New Empires and Kingdoms Class 6 History Chapter 11 Extra Questions and Answers Social Science CBSE Pdf free download are part of Extra Questions for Class 6 Social Science. Here we have given NCERT Extra Questions for Class 6 Social Science SST History Chapter 11 New Empires and Kingdoms.
You can also practice NCERT Solutions for Class 6 History Chapter 11 Questions and Answers on LearnInsta.com.
Class 6 History Chapter 11 Extra Questions and Answers New Empires and Kingdoms
New Empires and Kingdoms Class 6 Extra Questions and Answer History Chapter 11 Very Short Answers Type
Question 1.
Who was Samudragupta?
Answer:
Samudragupta was a famous ruler of dynasty known as the Guptas around 1700 years ago.
Question 2.
Who was the founder of the Gupta dynasty?
Answer:
Chandragupta Maurya was the founder of Gupta dynasty.
Question 3.
Name the title which was used by the Gupta dynasty.
Answer:
They were known as Maharaj-adhiraja.
Question 4.
Who was Harishena?
Answer:
Harishena was poet and a minister in the court of Samudragupta.
Question 5.
Which were important centres of the Gupta’s regime?
Answer:
Prayaga, Ujjain and Pataliputra were important centres of the Gupta rulers.
Question 6.
What is new name of Prayag?
Answer:
Allahabad is new name of Prayag.
Question 7.
What do you know about mother and father of Samudragupta?
Answer:
Samudragupta’s mother’s name was Kumara Devi. She belonged to the Lichchhavi gana. His father’s name was Chandragupta, who was first ruler of the Gupta dynasty.
Question 8.
Who was Kalidasa?
Answer:
Kalidasa was a poet and was in the court of Chandragupta II.
Question 9.
Who was Aryabhata?
Answer:
Aryabhata was a famous astronomer and was in the court of Chandragupta II.
Question 10.
Who was Banbhatta?
Answer:
Banbhatta was a poet of Harshavardhana’s court.
Question 11.
Give the name of book written by Banbhatta.
Answer:
Banbhatta wrote a famous book called Harshacharita.
Question 12.
In which court did Xuan Zang spend a lot of time?
Answer:
Xuan Zang spent a lot of time in the court of Harshavardhana.
Question 13.
Which were dynasties in the South India?
Answer:
During the same period, in south India there were most important ruling dynasties—the Pallavas and Chalukyas.
Question 14.
Which was the capital of the Pallavas?
Answer:
Kanchipuram was the capital of the Pallavas.
Question 15.
Who was the best known Chalukya ruler?
Answer:
The best known Chalukya ruler was Pulakeshin-II.
Question 16.
Name the Chalukyas capital. Why was the capital famous?
Answer:
The Chalaukyas capital was Aihole. The capital was an important trading centre and a religious centre with a number of temples.
Question 17.
Where was reign of the Chalukyas situated?
Answer:
It was centered around the Raichur Doab, between the rivers Krishna and Tungabhadra.
Question 18.
Which dynasties raided one another?
Answer:
The Pallavas and Chalukyas frequently raided one another.
Question 19.
What do you understand about hereditary post?
Answer:
In the regime of some ruler, some important administrative posts were now hereditary. This means that sons succeeded fathers to these posts.
Question 20.
What was the Chief judicial officer called?
Answer:
He was called maha-danda-nayaka.
Question 21.
What was the Minister of war and peace called?
Answer:
He was called sandhi-vigrahika.
Question 22.
What was given by the king to the samantas for providing troops?
Answer:
The King provided lands to the samantas.
Question 23.
Which was the language used by the King and brahmins in regime of Guptas?
Answer:
As written by Kalidasa that king and most Brahmins used Sanskrit.
Question 24.
What do you understand about ‘ur* assembly?
Answer:
The W was a village assembly found in areas where the land owners were not brahmins.
Question 25.
What was ‘nagram’?
Answer:
‘Nagram’ was an organization of merchants.
New Empires and Kingdoms Class 6 Extra Questions and Answer History Chapter 11 Short Answers Type
Question 1.
Write a short note on new kind of army of this period.
Answer:
There were military leaders who provided the king with troops whenever he needed them. They were not paid regular salaries. Instead, some of them received grants of land. They collected revenue from the land and used this to maintain soldiers and horses, provide equipment for warfare. These men were known as samantas.
Question 2.
What was the system adopted by the Pallava rulers?
Answer:
In the Pallavas ruling, there were many local assemblies of Brahmin land owners. Assemblies functioned through sub-committees. These looked after irrigation, agricultural operations, making roads, local temples, etc.
Question 3.
How did the Islam come in India?
Answer:
Within a hundred years, Islam spread to north Africa, Spain, Iran and India. Arab sailors, who were already familiar with the coastal settlements of the subcontinent, brought the new religion with them. Arabs soldiers conquered Sind about 1300 years ago.
Question 4.
Describe the livelihood of Arabian people.
Answer:
Arab merchants and sailors played an important role in the sea trade between India and Europe. They lived in Arabia and were Bedouins, pastoral tribes depending mainly on camels as hardly any animal could survive in the desert.
New Empires and Kingdoms Class 6 Extra Questions and Answer History Chapter 11 Long Answers Type
Question 1.
Write a short note on the untouchability existing in the society as stated by the Fa Xian.
Answer:
The Chinese pilgrim Fa Xian noticed that there were problems existing for those who were treated as untouchables by the high and mighty. Untouchables were expected to live on the outskirts of the city. If such a man entered in a town or a market place, he/she was required to strike a piece of wood, in order to keep himself separate. People hearing this sound, knew what it meant and avoided touching him.
Question 2.
Write a short note on the teaching of Islam.
Answer:
Around 1400 years ago, Prophet Muhammad introduced a new religion, Islam, in Arabia. Islam was a religion that laid stress on the equality and unity of all. No one is supreme, but Allah, who is only one supreme God. No one has partnership with Allah. Neither he takes birth and nor dies. Anyone cannot see him but no one is out of reach of Allah.
Holy Quran is the book of Islam. As per Islam, the Muslims who believe in Islamic teaching, are devout, patient and constant, humble, gives charity to the poor or needy, who fast in love of Allah, guard their chastity, engage much in Allah’s remembrance and follow the path of Prophet etc., for them Allah prepared forgiveness and great rewards. Islamic teachings are very much broad which cover almost whole life activities.
Question 3.
Write a note on assemblies and their functions in the southern kingdoms.
Answer:
We find descriptions from inscriptions about the Pallavas regime. These assemblies included the ‘sabha’. Sabha was an assembly of Brahmin land owners. This assembly functions with the help of sub-committees. These sub-committees look into the work of irrigation, agriculture, road making, temple making etc. The ‘ur’ were assemblies at village level.
The ‘ur’ was in the areas where landowners were not Brahmins. An another type of assembly was in existence that was called nagaram, which was organization of merchants that were also controlled by rich and powerful landowners and merchants. No doubt, these assemblies played an important role in strengthening the kingdom.
Question 4.
Give the genealogies of the Gupta dynasty.
Answer:
The evidence of genealogy of the Gupta dynasty is found from an inscription. One prashasti mentions Samudragupta’s great grandfather, father and mother. His mother’s name was Kumara Devi. She belonged to the Lichchhavi gana.
His father Chandragupta was the ruler who adopted title of maharaj- adhiraj. His grandfather simply used maharaja. His son was Chandragupta-II who led to western India.
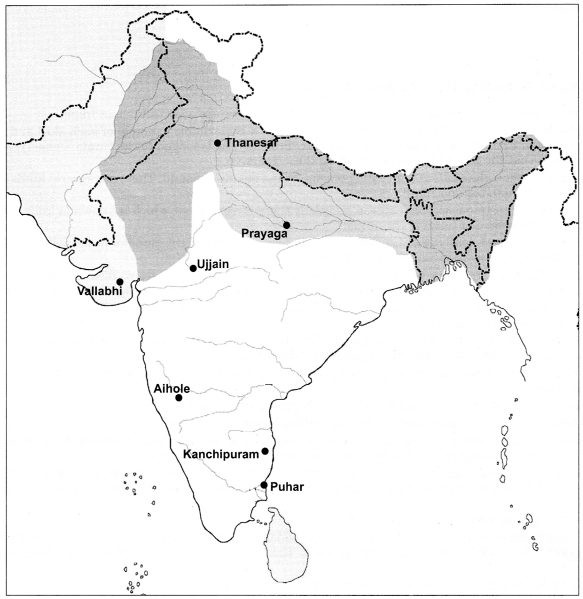
Map-Based Questions Class 6 History Chapter 11 Traders, Kings and Pilgrims
Question 1.
Indicate following locations in the map:
(a) Thanesar
(b) Kanchipuram
(c) Puhar
(d) Vallabhi
(e) Prayaga
(f) Ujjain
(g) Aihole
Answer: