Diversity in the Living World Class 6 Extra Questions and Answers Science Chapter 2
Diversity in the Living World Class 6 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
List few plants found around your house.
Answer:
Mango, neem, grass, chilli, palak and banyan tree.
Question 2.
Are all the plants same in size?
Answer:
No, all plants are of different sizes.
Question 3.
How many kinds of plants are there?
Answer:
There are three kinds of plants:
- Herbs
- Shrubs
- Trees
Question 4.
Name two plants that belong to herbs.
Answer:
- Tomato
- Potato
Question 5.
Give two examples of shrubs.
Answer:
- Lemon
- Orange
![]()
Question 6.
Give two examples of trees.
Answer:
- Mango
- Neem
Question 7.
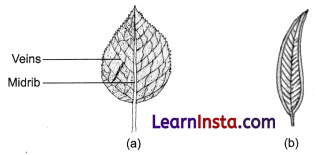
What are veins?
Answer:
The lines on the leaf are called veins.
Question 8.
What is leaf venation?
Answer:
The design made by veins in a leaf is called leaf venation.
Question 9.
How many types of leaf venation are there?
Answer:
There are two types of leaf venation:
- Reticulate venation
- Parallel venation
Question 10.
Name the types of roots shown in the Fig.
im-1
Answer:
(a) Taproot
(b) Fibrous roots
Question 11.
What are taproots?
Answer:
The roots in which one root is main root and other side roots grow on it are called taproots.
Question 12.
Give names of two plants which have taproot.
Answer:
Gram and mustard.
Question 13.
Name two plants which have fibrous root.
Answer:
- Wheat plant
- Maize plant
Question 14.
What are fibrous roots?
Answer:
The roots which do not have any main root instead all roots are thin, of the same size and arise from the base of the stem are called fibrous roots.
Question 15.
Name a plant found on mountains.
Answer:
Deodar.
Question 16.
What is habitat?
Answer:
The place where organisms live and which provide food and safety for them is called habitat.
![]()
Question 17.
Name a few habitats.
Answer:
Forests, grasslands, mountains, ponds and oceans, etc.
Question 18.
Name two organisms that live in deserts.
Answer:
Cactus and camel.
Question 19.
Name the habitats where various types offish live.
Answer:
Pond, river, sea.
Question 20.
Name a common thing in all fish.
Answer:
Streamlined body.
Question 21.
Name two aquatic animals.
Answer:
- Fish
- Turtle
Question 22.
Name two terrestrial organisms.
Answer:
- Cat
- Dog
Diversity in the Living World Class 6 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Classify plants and give an example of each.
Answer:
On the basis of various characteristics most of the plants can be classified into three categories:
- Herbs, e.g. tomato
- Shrubs, e.g. lemon
- Trees, e.g. mango
Question 2.
What are herbs? Give two examples.
Answer:
The plants with green and tender stems are called herbs. They are usually short and may have no or less branches. For example, tomato, potato.
Question 3.
What are shrubs? Give two examples.
Answer:
The plants which have a hard but not a very thick stem are called shrubs. Such plants have the stem branching out near the base. For example, lemon, rose plants.
Question 4.
What are trees? Give two examples.
Answer:
The plants which are very tall and have hard and thick brown stem are called trees. The stems have branches in upper part and much above the ground. For example, mango, neem.
Question 5.
What are creepers? Write an example.
Answer:
The plants with weak stem that cannot stand upright and spread on the ground are called creepers. Various types of grasses are the example of creepers.
Question 6.
What are climbers?
Answer:
The plants that take support of neighbouring structures and climb up are called climbers. They have weak stems. For example, grapes, money plant.
Question 7.
Differentiate between taproot and fibrous root.
Answer:
| Taproot | Fibrous root |
| 1. Taproot has only one main and long root. The smaller roots that grow from the main root are called lateral roots. | 1. Fibrous roots do not have a main root. All roots seem similar. |
| 2. Taproot goes deep into the soil. | 2. They do not go deep into the soil. |
| 3. Taproots are found in plants which have reticulate venation in their leaves. | 3. These are found in plants which have parallel venation in their leaves. |
Question 8.
What is a habitat?
Answer:
The surroundings where animals live are called their habitats. The organisms depend on their habitat for their food, water, air, shelter and other needs. Habitat means a dwelling place.
![]()
Question 9.
How is cactus adapted to survive in a desert?
Answer:
Cactus is adapted to survive in a desert as it has:
- No leaves or spiny leaves to prevent water loss through transpiration.
- It stores water in its fleshy stems.
- Its roots go very deep into the soil for absorbing water.
Question 10.
What are the differences in the desert and sea regions?
Answer:
In the sea, plants and animals are surrounded by sally water. In desert, a very little amount of water is available. It is very hot in the day time and very cold at night.
Question 11.
How are camels adapted to live in desert?
Answer:
- The feet of the camels have thick, flat large soles which help them in the movement on sand.
- The long legs of camel help in keeping the body away from the heat of the sand.
- They can live without water for a long time. When water is available, it drinks large amount of water at a time.
- They release very little urine to prevent loss of water.
Question 12.
Explain the adaptation of trees to live in mountain regions.
Answer:
- The shape of the trees is of normally cone type.
- Branches are sloping.
- The leaves of these trees are needle-like.
Question 13.
Explain the adaptation of animals to live in mountain region.
Answer:
- The animals have thick skin or fur to protect themselves from the cold.
- Some animals have thick fur on their body, feet and toes which protect them from cold on walking in the snow.
- The goats have strong hooves for running up on rocky slopes.
Question 14.
What are sacred groves?
Answer:
Sacred groves are undisturbed patches of forests. These are protected by the local community and no one is allowed to harm any animals and cut trees in these groves, or disturb the area. This way, sacred groves are a community protected treasure of biodiversity.
Question 15.
Why do humps of camels living in cold deserts of Ladhak shrink in late winters?
Answer:
Camels store food in their humps. Camels in the cold desert have two humps each. These two humps shrink in late winters because there is not much food available in the cold desert and they have to use food stored in their humps during that time.
Diversity in the Living World Class 6 Long Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Identify the following plants as herbs, shrubs and trees.
(i) tomato
(ii) rice
(iii) eucalyptus
(iv) blueberry
(v) China rose
(vi) lavender
(vii) mango
Answer:
(i) tomato-herb
(ii) rice-herb
(iii) eucalyptus-tree
(iv) blueberry-shrub
(v) China rose-shrub
(vi) lavender-herb
(vii) mango-tree
![]()
Question 2.
What do you mean by leaf venation? Explain various types of leaf venation with example.
Answer:
Leaf venation: The design made by veins in a leaf is called leaf venation. There are the following two types of leaf venation:
(i) Reticulate venation: If the design of veins makes a net-like structure on both the sides of midrib then it is called reticulate venation. For example, mango leaf, gram leaf.
(ii) Parallel venation: If the veins are parallel to each other or to midrib then such type of venation is called parallel venation. For example, wheat leaf, barley
Question 3.
Explain various kinds of roots with the help of an example.
Answer:
There are following two types of roots:
(i) Taproots: The roots which have one main root and other smaller lateral roots are called taproots. For example, mustard plant, gram.
(ii) Fibrous roots: The roots which have no main root but all the roots appear similar are called fibrous roots. For example, maize, wheat.
Question 4.
What do you mean by the terms dicot plants and monocot plants? Is there any relation exist among leaf venation, root types and the number of cotyledons in seeds of a plant?
Answer:
Some seeds such as chickpea seeds can split into two parts, each called a cotyledon. Plants that have seeds with two cotyledons are called dicot plants. On the other hand, some other seeds such as maize has a single thin cotyledon. Plants with such seeds are called monocot plants.
Dicot plants (plants that have seeds with two cotyledons) have reticulate venation and a taproot system while monocot plants (plants that have seeds with one cotyledon) have parallel venation and a fibrous root system.
Question 5.
How are camels living in hot desert differ from the camels living in cold desert?
Answer:
| Camels living in hot desert | Camels living in cold desert |
| 1. The camels in the hot desert have long legs with wide hooves. | 1. The height and legs of camels in a cold desert are comparatively shorter than those found in a hot desert. |
| 2. Camels in the hot desert have one hump. | 2. Camels in the cold desert have two humps which shrink in late winters. |
| 3. Camels in the hot desert do not grow long hair from head to neck. | 3. Camels in the cold desert grow long, hair from head to neck, which help them survive in the cold winters. |
Diversity in the Living World Class 6 Skill-Based Questions
Question 1.
Draw a diagram to show (a) herb, (b) shrub and (c) tree.
Answer:

Question 2.
Identify the following figure and write two characteristics of it.

Answer:
It is figure of a fibrous root.
Characteristics:
- All roots emerge from the base of stem.
- These roots do not go deep into the soil.
![]()
Question 3.
Identify the seeds a and b. How many cotyledons do these seeds have? In which category (dicot or monocot) would you keep their plants?
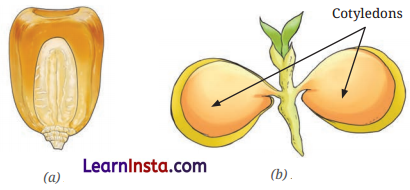
Answer:
Fig. a is maize seed which has only one cotyledon. This is a monocot seed.
Fig. b is a gram seed which has two cotyledons. This is a dicot seed.
Question 4.
Write the names of movements performed by the following animals and the organs that they use to move from one place to another.
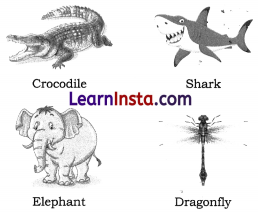
Answer:
- A crocodile crawls with its four short legs.
- A shark swims with its fins.
- An elephant runs and walks with its four legs.
- A dragonfly flies with its wings.
Question 5.
Identify the animal shown in the figure. Why this animal is known as amphibian? Give an adaptation found in this animal.

Answer:
In the figure, a frog is shown. This is known as amphibian because it can live on land as well as in water. It has strong hindlimbs to jump on the land and webbed feet to swim in water.
Diversity in the Living World Class 6 Case-Based Questions
Question 1.
Plants can be divided into mainly three categories: herbs, shrubs and trees. Plants with green and tender stems are called “herbs’. They are usually short and may not have many branches. For instance- tomato. Some plants develop branches near the base of stem. The stem is somewhat hard but not very thick. Such type of plants are called ‘shrubs’. For example- lemon. Some plants are very tall and have hard and thick stem. In such plants, the stems have branches in the upper part, Question uite above the ground. Such plants are called “trees’. For instance- apple. Plants with weak stems that cannot stand upright but spread on the ground are called ‘creepers’, while those that take support and climb up are called ‘climbers’. These are different from the above discussed three categories.

I. Give an example of herb.
II. Which term we use to define the plants that spread on the ground.
III. Name the plant type, in which the stems have branches in the upper part, much above the ground.
IV. What do you mean by shrubs? Give an example too.
Answer:
I. Tomato.
II. Creepers.
III. Trees.
IV. Some plants develop branches near the base of stem. The stem is somewhat hard but not very thick. Such type of plants are called shrubs. For example- lemon.
![]()
Question 2.
There is very little water available in the desert. It is very hot in the day time and very cold at night in the desert. The animals and plants of the desert live on the desert soil and breathe air from the surroundings. The body structure of a camel helps it to survive in desert conditions. Camels have long legs which help to keep their bodies away from the heat of the sand. They excrete small amount of urine, their dung is dry and they do not sweat.
In the sea, plants and animals are surrounded by saline (salty) water. Most of them use the air dissolved in water. If you see different types of fish, you will find that all fish have streamlined shape, which helps them move inside the water. Their bodies are covered with scales and these scales do not let water to enter inside their bodies. Fish have fins and tails that they use to change direction and maintain balance in water. Fish have gills to breathe. Gills allow the fish to take up dissolved oxygen from the water.
I. What help fish to change their directions in water?
II. How do fish breathe in water?
III. What is the advantage of scales to fish?
IV. Describe the features that enable camels to survive in desert conditions.
Answer:
I. Fish use fins and tails to change their direction.
II. Fish have gills to breathe. Gills allow the fish to take up dissolved oxygen from the water.
III. The body of fish is covered with scales. These scales do not let water to enter inside the body.
IV. (a) Camels have long legs which help to keep their bodies away from the heat of the sand.
(b) They excrete small amount of urine,
(c) Their dung is dry and they do not sweat.