Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 6 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Term 2 Set 6 with Solutions
Time : 2 Hours
Max. Marks : 40
General Instructions:
- This Question paper is divided into five sections-Section A, B, C, D and E.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Section-A: Question no. 1 to 5 are very short answer type questions of 2 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 40 words.
- Section-B: Question no. 6 to 8 are short answer type questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 80 words.
- Section-C: Question no. 9 and 10 are long answer type questions, carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
- Section-D: Question no. 11 and 12 are Case Based questions.
- Section-E: Question no. 13 is map based, carrying 3 marks with two parts, 13.1 from History (1 mark) and 13.2 from Geography (2 marks).
- There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in a few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions have to be attempted.
- In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section – A
Very Short Answer Type Questions (2 x 5 = 10)
Question 1.
When and where did the Jallianwala Bagh Massacre take place? Briefly describe the incident. (2)
Answer:
The Jallianwala Bagh Massacre took place on the 13th of April 1919, in Amritsar, Punjab.
(i) In the enclosed ground of Jallianwala Bagh, a large crowd gathered to protest against the repressive measures of the government.
(ii) The Brigadier-General Dyer entered the area and blocked the exit gates and ordered the British Army to open fire on the unarmed civilians, killing hundreds of people and children.
(iii) The purpose of General Dyer was to create a feeling of terror in the minds of the satyagrahis.
Question 2.
What is communication? What are the two major means of communication? (2)
Answer:
Communication is a process of exchanging information, ideas, thoughts, feelings and emotions through speech, signals, writing, or behaviour.
The two major means of communication are:
(i) Personal communication, which includes letter, e-mail, telephone, etc.
(ii) Mass communication, which includes television, radio, press, films, etc.
Question 3.
What are “Opposition Parties”? Discuss some of the functions of the opposition parties. (2)
Answer:
The parties that do not receive the people’s mandate for forming the government serve as the opposition parties in the parliament. Some of the major tasks undertaken by them are:
(i) They resist the policies of the ruling government and put a check on arbitrary decisions of the government.
(ii) They represent the interest of the unrepresented sections of the society, thus making the democratic process more robust in the country.
(iii) They carry out rallies and protest against the discriminatory and unpopular decisions of the government.
Question 4.
What is demand deposit? How does it share essential features of money? (2)
Answer:
People who have deposited their money in the banks have the provision to withdraw it as and when they require. These deposits of people with the bank are called demand deposits.
Demand deposits share the essential features of money because:
(i) With demand deposits, we can directly settle payments without the use of cash. The facility of cheques helps in this manner.
(ii) Along with currency, demand deposits are commonly accepted as a means of payment. Thus, they constitute money in the modern economy.
Question 5.
Read the given table and answer the following questions: (2)
| Features of transportation | Domain of Earth |
| (a) National Highways | (1) Land Transportation |
| (b) Shipping Ports | (2) Water Transportation |
| (c) Airports | (3) Air Transportation |
Question i.
Which of the following transportation is fastest and most expensive out of the given three? (1)
Answer:
Air transportation is the fastest mode of transportation. However, the cost of air transportation is high as compared to the other two modes.
Question ii.
How national highways are important for road transportation? (1)
Answer:
National Highways has established a robust link between the different states of the country due to which the transition of goods has become very smooth.
Section – B
Short Answer Type Questions (3 x 3 = 9)
Question 6.
Define the term banking. List the characteristics of commercial banking.
OR
‘The economic condition of the rural people have deteriorated due to the informal loans’. Analyse this statement. (3)
Answer:
A bank handles credit, cash and various other financial transactions. Bank provides safety to its depositors. It provides various types of accounts to its customers like current accounts, saving accounts and certificates of deposits.
The main features of commercial banks are as follows:
(i) It is a commercial institute, aiming to earn profits. It has the power to create credit. It advances loans and accepts deposits.
(ii) It is a distinctive financial institution that creates demand. It deals with the general public.
OR
The economic condition of the people have deteriorated due to the informal loans in the following ways:
(i) These loans are offered at higher rates of interest to the people, which sometimes puts them under heavy debt.
(ii) The landlords and moneylenders, on several occasions, exploit the weak financial situation of the rural people and take control over their property.
(iii) Informal loans put the rural people under severe debt obligations which they are mostly unable to repay, which ultimately leads to their loss of property or they have to perform begar in the fields of moneylenders.
Question 7.
“Developed countries can adopt democracy but the poor nation required dictatorship to be rich.” Defend or Refute the statement with appropriate reasons. (3)
Answer:
No, I don’t agree with this statement, because the scope and nature of democracy are not limited or
confined to industrialised or rich countries only.
(i) Democracy provides representative, accountable, responsible and legitimate government to the people.
(ii) It also tries to promote economic growth and accommodate the social differences, which a dictatorship cannot.
(iii) Hence, a poor nation can also afford democracy for popular government and economic growth.
Question 8.
Collaterals are required by lenders while lending. Explain this statement. (3)
Answer:
Lenders ask for collateral while lending money to the borrowers because it acts as a security against the
loan.
(i) Collateral is an asset that the borrower owns and uses as a guarantee for the lender until the loan is repaid.
(ii) If the borrower fails to repay the loan, the lender owns the right to sell the asset or collateral to obtain the due payment.
(iii) Property such as land title/deed, deposits with banks, gold, livestock are some examples of collateral.
Section – C
Long Answer Type Questions (5 x 2 = 10)
Question 9.
“Democracy leads to peaceful and harmonious life among citizens.” Examine the statement.
OR
List the reasons that establish the significance of the political parties in the country. (5)
Answer:
Democracy develops a harmonious social life as:
(i) It accommodates various social divisions. It develops a procedure to conduct fair competition. This reduces the possibility of tensions becoming violent.
(ii) In democracies, people understand to respect the differences and also develop a mechanism to negotiate them.
(iii) The majority community is required to work with the minorities so that the government functions to represent the general view. Democracy can manage social divisions, differences and conflicts.
(iv) Democracy provides an opportunity fdr the people to seek information from the government and hold it accountable for its wrong decisions.
(v) Democracy allows people to negotiate peacefully for the implementation of their requirements.
OR
There are a plethora of reasons which establish the usefulness of political parties in the society:
(i) A party brings consistency in policies as it brings people with similar ideologies together.
(ii) A party addresses the interests of a large section of the society as it has representatives from every section.
(iii) A party provides collective responsibility and accountability of their decisions in the society to the common people.
(iv) Political parties also serve as a strong resistive force in the government when they are in opposition. They put suitable checks and balances on the ruling government.
(v) Political parties allow the common people to address their grievances with the local leaders as they have difficulty in accessing administrative authorities.
Question 10.
What steps are required to control environmental degradation caused by the industries?
OR
Why waterways are important? (5)
Answer:
The steps to prevent environmental degradation caused by industries are as follows:
(i) Harvesting of rainwater to meet water requirements.
(ii) Saving water by various processes of reusing and recycling.
(iii) Proper treatment of effluents and hot water before discharging into the rivers and other water bodies. Industrial effluents can be treated at three stages. Primary treatment consists of mechanical processes like grinding, screening, sedimentation and flocculation. Secondary treatment consists of a biological process. Tertiary treatment comprises chemical, biological and physical processes.
(iv) Aerosol emissions can be reduced by the use of scrubbers, niters, separators, precipitators, etc.
(v) Better maintenance of equipment and selection of fuel.
(vi) Use of silencers for noise pollution.
(vii) Redesigning the machinery.
(viii) Shifting industries outside the cities.
OR
Since time immemorial, India has been one of the major sea-facing countries. Its importance can be judged based on the following reasons:
(i) Waterways are the cheapest means of transport.
(ii) They are most suitable for carrying heavy and bulky goods.
(iii) It is a fuel-efficient and environment-friendly mode of transport.
(iv) India’s trade with foreign countries is carried out through the ports located along the coasts.
(v) 95% of the country’s trade is moved by sea.
Section – D
Case Based Questions (4 x 2 = 8)
Question 11.
Read the text given below and answer the following that questions: (4)
Not all social groups were moved by the abstract concept of swaraj. One such group was the nation’s ‘untouchables’, who from around the 1930s had begun to call themselves Dalit or oppressed. For long the 294 CBSE Social Science – X Congress had ignored the Dalits, for fear of offending the sanatanis, the conservative high-caste Hindus. But Mahatma Gandhi declared that swaraj would not come for a hundred years if untouchability was not eliminated. He called the ‘untouchables’ Harijans, He cleaned toilets to dignify the work of the sweepers, and persuaded upper castes to change their hearts and give up ‘the sin of untouchability’. But many Dalit leaders were keen on a different political solution to the problems of the community. They began organising themselves, demanding reserved seats in educational institutions, and a separate electorate that would choose Dalit members for legislative councils. This provision came true with the signing of the Poona Pact between B.R. Ambedkar and Mahatma Gandhi.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
Question i.
Why did Congress ignore the rights of the Dalits during the early years of their politics? (1)
Answer:
Congress did not want to offend the Sanatanis, the high-caste Hindus, as they had a strong influence in the society. Due to this reason, they did not fight for the cause of Dalits.
Question ii.
What was the significance of the Poona Pact? (1)
Answer:
Poona Pact was signed between B.R. Ambedkar and Mahatma Gandhi. It granted reservation to the depressed classes in the provincial councils.
Question iii.
What was the view of Gandhiji on untouchability? (2)
Answer:
Mahatma Gandhi was sympathetic towards the cause of the depressed classes. He said that Swaraj will not come if the menace of untouchability is not eliminated from society.
(i) He gave the name of Harijans to the untouchables.
(ii) On several occasions, Mahatma Gandhi was seen cleaning the toilets to dignify the work of the sweepers.
Question 12.
Read the source given and answer the following questions: (4)
In ancient India, cotton textiles were produced with hand spinning and handloom weaving techniques. After the 18th century, powerlooms came into use. Our traditional industries suffered a setback during the colonial period because they could not compete with the mill made cloth from England. In the early years, the cotton textile industry was concentrated in the cotton growing belt of Maharashtra and Gujarat. Availability of raw cotton, market, transport including accessible port facilities, labour, moist climate, etc. contribute toward its localisation. This industry has close links with agriculture and provides a living to farmers, cotton boll pluckers and workers engaged in ginning, spinning, weaving, dyeing, designing, packaging, tailoring and sawing. The industry by creating demands supports many other industries, such as, chemicals and dyes, packaging materials and engineering works.
Question i.
Which factors contributed towards the localisation of cotton industry? (1)
Answer:
Availability of raw cotton, market, transport including accessible port facilities, labour, moist climate, etc., contributed towards its localisation.
Question ii.
Why did our traditional industries suffer a setback during colonial period? (1)
Answer:
Our traditional industries suffered a setback during the colonial period because they could not compete with the cheap mill-made cloth from England.
Question iii.
How this industry has close link with agriculture and other industries? (2)
Answer:
(i) This industry has close links with agriculture and provides a living farmers, cotton boll pluckers
and workers engaged in ginning, spinning, weaving, dyeing, designing, packaging, tailoring and saving.
(ii) The industry by creating demands supports many other industries, such as, chemicals and dyes, packaging materials and engineering works.
Section – E
Map Skill Based Question (1 x 3 = 3)
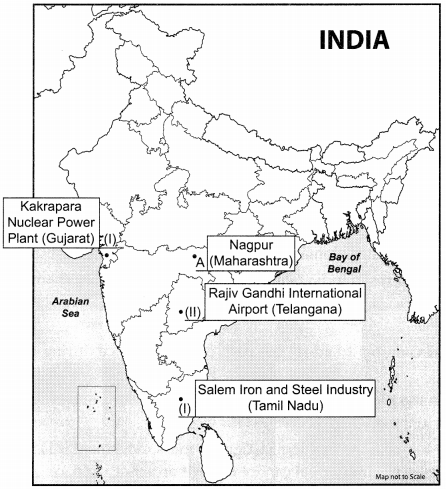
Question 13.
Question i.
On the given outline Political Map of India, identify the place marked as A with the help of following information and write its correct name on the line marked near it. (1)
(A) The place where Indian National Congress of December 1920 to launch Non-Cooperation Movement.
Question ii.
On the same given map of India, locate the following:
(I) Kakrapara Nuclear Power Plant (1)
OR
Salem-Iron and Steel Industry
(II) Rajiv Gandhi International Airport (1)
Answer: