Class 6 Science Chapter 2 Notes Diversity in the Living World
→ Biodiversity: The variety of plants and animals found in a region contributes to the biodiversity of that region.
→ Grouping: The method of arranging plants and animals into groups based on their common features is called grouping.
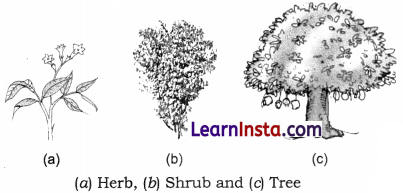
→ Herbs: The small plants with soft, tender, green, shorter stem are called herbs. Herbs hardly attain height more than 1.5 metres. Their stems are not woody and can be bent. A herb may or may not have branches, e.g. tomato, mint, paddy, mustard, etc.
→ Shrubs: The medium-sized plants with hard and partly woody stem are called shrubs. Branches arise mostly from the base of the stem giving the plant a bushy appearance without a clear trunk, e.g. China rose, duranta, lemon, jasmine, bougainvillea.
![]()
→ Trees: Trees are very tall plants with height of several metres. They have stout trunks which mostly bear branches near the top. The trunk is very hard and woody, e.g. mango, eucalyptus, gulmohar.
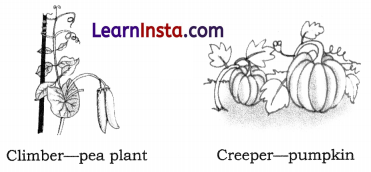
→ Climbers: Those plants that take support of neighbouring structures, as their stems are weak and climb up are called climbers. Climbers may have special organs such as hooks, tendrils and petioles that help the plant to climb, e.g. pea plant. Creepers: Some plants which have weak stems which cannot stand upright and are spread on the ground are called creepers, e.g. pumpkin, watermelon.
→ Veins: The lines on the leaf are called veins.
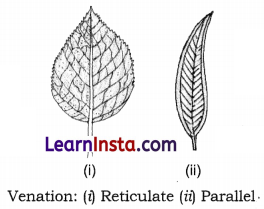
→ Leaf Venation: The design made by veins in a leaf is called leaf venation.
→ Reticulate Venation: When design of veins is net-like on both sides of the midrib, the venation is called reticulate venation, for example, leaves of peepal.
→ Parallel Venation: When veins are designed parallel to one another, it is called parallel venation. For example, in leaves of grass and wheat.
![]()
→ Taproots: The roots in which one root is the main root and small side roots arise from the main root are called taproots. Example: China rose and mustard.
→ Fibrous Roots: The roots which do not have any main root instead all roots are thin, of the same size and arise from the base of the stem are called fibrous roots. Example: Wheat and rice.
→ Seed coat: The outer covering of a seed is called the seed coat.
→ Cotyledon: Cotyledon is a part inside a seed which stores and provides food for the developing plant at the time of germination.
→ Dicotyledons: Plants that have seeds with two cotyledons are called dicotyledons.
→ Monocotyledons: Plants that have seeds with one cotyledon are called monocotyledons.
→ Rhododendron: Rhododendron is a plant with beautiful bright flowers found in the hilly areas.
→ Adaptations: The special features that enable plants and animals to survive in a particular region are called adaptations.
→ Movement: Change in the position from one place to another is called movement.
→ Habitat: The place where plants and animals live is called their habitat. For example, the habitat of sea turtles is the sea or the oceans.
![]()
→ Terrestrial habitats: The habitats of plants and animals that live on land are called terrestrial habitats. Some examples of terrestrial habitats are forests, deserts, grasslands, and mountains.
→ Aquatic habitats: The habitats of plants and animals that live in water are called aquatic habitats. Some examples of aquatic habitats are ponds, lakes, rivers, and oceans.
→ Amphibians: Animals which can live in water as well as on land are called amphibians. For example, frog and crocodiles.
→ Sacred groves: Sacred groves are undisturbed patches of forests that have special religious importance within a particular culture. These groves are protected by the local community and no one is allowed to harm any animal and cut tree in these groves.
→ Adaptation : The presence of specific features in the body which help a plant or animal to live or survive is called adaptation.
→ Monocot plants : Plants in which seeds have only one cotyledons are called monocot plants.
→ Analyse : It is examining of something by examing its parts and their relationship.
→ Amphibians : The organisms which use both water and land as their habitat are known as amphibians.
→ Parallel Venation : If the veins are parallel to each other, the venation is called parallel venation.
→ Compare : To be like or equal is to compare.
![]()
→ Aquatic : The organisms that live and breed in water are called aquatic.
→ Reticulate Venation : If the design of veins makes a net-like structure on both the sides of mid-rib, then it is called reticulate venation.
→ Create : Make or produce.
→ Biodiversity : It means different forms of living organisms or a variety of life forms found in a particular region.
→ Sacred groves : Group of trees.
→ Explore : Travel into or through in order to learn about it.
→Cotyledon : Plant embryos in seeds have structures called cotyledons.
→ Shrubs : They are medium-sized plants (1-3m in height) with thin branches starting from just above the ground.
→ Group : Number of people or things gathered.
→ Dicot Plants : Plant with seeds having two cotyledons are called dicots.
→ Tap-root : The tap-root is the main root from which many branching roots grow sideways.
→ Observe : To see or notice.
![]()
→ Fibrous root : A cluster of thin fibre like roots at the base of the stem is called fibrous root.
→ Terrestrial : Land.
→ Record : Write down facts.
→ Habitat : The place where a plant or animal lives is called its habitat.
→ Tree : Tree is tall and big plant with hard and thick woody stem.
→ Relate : Give an account
→ Herbs : Small plants (< 1 m in height) with green and soft stem are called herbs.
→ Venation : The design made by the veins in a leaf is called venation.
→ We are surrounded by a large variety of plants and animals. Such variety of plants and animals is a part of a biodiversity.
→ Bio-diversity means different forms of living organisms or a variety of life forms found in a particular region.
![]()
→ Plants and animals can be grouped on the basis of similarities and differences among them.
→ Plants have similarities and differences based on features associated with roots, stems, leaves, flowers and so on.
→ The method of arranging things into groups based on their common features is called grouping.
→ Plants can be grouped into herbs, shrubs, and trees based on their heights, types of stem and branching patterns.
→ Plants can also be grouped as dicotyledons (dicots) and monocotyledons (monocots) based on the number of cotyledons in their seeds.
→ Plants with seeds having a single cotyledon are called mono-cotyledonous or monocots.
→ Plants with seeds having two cotyledons are called dicots.
→ Monocots generally exhibit parallel venation in their leaves and possess fibrous roots while dicots typically exhibit reticulate venation in their leaves and possess taproots.
→ Animals have different type of movement that can be a basis for their grouping.
→ Biodiversity of different regions varies because of district environmental conditions.
![]()
→ The special features that enable plants and animals to survive in a particular region is called adaptations.
→ The place where plants and animals live in their habitat.
→ Based on their habitats, animals and plants can be grouped into terrestrial and aquatic.
→ Due to damage of their habitats, plants and animals lose their homes, food and other resources resulting in the loss of biodiversity.
→ The plants having leaves with reticulate venation have tap roots.
→ The fleshy stems of plants found in the desert can store water and help them tolerate the hot conditions in these places.
→ We must protect bio-diversity to ensure that our planet is full of life, helping plants and animals to survive and thrive.
Introduction
We see different kinds of plants at various places. Some are found in water and others are present on land in your house, school, farmhouses and on roadside. Different plants give flowers of different colours and sizes.
→ Diversity in Plants: Depending on their features plants are divided into herbs, shrubs and trees. Herbs : Herbs are small ( <1m} in height) plants having a soft and delicate stem. Herbs have a green and tender stem. They live for a few months. Examples: Mustard, Coriander, Tomato, Radish, Carrot, Ginger, Turnip etc.
→ Shrubs: Shrubs are medium-sized (1-3m) plants with hard and woody stems. Shrubs live for many years. Shrubs are not small like the herbs. May branches are seen rising just above the ground. Examples: China rose, rose, lemon, bougainvillea, henna (mehndi) etc.
→ Trees : Trees are tall and large plants (>3m in height) with hard and woody stem. They have one main stem, called trunk. The trunk gives out many branches at certain height. Trees live for many years. Examples : Mango, neem, peepal, babool, gulmohar, amattes etc. Some plants do not have a strong stem and cannot stand erect. These plants grow along the ground. They are called creepers. A creeper grows along the ground or other surfaces by extending long shoots or branches. Examples: Strawberry plant, mont etc. Most creepers live for few months.
![]()
→ Climbers: Some plants have weak stems that take support of the neighbouring plant/ support to climb up. Such plants are called climbers. Examples: Pea, money plants etc. The climber plants have climbing organs like tendrils on their stems or leaves.
How To Group Plants And Animals ?
We are surrounded by a variety of plants and animals with different features. We can group them based on similarities and differences among them.
→ Grouping of Plants : We can group them based on similarities and differences among them. By studying one representative of a group, a broad idea regarding all organisms of the group can be obtained.
→ How to group plants? Plants show variation in the features related to stems, leaves, flowers etc. The stems of different plants vary in thickness, height and hardness, while the leaves vary in the shape, colour, size and arrangements.
Plants can also be grouped into herbs, shrubs and trees based on their height and types of stem.
![]()
Types Of Plants
→ Tree: Trees are tall and large plants (>m in height). They have hard, thick, brown and woody stems. Their branches typically start higher up on the stem and away from the ground.
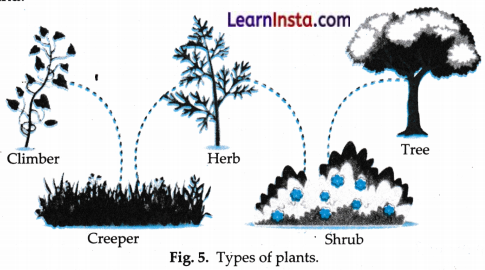
→ Shrubs: Shrubs are medium sized plants (1-3 m in height) with thin branches from just above the ground. Their stem is hard and thin. For example, a rose plant is a shrub [Fig. 5 (b)].
→ Herbs: Small plants (< 1 m in height) with green and soft stem are called herbs. For example, a tamato plant is a herb [Fig. 5 (c)].
→ Climbers: Some plants with weak stems need support to climb and grow, are called climbers. For example, pea and money plant.
→ Creepers: Some plants creep along the ground and are called creepers. For example, mint and gourd.
→ Leaf : The leaf is a thin, broad, flat and green part of a tree which is attached to the stem (or branch). The leaves of most plants are flat and green. There are, however, some plants whose leaves are coloured.
![]()
→ Parts of a leaf: A leaf consists mainly of two parts: lamina and petiole. Lamina is commonly known as leaf blade and petiole is commonly known as leaf stalk. The broad green part of the leaf is called lamina. The thin stalk with which leaf is attached to the stem (or branch) is called petiole. There is a mid-rib (main vein) in the centre of lamina. A large number of veins spread out from the mid-rib to all the parts of the leaf.
→ Venation: The arrangement of veins on the leaf blade is called venation. If the design is not like on both the slides of mid-rib, the venation is called reticulate. If the veins are parallel to each other, the venation is called parallel venation.
→ Roots of the plant: The part of a plants which is below the ground (in the soil) is called root.
→ Roots are mainly of two types:
- Tap Roots: The tap root is the main root from which many branching roots grow sideways. Some of plants having tap roots are: Pea plant, Neem tree, Mango tree, Carrot, Radish etc.
- Fibrous Roots: A cluster of thin fibre like roots at the base of the stem is called fibrous root. Plants of wheat, maize, grass, millet etc., have fibrous roots.
![]()
→ Cotyledons : Plants embryos in seeds have structures called cotyledons. Plants with seeds having a single cotyledon are called monocotyledons or monocots. Examples: Wheat, Rice, Maize etc. Plants with seeds having two cotyledons are called dicots. Example : Pea, Green Mustard, etc.
How To Group Animals?
Animals move from place to place. It is necessary for the animals to be able to move from one place to another to find food and escape from the enemies. Many animals walk with their legs. Different animals use different organs to move from one place to another.
Janaki Ammal (1897—1984):
She was an Indian botanist. She was dedicated to environmental work. She helped to document and preserve India’s rich plant biodiversity. She played a main role in the “Save Silent Valley” movement.

→ Success Story— Save Silent Valley Movement: This is a real story of a forest in Palakkad district of Kerala. The famous silent valley was saved by a movement led by common people who were not even residing in the vicinity of the forest. The battle against the proposal of a hydro-electric dam across the Kunthipuzha river persisted for 10 years. People used all possible available means, such as awareness, programmes, letters to editors, articles in newspapers, seminars and petitions and appeals in court. The movement was successful in saving the silents valley.
→ Plants And Animals In Different Surroundings:
Different animals live in different surroundings. The movement of these animals depend upon their surroundings. Fish live in water. They have streamlined bodies and fins for movement in water Fig. 10(a)]. Goats live in grassy areas and move with the help of legs (Fig. 10(b)]. The sizes and shape of animals also differ from one another.

→ The plants and animals found in one region are different from those found in another kind of region.

→ Features of desert plants/animals (Cactus)
- The leaves in desert plants are either absent or very small.
- Leaves are converted into spines which help to reduce loss of water.
- The stems become thick, flat and green.
- The stem is covered with waxy layer which helps to retain water.
- The roots go very deep in the soil to absorb water.
![]()
→ Features of mountain plants / (Deodar)
- The shape of the trees is normally cone type.
- Branches are sloping.
- The leaves of these trees are needle like.
These adaptations help the rainwater and snow to slide off easily. The biodiversity varies from region to region because of diverse conditions There is a very little water available in deserts. A desert is typically very hot during the day and very cold of night. Hence, we find plants and animals in these areas that can tolerate and survive both the hot conditions during the day and cold conditions at night. The fleshy stems of plants found in the desert can store water and help them tolerate the hot conditions in these places.

The mountains in extremely cold regions experience frequent snowfall. To survive in such conditions, some of the trees have the ability to let the snow slide off easily. Conical shape and sloping branches of deodar trees make able them to do so easily.
→ Camel : Observe the images of a candle from hot desert of Rajasthan and a camel from the cold deserts of Ladakh.

→ The camel in the hot desert has long legs with wide hooves. The long legs and wide grooves help these camels to walk on the sandy desert without sinking into the saved. On the other hand, the height and legs of camels in a cold desert are comparatively shorter than those found in a hot desert. These short legs allow them to walk easily in mountainous region.
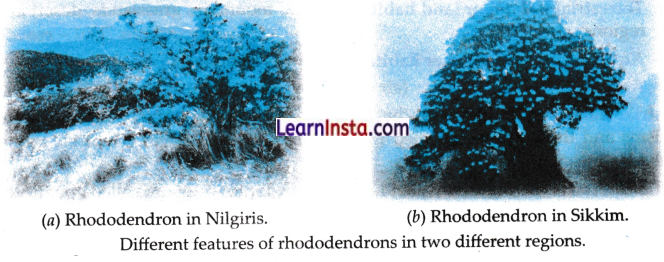
→ Rhododendrons: Even plants such as rhododendrons may show different features in different regions to survive the conditions of those regions. In the Shola forests of Nilgiris, rhododendrons are of shorter height and have smaller leaves to survive through the heavy winds on mountain tops. Rhododendrons in nearby mountains of Sikkim are taller.
→ We saw huge whales and colourful fish in the ocean of Andaman and Nicobar islands. The head, trunk and tail of a fish merge to form a streamlined shape. The streamlined body shape helps the fish to move through the water easily because such a shape offers least resistance to motion.
The plants and animals living in a particular region have special features that make them fit to survive there. The special features that enable plants and animals to survive in a particular region are called adaptations.
→ Habitat: The place where plants and animals live is called their habitat. The habitat of sea turtles is the sea or the ocean. The habitat of a camel is the hot or the cold desert, and the habitat of a rhododendron is the mountains.
![]()
→ A habitat must provide to the organisms living there-in the following:
- Food
- Shelter and
- Favourable climate conditions to survive, breed and flourish.
Many type of plants and animals may share the same habitat. Habitat plays an important role in shaping the biodiversity of a region.
Salim Ali (1896-1987)
→ Salim Ali (1896-1987) a scientist: Salim Ali (a scientist) travelled across India to observe diversity in birds. He prepared a list of birds and documented their travel routes and habitats. He recorded the regions with high diversity of birds and took measures to conserve these regions.

→ Keoladao National Park : In Bharatpur, Rajasthan and Ranganathittu Bird Sanctuary in Mandya, Karnataka are examples of regions be preserved.
He wrote a series of 10 books on birds of the Indian sub-continent. He is referred to as the ‘Birdman of India’. He was awarded Padma Vibhushan in 1976.
→ Types of Habitat : There are three main habitats in the biosphere.
- Terrestrial habitat or land habitat : Forest, mountain, grasslands, desert and coastal regions.
- Aquatice habitat or water habitat: Sea, lake, river, pond.
- Aerial or arboreal habitat : (air or tree)-Tropical forests.
→ Terrestrial Habitat: The organisms that live, grow and propagate on land are called terrestrial organisms and their habitat is called terrestrial habitat. Man, Tiger, Trees etc are terrestrial organisms.
→ Aquatic Habitat : The organisms that live and breed into water are called aquatic organisms and their habitat is called aquatic habitat. Fish, whales etc. are aquatic organisms, oceans, seas, rivers, lakes etc. are aquatic habitat.
![]()
→ Arboreal Habitat : The organisms that use trees for their activities are known as arboreal organisms. All birds, such as Eagle, Swallow etc are arboreal.
The organisms which use both water and land as their habitat are known as ambhibian organism. Frog, Crocodile, etc. are ambhibians.
The damage to habitats of plants and animals result in loss of their homes, food and other resources. This lead to the loss of biodiversity.
The population of the Bengal Tiger, Cheetah and Great Indian Bustard have declined in India due to loss of natural habitats caused by human activities. The Government of India has initiated several projects to conserve our biodiversity. “Project Tiger” was initiated in 1973 to protect the declining population of the Bengal Tiger. The Cheetah Reintroduction was initiated in 2022 to restore the population of the Cheetah. Habitats of the Great Indian Bustard have been declared as protected areas in the States of Gujarat, Rajasthan and Maharashtra.

→ Traditionally Protected Forests: Sacred Groves are undisturbed patches of forests. Their sizes may vary from quite small to very large. Sacred groves are found all over India. They are home to different kinds of plants and animals. These are protected by the local community. No one is allowed to horn any animals and cut trees in these groves. In this way, sacred groves are a community protected treasure of biodiversity. We must protect biodiversity to ensure our planet full of life, helping plants and animals to survive and thrive.
