Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science with Solutions and marking scheme Set 1 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set 1 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions
- Question paper comprises five Sections – A, B, C, D, and E. There are 37 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
- Section A – From questions 1 to 20 are MCQs of 1 mark each.
- Section B – Questions no. 21 to 24 are Very Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 2 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 40 words.
- Section C – contains Q.25 to Q.29 are Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 60 words.
- Section D – Questions no. 30 to 33 are long answer-type questions. carrying marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words
- Section-E – Questions no. from 34 to 36 are case-based questions with three sub-questions and are of 4 marks each.
- Section F – Question no. 37 is map-based, carrying 5 marks with two parts, 37a from History (2 marks) and 37b from Geography (3 marks).
- There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions have to be attempted.
- In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section – A (20×1=20 Marks)
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Identify the correct option that describes the act given below. (1)
(i) The Act was passed by the Imperial Legislative Council.
(ii) It gave power to the government to repress political activities.
(iii) It empowered the government to detain political prisoners without trial.
(A) RowlattAct
(B) Vernacular Press Act
(C) Government of India Act
(D) Inland Emigration Act
Answer:
(A) RowlattAct
Explanation: The Rowlatt Act was passed by the Imperial Legislature Council. It gave power to the government to repress political activities and also empowered the government to detain political prisoners without trial.
Question 2.
Which place in India has an artificial lake to conserve water that dates to the 11th century? (1)
(a) Delhi
(b) Bhopal
(c) Mumbai
(d) Kolhapur
Answer:
(b) Bhopal
![]()
Question 3.
Read the data given below and answer the question. (1)
Educational Achievement of Rural Population of Uttar Pradesh
| Category | Male | Female |
| Literacy rate for rural population | 76% | 54% |
| Literacy rate for rural children in age group 10-14 years | 90% | 87% |
| Percentage of rural children aged 10-14 attending school | 85% | 82% |
As per the data given above who has the least percentage of literacy rate in rural population?
(A) Male
(B) Children
(C) Male & Female
(D) Female
Answer:
(D) Female
Explanation: Females have the lowest rate of literacy population in rural areas as per the survey reports conducted at several levels.
Question 4.
Which of the following options potential measures that can mitigate the threats posed on population and biodiversity?
I. Banning hunting, giving legal protection to their habitats, and restricting wildlife trade. (1)
II. Prohibiting the visit of public into forest area.
III. Establishing wildlife sanctuaries and national parks.
IV. Converting forests into reserved and protected forests.
Codes
(a) Statements I and II are correct
(b) Statements II, III, and IV are correct
(c) Statements II is correct
(d) Statements I, III, and IV are correct
Answer:
(d) Statements I, III, and IV are correct
Question 5.
When many countries of Europe came together to form the European Union, _______________ was chosen as its headquarters. (1)
(A) Brussels
(B) Paris
(C) London
(D) Zurich
Answer:
(A) Brussels
Explanation: When many countries of Europe came together to form, the European Union, Brussels was chosen as its headquarters.
![]()
Question 6.
Which of the following statements accurately distinguishes between majoritarianism and power-sharing? (1)
(a) Majoritarianism emphasises the dominance of the majority community while power-sharing emphasiscs the sharing of power among different groups.
(b) Majoritarianism emphasizes the need for consensus building, while power sharing emphasises the exclusion of minority groups.
(c) Majoritarianism emphasises the importance of accommodating minority interests, while power sharing emphasises the need for majority rule.
(d) Majoritarianism emphasises the need for peaceful resolution of conflicts, while power-sharing emphasises the use of force to impose the majority’s will.
Answer:
(a) Majoritarianism emphasises the dominance of the majority communit while power-sharing emphasiscs the sharing of power among different groups.
Question 7.
There are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Mark your answer as per the codes provided below: (1)
Assertion (A): Democracies are based on political equality
Reason (R): All individuals have equal say in electing representatives.
(A) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(B) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(C) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong
(D) (A) is wrong but (R) is correct
Answer:
(A) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
Question 8.
Rahul has a sack of cotton but he needs wheat and Anush has a sack of wheat and needs cotton, under this situation both will be able to exchange their goods. In case of the absence of such coincidence of wants, they may not exchange their goods. Which one of the following would be the best option that describes the mutual exchange of goods and eliminates the exchange of goods? (1)
(a) Double coincidence of want, exchanging commodity for commodity
(b) Double coincidence of wants, commodity credit.
(c) Double coincidence of want, loan on commodity.
(d) Double coincidence of want, and money.
Answer:
(d) Double coincidence of want, and money.
Question 9.
You are a citizen of a country that has a democratic form of government. You want to ensure that the system of power-sharing in your country is effective and that no one branch of government has absolute power. Which of the following measures would best meet this goal? (1)
(A) All power is concentrated in the hands of the central government, which has the final say in all matters.
(B) Power is divided between the central government and the states or provinces, with each level having its sphere of influence.
(C) Power is separated among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, with each branch having its responsibilities and powers.
(D) Power is shared among different levels of government, such as the national, regional, and local governments, with each level having some degree of autonomy.
Answer:
(C) Power is separated among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, with each branch having its responsibilities and powers.
Explanation: Power is separated among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, with each branch having its responsibilities and powers.
![]()
Question 10.
Identify the painting from the options given below. (1)
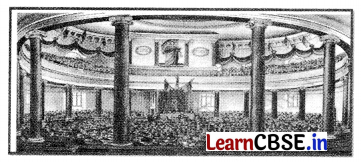
(a) Frankfurt Parliament
(b) Reichstag
(c) Duma
(d) The House of Parliament
Answer:
(a) Frankfurt Parliament
Question 11.
Evaluate the impacts of opening foreign trade on the global economy by identifying the appropriate statements among the following options: (1)
(i) The choice of goods in the markets increases.
(ii) Producers from two countries closely compete against each other despite the distance between their locations.
(iii) Foreign trade thus results in connecting the markets or integration of markets in different countries.
(iv) The quality of the product is always good.
(A) Statements i and ii are appropriate.
(B) Statements i, ii and iii are appropriate.
(C) All the statements are appropriate
(D) Only statement iv is appropriate.
Answer:
(B) Statements i, ii and iii are appropriate.
Explanation:
i. The choice of goods in the markets increases.
ii. Producers from two countries closely compete against each other despite the distance between their locations.
iii. Foreign trade thus results in connecting the markets or integration of markets in different countries.
Question 12.
If a government provides its citizens a right and means to examine the process of decision, it is ……………………… . (1)
(a) an accountable government
(b) responsible government
(c) transparent government
(d) stable government
Answer:
(a) an accountable government
![]()
Question 13.
Arrange the following statements in sequential order based on the events that shaped the Non-cooperation movement. (1)
i. General Dyer opened fire at the large crowd gathered in the enclosed ground of Jallianwalla Bagh.
ii. “Forced recruitment” carried out by the British government and the economic hardships faced by the people during the first world war.
iii. The defeat of the Ottoman Emperor of Turkey led to the formation of the Khilafat movement.
iv. Gandhiji launched a nationwide satyagraha against the Rowlatt Act
Options:
(A) iv, iii, ii, i
(B) ii, i, iii, iv
(C) i, iv, iii, ii
(D) i, ii, iii, iv
Answer:
(B) ii, i, iii, iv
Explanation: Between 1913- 18, forced recruitment carried out by the British government and the economic hardships faced by the people during the first world war. In 1919, General Dyer opened fire at the large crowd gathered in the enclosed ground of Lallianwala Bagh. Between 1919-24, the defeat of the Ottoman Emperor of Turkey led to the formation of the Khilafat Movement. In 1919, Gandhiji launched nationwide satyagraha against the Rowlett act.
Question 14.
If there is a disruption by transporters and lorries refusing to transport vegetables, milk, etc from rural areas to urban areas, food will become scarce in urban areas, whereas farmers will be unable to sell their products. Which of the following sectors will be affected due to the situation stated above? (1)
(a) Primary and Secondary
(b) Secondary and Tertiary
(c) Tertiary Primary and Secondary
(d) Tertiary and Primary
Answer:
(c) Tertiary Primary and Secondary
Question 15.
Consider the statements given below and choose the correct answer: (1)
Statement I: Western printing techniques and mechanical press were imported in the late 19th Century as western powers established their outposts in China.
Statement II: Beijing became the hub of the new print culture, catering to Western-style schools.
(A) Statement (i) is correct and (ii) is incorrect.
(B) Statement (i) is incorrect and (ii) is correct
(C) Both (i) & (ii) are incorrect
(D) Both (i) & (ii) are correct.
Answer:
(A) Statement (i) is correct and (ii) is incorrect.
Explanation: Western printing techniques and mechanical press were imported in the late 19th century as Western powers established their outposts in China. Shanghai is the hub of new print culture/ catering to Western-style school
![]()
Question 16.
“M” gave his friend clues about a type of soil that suits for growing cotton. Which of the following clues provided by “M» would be most useful in identifying the ideal type of soil? (1)
I. It is well-known for its capacity to hold moisture.
II. It turns yellow when it is hydrated.
III. It is rich in kankar and bhangar nodules.
IV. It is a well-drained loamy soil.
Codes
(a) Only I
(b) I and III
(c) Only I and II
(d) Only IV
Answer:
(a) Only I
Question 17.
Choose the right option to fill in the blank. (1)
The emergence of ______________ is directly connected to the rise of political parties.
(A) Monitory democracies
(B) Direct democracies
(C) Representative democracies
(D) Constitutional democracies
Answer:
(C) Representative democracies
Explanation: The emergence of Representative democracies is directly connected to the rise of political parties.
Question 18.
The process of rapid integration or interconnection between countries through the movement of goods and services, investments, and technology between countries is called……………………….. . (1)
(a) privatisation
(b) globalization
(c) liberalization
(d) competition
Answer:
(b) globalisation
Question 19.
Which of the following statements is correct keeping the requirement of formation of government? (1)
Statement i: Independent candidates can form a government.
Statement ii: Government formation is exclusively reserved for political parties.
Statement iii: The formation of government is limited to only elected political parties.
Statement iv: Government can only be formed by political parties that are elected and hold a majority.
Options:
(A) Statement i and ii are right.
(B) Statement i, ii and iii are right.
(C) Statement iii is right.
(D) Only statement iv is right.
Answer:
(D) Only statement iv is right.
Explanation: Explanation: The formation of the government is done by the elected political parties which have the required majority for the formation of the government.
![]()
Question 20.
Miss ‘S’ approached a bank nearby to avail loan for her own business, as well as a Self-Help Group that is operating in her
village, the bank rejected her loan application whereas the Self-Help Group agreed to support her by providing the loan.
Which one of the following documents is required by the bank, but not required by the Self-Help Group to approve Miss’s loan application for her business? (1)
(a) Application for loans
(b) Arrangement letter
(c) Document on collateral
(d) Demand promissory note and take delivery letter
Answer:
(c) Document on collateral
Section – B (2×4=8 Marks)
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 21.
Study the map thoroughly and mention the languages that are dominantly present in Belgium. (4)
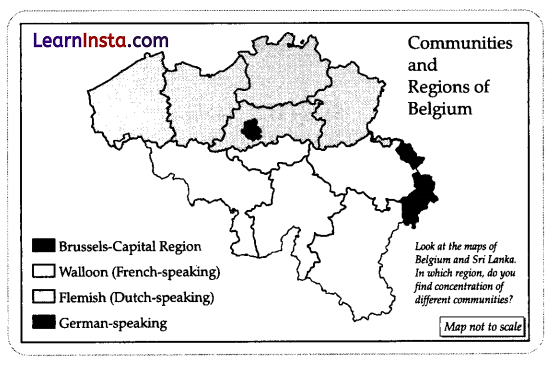
Answer:
The languages that are dominantly spoken in Belgium are Dutch and French.
Question 22.
‘The most powerful weapon of the Spanish conqueror was not a conventional military weapon at all.” Justify the above statement by giving two reasons,
Or
“Traders and travellers introduced new crops to lands they travelled.” Substantiate this statement with illustrations. (2)
Answer:
The Spanish conquerors most powerful weapon was not a conventional military weapon because They used germs like smallpox which spread deep into the continent before any European could reach there, Americas original inhabitants had no immunity against these diseases that came from Europe. This disease erased the whole community, leading to conquest.
Or
“Traders and travellers introduced new crops to lands they travelled. It is believed that many of our common foods such as potatoes, soya, groundnuts, maize, tomatoes, chilies, and sweet potatoes. and so on were not known to our ancestors until about five centuries ago. These foods were only introduced in Europe and Asia after Christopher Columbus accidentally discovered the vast continent that would later become known as America many of our common foods came from America’s original inhabitants i.e. the American Indians.
![]()
Question 23.
Mr. Palani is from Tamil Nadu and wishes to cultivate either Tea or Wheat. Which one of the crops out of the two can he cultivate in his state? Substantiate your answer with any two reasons. (4)
Answer:
Mr. Palani must cultivate Tea in Tamilnadu as the soil and climatic conditions in Tamil Nadu are suitable to grow Tea.
- The tea plant grows well in tropical and sub-trop¬ical climates endowed with deep and fertile well-drained laterite soil, rich in humus and organic matter. Tea bushes require a warm and moist frost-free climate all through the year.
- Frequent showers evenly distributed over the year ensure continuous growth of tender leaves.
Question 24.
Mention any two reasons to prove that India is a federal country. (2)
Answer:
The following are the reasons which prove that India is a federal country. Division of Powers The Constitution of India clearly
demarcates the powers of the Central and State Governments, and both have their separate areas of jurisdiction. The Seventh Schedule of the Indian Constitution lists, the Union list, State List and Concurrent list, which define the powers and responsibilities of the Central and State Governments.
Independent Judiciary India has an independent judiciary with the power of judicial review. The Supreme Court of India is the highest judicial authority in the country and has the power to interpret the Constitution and resolve disputes between the Central and State Governments.
Section – C (3×5=15 Marks)
Short Answer – Based Questions
Question 25.
Provide evidence to support the claim that print culture had a significant impact on the social lives of women in India. (3)
Answer:
The rise of print culture in India during the 19th century played a crucial role in awakening the social life of women. The printing press allowed women to access information, knowledge and ideas that were previously inaccessible to them. Women’s magazines, newspapers and books provided a platform for women to express their views, ideas and opinions on various social issues such as education, gender equality, women’s rights, and social reform.
(i) Liberal husbands and fathers began educating their womenfolk at home and sent them to schools. In East Bengal, Rashsundari Debi, a young married girl in a very orthodox household, learnt to read in the secrecy of her kitchen and wrote her autobiography Amar Jiban (1876). It was the first full-length autobiography published in the Bengali language.
(ii) Bengali women like Kailashbashini Debi wrote books highlighting the experiences of women- about how women were imprisoned
at home, kept in ignorance, forced to do hard domestic labor and treated unjustly by their families.
(iii) In Maharashtra, Tarabai Shinde & and Pandita Ramabai wrote with passionate anger about the miserable lives of upper-caste Hindu women, especially widows.
(iv) A woman in a Tamil novel expressed what reading meant to women who were confined by social regulations:’ For various reasons, my world is small….. More than half my life’s happiness has come from books …’ Therefore, print culture helped awaken social consciousness and contributed to the progress of women’s rights and empowerment in India.
![]()
Question 26.
A worker in an urban area, who was working in a small factors ‘was not paid his wages properly he was forced to work extra hours under poor working conditions, there was no job security, recently he lost his job and was found selling electrical items in a pushcart. Analyze the role of the government in protecting the workers working in an unorganized sector.
Or
Mr Pawan, a village head wanted to create more job opportunities to increase the income of the people of his village under the MNREGA Act. Suggest any three activities, so that Mr Pawan could initiate in his village. (3)
Answer:
Answer:
- The role of the government in protecting the workers working in an unorganized sector are
- The small factories must be registered by the government and have to follow its rules and regulations which are given in various laws such as the Factories Act, Minimum Wages Act, Payment of Gratuity Act, Shops and Establishments Act, etc.
- The government can provide loans to help unemployed educated youth to start their own business.
- The workers are supposed to get medical benefits and under the laws, the factory manager has to ensure facilities like drinking water and a safe working.
Or - The three activities under the MNREGA Act, through which Mr. Pawan can create more job opportunities to increase the income of the people living in his village are Cleaning the Lake/Pond Cleaning and maintaining water bodies such as lakes and ponds can help to improve the quality of water and make it suitable for irrigation purposes. This can lead to increased agricultural productivity, which, in turn, can increase the income of the farmers.
Village Road Construction The construction of village roads can improve connectivity and accessibility within the village, making it easier for people to commute to work or transport goods. This can help to increase economic activity in the village, creating more job opportunities and boosting the income of the local people.
Construction Work The construction of houses, community centers, and other infrastructure projects can generate employment opportunities for the local people, helping to boost their income. This can also improve the living standards of the villagers, making it a sustainable solution for poverty reduction.
Question 27.
‘Agriculture gives boost to the industrial sector’. Justify the statement with any 3 relevant points. (3)
Answer:
Agriculture gives boost to the industrial sector.
- Raw Material Supply: Agriculture is a significant source of raw materials for various industries, such as food processing, textiles, and paper. For instance, the cotton industry relies heavily on the production of cotton from agricultural fields. Similarly, food processing industries rely on agricultural products such as fruits, vegetables, and cereals. Thus, a healthy agricultural sector can ensure a steady supply of raw materials for industries, which, in turn, can boost their productivity and growth.
- Market Expansion: Agriculture provides a vast market for industrial products. For example, the use of agricultural machinery such as tractors, tillers, and harvesters creates a demand for indus¬trial goods, including steel, plashes, and rubber. Moreover, the growth of the agricultural sector increases the purchasing power of farmers, who become a significant consumer group for industrial products such as consumer goods/automobiles, and appliances.
- Employment Generation: Agriculture is a labor-intensive sector that generates employment opportunities for a significant population in India. A healthy agricultural sector can increase the income levels of farmers and agricultural workers, which, in turn, can create a demand for industrial products and services. Additionally, agriculture-related industries such as food processing and agrochemicals also create job opportunities, especially in rural areas. Thus, a robust agricultural sector can help to reduce unemployment and poverty, which are major challenges in India.
![]()
Question 28.
The Indian Constitution provides three lists to distribute the legislative power. State any two subjects that are included in the Union List. In which list the subject “Education is included and why? (3)
Answer:
The Indian Constitution has a three-fold distribution of legislative power, which contains three lists-the Union List, the State List, and the Concurrent List.
The subjects that are included in the Union List are those that are under the exclusive jurisdiction of the Union Government. Some of the subjects that are included in the Union List are Defense of the country and Foreign affairs and relations.
The subject Education” comes under the Concurrent List. which means that both the Union Government and the State Governments have the power to make laws on this subject. The Concurrent List contains subjects that are of common interest to both the Union and the State Governments.
Question 29.
Compare Tables “A” & “B” and answer the question given below. (3)
Table – A
| Share of Sectors in GDP in % | |||
| Year | Tertiary | Secondary | Primary |
| 1973-74 | 50 | 10 | 40 |
| 2013-14 | 68 | 21 | 11 |
Table – B
| Share of sectors in employment in % | |||
| Year | Tertiary | Secondary | Primary |
| 1977-78 | 18 | 11 | 71 |
| 2017-18 | 31 | 25 | 44 |
A remarkable fact about India is that while there has been a change in the share of the three sectors in GDP, a similar shift has not taken place in employment. Why didn’t a similar shift out of the primary sector happen in the case of employment? Substantiate your answer.
Answer:
(a) A substantial shift in employment in the primary Sector hasn’t happened because of the following reasons.
- Insufficient job creation in the secondary and tertiary sectors: The primary reason for the limited shift in employment from the primary sector is the failure to generate an adequate number of jobs in the secondary (industrial) and tertiary (service) sectors. The growth of Industrial output and service sector production has been significant, but the corresponding increase in employment opportunities has been comparatively lower.
- Underemployment in the agricultural sector: The primary sector, particularly agriculture, suffers from underemployment, with more people engaged in farming than necessary. Even if a few individuals are moved out of agriculture, it does not significantly affect production. This indicates that workers in the agricultural sector are not fully utilized, leading to a lower productivity level.
- Share of Sectors in Employment Though industrial output or the production of goods went up by more than nine times during the period, employment in the industry went up by around three times. The same applies to the tertiary sector as well. While production in the service sector rose by 14 times, employment in the service sector rose by around five times. As a result, more than half of the workers in the country are working in the primary sector, mainly in agriculture, producing only about one-sixth of the GDE In contrast to this, the secondary and tertiary sectors produce the rest of the produce whereas they employ less about half the people.
Section – D (5 ×4=20 Marks)
Long Answer-Based Questions
Question 30.
Analyze the impact of mining activities on the local environment and the health of the surrounding communities.
Or
”Non-conventional resources are the best option to conserve the natural resources”. Substantiate this statement -with examples. (2)
Answer:
The impact of mining activities on the local environment and the health of the surrounding communities are
The dust and noxious fumes inhaled by miners make them vulnerable to pulmonary diseases
The risk of collapsing mine roofs, inundation and fires in coal mines are a constant threat to miners.
The fact that mining is one of the most dangerous jobs, mining usually hurts the environment with the production of a lot of waste disruption to the local flora and fauna, and contamination of local water sources.
It could require the removal of massive amounts of topsoil, leading to erosion, loss of habitat and pollution.
Or
Non-conventional resources are the best option to conserve the natural resources. Non-conventional sources are also known as renewable sources of energy. Examples of non-conventional sources of energy include solar energy, bioenergy, tidal energy.
wind energy, geothermal energy. natural gas, etc. They are inexhaustible and renewable. They are also considered as clean sources of energy.
Optimal use of resources of energy minimises environmental impact and non-conventional resources produce minimum secondary waste compared to use conventional sources. Rising prices of oil and gas and their potential shortages have raised uncertainties about the security of energy supply in future, which in turn has serious repercussions on the growth of the national economy. Natural gas is considered an environmentally friendly fuel because of low carbon dioxide emissions. It does not cause air pollution o environmental degradation.
Thus, it is the fuel for present century. Renewable energy resources technologies provide an excellent opportunity for mitigation of greenhouse gas emission and reducing global warming through substituting conventional energy sources.
![]()
Question 31.
How would you evaluate Napoleon as an administrator who created a more rational and efficient system? Elucidate with suitable examples. (5)
OR
Analyze the decisions taken by the conservatives at the Congress of Vienna in the year 1815.
Answer:
The Civil Code of 1804 – usually known as the Napoleonic Code, secured the right to property,
established equality before the law, and removed all privileges based on birth.
- The Napoleonic Code was followed by the regions under the French control.
- New businessmen, artisans, peasants, and workers enjoyed a new-found freedom.
- In territories under French control such as Italy, Germany, Switzerland, and Dutch Republic, peasants were freed from manorial dues, peasants were freed from serfdom, feudal system was abolished, administrative divisions were simplified.
- Guild restrictions were removed in towns.
- There were improvements in communication and transport systems.
- To facilitate the movement and exchange of goods and capital from one region to another, small-scale producers of goods and businessmen began to realise that common national currency, standardised measures and weights, and uniform laws were of great help.
(OR)
The representatives of the four great European powers – Britain, Russia, Prussia and Austria who had collectively defeated Napoleon, met at Vienna to draw up a settlement for Europe. The Congress was hosted by the Austrian Chancellor Duke Metternich. The result was the Treaty of Vienna of 1815.
- Its object was to undo the changes that had come about in Europe during the Napoleonic wars and to restore the monarchies that had been overthrown by Napoleon, and create a new conserva¬tive order in Europe.
- The Bourbon dynasty, (deposed during the French Revolution) was restored to power.
- France lost the territories it had annexed under Napoleon.
- A series of states were set up on the boundaries of France to prevent it from expansion in the future. E.g., kingdom of the Netherlands, which included Belgium, was set up in the north.
- Genoa was added to Piedmont in the south. Prussia was given territories on its western frontiers. Austria was given control of northern Italy.
- The German confederation of 39 states set up by Napoleon was left untouched. In the east, Russia was given part of Poland while Prussia was given a portion of Saxony. Thus conservative regimes set up in 1815 were autocratic. They did not tolerate criticism and dissent. They curbed activities that questioned the legitimacy of autocratic governments.
Question 32.
Analyse the role of a multi-party system in a democratic country like India. (5)
Or
Evaluate the significant distinction between the national and regional parties and assess the requirements for a regional party to become a national party.
Answer:
In a democratic system like India, multi-party politics plays a crucial role in representing the diverse interests and aspirations of the citizens.
The multi-party system allows for a competitive and dynamic political environment, where parties with different ideologies and agendas can participate and compete for the support of the electorate. The presence of multiple parties also provides a check
and balance against any one party becoming too powerful and dominant. This system allows a variety of interests and opinions to enjoy political representation.
People can choose between several candidates. Through this system, different and diverse parties could represent the sections of society and power is not absorbed in the hands of one single party. India adopted this system because of the vast diversity and plurality in the nation.
Or
The significant distinction between the national and regional parties is National parties are powerful in the nation; it deals with national issues. Regional parties, power is limited to a specific region or state, only the issues and demands of a specific region are discussed by regional parties, National parties, actions offer preference to national issues over regional problems. Regional parties, operations are confined to the state Requirements of a regional party to become a national party area party must gain at least six percent of the total votes in Lok Sabha or Assembly Elections in four states to be a national party and win at least four seats in Lok Sabha.
A party has to receive at least six percent of the total votes in the legislative election to become a regional party and win at least two seats. Examples of national parties are the BJP Congress and BSP The examples of regional parties are DMK, and MM Aadmi Party.
![]()
Question 33.
(A) A farmer has borrowed money from a money lender at a high rate of interest, as he could not pay the interest.
Mr “X” was forced to borrow from another landlord to settle the amount for the interest borrowed, to the money lender. State the consequences he may face in this situation. (5)
(OR)
(B) “Self-help groups eliminates poverty and empowers women”. Substantiate with suitable answer.
Answer:
The Farmer has fallen into “Debt trap”, He is in a situation where he will not be able to repay the debt incurred because: The Informal sector was the source of credit opted by Mr “X”, where
- The Rate of interest is high,
- No proper documentation is sought,
- No set of rules and regulations will be followed
- The lenders were often punished and will be ill treated
- The prime motive of the informal sources of this kind of credit is to make profit.
He may face the following Consequences: - Mr. “X” may face ongoing harassment and physical harm from the men sent by the money lender.
- He will not be able to make regular interest payments or repay the full amount borrowed. This could lead to significant stress and anxiety, as well as potential physical injuries.
- Borrowing from another landlord to repay the original loan may create a cycle of debt for Mr. “X”, particularly if the interest rates on the second loan are also high.
The Farmer may experience personal consequences, such as mental stress, anxiety, and depression due to the constant pressure of repayments and harassment from the lenders.
OR
- Self Help Groups help the poor to become self-reliant in terms of savings and generating income.
- They avail the facilities of loans from formal sources like banks at low rate of interest.
- They do not demand collateral and so it is easy to access by the poor.
- Self-help groups are exclusively meant for rural women to make them Economically independent through self-employment opportunities.
- Helps to improve other development factors such as literacy levels, improved healthcare and better family planning.
- Economic empowerment. SHGs provide women with a platform to save and access credit at affordable rates, which enables them to start and expand small businesses. Thus improving the standard of living.
- Skill development: SHGs in India have also been successful in providing skill development and training opportunities to women. Through training programs, women are equipped with the necessary skills to start and run successful businesses.
- Social empowerment. By providing a platform for women to come together, share their experiences, and support each other, SHGs have empowered women to take charge of their lives and become active participants in their communities.
Section – E (4×3=12 Marks)
Case-Based Questions
Question 34.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow.
It is said that “passive resistance” is the weapon of the weak, but the power which is the subject of this article can be used only by the strong. This power is not passive resistance; indeed, it calls for intense activity. The movement in South Africa was not passive but active.
‘Satyagraha is not physical force. A satyagraha does not inflict pain on the adversary; he does not seek his destruction … in the use of satyagraha, there is no ill will whatever. Satyagraha is pure soul force. Truth is the very substance of the soul. That
is why this force is called satyagraha. The soul is informed with knowledge. In it burns the flame of love. … Non-violence is the
supreme dharma …‘ It is certain that India cannot rival Britain or Europe in force of arms.
The British worship the war God and they can all of them become, as they are becoming, bearers of arms. The hundreds of millions in India can never carry arms. They have made the religion of non-violence their Own In his famous book Hind Swaraj (1909) Mahatma Gandhi declared that British rule was established in India, with the cooperation of Indians, and had survived only because of this cooperation. If Indians refused to cooperate, British rule will collapse within a year.
(i) Gandhiji said, “Passive resistance is not the weapon of the weak”. Why?
(ii) “Satyagraha is pure soul-force” Substantiate this statement in 20 words.
(iii) What according to Mahatma Gandhi is the best weapon to use to collapse British rule in India? (4)
Answer:
(i) Gandhi it said, passive resistance is not the weapon of the weak because ¡t calls for intense activity with a lot of inner strength.
(ii) Truth is the very substance of the soul that is informed with knowledge and thus this force is called Satyagraha.
(iii) Mahatma Gandhi in his book Hind Swaraj’ declared that through non-cooperation (Satyagraha) only British rule could be collapsed in India as they could build their empire only with the cooperation of Indians.
![]()
Question 35.
Read the given source below and answer the following questions: (4)
Maharashtra is a state located in western India, with a population of over 110 million people. The state is home to several large cities, including Mumbai, and has a significant agricultural sector. However, the state is facing a severe water crisis, with its water resources coming under increasing pressure due to climate change, industrialization, and urbanization. The main challenges faced by water resource management in Maharashtra are:
i. Overexploitation of groundwater: Maharashtra is one of the most groundwater-stressed states in India, with the demand for water exceeding the supply. Overexploitation of groundwater for agriculture and urban use has led to a decline in water levels, which has severe implications for the sustainability of water resources.
ii. Pollution of surface water: Industrialization and urbanization have led to the pollution of surface water bodies such as rivers and lakes. The pollution has led to water quality degradation, which poses risks to human health and the environment.
iii. Inefficient irrigation practices: The agricultural sector is the largest user of water in Maharashtra, accounting for around 80% of total water use. However, traditional irrigation practices such as flood irrigation are inefficient and lead to the wastage of water.
(a) Mention any one reason for the water crisis faced by the state of Maharashtra.
Answer:
Two reasons for Maharashtra facing a water crisis are overexploitation of groundwater and pollution of surface water bodies due to industrialization and urbanization.
(b) Propose any one solution to mitigate the water crisis faced by Maharashtra state.
Answer:
Despite receiving the second-highest rainfall in the country, traditional irrigation practices like flood irrigation leading to water shortages in Maharashtra. This is because flood irrigation involves excessive water use, and the water gets lost due to runoff, leading to less water available for other uses.
(c) Despite being the second highest rainfall-receiving state of the country, Maharashtra still faces water crisis.
Substantiate this statement in 40 words.
Answer:
To mitigate the water crisis in Maharashtra, one solution could be to promote the adoption of more efficient irrigation practices, such as drip irrigation and sprinkler systems, that use less water and are more targeted in their delivery. The state can also use a rainwater harvesting system to improve groundwater levels along the western side of Western Ghats which receive maximum rainfall. This will increase the efficiency of water use in the state of Maharashtra
Question 36.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow.
For comparing countries, their income is considered to be one of the most important attributes. Countries with higher incomes are more developed than others with less income. This is based on the understanding that more income means more of all things that human beings need. Whatever people like, and should have, they will be able to get with greater income. So, greater income itself is considered to be one important goal. Now, what is the income of a country?
Intuitively, the income of the country is the income of all the residents of the country. This gives us the total income of the country However, for comparison between countries, total income is not such a useful measure. Since, countries have different populations, comparing total income will not tell us what an average person is likely to earn. Are people in one country better off than others in a different country? Hence, we compare the average income which is the total income of the country divided by its total population. The average income is also called per capita income. In World Development Reports, brought out by the
World Bank, this criterion is used in classifying countries. Countries with per capita income of US $ 49,300 per annum and above in 2019, are called high-income or rich countries and those with per capita income of US $ 2500 or less are called low-income countries. The rich countries, excluding countries of the Middle East and certain other small countries are generally called developed countries.
(i) Explain the significance of per capita income.
(ii) What are the classifications of countries based on per capita income, and which entity is responsible for determining
these classifications? (4)
Answer:
(i) The per capita income enables comparisons between countries and provides insights into the relative economic performance and living standards across different nations. Per capita income also serves as an important indicator of the standard of living in a country.
(ii) The courtiers are classified into high-income or rich countries and low-income countries based on their per capita Income. If it is US $ 49300 per annum they will be classified as a rich country and if the per capita income is US $ 2500 per annum it will be called a poor country. World Bank is responsible for determining this classification.
Section – F (2+3=5 Marks)
Map Skill-Based Question
Question 37.
Two places A and B have been marked on the given outline map of India.
(a) Identify them and write their correct names on the lines drawn near them.
(A) Indian National Congress session at this place in 1920.
(B) The place where Mahatma Gandhi broke the salt law.
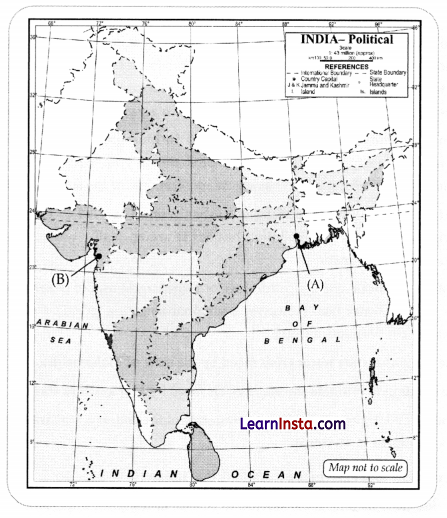
Answer:
(A) Calcutt
(B) Dandi
![]()
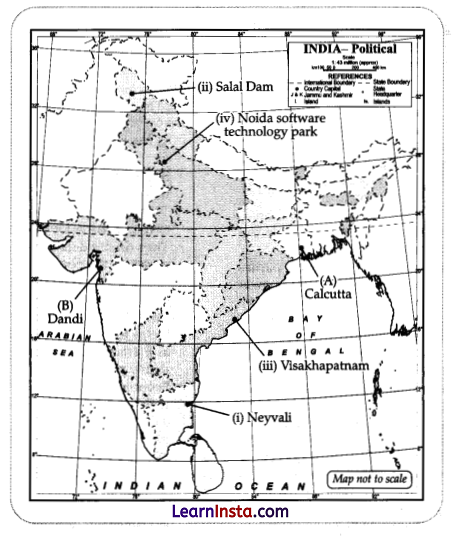
(b) On the same outline map of India locate and label any 3 of the following with suitable symbols.
(i) A Coal mine in Tamil Nadu
(ii) A dam built on river Chenab.
(iii) A large natural seaport located in Andhra Pradesh
(iv) Noida Software Technology Park
Answer: