence is a way of making a computer, a computer-controlled robot, or a software think intelligently, in a similar manner to intelligent humans think.
AI is accomplished by studying how the human brain thinks, and how humans learn, decide, and work while trying to solve a problem, and then using the outcomes of this study as a basis for developing intelligent software and systems.
Intelligence has been defined in many ways:
The capacity for logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving.
More generally, it can be described as the ability to perceive or infer information and to retain it as knowledge to be applied toward adaptive behaviours within an environment or context.
Goals of AI:
To Create Expert Systems-The systems which exhibit intelligent behaviour, learn, demonstrate, explain, and advise its users.
To Implement Human Intelligence in MachinesCreating systems that understand, think, learn, and behave like humans.
AI vs Automation:
Washing Machine : A fully automatic washing machine can work on its own, but it requires human intervention to select the parameters of washing and to do the necessary preparation for it to function correctly before each wash, which makes it an example of automation, not AI.
Air Conditioner : An air conditioner can be turned on and off remotely with the help of the internet but still needs a human touch.
![]()
What is Intelligence?
The ability of a system to calculate, reason, perceive relationships and analogies, learn from experience, store and retrieve information from memory, solve problems, comprehend complex ideas, use the natural language fluently, classify, generalise, and adapt to new situations.
Keynote:
Intelligence means ” ability to perceive information”
Types of Intelligence:
As described by Howard Gardner, an American developmental psychologist, Intelligence comes in multifold-
- Linguistic Intelligence: The ability to speak, recognise, and use mechanisms of phonology (speech sounds), syntax (grammar), and semantics (meaning).
- Musical Intelligence: The ability to create, communicate with, and understand meanings made of sound, understanding of pitch, and rhythm.
- Logical Mathematical Intelligence: The ability to use and understand relationships without action or objects. Understanding complex and abstract ideas.
- Spatial Intelligence: The ability to perceive visual or spatial information, change it, and re-create visual images without reference to the objects, construct 3 D images, and move and rotate them.
- Bodily-Kinesthetic Intelligence: The ability to use complete or part of the body to solve problems or fashion products, control fine and coarse motor skills, and manipulate objects.
- Intra Personal Intelligence: The ability to distinguish among one’s own feelings, intentions, and motivations.
- Interpersonal Intelligence: The ability to recognise and make distinctions among other people’s feelings, beliefs, and intentions.
- Naturalist: reading natural activity, nature and living things understanding We can say a machine or a system is artificially intelligent when it is equipped with at least one and at most all intelligence in it.
- Existential: study of why we live and why we die.
What is intelligence composed of?
- Intelligence is intangible. It is composed of:
- Reasoning
- Learning
- Problem-Solving
- Perception
- Linguistic Intelligence
Reasoning: It is the set of processes that enables us to provide the basis for judgment, making decisions, and predictions. There are broadly two types-
Inductive Reasoning: It conducts specific observations to make broad general statements.
Example: “Nita is a teacher. Nita is studious. Therefore all teachers are studious.”
Deductive Reasoning: It starts with a general statement and examines the possibilities to reach a specific, logical conclusion.
Example:”All women of age above 60 years are grandmothers. Shalini is 65 years. Therefore, Shalini is a grandmother.”
Learning: It is the activity of gaining knowledge or skill by studying, practicing, being taught, or experiencing something. Learning enhances the awareness of the subjects of the study.
The ability of learning is possessed by humans, some animals, and AI-enabled systems. Learning is categorised as-
- Auditory Learning: It is learning by listening and hearing. For example, students listen to recorded audio lectures.
- Episodic Learning: To learn by remembering sequences of events that one has witnessed or experienced. This is linear and orderly.
- Motor Learning: It is learning by the precise movement of muscles. For example, picking objects, writing, etc.
- Observational Learning: To learn by watching and imitating others. For example, the child tries to learn by mimicking her parent.
- Perceptual Learning: It is learning to recognise stimuli that one has seen before. For example, identifying and classifying objects and situations.
- Relational Learning: It involves learning to differentiate among various stimuli on the basis of relational properties, rather than absolute properties.
For example: add ‘little less’ salt at the time of cooking potatoes that came up salty last time, when cooked with adding say a tablespoon of salt. - Spatial Learning: It is learning through visual stimuli such as images, colors, maps, etc. For example, a person can create a roadmap in mind before actually following the road.
- Stimulus-Response Learning: It is learning to perform a particular behaviour when a certain stimulus is present. For example, a dog raises its ear on hearing a doorbell.
![]()
Problem Solving: It is the process in which one perceives and tries to arrive at a desired solution from a present situation by taking some path, which is blocked by known or unknown hurdles.
Problem-solving also’ includes decision-making, which is the process of selecting the best suitable alternative out of multiple alternatives to reach the desired goal are available.
Perception: It is the process of acquiring, interpreting, selecting, and organising sensory information.
Perception presumes to sense. In humans, perception is aided by sensory orgAnswer:In the domain of AI, the perception mechanism puts the data acquired by the sensors together in a meaningful manner.
Linguistic Intelligence: It is one’s ability to use, comprehend, speak, and write the verbal and written language. It is important in interpersonal communication.
Difference between Human and Machine:
- Humans perceive by patterns whereas machines perceive by a set of rules and data.
- Humans can figure out the complete object even if some part of it is missing or distorted; whereas the machines cannot do it correctly.

How does Machine Learning work?
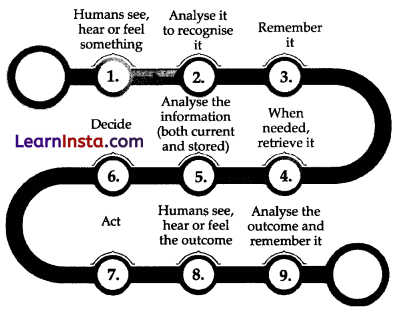
Machine learns just like human learns. Well, let’s quickly see How Humans Learn?
How do Humans learn?
To understand the human learning process, let us illustrate it through a simple sequence of activities involved.
A computer learns in a similar way. However, it needs a lot of information, to ensure that it recognises things accurately. Machines need to be trained to make decisions and act based on goals
How to Train Machines? Computers need a lot of information to ensure accurate recognition of things Let’s take an example, now think, how can a computer recognise a flame?
This could be using color, size, shape, origin, temperature, etc. Once it recognises the flame, it needs to be trained to make the decision to act, as in this case, whether it should touch the flame or not. This is based on the goals set for the computer.
For example, a computer sets the goal to extinguish the flame by touching or stamping. So, it will see a flame and act to touch it and extinguish it, whereas another way to avoid burning and damage is to see a flame as a danger and not touch it.

Now think, how will a computer differentiate between an actual flame and a photo of the flame?
A wrongly trained computer may try and extinguish the flame in the painting or touch a live flame again to get damaged. So, is it possible that they can discern based on temperature, movement, etc.?
![]()
Artificial Intelligence vs Machine Learning: The learning of both AI and ML is based on statistics and mathematics but still both are not the same thing.
| Artificial Intelligence | Machine Learning |
| It is the study of how to train computers so that computers can do things that at present humans can do better. | Machine Learning is the learning in which a machine can learn on its own without being explicitly programmed. |
| Perform tasks that require human intelligence. | Helps machines to learn certain things on their own. |
| The aim is to increase the chance of success and not accuracy. | The aim is to increase accuracy, but it does not care about success. |
| It works as a computer program that does smart work. | It is a simple concept machine that takes data and learns from data. |
| AI is decision making | ML allows systems to learn new things from data. |
| AI leads to intelligence or wisdom. | ML leads to knowledge. |
AI tries to make machines intelligent that can take accurate decisions, whereas ML tries to train machines to do certain tasks.
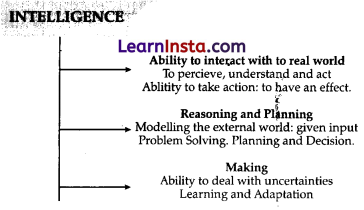
Decision making:
Decision-making refers to the cognitive process of selecting a course of action among several available alternatives. It involves evaluating different options, considering their potential consequences or outcomes, and choosing the most appropriate or desirable option based on certain criteria or goals.
The process of decision-making typically involves seven stages:
- Identification of the problem or decision to be made: Recognising the need to make a decision and clearly defining the issue or goal.
- Gathering information: Acquiring relevant information about the alternatives, potential outcomes, and relevant factors that may influence the decision.
- Evaluating alternatives: Assessing and comparing the available options based on various criteria, such as feasibility, cost, risks, benefits, and potential consequences.
- Weighing pros and cons: Considering the advantages and disadvantages of each alternative and determining their relative importance or priority.
- Making a choice: Selecting the option that is deemed most suitable or optimal based on the information and analysis conducted.
- Implementation: Putting the chosen decision into action and carrying out the necessary steps to execute the chosen course of action.
- Evaluation and feedback: Assessing the outcomes of the decision and gathering feedback to determine if the chosen option achieved the desired results or if adjustments are needed.
Decision-making in AI: It refers to the process by which artificial intelligence systems analyse information, evaluate options, and choose a course of action or make a recommendation. AI decision-making can be divided into two main categories:
Rule-based systems and machine learning-based systems.
(a) Rule-based Systems: Rule-based decision-making in AI involves creating a set of predefined rules that the AI system follows to make decisions. These rules are typically created by human experts in the domain and are based on their knowledge and experience. The AI system applies these rules to the input data and produces an output or decision. Rule-based systems are deterministic and provide explicit explanations for their decisions.
(b) Machine Learning (ML)-based Systems: Machine learning (ML) techniques enable Al systems to learn from data and make decisions based on patterns and statistical models. These systems use algorithms to automatically extract features from the data and build models that can predict outcomes or classify inputs. MLbased decision-making is particularly effective when dealing with large and complex datasets. However, it can be challenging to interpret the decisions made by ML models, as they operate as black boxes and do not provide explicit explanations.
What is not AI?
Everything that is automatic is not AI.
AI do not think on their own but it simply acting upon the set of instructions which is given by users.
How do you make decisions?
We took decision based on the reason ,our past experiences and availability of information.
Make your choices
You are given the option of choosing one gift voucher out of three options.
Where 1st gift voucher has foreign trip to Singapore. the 2nd has 1 year free coaching for IIT/Medical and 3rd has a meeting card of your ideal. Choose wisely and decide which option you would choose and why?
Basics of AI Class 10 Notes
AI and Related Terminologies
- AI is techniques of making intelligent.
- As per NITI Aayog: AI refers to the ability of machines to perform cognitive tasks like thinking , perceiving, learning ,problem solving and decision making.
What is Machine Learning?
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence (AI) that involves the development of algorithms and models that enable computers to learn and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed. It is a field that focuses on the development of computational systems that can learn from and adapt to data, allowing them to improve their performance over time.
In traditional programming, a programmer writes explicit instructions for a computer to follow. In machine learning, however, the computer learns from data patterns and examples to generate its own rules or models. These models can then be used to make predictions or decisions when presented with new or unseen data.
Machine learning algorithms are designed to identify patterns, extract insights, and make predictions or decisions based on training data. The training data is a set of labelled examples or historical data that the algorithm uses to learn from. By analysing the patterns in the training data, the algorithm learns to generalise and make predictions on new, unseen data.
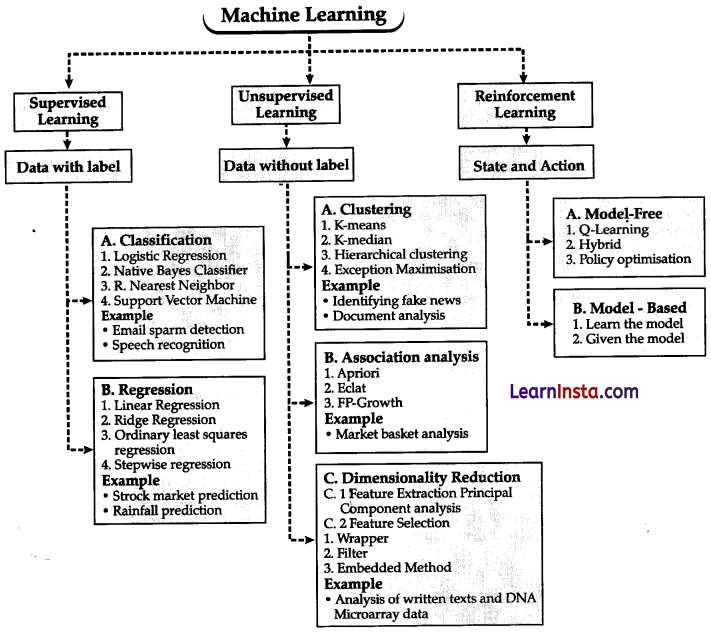
Thereare different types of machine learning algorithms, including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. In supervised learning, the algorithm learns from labelled examples where the desired output is known, such as classifying emails as spam or not spam.
Unsupervised learning involves finding patterns or structures in unlabelled data, such as clustering similar customer groups based on their behaviour. Reinforcement learning involves an agent learning to interact with an environment and taking actions to maximise rewards or achieve specific goals.
![]()
Machine learning has a wide range of applications, including image and speech recognition, natural language processing, recommendation systems, fraud detection, autonomous vehicles, and many others. Its capabilities have significantly advanced in recent years due to improvements in computing power, the availability of large datasets, and advancements in algorithms and techniques.
What is Deep Learning?
Deep learning is a type of machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) that imitates the way humans gain certain types of knowledge.
Deep learning is an important element of data science, which includes statistics and predictive modeling.
Deep Learning has very complex algorithms and requiresa very large amount of dataset.
Deep learning utilises both structured and unstructured data for training.
Practical examples of deep learning are virtual assistants, vision for driverless cars, money laundering, face recognition, and many more.
Deep learning is an AI function that mimics the workings of the human brain in processing data for use in detecting objects, recognising speech, translating languages, and making decisions.
How Deep Learning Works?
Deep learning is based on ML but it can work with unstructured data and learns on its own through reading the data, so it requires a large number of datasets called Big Data which is drawn from sources like social media, internet search engines, e-commerce platforms, etc
These datasets are then processed through complex ML algorithms
Machine Learning vs Deep Learning
| Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
| Machine Learning is a superset of Deep Learning | Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning |
| The data represented in Machine Learning is quite different as compared to Deep Learning as it uses structured data. | The data representation is used in Deep Learning is quite different as it uses Artificial neural networks (ANN). |
| Machine learning consists of thousands of data points. | Big Data: Millions of data points. |
| Machine Learning is highly used to stay in the competition and learn new things. | Deep Learning solves complex machine learning issues. |
Your data is used by companies to do deep learning and make products on the current trends in mentality and what people like.
The choice of decision-making approach in AI depends on factors such as the problem domain, available data, interpretability requirements, and the trade-off between accuracy and explainability. Ethical considerations, transparency, and accountability are crucial aspects of AI decision-making, as ensuring fairness and avoiding biases in the decision-making process is of paramount importance.
![]()
How to say a machine is AI?
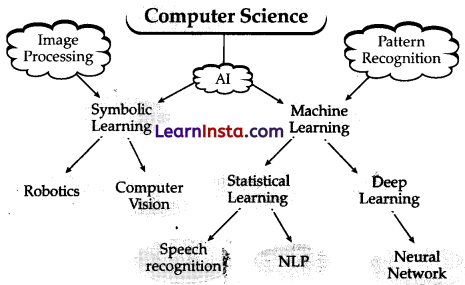
A machine is considered to be AI if it can apply the 3 domains of AI that are Data, Computer Vision, and Natural Language Processing.
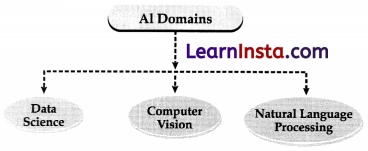
The flowchart below is representing the 3 domains of Artificial Intelligence
What are the Domains of AI?
Domains of AI refer to the main branches of Artificial Intelligence for ex: Data, Computer Vision, and Natural Language Processing
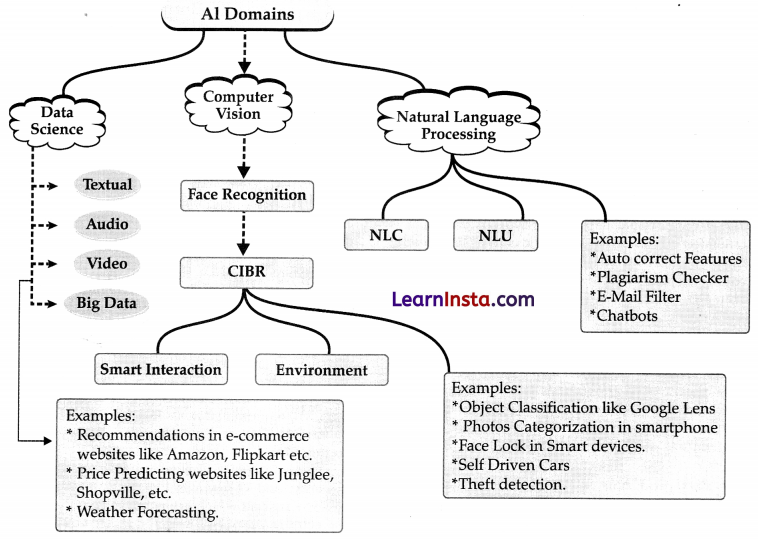
Data Sciences (Data)
“Data Scientist is an artist who joins all the loose ends of data together to find the optimum solution for a problem and make it into Artful Intelligence.”
Data Science is all about applying mathematical and statistical principles to data in simple words, Data Science is the study of data, this data can be of 3 types – Audio, Visual and Textual.
Data Sources:
DataSets-DataSet is a collection of different kinds of Data.

For example:
If someone posts something on Facebook he may get Likes, Shares, Dislikes, Comments, etc. All of this is Data, This collection is one Dataset
There are two types of data sets:
| Training Dataset | Used for Training the Model (70% of the Data). |
| Testing Dataset | Used for Testing the model ( 30 % of the data) |

TYPES OF DATA IN AI: The types of data commonly used in AI
Audio data: Audio data. is the type of data that is generated by capturing sound waves. This type of data is used in various AI applications like speech recognition, natural language processing, and voicebased search. Examples of audio data include voice recordings, music files, podcasts, and sound effects.
Visual data: Visual data is the type of data that is generated by capturing images or videos. This type of data is used in various AI applications like computer vision, object detection, and facial recognition. Examples of visual data include digital photos, video footage, satellite imagery, and medical scans like X-rays and MRIs.
Numeric data: Numeric data is the type of data that is represented in numerical form. This type of data is used in various AI applications like machine learning, predictive analytics, and financial analysis. Examples of numeric data include stock prices, sales figures, temperature readings, and sensor data from IoT devices.
![]()
Text data: Text data is the type of data that is represented in written or typed form. This type of data is used in various AI applications like natural language processing, sentiment analysis, and chatbots. Examples of text data include emails, social media posts, news articles, and product reviews.

COMPUTER VISION (CV)
This is a technology of AI with which robots can see. Computer vision plays a vital role in the domains of safety, security, health, access, and entertainment.
Computer vision automatically extracts, analyses, and comprehends useful information from a single image or an array of images. This process involves the development of algorithms to accomplish automatic visual comprehension.
Computer Vision in simple words is identifying the symbols from the given object (pictures) and learning the pattern and alerting or predicting the future object using the camera.
The goal of computer vision is to understand the content of digital images.
Computer vision was first introduced in the 1970s and now its applications are seen by everyone everywhere
- Facial recognition
- Face filter
- Google lens
- Retail stores
- Automotive
- Healthcare
- Google translate app
Facial Recognition:
A system is a technology that is capable of identifying or verifying a person from a digital image or a video from a video source. For example, it is used by crime investigation department and police.
Face filters :
By using the applications like Instagram and Snapchat, we can click photographs of various themes, which are based on the usage of computer vision.
![]()
Google lens :
To search data, Google uses computer vision for comparing different features of the input image to the database of images and then gives us the search.
Retail stores :
The newest and most exciting application of computer vision is ‘Amazon Go’. It’s an innovative retail store, where there are no cashiers or checkout stations. It is a partially automated store that is created by utilising computer vision, and deep learning.
Automotive :
Computer vision is also taking over the automotive industry, and companies like Tesla have developed self-driving cars which are going to rule the streets in the coming years. Automated cars are equipped with sensors and software which can detect the 360 degrees of movements of pedestrians, cyclists, vehicles, and road work.
Healthcare :
Technology is helping healthcare professionals accurately classify conditions and illnesses by reducing and eliminating any inaccurate diagnosis and saving patients’ lives.
Google translate App :
Google Translate is a free multilingual statistical and neural machine translation service that is provided by Google, to translate text and websites from one language to another language using the device camera.
Natural Language Processsing (NLP):
Natural Language Processing (NLP) refers to the AI method of communicating with an intelligent system using a natural language such as English:
Processing of Natural Language is required when you want an intelligent system like a robot to perform as per your instructions, when you want to hear decision from a dialogue-based clinical expert system, etc.
The field of NLP involves making computers to perform useful tasks with the natural languages humans use. The input and output of an NLP system can be-
- Speech
- Written Text What is NLP?
The ability of a computer to understand human language (command) as spoken or written and to give an output by processing it, is called Natural Language Processing (NLP). It is a component of Artificial Intelligence.
Let’s understand it in simple words!
Now question yourself why you are able to talk with your friend? because the words spoken by your friend are taken as input from your ears, your brain processes them and as an output, you respond and the most important thing the language you are using for communication is known to both of you. That’s NLP in simple words!

Language is a method of communication with the help of which we can speak, read and write. For example, we think, we make decisions, plans and more in natural language; precisely, in words. However, the big question that confronts us in this AI era is that can we communicate in a similar manner with computers.
![]()
In other words, can human beings communicate with computers in their natural language? It is a challenge for us to develop NLP applications because computers need structured data, but human speech is unstructured and often ambiguous in nature.
In this sense, we can say that Natural Language Processing is the sub-field of computer science especially Artificial Intelligence that is concerned with enabling computers to understand and process human language. Technically, the main task of NLP would be to program computers for analysing and processing huge amount of natural language data.
Applications of NLP:
3 Applications of NLP
| Speech Recognition | Speech recognition is when a system is able to give output by understanding or interpreting a user’s speech as an input or a command. Used in: Google Assistant, Apple Siri, Amazon Alexa, etc. |
| Sentimental Analysis | Sentimental Analysis is a process of detecting bad and positive sentiments in a text. Used in: Youtube’s violent or graphic content policies, review of products, identifying spam messages. |
| Machine Translations | Translations of text in a language to another different language by machines. Used in: Google Translate, Youtube cc, Chatbot(s), etc. |
AI Applications and Ethics Class 10 Notes
Here are some examples:
Commercial: AI is used in commercial applications such as marketing and advertising, customer service, and sales forecasting. For example, companies use AIpowered chatbots to provide 24 / 7 customer support and improve customer engagement.
Industry: In the industrial sector, AI is used to optimise manufacturing processes, predictive maintenance, quality control, and supply chain management. For example, AI-powered robots are used to automate repetitive tasks and increase efficiency in production lines.
Medical: AI is used in medical applications such as disease diagnosis, drug discovery, and personalised medicine. For example, AI-powered tools can analyse medical images to detect early signs of diseases like cancer.
Defense: AI is used in defense applications such as surveillance and reconnaissance, autonomous weapons systems, and cybersecurity. For example, AI-powered drones can provide real-time situational awareness in the battlefield.
Banking: In the banking sector, AI is used for fraud detection and prevention, risk assessment, and customer service. For example, Al-powered algorithms can detect anomalies in financial transactions to prevent fraud.
Transport AI is used in transport applications such as self-driving cars, traffic management, and logistics optimisation. For example, self-driving cars use AIpowered sensors and algorithms to navigate and avoid obstacles.
![]()
Security: AI is used in security applications such as facial recognition, behaviour analysis, and threat detection. For example, Al-powered video analytics can detect suspicious behaviour and alert security personnel.
Agriculture: AI is used in agriculture applications such as crop monitoring, yield prediction, and precision farming. For example, AI-powered sensors and drones can collect data on crop health and soil moisture to optimise farming practices.

Commonly Used AI Applications:
There are several AI applications that are commonly used in daily life, such as:
Virtual assistants: Virtual assistants like Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa use AI algorithms to understand natural language and provide information or perform tasks.
Personalised recommendations: AI algorithms are used by platforms like Netflix, Spotify, and Amazon to recommend content or products based on users’ preferences and browsing history.
Social media: AI algorithms are used by social media platforms to curate content, filter spam, and detect and remove inappropriate content.
Navigation apps: Navigation apps like Google Maps and Waze use AI algorithms to provide real-time traffic updates and suggest alternate routes based on traffic conditions.
Ride-sharing apps: Ride-sharing apps like Uber and Lyft use AI algorithms to match riders with drivers, estimate ride fares, and optimise routes.
Online customer service: AI-powered chatbots are used by companies to provide 24 / 7 customer service and support through websites and social media.
E-mail spam filters: E-mail providers like Gmail and Outlook use AI algorithms to filter spam and prioritise important emails based on user behaviour.
![]()
Smart home devices: Smart home devices like smart thermostats, lights, and security cameras use AI algorithms to learn user preferences and automate tasks based on their behaviour.
These are just a few examples of how AI is already being used in our daily lives, and as technology advances, we can expect to see even more applications of AI in our everyday routines.
Where we can use AI:
Assisting humans: AI-powered chatbots can provide $24 / 7$ customer service support, answering frequently asked questions and freeing up human staff to focus on more complex issues.
Remote patient monitoring: AI can be used to remotely monitor patients with chronic conditions, alerting healthcare providers of any changes in their condition before they become serious. This can help reduce hospital readmissions and improve patient outcomes.
Monitoring contagious diseases: AI can analyse large amounts of data from social media, news reports, and other sources to identify potential outbreaks of contagious diseases. For example, the BlueDot AI platform was able to identify the potential spread of COVID-19 before it was officially recognised by the World Health Organisation.
Analysis of data for research and development: AI can analyse large amounts of data to identify patterns and trends that can inform research and development efforts. For example, pharmaceutical companies can use AI to analyse genomic data and identify potential drug targets.
Efficiently solving complex problems: AI can be used to solve complex problems that are beyond the capabilities of humAnswer:For example, Al algorithms can be used to optimise supply chain logistics, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Speedy disaster recovery strategy: AI can help with disaster response efforts by quickly analysing satellite imagery to identify areas that need help. For example, the Red Cross used AI to analyse satellite imagery after Hurricane Irma to identify areas that needed immediate assistance.
Performing recurring business tasks: AI can be used to perform repetitive tasks, such as data entry or invoice processing, freeing up human staff to focus on more complex tasks.
Reducing the chances of manual error: AI can help reduce the chances of human error by automating processes that are prone to error. For example, AI algorithms can be used to proofread written content and identify errors that humans may have missed.
![]()
Ensuring 24-hour service with the same performance and consistency: AI can provide consistent and reliable service 24 / 7, without the need for breaks or time off. For example, AI-powered chatbots can provide customer service support around the clock, ensuring that customers receive timely assistance regardless of the time of day.
The use of AI automation can provide numerous benefits to businesses and society, including increased efficiency, improved decision-making, and better outcomes for individuals.
Ethics in AI:
Ethics in AI is a field of study that focuses on the ethical implications of the development and use of artificial intelligence systems. As AI technology becomes increasingly sophisticated and integrated into our daily lives, it is important to consider the potential ethical concerns and ensure that AI systems are designed and used in a responsible and ethical manner.
Some of the key ethical issues in AI include:
Bias: Bias refers to the tendency of AI systems to make decisions or recommendations that favor certain groups or outcomes over others. This can happen when the data used to train the AI system is itself biased, or when the system is designed in a way that unintentionally favors one group over another. For example, facial recognition systems have been shown to be less accurate in identifying people with darker skin tones, due to biases in the training data.
Prejudice: Prejudice refers to the use of AI systems to discriminate against certain groups of people based on characteristics such as race, gender, or age. This can happen when the AI system is designed to make decisions based on criteria that are discriminatory, or when the system is trained on data that reflects existing prejudices in society. For example, some companies have been accused of using AI-powered hiring systems that discriminate against women or people of color.
Fairness: Fairness refers to the principle that AI systems should be designed and deployed in a way that is fair to all people, regardless of their background or characteristics. This can involve ensuring that the system is designed to treat everyone equally, or that it takes into account relevant differences between groups of people. For example, an Al system used to allocate medical resources should be designed to ensure that everyone has an equal chance of receiving treatment, regardless of their socioeconomic status.
Accountability: Accountability refers to the principle that those who create and deploy AI systems should be held responsible for any negative consequences that result from their use. This can involve establishing clear lines of responsibility for the system’s operation, as well as mechanisms for detecting and addressing any harmful impacts that arise. For example, a company that uses an AI system to make decisions about customer service should have clear policies in place for handling complaints and addressing any negative impacts on customers.
Transparency: Transparency refers to the principle that AI systems should be designed and deployed in a way that is transparent to users and stakeholders. This can involve providing clear explanations of how the system works, as well as making its output and decision-making processes accessible to those who are affected by it. For example, a company that uses an AI system to make hiring decisions should be transparent about how the system evaluates candidates and what criteria it uses.
![]()
Interpretability: Interpretability refers to the ability to understand and interpret the output of an AI system. This is important because it allows users to make informed decisions about how to act on the system’s recommendations. For example, an Al system used to diagnose medical conditions should be designed in a way that allows doctors to understand how the system arrived at its diagnosis and what factors it considered.
Explainability: Explairfability refers to the ability to provide clear explanations of how an AI system arrived at a particular decision or recommendation. This is important because it allows users to understand why the system made a particular decision, and to identify any potential biases or errors in its decision-making processes. For example, an AI system used to evaluate job candidates should be designed in a way that allows the system to explain why it recommended one candidate over another
Privacy and security: Al systems can collect, store, and analyse vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about privacy and security. It is important to ensure that AI systems are designed to protect user privacy and are secure from cyber-attacks.
Social and economic impact: AI has the potential to transform many aspects of society, including the workforce, healthcare, and transportation. It is important to consider the potential social and economic impacts of AI and ensure that the benefits are distributed fairly.
Safety: AI systems can have physical and psychological impacts on individuals, and it is important to ensure that they are designed and used in a safe and responsible manner.
What is AI Ethics?
The discipline deals with right vs wrong and the moral obligations and duties of humans. It’s called AI ethics.

Ethics is the branch of philosophy concerned with grounding decisions, beliefs, policies, etc. In some sort of framework for deciding right or wrong. Ethics looks to resolve such questions as human morality. By deriving some moral system we can prescribe value to some actions or beliefs.
Ethical concerns of AI:
Can AI assure this:
| Unemployment | What will happen after the end of jobs? |
| Inequality | How are we going to distribute the wealth created by machines? |
| Humanity | How do machines affect our behaviour and interaction? |
| Artificial Stupidity | How can we guard against mistakes? |
| Security | How do we keep AI safe from adversaries? |
Taking over human jobs leading towards the era of Unemployment.
Making humans less efficient for example: Asking for everything from an artificially intelligent machine and making their own decisions.
- Wealth inequalities, where wealthy people will become richer by the influence of machines whereas poor people will become poor because of lack of jobs.
- Machines will affect humanity and make them less interacting with other people.
- Machines don’t know the desired output that humans want.
- Facing racism from machines, which is also called AI Bias.
![]()
What is AI bias?
AI Bias means favoring someone or something. AI bias focuses on training the machines with unbiased data, when Bias Data is fed to an AI machine while creating the model then the machine will also be biased.

Examples of AI Bias:
| Machine Voices | What will happen after the end of jobs? |
| Google Recommendations | How are we going to distribute the wealth created by machines? |
| Search Results | How do Machines affect our behaviour and interaction? |
We have seen that in most of artificial assistants have a female voice and not a male voice.
When a camera missed the mark on racial sensitivity, or when a software used to predict future criminals showed bias against black people.
Security systems are trained, based on an individual’s race of gender rather than their actions and movements to commit the crime etc. Facial recognition systems look at a diverse Training set resulting in only detecting the racefor which they are trained.
How to avoid AI bias?
In simple terms AI access means making AI more accessible.
Al access discusses the gap in society, where only upper-class people who can afford AI-enabled devices have the opportunity to access it and people below the poverty line don’t have access to it.
Because of this, a gap has emerged between these two classes of people and it gets widened with the rapid advancement of technology.
![]()
The Government has’to bring balance in society by providing infrastructure to common students/people so that everyone will get a chance to access emerging technologies like AI.
void biases in output
Data Privacy:
Data privacy is defined as one able to control how our digital data is being stored, modified, and exchanged between different parties.
As technology advances Artificial Intelligence becomes more and more integrated with every aspect of our lives. Numerous different industries use it to improve products and services but because machine learning often uses million of pieces of personal data to train the algorithms it is by strict privacy laws including EU GDPR or the California consumer privacy act. This means you need to protect your consumer’s data at all times.

Applications of AI:
AI in Gaming :
Playing games with AI Bots is the usage of Ai in Gaming.
AI can think large number of possible moves with restrict knowledge.
AI is trained with data about the position, strategies, concepts and rules of the game and is made to play with a partner.
These AI Bots can be digital or physical but generally, they are digital.
Game play relies on the data fed and the algorithm developed by their developers.
Some advance AI game-bots set their difficulty level by analysing the gameplay of their competitor Example: AI game-bots are used in digital games like chess, poker, and tic-tac-toe.
AI in NLP :
Two understand the naturally spoken language of humans by machines is known as NLP Recommended Natural Language Processing (NLP) AI helps the machine to understand the commands in the naturally spoken language of humans.
AI in Decision making :
AI is now inheriting the decision-making capacity of humans used it in providing explanations and solutions of the problems to its user.
Example: Self-driving cars
AI in Health-Care :
One of the most prominent use of AI can be seen in the healthcare industry
With the use of Al , our doctors are getting help in various tasks like fast diagnosis of various diseases.
Robotic Surgery: With help of certain machines surgeons can now perform surgeries from a distance.
![]()
AI in Finance :
In finance AI is used as adaptive intelligence to make automating chat-bots and algorithms.
AI in Data Security :
Companies and government are using AI to improve the data-security of applications and huge data-bases.
Example: AEG bot and AI2. This AI-bots can find cyberbugs in a system and thus help to improve data-security
AI in Expert System :
Integration of special software, machine and special information obtained from learning algorithms to provide reasoning and advices.
Computer Vision :
Using of AI in computer-vision means to train the system such that, it can perform visual tasks such as image Processing, face-recognition
Example: Face-locks of different devices
Speech Recognition :
Extracting the real meaning of sentence by human talk.
Example: Siri, Google Assistant, Alexa, Cortana
![]()
Robotics :
Today’s robots are based on AI technologies, which uses different applications of AI discussed above, depending upon their work.
Today’s most advance robot is Erica and Sophia. They can talk and behave like humans so they are also called as Humanoid.
AI in E-commerce :
AI uses an algorithm and automatically generates a list of items based on your search or history. It also handles the service requirements of the customer.
Examples: Youtube’s feed, Filpkarts products on the home page, Google ads, etc.