Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 7 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Term 2 Set 7 with Solutions
Time : 2 Hours
Max. Marks : 40
General Instructions:
- This Question paper is divided into five sections-Section A, B, C, D and E.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Section-A: Question no. 1 to 5 are very short answer type questions of 2 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 40 words.
- Section-B: Question no. 6 to 8 are short answer type questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 80 words.
- Section-C: Question no. 9 and 10 are long answer type questions, carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
- Section-D: Question no. 11 and 12 are Case Based questions.
- Section-E: Question no. 13 is map based, carrying 3 marks with two parts, 13.1 from History (1 mark) and 13.2 from Geography (2 marks).
- There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in a few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions have to be attempted.
- In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section – A
Very Short Answer Type Questions (2 x 5 = 10)
Question 1.
Write a short note on the Khilafat Movement. (2)
Answer:
Khilafat movement was a movement initiated by the Ali brothers, Shaukat Ali and Mohammad Ali.
(i) The movement was started to show the loyalty of Muslims to the head of the Ottoman empire, the Khalifa.
(ii) It was started to save the Khalifa, who was removed by the British after the First World War. The movement proceeded with the formation of a Khilafat committee in India.
Question 2.
Explain how India is well-linked with the rest of the world despite its vast size, diversity, linguistic and socio-cultural plurality? (2)
Answer:
India is well-linked with the rest of the world despite its vast size, diversity, linguistic and socio-cultural plurality because:
(i) Railways, airways, waterways, newspapers, radio, television, cinema and internet, etc., have been contributing to its socio-economic progress in many ways.
(ii) The trades from local to international levels have added to the vitality of its economy.
(iii) It has enriched our life and added substantially to growing amenities and facilities for the comforts of life.
Question 3.
How the democracy manage to resolve the social differences between the different sections of the society? (2)
Answer:
Democracy provides the opportunity for all the sections of the society to present their problems in front of the government.
(i) The social differences are resolved through the process of negotiations and mutual understanding. The conflicting parties accept some of the demands of each other.
(ii) Democracy generally helps in the avoidance of violent clashes between different social groups. Problems are resolved amicably most of the time.
(iii) Democracy gives opportunity to every’minority to gain majority status in some sphere of life.
Question 4.
Write a short note on the ‘terms of credit.’ (2)
Answer:
(i) Terms of credit refer to the terms and conditions stated by the lender to the borrower while giving
out a loan.
(ii) They include collateral and interest rate.
(iii) Mode of payment and documentation required are also stated in the terms of credit.
Question 5.
Study the given table and answer the following questions: (2)
The given table has provided the total production of steel in India in the following years.
| Year | Production |
| 2015-2016 | 106.60 |
| 2016-2017 | 120.14 |
| 2017-2018 | 120.14 |
| 2018-2019 | 101.29 |
| 2019-2020 | 102.62 |
Question i.
What are some of the uses of steel? (1)
Answer:
Steel is the primary component of a variety of industries ranging from infrastructure, automobiles, electronics and electrical appliances, etc.
Question ii.
What is the rank of India among the crude steel producers in the world? (1)
Answer:
India ranks second in the production of crude steel in the world.
Section – B
Short Answer Type Questions (3 x 3 = 9)
Question 6.
Explain the effect of colonialism on modern nationalism.
OR
Discuss the reasons which led Gandhiji to adopt the path of non-violence during the national struggles. (3)
Answer:
Effect of colonialism on modern nationalism:
(i) Colonialism led to the growth of modern nationalism.
(ii) While struggling during colonialism, people started realising their unity.
(iii) Many different groups in India tied up with each other as they shared a bond by being collectively oppressed.
OR
Several reasons led Gandhiji to adopt the path of non-violence during the freedom struggle in India. Some of them are:
(i) He believed in the power of truth and had faith in the idea of satyagraha. He said that if the cause for struggle is just then there is no need for violence.
(ii) He knew that to make the freedom struggle a mass movement it is important to adopt the path of non-violence as every individual cannot commit an act of violence.
(iii) He also knew that any violent method will face the severe repression of the British government which will break the morale of the people.
Question 7.
What was the purpose of the establishment of the World Trade Organisation? (3)
Answer:
The establishment of the World Trade Organisation was done for several reasons:
(i) To facilitate the sound exchange of trade among the different nations of the world.
(ii) To regulate and control the tariffs and other trade barriers in international trade.
(iii) To spread the benefit of globalisation equitably to all the nations of the world.
Question 8.
Describe the ideology of the Bharatiya Janata Party as a political entity? (3)
Answer:
The Bharatiya Janata Party was formed in the year 1980 and it believes in the following set of ideologies:
(i) It wants to build modern India on the lines of India’s ancient culture and values.
(ii) It extends its support for the Deendayal Upadhyaya’s ideas of antyodaya (uplifting the poor section of the society) and humanism.
(iii)It supports the idea of the political and cultural integration of Jammu and Kashmir with India.
Section – C
Long Answer Type Questions (5 x 2 = 10)
Question 9.
“Democracy must provide accountable, responsive and legitimate government.” Examine the statement.
OR
“Democracy cannot reduce economic disparities.” Examine the statement. (5)
Answer:
Democracy provides an accountable, responsive and legitimate government:
(i) Democracy provides an accountable government, as the people in a democracy have the right to choose their representatives through the electoral process.
(ii) If the elected representatives do not work properly, people can choose not to elect them in the next election.
(iii) Democracy provides a responsive government, as democratic governments are elected by the people and work for the welfare of the people.
(iv) These governments function based on public opinion and take care of the needs of the general public.
(v) Democracy provides a legitimate government, as it functions based on elections. The party which secures the majority in the country forms, the government. The decisions in a democracy are taken transparently.
OR
Democracies cannot reduce economic disparities, because of the following reasons:
(i) A small number of rich people enjoy a disproportionate share of income and wealth.
(ii) The lower-income group people, who are at the bottom of the society, have income levels always falling.
(iii) People below the poverty line sometimes find it difficult to meet the ends and fulfil the necessities of life such as food, housing and clothing.
(iv) The people who form a majority in the country sometimes ignore the needs of the people who are in a minority. It further adds to income inequality.
Question 10.
Explain the effects of globalisation in the Indian economy. (5)
OR
How does the use of money make it easier to exchange things? Give an example.
Answer:
Impact of globalisation:
(i) Increased variety of better quality goods are now available at lower prices. This helps to increase the standard of living of people.
(ii) New jobs are created in industries like electronics and automobiles.
(iii) Local companies get prosperous by supplying raw material to other industries.
(iv) Small manufacturing companies get disadvantaged because of an increase in competition level.
(v) Workers lose jobs as employers try to cut the cost of the products by cutting labour costs.
OR
Money makes things easier as:
(i) It is in the form of authorised paper currency that gives the guarantee of the mentioned price to the owner.
(ii) It has universal acceptance.
(iii) Its price remains constant as compared to other commodities.
(iv) Money can be stored easily and it doesn’t need much space.
Section – D
Case Based Questions (4 x 2 = 8)
Question 11.
Read the given text and answer the following questions: (4)
In February 1922, Mahatma Gandhi decided to withdraw the Non-Cooperation Movement. He felt the movement was turning violent in many places and satyagrahis needed to be properly trained before they would be ready for mass struggles. Within the Congress, some leaders were by now tired of mass . struggles and wanted to participate in elections to the provincial councils that had been set up by the Government of India Act of 1919. They felt that it was important to oppose British policies within the councils, argue for reform and also demonstrate that these councils were not truly democratic. C. R. Das and Motilal Nehru formed the Swaraj Party within Congress to argue for a return to council politics. But younger leaders like Jawaharlal Nehru and Subhas Chandra Bose pressed for more radical mass agitation and full independence.
Question i.
Which incidence led to the withdraw of the non-cooperation movement in India? (1)
Answer:
The Non-Cooperation movement was withdrawn in India after the Chauri-Chaura incident. Here, a police station was set on fire by a crowd in which several policemen died.
Question ii.
Who formed the Swaraj Party? (1)
Answer:
Swaraj Party was formed by the Congress leaders C.R. Das and Motilal Nehru, who were determined to return to the council politics.
Question iii.
Why did Gandhiji decide to call off the Non-Cooperation movement? (2)
Answer:
Gandhiji called off the Non-Cooperation movement due to the following reasons:
(i) The movement was turning violent and Gandhiji felt that people must be taught clearly to adopt the path of non-violence.
(ii) On the other hand, some of the political leaders in Congress wanted to participate in the provincial elections as they were tired of the mass struggles.
Question 12.
Read the given text and answer the following questions: (4)
India stands second as a world producer of sugar but occupies first place in the production of gur and khandsari. The raw material used in this industry is bulky, and in haulage its sucrose content reduces. The mills are located in Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Punjab, Haryana and Madhya Pradesh. Sixty per cent of mills are in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar. This industry is seasonal so, it is ideally suited to the cooperative sector. In recent years, there is a tendency for the mills to shift and concentrate in the southern and western states, especially in Maharashtra, This is because the cane produced here has a higher sucrose content. The cooler climate also ensures a longer crushing season. Moreover, the cooperatives are more successful in these states.
Answer the following questions:
Question i.
What is the position of India in the production of sugar, gur and khandsari? (1)
Answer:
India is the second-largest producer of sugar in the world. In the production of gur and khandsari, it occupies the first place in the world.
Question ii.
Why the sugar industry is suited for the cooperative sector? (1)
Answer:
The sugar industry is seasonal, which requires contractual employment due to which it is best suited for the cooperative sector.
Question iii.
Why the concentration of the sugar industries are increasing in the western and southern states of India? (2)
Answer:
The shift for the sugar industry to the western and southern industries is due to the following reasons:
(a) More juice content in cane produced in these states.
(b) More capital and a developed cooperative system.
(c) The climate in these states is cooler due to which the crushing season is longer.
Section – E
Map Skill Based Question (1 x 3 = 3)
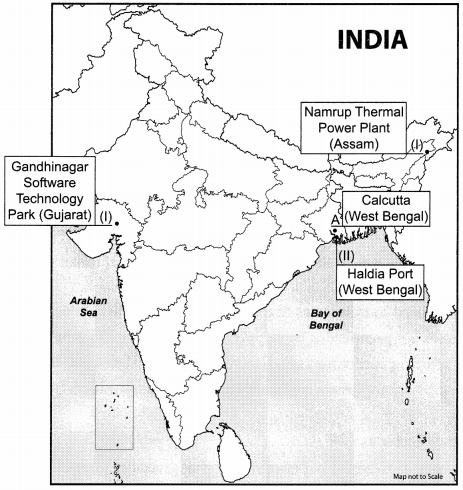
Question 13.
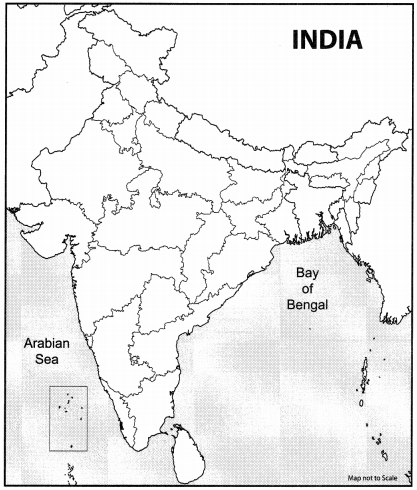
Question i.
On the given outline Political Map of India, identify the place marked as A with the help of following information and write its correct name on the line marked near it. (1)
(A) The place where Indian National Congress Session of September 1920 was held.
Question ii.
On the same given map of India, locate the following:
(I) Namrup Thermal Plant (1)
OR
Gandhinagar Software Technology Park (II) Haldia Port (1)
Answer: