Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 5 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Term 2 Set 5 with Solutions
Time : 2 Hours
Max. Marks : 40
General Instructions:
- This Question paper is divided into five sections-Section A, B, C, D and E.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Section-A: Question no. 1 to 5 are very short answer type questions of 2 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 40 words.
- Section-B: Question no. 6 to 8 are short answer type questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 80 words.
- Section-C: Question no. 9 and 10 are long answer type questions, carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
- Section-D: Question no. 11 and 12 are Case Based questions.
- Section-E: Question no. 13 is map based, carrying 3 marks with two parts, 13.1 from History (1 mark) and 13.2 from Geography (2 marks).
- There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in a few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions have to be attempted.
- In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section – A
Very Short Answer Type Questions (2 x 5 = 10)
Question 1.
Mention the economic problems faced by Indians during World War-I. (2)
Answer:
The following problems were faced by Indians during World War-I:
- To meet the defence expenditure, taxes were increased.
- Customs duties were raised and income tax was introduced.
- During Wartime, the prices of goods increased, leading to extreme hardship to the common people.
Question 2.
Discuss the significance of the aluminium smelting industry in India. (2)
Answer:
The aluminium smelting industry is the second most important metallurgical industry in India. Aluminium has several distinct features:
- Aluminium is a light metal that is resistant to corrosion and is a good conductor of heat.
- This metal is also malleable and gains strength when it is mixed with other metals. This metal is used in the manufacturing of aircraft, utensils and wires.
- The major aluminium smelting plants are located in the states of Odisha, West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh and Maharashtra.
Question 3.
Describe the numerous functions that the political parties undertake. (2)
Answer:
Some of the essential functions that the political parties perform are:
- Their foremost responsibility is to contest the elections in a region, state or at the national level.
- They generally prepare a manifesto of their policies and put them in front of people, seeking support for their policies and programmes.
- After assuming power, political parties formulate the laws and run the administration of the nation.
Question 4.
Why collateral is important in a credit arrangement? (2)
Answer:
Collateral is a kind of movable or immovable asset that a bank keeps as a guarantee while issuing a loan to a borrower. This piece of asset is kept as a safeguard by the bank in case the borrower defaults on the loan. Collateral has become a formal part of the credit market in India and it has many benefits:
- It protects the money of the financial institutions.
- It puts the borrower under the obligation of repaying his loan promptly.
Question 5.
Read the given table and answer the following questions: (2)
| Sector | Organisation |
| Public | BHEL |
| Public | SAIL |
| ? | Dabur |
| Joint | Oil |
1. Identify the question mark in the table: (1)
- Public
- Private
- Joint
- Cooperative
2. What is the difference between private sector and public sector industries? (1)
Answer:
1. Cooperative.
2. The majority of stakes in the public sector industries are held by the government. On the other hand, private sector industries are generally owned and run by individuals or groups of individuals.
Section – B
Short Answer Type Questions (3 x 3 = 9)
Question 6.
Who formed Awadh Kisan Sabha? Mention any two of its objectives.
OR
Why do you think the business classes supported the civil disobedience movement? (3)
Answer:
Baba Ramachandra, a Sanyasi, formed the Awadh Kisan Sabha.
Two objectives of Awadh Kisan Sabha were as follows:
- To fight against the talukdars and landlords, who demanded exorbitant taxes and rents.
- To prevent peasants from doing begar (forced labour) at the landlord’s farms.
OR
The business classes and industrialists in India made significant profits during World War I. However, after the end of the war, they did not get the chance to expand. Some of their issues were:
- The colonial policies restricted the business activities which led to the reduction in the profits of industrialists.
- These classes wanted protection against imported foreign goods and severe restrictions on them.
- Leading industrialists like G.D. Birla and Purshottamdas Thakurdas supported the Civil Disobedience
- Movement as they felt that the native government will look after the interests of the business classes.
Question 7.
What do banks do with the majority of the cash that is deposited by the depositors? (3)
Answer:
The banks keep only a small portion of around 15% with them as cash to meet the emergency requirements of their depositors. With the remaining amount they perform the following functions:
- They extend several types of loans such as home loans, educational loans, etc. to the people at higher interest rates than they pay to their customers.
- They make investments in stocks, mutual funds and other financial instruments to earn money.
- The major source of revenue for the banks is the high-interest rates they charge from the borrowers.
Question 8.
“Democracy stands much superior to any form of government in promoting dignity and freedom of the individual.” Justify the statement. (3)
Answer:
The statement can be justified by addressing the following points:
- Every individual wants to receive respect from fellow beings.
- The passion for respect and freedom is the basis of democracy.
- Throughout the world, the ‘concept of respect’ has been prioritised. It has been achieved in various degrees in various democracies.
- Long struggles by women have earned them respect and equal treatment.
- In many democracies, women were deprived of their right to vote for a long time, which they have achieved
- now.
Section – C
Long Answer Type Questions (5 x 2 = 10)
Question 9.
How are the candidates of the political parties chosen for contesting the elections?
OR
“There is an overwhelming support for the idea of democracy all over the world.” Support the statement. (5)
Answer:
The candidates contesting the elections are chosen according to different methodologies:
- In developed countries like the USA, a candidate is generally selected by the members and the supporters of a political party.
- On the other hand, in countries like India, the candidates are generally chosen by the top leadership of the political party.
- In some advanced European nations, there is also an opinion of the common people in choosing the candidates for contesting elections.
- Several parameters are considered while choosing a candidate for the election. In India, caste and religion plays an effective role in considering the candidature for election ticket.
- Democracy provides an opportunity for minorities as well as the majority sections of the society to keep their interests in front of the government.
OR
“There is an overwhelming support for the idea of democracy all over the world,” due to the following reasons:
- It promotes equality among citizens.
- It helps in improving the dignity of the individual.
- It helps in improving the quality of decision-making.
- It offers a way of resolving conflicts.
- It gives chances for rectifying mistakes.
- It ensures the creation of an accountable, legitimate and responsive government.
- It helps in accommodating social diversities.
- It helps in lowering economic inequalities and poverty.
- It ensures the upliftment of discriminated sections of society.
- It has a formal constitution and elections are held regularly.
- It guarantees rights to the citizens.
Question 10.
Define the term ‘MNC’ and also explain the three ways in which MNCs can spread their production.
OR
What is the contribution of information technology in spreading globalisation in the world? (5)
Answer:
MNC stands for Multinational Corporations. MNCs are the companies that own or controls production in more than one nation. MNCs set up offices and factories for production in the region where they can get cheap labour and other resources, closer to the markets.
MNCs can spread their production by:
- Setting up joint production units with local companies.
- To buy up local companies and expand their production base.
- Placing orders with small and local manufacturers.
OR
In today’s time, we have seen that every industry is utilizing computers for carrying out its processes. With the developments in the field of the internet and other IT technologies, the world has become an integrated place. Some of the contributions of IT are:
- The sharing of information between the different nations and companies has become more robust.
- Majority of the works have become automated, which has increased the efficiency and productivity of companies.
- The links of communication has developed significantly, which has helped the Multi-National Corporations to establish their offices in different parts of the world.
- The age of the internet and computers have made the process of information sharing very easy and at lightning speed.
- The use of electronic mails have become prominent for formal communication purposes.
Section – D
Case Based Questions (4 x 2 = 8)
Question 11.
Read the given text and answer the following questions: (4)
The idea of satyagraha emphasised the power of truth and the need to search for truth. It suggested that if the cause was true, if the struggle was against injustice, then the physical force was not necessary to fight the oppressor. Without seeking vengeance or being aggressive, a satyagrahi could win the battle through non-violence. This could be done by appealing to the conscience of the oppressor. People – including the oppressors – had to be persuaded to see the truth, instead of being forced to accept truth through the use of violence. By this struggle, the truth was bound to ultimately triumph. Mahatma Gandhi believed that this dharma of non-violence could unite all Indians. After arriving in India, Mahatma Gandhi successfully organised satyagraha movements in various places. In 1917 he travelled to Champaran in Bihar to inspire the peasants to struggle against the oppressive plantation system. Then in 1917, he organised a satyagraha to support the peasants of the Kheda district of Gujarat. Affected by crop failure and a plague epidemic, the peasants of Kheda could not pay the revenue, and were demanding that revenue collection be relaxed. In 1918, Mahatma Gandhi went to Ahmedabad to organise a satyagraha movement amongst cotton mill workers.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
1. What was the basic idea of Satyagraha? (1)
2. How a satyagrahi can win the battle for truth? (1)
3. What were some of the places where Mahatma Gandhi implemented his idea of Satyagraha? (2)
Answer:
1. Satyagraha has emphasized the astounding power of truth. It believes that one needs to search for the truth and fight for it without any violence.
2. A satyagrahi can win the battle for truth without actually committing violence and being aggressive. The satyagrahis must appeal to the conscience of the oppressor and persuade them to see the truth.
3. Some of the places where Mahatma Gandhi implemented his idea of satyagraha are:
- He used his idea in the peasant struggle in Champaran, Bihar in 1917 against the oppressive plantation system.
- He used satyagraha to support the cause of the peasants in the Kheda district of Gujarat.
- He even went to Ahmedabad to organise a satyagraha movement for securing the rights of the cotton mill workers.
Question 12.
Read the given text and answer the following questions: (4)
For a long time, trade and transport were restricted to limited space. With the development in science and technology, the area of influence of trade and transport expanded far and wide. Today, the world has been converted into a large village with the help of efficient and fast moving transport. Transport has been able to achieve this with the help of an equally developed communication system. Therefore, transport, communication and trade are complementary to each other.
Today, India is well-linked with the rest of the world despite its vast size, diversity and linguistic and socio-cultural plurality. Railways, airways, waterways, newspapers, radio, television, cinema and internet, etc. have been contributing to its socio-economic progress in many ways. The trades from local to international levels have added to the vitality of its economy. It has enriched our life and added substantially to growing amenities and facilities for the comforts of life.
1. How the development of science and technology has helped the trade? (1)
2. How India has been connected with the rest of the world? (1)
3. Suggest some methods by which India can expand its global trade.(2)
Answer:
1. The developments in the field of science and technology have led to the expansion of trade to a significant level. The transition of goods and services has become very easy due to development in transport and communication technology respectively.
2. India has been connected with the rest of the world through the development of efficient transportation systems like railways, airways and waterways. On the other hand, the development in the field of communication such as radio, television and the internet has made the world integrated.
3. India can expand its global trade in the following ways:
- Improving its transportation system by ensuring smooth connectivity between the trading centres of the world.
- Improvements should be made in the communication technologies like the internet to provide information access to a large number of people.
Section – E
Map Skill Based Question (1 x 3 = 3)
Question 13.
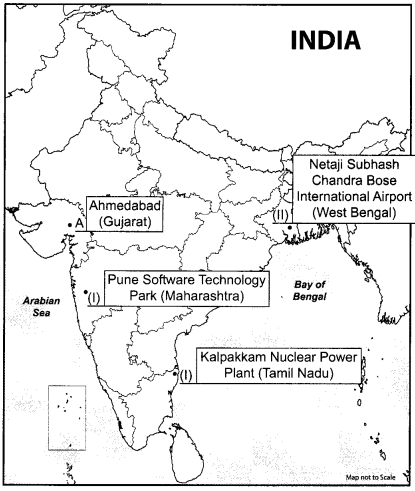
1. On the given outline Political Map of India, identify the place marked as A with the help of following information and write its correct name on the line marked near it. (1)
(A) The place where Satyagraha by Cotton Mill workers took place.
2. On the same given map of India, locate the following:
(I) Kalpakkam Nuclear Power Plant (1)
OR
Pune Software Technology Park
(II) Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose International Airport (1)
Answer: