Find free online Chemistry Topics covering a broad range of concepts from research institutes around the world.
Enthalpy (H)
The enthalpy (H), is a thermodynamic property of a system, is defined as the sum of the internal energy (U) of a system and the product of pressure and volume of the system. That is,
H = U + PV …………………. (7.8)
It reflects the capacity to do mechanical work and the capacity to release heat by the system. When a process occurs at constant pressure, the heat involved (either released or absorbed) is equal to the change in enthalpy.
Enthalpy is a state function which depends entirely on the state functions T, P and U. Enthalpy is usually expressed as the change in enthalpy (ΔH) for a process between initial and final states at constant pressure.
ΔH = ΔU + PΔV …………………. (7.9)
The change in enthalpy (ΔH) is equal to the heat supplied at the constant pressure to a system (as long as the system does no additional work).
ΔH = qP
In an endothermic reaction heat is absorbed by the system from the surroundings that is q>0 (positive). Therefore, ΔH is also positive. In an exothermic reaction heat is evolved by the system to the surroundings that is, q<0 (negative). If q is negative, then ΔH will also be negative.
Relation Between Enthalpy ‘H’ and Internal Energy ‘U’
When the system at constant pressure undergoes changes from an initial state with H1, U1 and V1 to a final state with H2, U2 and V2 the change in enthalpy ΔH, can be calculated as follows:
H = U + PV
In the initial state
H1 = U1 + PV1 ………….. (7.10)
In the final state
H2 = U2 + PV2 …………… (7.11)
change in enthalpy is (7.11) – (7.10)
(H2 – H1) = (U2 – U1) + P(V2 – V1)
ΔH = ΔU + PΔV ……………… (7.12)
As per first law of thermodynamics,
ΔU = q + w
Equation 7.12 becomes
ΔH = q + w + PΔV
w= – PΔV
ΔH = qp – PΔV + PΔV
ΔH = qp ……………….. (7.13)
qp – is the heat absorbed at constant pressure and is considered as heat content. Consider a closed system of gases which are chemically reacting to form gaseous products at constant temperature and pressure with Vi and Vf as the total volumes of the reactant and product gases respectively, and ni and nf as the number of moles of gaseous reactants and products, then,
For Reactants (Initial State):
PVi = niRT ……………….. (7.14)
For Products (Final State):
PVf = nfRT ………………. (7.15)
(7.15) – (7.14)
P (Vf – Vi) = (nf – ni) RT
PΔV= Δn(g)RT ………………… (7.16)
Substituting in 7.16 in 7.12
ΔH = ΔU + Δn(g)RT ……………… (7.17)
Enthalpy Changes for Different Types of Reactions and Phase Transitions:
The heat or enthalpy changes accompanying chemical reactions is expressed in different ways depending on the nature of the reaction. These are discussed below.
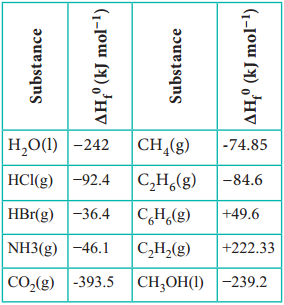
Standard Heat of Formation
The standard heat of formation of a compound is defined as “the change in enthalpy that takes place when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements, present in their standard states (298 K and 1 bar pressure)”. By convention the standard heat of formation of all elements is assigned a value of zero.
Fe(s) + S(s) → FeS(s)
ΔHf° = – 100.42 kJ mol-1
2C(s) + H2(g) → C2H2(g)
ΔHf° = + 222.33 kJ mol-1
\(\frac{1}{2}\)Cl2(g) + \(\frac{1}{2}\)H2(g) → HCl (g)
ΔHf° = – 92.4 kJ mol-1
The standard heats of formation of some compounds are given in Table 7.4.
Standard Heat of Formation of Some Compounds