MCQ on Fractions Class 6
Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 MCQ Fractions
Multiple-Choice Questions
Question 1.
\(\frac{5}{6}\) is a:
(a) proper fraction
(b) improper fraction
(c) mixed fraction
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) proper fraction
Question 2.
Which of the following is an improper fraction?
(a) \(\frac{3}{4}\)
(b) \(\frac{4}{3}\)
(c) \(\frac{4}{7}\)
(d) \(\frac{5}{16}\)
Answer:
(b) \(\frac{4}{3}\)
![]()
Question 3.
\(\frac{3}{7}-\frac{1}{21}\) is equal to:
(a) \(\frac{6}{7}\)
(b) \(\frac{4}{19}\)
(c) \(\frac{8}{21}\)
(d) \(\frac{10}{23}\)
Answer:
(c) \(\frac{8}{21}\)
Question 4.
Which of the following fractions is non-equivalent to \(\frac{3}{4}\)?
(a) \(\frac{12}{16}\)
(b) \(\frac{21}{28}\)
(c) \(\frac{27}{36}\)
(d) \(\frac{15}{24}\)
Answer:
(d) \(\frac{15}{24}\)
Question 5.
Which of the following is the simplest form of \(\frac{24}{108}\)?
(a) \(\frac{1}{9}\)
(b) \(\frac{2}{9}\)
(c) \(\frac{3}{9}\)
(d) \(\frac{4}{9}\)
Answer:
(b) \(\frac{2}{9}\)
Question 6.
What fractions of numbers from 1 to 10 are prime
Answer:
Option (a) is correct.
Explanation:
Prime numbers from 1 to 10 are 2,3,5,7. Total numbers = 10
Fraction = \(\frac{4}{10}\)
Question 7.
Fill in the missing number.
\(\frac{4}{5}=\frac{?}{25}\)
(a) 5
(b) 20
(c) 16
(d) 24
Answer:
Option (b) is correct.
Explanation:
\(\frac{4}{5}=\frac{x}{25}\)
5x = 25 × 4
x = \(\frac{25 \times 4}{5}\) = 20
Question 8.
A fraction equivalent to \(\frac{18}{30}\) with numerator 3 is equal to ____.
(a) \(\frac{54}{90}\)
(b) \(\frac{6}{10}\)
(c) \(\frac{3}{5}\)
(d) \(\frac{9}{15}\)
Answer:
Option (c) is correct
Explanation:
\(\frac{18 \div 6}{30 \div 6}=\frac{3}{5}\)
Question 9.
\(\frac{3}{12}\) is greater than \(\frac{3}{17}\) (True/False)
Answer:
True

Question 10.
Shweta made Biryani. She gave \(\frac{9}{23}\) parts to Yash, \(\frac{4}{23}\) parts to Raj, \(\frac{7}{23}\) parts to Rahul and she kept the remaining biryani for herself. Then find out who got more biryani?
(a) Shweta
(b) Yash
(c) Raj
(d) Rahul
Answer:
Option (b) is correct.
Explanation:
Given fractions are \(\frac{9}{23}, \frac{4}{23}, \frac{7}{23}\) and \(\frac{3}{23}\)
Since \(\frac{9}{23}<\frac{7}{23}<\frac{4}{23}<\frac{3}{23}\)
Yash got more biryani.
Question 11.
Abhishek, Bani and Chitra take \(\frac{7}{11}, \frac{4}{9}\) and \(\frac{9}{17}\) hours respectively to reach their friend Dhruv’s home. Who will take the least time?
(a) Abhishek
(b) Bani
(c) Chitra
(d) All of them will take equal time
Answer:
Option (b) is correct.
Explanation:
\(\frac{7}{11}, \frac{4}{9}\) and \(\frac{9}{17}\)
LCM of denominators 11,9 and 17 is 1683.
Converting the fractions into like fractions with denominator 1683 as
\(\frac{7}{11}=\frac{11 \times 153}{11 \times 153}=\frac{1071}{1683}\)
\(\frac{4}{9}=\frac{4 \times 187}{9 \times 187}=\frac{748}{1683}\)
\(\frac{9}{17}=\frac{9 \times 99}{17 \times 99}=\frac{891}{1683}\)
Since the denominators are same, we can compare fractions by comparing their numerators.
Since 748 < 891 < 1071
Therefore, \(\frac{748}{1683}<\frac{891}{1683}<\frac{1071}{1683}\)
i.e., \(\frac{4}{9}<\frac{9}{17}<\frac{7}{11}\)
Hence, Bani will take least time to reach Dhruv’s home.
Question 12.
Assertion (A): \(\frac{7}{11}\) is a proper fraction.
Reason (R): In a proper fraction numerator is great¬er than the denominator.
(a) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(b) Assertion is false but reason is true.
(c) Both assertion and reason are true.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
Option (a) is correct.
Explanation:
\(\frac{7}{11}\) is a proper fraction where numerator is less than the denominator.
Question 13.
Assertion (A): are equivalent fraction.
Reason (R): Two or more fractions having the same value or representing the same part of a whole are called equivalent fraction.
(a) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(b) Assertion is false but reason is true.
(c) Both assertion and reason are true.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
Option (c) is correct.
Explanation:
Both are true if numerator and denominator of a given fraction are multiplie and divided by same non-zero number we get equivalent fraction.
Fill in the blanks:
(i) A ______________ is a number representing a part of a whole.
Answer:
fraction
(ii) In a ______________ fraction, the numerator is smaller than the denominator.
Answer:
proper
(iii) In an improper fraction, the denominator is ______________ than the numerator.
Answer:
smaller
(iv) The numerator of \(\frac{6}{11}\) is ______________
Answer:
6
(v) Fractions with the ______________ denominators are called like fractions.
Answer:
same
(vi) Fractions with ______________ denominators are called unlike fractions.
Answer:
different
(vii) Fractions having ______________ as the numerator are called unit fractions.
Answer:
1
(viii) All ______________ are in the lowest terms.
Answer:
unit fractions
(ix) A combination of whole number and a proper fraction is called a ______________ number.
Answer:
mixed
(x) A fraction is said to be in its ______________ if the HCF of its numerator and denominator is 1.
Answer:
lowest terms
(xi) To reduce a fraction to its lowest terms, we divide the numerator and denominator of the given fraction by their ______________
Answer:
HCF
(xii) Fraction having the same value are called ______________ fractions.
Answer:
equivalent
(xiii) 2\(\frac{3}{5}\) is a ______________ fraction. [improper/mixed]
Answer:
mixed
(xiv) \(\frac{1}{28}\) is a ______________ fraction. [mixed/unit]
Answer:
unit
![]()
Tick the correct option:
(i) Three seventh is written as ______________ [\(\frac{3}{7}\)/\(\frac{7}{3}\)].
Answer:
\(\frac{3}{7}\)
(ii) A fraction having its ______________ [numerator/denominator] as 1 is called a unit fraction.
Answer:
numerator
(iii) Fractions having ______________ [same/different] denominators are like fractions.
Answer:
same
Match the following:
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) Equivalent fraction of \(\frac{7}{12}\) is: | (i) Proper fraction |
| (b) 2\(\frac{1}{5}\) is equal to: | (ii) Improper fraction |
| (c) \(\frac{7}{11}\) is: | (iii) \(\frac{21}{36}\) |
| (d) \(\frac{19}{5}\) is: | (iv) \(\frac{11}{5}\) |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) Equivalent fraction of \(\frac{7}{12}\) is: | (iii) \(\frac{21}{36}\) |
| (b) 2\(\frac{1}{5}\) is equal to: | (iv) \(\frac{11}{5}\) |
| (c) \(\frac{7}{11}\) is: | (i) Proper fraction |
| (d) \(\frac{19}{5}\) is: | (ii) Improper fraction |
Fun Activity
Question 1.
Complete the following crossword puzzle using the given directions:
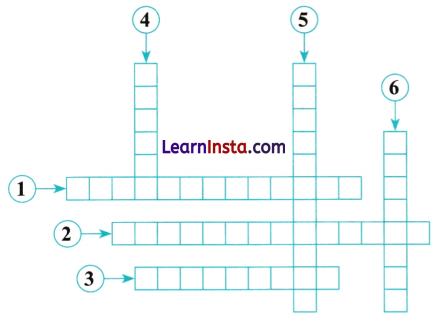
Directions:
Across:
(1) A ______________ consists of a whole number and a fractional part.
(2) A fraction in which the numerator is less than the denominator is called a ______________
(3) In a fraction the numeral above the bar is called the ______________ of the fraction.
Down:
(4) Fractions with different denominators are called ______________ fractions.
(5) In a fraction, the numeral below the bar is called the ______________ of the fraction.
(6) A fraction is called an ______________ fraction if numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator.
Answer:
Across
(1) Mixed Fraction
(2) Proper Fraction
(3) Numerator
Down
(4) Unlike
(5) Denominator
(6) Improper
Answer the following.
Question 1.
What fraction of a day is 7 hours?
Answer:
\(\frac{7}{24}\)
Question 2.
What fraction of an hour is 9 minutes?
Answer:
\(\frac{3}{20}\)
Question 3.
What fraction of a metre is 3 centimeters?
Answer:
\(\frac{3}{100}\)
Question 4.
What fraction of a kilogram is 30 grams?
Answer:
\(\frac{3}{100}\)
Question 5.
Reduce \(\frac{48}{216}\) in its simplest form.
Answer:
\(\frac{2}{9}\)
![]()
Question 6.
Write a fraction equivalent to \(\frac{7}{12}\) with 63 as its numerator.
Answer:
\(\frac{63}{108}\)
Question 7.
Is adding one-half and three-fourth same as adding \(\frac{2}{4}\) and \(\frac{3}{4}\)?
Answer:
Yes
Question 8.
Is subtracting one-half from three-fourth the same as subtracting \(\frac{1}{2}-\frac{3}{4}\)?
Answer:
No
Question 9.
Write the following fractions in ascending order:
(a) \(\frac{13}{17}, \frac{11}{17}, \frac{15}{17}, \frac{3}{17}, \frac{4}{17}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{3}{17}<\frac{4}{17}<\frac{11}{17}<\frac{13}{17}<\frac{15}{17}\)
(b) \(\frac{11}{13}, \frac{7}{13}, \frac{9}{13}, \frac{3}{13}, \frac{10}{13}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{3}{13}<\frac{7}{13}<\frac{9}{13}<\frac{10}{13}<\frac{11}{13}\)
(c) \(\frac{4}{17}, \frac{4}{4}, \frac{4}{13}, \frac{4}{2}, \frac{4}{5}, \frac{4}{11}, \frac{4}{7}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{4}{17}<\frac{4}{13}<\frac{4}{11}<\frac{4}{7}<\frac{4}{5}<\frac{4}{4}<\frac{4}{2}\)
Question 10.
Write the following fractions in descending order:
(a) \(\frac{11}{12}, \frac{15}{12}, \frac{13}{12}, \frac{4}{12}, \frac{3}{12}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{15}{12}>\frac{13}{12}>\frac{11}{12}>\frac{4}{12}>\frac{3}{12}\)
(b) \(\frac{3}{2}, \frac{3}{5}, \frac{3}{17}, \frac{3}{4}, \frac{3}{7}, \frac{3}{11}, \frac{3}{13}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{3}{2}>\frac{3}{4}>\frac{3}{5}>\frac{3}{7}>\frac{3}{11}>\frac{3}{13}>\frac{3}{17}\)
Question 11.
Compare the following fractions and put < or > in the boxes:
(i) \(\frac{7}{6}\) ![]() \(\frac{3}{6}\)
\(\frac{3}{6}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{7}{6}\) > \(\frac{3}{6}\)
(ii) \(\frac{1}{4}\) ![]() \(\frac{1}{7}\)
\(\frac{1}{7}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{1}{4}\) > \(\frac{1}{7}\)
(iii) \(\frac{0}{5}\) ![]() \(\frac{4}{5}\)
\(\frac{4}{5}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{0}{5}\) < \(\frac{4}{5}\)
(iv) \(\frac{4}{20}\) ![]() \(\frac{1}{20}\)
\(\frac{1}{20}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{4}{20}\) > \(\frac{1}{20}\)
(v) \(\frac{5}{8}\) ![]() \(\frac{7}{8}\)
\(\frac{7}{8}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{5}{8}\) < \(\frac{7}{8}\)
Question 12.
Which fraction is greater?
(i) \(\frac{3}{2}\) and \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{3}{2}\)
(ii) \(\frac{2}{3}\) and \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{3}{4}\)
(iii) \(\frac{5}{6}\) and \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{5}{6}\)
(iv) \(\frac{7}{12}\) and \(\frac{5}{13}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{7}{12}\)
![]()
Question 13.
Add with the help of diagrams:
(i) \(\frac{1}{6}+\frac{1}{6}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{1}{3}\)
(ii) \(\frac{2}{3}+\frac{1}{3}\)
Answer:
1
(iii) \(\frac{1}{8}+\frac{1}{8}+\frac{1}{8}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{3}{8}\)
(iv) \(\frac{1}{4}+\frac{1}{4}+\frac{1}{4}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{3}{4}\)
(v) \(\frac{2}{5}+\frac{1}{5}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{3}{5}\)
Question 14.
Subtract pictorially:
(i) \(\frac{3}{4}-\frac{1}{4}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{1}{2}\)
(ii) \(\frac{4}{5}-\frac{2}{5}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{2}{5}\)
(iii) \(\frac{5}{8}-\frac{3}{8}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{1}{4}\)
Question 15.
Fill in the missing fractions:
(i) ![]() – \(\frac{3}{10}\) = \(\frac{4}{10}\)
– \(\frac{3}{10}\) = \(\frac{4}{10}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{7}{10}\)
(ii) ![]() + \(\frac{5}{18}\) = \(\frac{12}{18}\)
+ \(\frac{5}{18}\) = \(\frac{12}{18}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{7}{18}\)
(iii) ![]() – \(\frac{3}{5}\) = \(\frac{3}{5}\)
– \(\frac{3}{5}\) = \(\frac{3}{5}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{6}{5}\)
(iv) \(\frac{5}{9}\) + ![]() = \(\frac{11}{9}\)
= \(\frac{11}{9}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{6}{9}\)
Question 16.
Solve:
(a) \(\frac{8}{11}+\frac{3}{11}\)
Answer:
1
(b) \(\frac{1}{22}+\frac{21}{22}\)
Answer:
1
(c) \(\frac{12}{13}-\frac{7}{13}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{5}{13}\)
(d) \(\frac{20}{23}-\frac{5}{23}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{15}{23}\)
![]()
Question 17.
The sum of two fractions is \(\frac{8}{13}\). If one of the fractions is \(\frac{6}{13}\), then find the other fraction.
Answer:
\(\frac{2}{13}\)
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
Question 1.
The fraction representing the shaded portion is
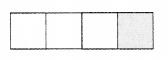
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 1 }{ 8 }\)
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 2.
The fraction representing the shaded portion is
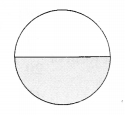
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 1 }{ 8 }\)
Answer
Answer: (b)
Question 3.
The fraction representing the shaded portion is
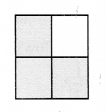
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\)
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: (c)
Question 4.
The fraction representing the shaded portion is
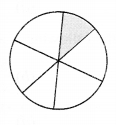
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 1 }{ 8 }\)
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: (c)
Question 5.
The fraction representing the shaded portion is
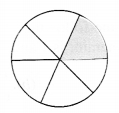
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\)
Answer
Answer: (d)
Question 6.
What fraction of ₹ 1 is 50 paise?
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 1 }{ 8 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 }\)
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 7.
What fraction of ₹ 1 is 25 paise?
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 1 }{ 8 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 }\)
Answer
Answer: (b)
Question 8.
What fraction of an hour is 30 minutes?
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 1 }{ 5 }\)
Answer
Answer: (b)
Question 9.
What fraction of a day is 12 hours?
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\)
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 10.
Which of the following is a proper fraction?
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 5 }{ 4 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 9 }{ 2 }\)
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 11.
Which of the following is a proper fraction?
(a) \(\frac { 0 }{ 1 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 5 }{ 2 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 7 }{ 4 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 11 }{ 3 }\)
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 12.
Which of the following is a proper fraction whose numerator is 1 and denominator is 3?
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 1 }{ 9 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 1 }{ 12 }\)
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 13.
Which of the following is an improper fraction?
(a) \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 4 }{ 5 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 5 }{ 4 }\)
Answer
Answer: (d)
Question 14.
Which of the following is an improper fraction?
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 3 }{ 8 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 11 }{ 3 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\)
Answer
Answer: (c)
Question 15.
Express \(\frac { 5 }{ 2 }\) as a mixed fraction.
(a) 1 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(b) 2 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(c) 3 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(d) 4 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
Answer
Answer: (b)
Question 16.
Express \(\frac { 9 }{ 4 }\) as a mixed fraction.
(a) 2 \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
(b) 3 \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
(c) 4 \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
(d) 5 \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 17.
Express the mixed fraction 1\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) as an improper fraction.
(a) \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\)
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: (b)
Question 18.
Express the mixed fraction 2 \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) as an improper fraction.
(a) \(\frac { 11 }{ 4 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 4 }{ 11 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 9 }{ 11 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 7 }{ 11 }\)
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 19.
The simplest form of \(\frac { 12 }{ 20 }\) is
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 5 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 3 }{ 5 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 4 }{ 5 }\)
Answer
Answer: (c)
Question 20.
The simplest form of \(\frac { 45 }{ 20 }\) is
(a) \(\frac { 9 }{ 4 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 4 }{ 9 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 9 }{ 8 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 2 }{ 9 }\)
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 21.
Which of the following fractions is not equivalent to \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) ?
(a) \(\frac { 5 }{ 15 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 6 }{ 18 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 4 }{ 12 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 7 }{ 20 }\)
Answer
Answer: (d)
Question 22.
Which of the following fractions is equivalent to \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\)?
(a) \(\frac { 6 }{ 11 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 9 }{ 10 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 15 }{ 20 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 21 }{ 25 }\)
Answer
Answer: (c)
Question 23.
The equivalent fraction of \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\) with numerator 4 is
(a) \(\frac { 4 }{ 10 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 4 }{ 12 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 4 }{ 16 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 4 }{ 20 }\)
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 24.
The equivalent fraction of \(\frac { 20 }{ 36 }\) with denominator 9 is
(a) \(\frac { 4 }{ 9 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 5 }{ 9 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 7 }{ 9 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 8 }{ 9 }\)
Answer
Answer: (b)
Question 25.
Which of the following pairs of fractions are equivalent?
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) , \(\frac { 2 }{ 4 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) , \(\frac { 3 }{ 7 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\) , \(\frac { 4 }{ 9 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 4 }{ 7 }\) , \(\frac { 8 }{ 13 }\)
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 26.
Which of the following pairs of fractions are not equivalent?
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) , \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 4 }{ 5 }\) , \(\frac { 12 }{ 15 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 6 }{ 7 }\) , \(\frac { 12 }{ 14 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 4 }{ 9 }\) , \(\frac { 36 }{ 81 }\)
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 27.
Which of the following pairs of fractions are like fractions?
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 5 }\) , \(\frac { 4 }{ 5 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) , \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 4 }{ 5 }\) , \(\frac { 5 }{ 6 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 5 }{ 6 }\) , \(\frac { 6 }{ 7 }\)
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 28.
Which of the following pairs of fractions are unlike fractions?
(a) \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) , \(\frac { 3 }{ 5 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 1 }{ 7 }\) , \(\frac { 6 }{ 7 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 2 }{ 9 }\) , \(\frac { 5 }{ 9 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 4 }{ 13 }\) , \(\frac { 12 }{ 13 }\)
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 29.
Apala typed 50 pages of a book containing 100 pages. Meenu typed 25 pages of the same book. Who typed more?
(a) Apala
(b) Meenu
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 30.
\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) + \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) =
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 31.
\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) =
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 32.
\(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) =
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 8
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 33.
\(\frac { 5 }{ 4 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) =
(a) 1
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 34.
\(\frac { 8 }{ 10 }\) – \(\frac { 3 }{ 10 }\) =
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 1 }{ 5 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 }\)
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 35.
1 – \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) =
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(b) 1
(c) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 36.
\(\frac { 0 }{ 1 }\) + \(\frac { 0 }{ 1 }\) =
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) -1
(d) 2
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 37.
\(\frac { 8 }{ 15 }\) – ? = \(\frac { 7 }{ 15 }\)
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 15 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 2 }{ 15 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 4 }{ 15 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 7 }{ 15 }\)
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 38.
? – \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 5 }{ 4 }\)
Answer
Answer: (b)
Question 39.
? + \(\frac { 2 }{ 7 }\) = \(\frac { 5 }{ 7 }\)
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 7 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 2 }{ 7 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 3 }{ 7 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 4 }{ 7 }\)
Answer
Answer: (c)
Question 40.
\(\frac { 25 }{ 7 }\) – \(\frac { 15 }{ 5 }\) =
(a) 3/4
(b) 4/7
(c) 1/2
(d) 7/4
Answer
Answer: 4/7
Question 41.
\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) =
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 1 }{ 8 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 42.
1 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) + 2 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) =
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
Answer: (d)
Question 43.
Apala bought 21/2 kg of potatoes whereas Meenu bought 11/2 kg of potatoes. Find the total amount of potatoes purchased by Apala and Meenu both.
(a) 1 kg
(b) 2 kg
(c) 3 kg
(d) 4 kg
Answer
Answer: (d)
Question 44.
A teacher finished \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) of his course. How much course is left?
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)
Answer
Answer: (b)
Question 45.
Mamsh read \(\frac { 5 }{ 6 }\) part of a book. Preeti read \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\) part of that book. What more part was read by Manish?
(a) \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 5 }{ 6 }\)
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: (a)