Find free online Chemistry Topics covering a broad range of concepts from research institutes around the world.
Homogeneous and Hetrogeneous Equilibrium
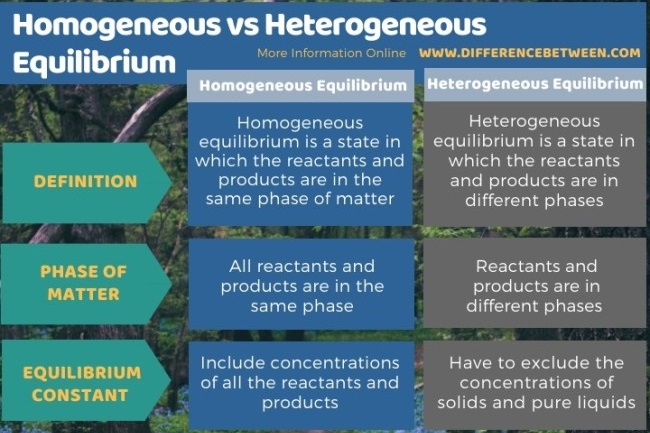
In a homogeneous equilibrium, all the reactants and products are in the same phase.
For example
H2(g) + I2(g) ⇄ 2HI(g)
In the above equilibrium, H2, I2 and HI are in the gaseous state.
Similarly, for the following reaction, all the reactants and products are in homogeneous solution phase.
CH3COOCH3(aq) + H2O(aq)
↑↓
Heterogeneous Equilibrium
If the reactants and products of a reaction in equilibrium, are in different phases, then it is called as heterogeneous equilibrium.
Example:
H2O(l) ⇄ H2O(g)
CaCO3(s) ⇄ CaO(s) + CO2(g)
A homogeneous equilibrium is one in which all species are present in the same phase. Common examples include gas-phase or solution reactions. A heterogeneous equilibrium is one in which species exist in more than one phase. Common examples include reactions involving solids and gases, or solids and liquids.
![]()
A homogenous equilibrium reaction is a reaction where all of the products and reactants are in the same phase. The reactants are on the left side of the arrows, and the products are on the right side of the arrows. A heterogeneous equilibrium reaction is when there are different phases in the reaction.
Homogeneous reactions are chemical reactions in which the reactants and products are in the same phase, while heterogeneous reactions have reactants in two or more phases. A reaction between a gas and a liquid, a gas and a solid or a liquid and a solid is heterogeneous.
In an equilibrium, the reactants and the products are present in two or more that two phases, it is called a heterogeneous equilibrium.
A heterogeneous equilibrium is one in which species exist in more than one phase. Common examples include reactions involving solids and gases, or solids and liquids.
![]()
By definition, a pure substance or a homogeneous mixture consists of a single phase. A heterogeneous mixture consists of two or more phases. When oil and water are combined, they do not mix evenly, but instead form two separate layers. Each of the layers is called a phase.
Homogeneous solutions are solutions with uniform composition and properties throughout the solution. For example a cup of coffee, perfume, cough syrup, a solution of salt or sugar in water, etc. Heterogeneous solutions are solutions with non-uniform composition and properties throughout the solution.