What, Where, How and When? Class 6 History Chapter 1 Extra Questions and Answers Social Science CBSE Pdf free download are part of Extra Questions for Class 6 Social Science. Here we have given NCERT Extra Questions for Class 6 Social Science SST History Chapter 1 What, Where, How and When?.
You can also practice NCERT Solutions for Class 6 History Chapter 1 Questions and Answers on LearnInsta.com.
Class 6 History Chapter 1 Extra Questions and Answers What, Where, How and When?
What, Where, How and When? Class 6 Extra Questions and Answer History Chapter 1 Very Short Answers Type
Question 1.
How can we know about the past?
Answer:
By studying History, we can know about the past.
Question 2.
Where did people live in the early period?
Answer:
In the early period, people lived on the banks of the river Narmada for several hundred thousand years.
Question 3.
Who lived near the river Narmada?
Answer:
Gatherers lived near the river Narmada.
Question 4.
From where did gatherers get their food?
Answer:
Gatherers got their food by hunting and they collected roots, fruits and other forest produce for their food.
Question 5.
Where are the ‘Sulaiman’ and ‘Kirthar’ Hills located?
Answer:
The ‘Sulaiman’ and ‘Kirthar’ hills are located in the modern-day Pakistan.
Question 6.
Give the name of the crops which were grown about 8000 years ago.
Answer:
Wheat and barley were grown about 8000 years ago.
Question 7.
Give the name of places where wheat and barley grew about 8000 years ago?
Answer:
In Sulaiman and Kirthar hills, wheat and barley grew about 8000 years ago.
Question 8.
Which animals were reared by the early people?
Answer:
Sheep, goat and cattle.
Question 9.
Where are Garo hills are located?
Answer:
The Garo hills are located in the north-east of India.
Question 10.
Where are Vindhyas located?
Answer:
Vindhyas are located in Central India.
Question 11.
What was developed in Vindhyas and Garo hills?
Answer:
Agriculture was developed in Vindhyas and Garo hills.
Question 12.
Give the name of places where rice was first grown.
Answer:
The places where rice was first grown are to the north of the Vindhyas.
Question 13.
Is the river SON tributary of the river Ganga?
Answer:
Yes, the river SON is tributary of the river Ganga.
Question 14.
What was the south of the Ganga called?
Answer:
Magadha was called the part of south Ganga.
Question 15.
Why was Magadha famous?
Answer:
Magadha was famous because its rulers were powerful, and set up a large kingdom.
Question 16.
Which languages were used for writing manuscripts?
Answer:
Sanskrit, Prakrit, and Tamil languages were used for writing manuscripts.
Question 17.
Name two words we often used for our country.
Answer:
Two of the words we often use for our country are India and Bharat.
Question 18.
What do scripts consist of?
Answer:
Scripts consist of letters or signs.
Question 19.
Where is ‘Rosetta’ town located?
Answer:
In Egypt.
Question 20.
Where was the inscribed stone found?
Answer:
Inscribed stone was found in Rosetta, a town on north coast of Egypt.
Question 21.
In which languages and scripts were inscriptions written on inscribed stone which was found in Rosetta?
Answer:
Greek and two forms of Egyptian.
Question 22.
What are the occupations of the people in the Andaman Islands?
Answer:
The people of the Andaman Islands are engaged in fishing, hunting and collecting forest produce.
Question 23.
Name the things that archaeologists found during excavation.
Answer:
The archaeologists found tools, pots, weapons, pans, coins and ornaments during excavation.
Question 24.
What was the job of religious teachers?
Answer:
Religious teachers moved from one place to another to offer instruction and advice to the people who they met on the way.
What, Where, How and When? Class 6 Extra Questions and Answer History Chapter 1 Short Answers Type
Question 1.
Why is it important to know about the past?
Answer:
It is important to know the past because it tells us how people lived in that time, what they used to eat, wear, what kind of animals they had, how much civilization was developed, how they were living. Additionally, history also warns us not to repeat the mistakes and points out its consequences.
Question 2.
What are the sources to know the past?
Answer:
Sources are referred to the information found from manuscripts, inscriptions and archaeology. Once sources are found, learning about the past becomes an adventure, as we reconstruct it bit by bit. So, historians and archaeologists use sources like clues to find out about our pasts.
Question 3.
Who are archaeologists? What are the works of archaeologists?
Answer:
There were things that were used in the past. Those who study these objects are called archaeologists. They study the remains of buildings made of stones and bricks, paintings and sculptures. They also explore and excavate to find tools, coins etc.
Question 4.
Why is South Asia called subcontinent?
Answer:
South Asia is called a subcontinent because although it is smaller than a continent, it is very large, and is separated from the rest of Asia by seas, hills and mountains.
Question 5.
What were the problems faced by people while travelling from one part to another part of subcontinent?
Answer:
While people travelled from one part to another part of subcontinent, they had to face the hills and high mountains including the Himalayas, deserts, rivers and seas that made journey dangerous at times but never impossible.
Question 6.
‘Historians and Archaeologists are like detectives’. Explain.
Answer:
Whatever the sources founded from the inscriptions, manuscript, etc., historians and archaeologists study those sources or objects. This is like an adventure for them to find about the History on the basis of sources. Sources are like clues for them. They are like detectives who use all these sources like clues to discover about the past.
Question 7.
What do you know about ‘Bharata’?
Answer:
The name ‘Bharata’ was used for a group of people who lived in the north west and it is mentioned in the Rigveda, later it was used for the country. Rigveda is the earliest composition among all the Veda and it is written in Sanskrit.
What, Where, How and When? Class 6 Extra Questions and Answer History Chapter 1 Long Answers Type
Question 1.
How was our country named?
Answer:
The word India comes from the Indus called Sindhu in Sanskrit. The two words we generally use for our country are India and Bharat. About 2500 years ago, the Iranians and Greeks who came through the northwest were familiar with the Indus, called it the Hindos or the Indos. The land to the east of the river (i.e., the Indus) called India.
About 35000 years ago in Rigveda (the earliest composition in Sanskrit), the name Bharata was mentioned which was used by a group of people who lived in the north¬west. Later, it was used for the country.
Question 2.
What do you mean by decipherment? Give example.
Answer:
Inscriptions are written on hard surfaces. Many were written several hundreds of years ago. All inscriptions contain both scripts and languages. Languages which were used, as well as script have changed over time. Scholars understand the written words by the process of decipherment.
One of the most famous stories of decipherment comes from Egypt where there were kings and queens about 5000 years ago. An inscribed stone was found in Rosetta, which contained inscriptions in three different languages. Scholars were able to read the inscriptions by identifying the sounds for which the Egyptian letter stood. Eg. Lion stood for L, and a bird for A.
Question 3.
How is living of the present Indian tribals different from the villages?
Answer:
There are many places in India where tribals are living. These tribals are living just adjoining to the forest areas or in the forest. Presently, most of the tribals are living in the state of Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Andaman and Nicobar etc. These communities are still depending on the natural resources. Gradually, they have been evolved in agricultural activities.
Apart from agriculture, their main livelihood is dependent on the rearing of cattles, hunting, fishing etc. They still like separation from the other population. Very rarely the children of tribals join school situated in the nearby area. They are almost unaware about the development of science and technology. Thus, we can say that the tribals are almost in the same condition since hundred of years.
In contrast, people of the Indian villages are enjoying many facilities such as schools, hospitals, roads, transport such as bikes, tractors, cars etc., agriculture with improved technology and now mobile has also reached Indian villages. Our villages are growing fast.
Question 4.
Define the terms:
(a) BC
(b) AD
(c) CE
(d) BCE
Answer:
(a) BC: the letter BC means Before Christ. Dates are generally counted (i.e., the day, the months and the years) from or assigned to the birth of Jesus Christ, the founder of Christianity. So 2000BC means 2000 years before the birth of the Jesus Christ. All dates before the birth of Jesus Christ are counted backwards and generally have the letter BC (Before Christ) added on.
(b) AD: we use AD before dates. This stands for two Latin words, “Anno Domini”, and means in the year of the Lord Jesus Christ.
(c) CE: sometimes, CE is used instead of AD. The letters CE stand for ‘Common Era’.
(d) BCE: sometimes BCE is used instead of BC. The letters BCE stand for ‘Before Common Era’.
Picture Based Questions Class 6 History Chapter 1 What, Where, How and When?
Question 1.
Look at the following picture given below and answer the following.
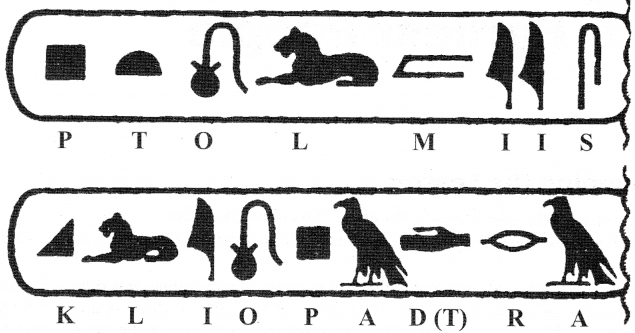
(a) What does the bird stand for?
(b) What does the lion stand for?
(c) Where was the inscribed stone found and what is the process of reading the letters, as describe above, called?
Answer:
(a) A bird is stood for the letter A.
(b) Lion is stood for the letter L.
(c) The stone was found in Rosetta, a town on the north coast of Egypt. The process is called decipherment.
Map Skills Class 6 History Chapter 1 What, Where, How and When?
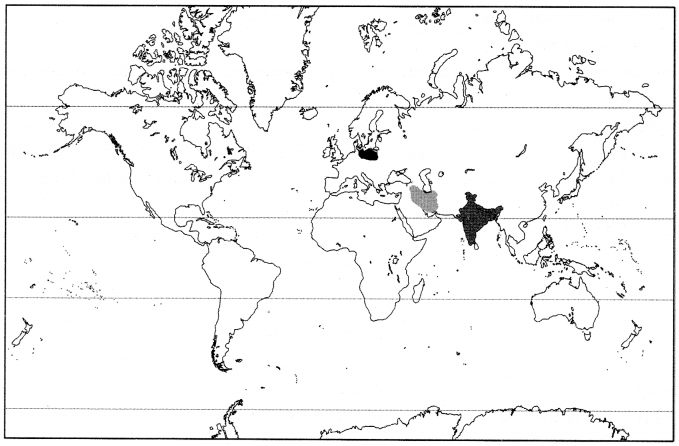
Question 1.
Locate the following on the world map.
(a) India
(b) Greek
(c) Iran
Answer:
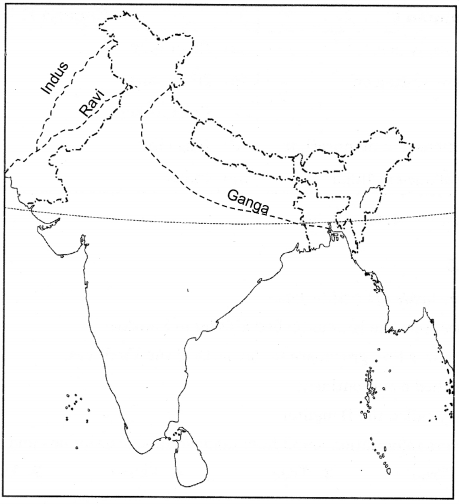
Question 2.
Locate the following on the map of India.
(a) Indus
(b) Ravi
(c) Ganga
Answer: