Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 5 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Term 2 Set 5 with Solutions
Time : 2 Hours
Max. Marks : 40
General Instructions :
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has three sections and 15 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Section-A has 7 questions of 2 marks each; Section-B has 6 questions of 3 marks each; and Section-C has 2 case based questions of 4 marks each.
- Internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
Section – A
Question 1.
Write one negative effect, on the environment, of affluent lifestyle of few persons of a society. (2)
Answer:
Affluent lifestyle results in:
1. Generation of excessive waste materials.
2. Excessive use of natural resources like coal and petroleum which causes pollution.
3. Use of excessive non-biodegradable material in packaging.
Question 2.
What is a homologous series? Explain with an example. (2)
OR
Write the molecular formula of the 2nd and 3rd member of the homologous series whose first member is ethene.
Answer:
A homologous series is a series of carbon compounds that have different numbers of carbon atoms but contain the same functional group. There is a difference of -CH2 unit between each successive member and mass differ by 14 u. For example, methane, ethane, propane, butane, etc., are all part of the alkane homologous series. The general formula of this series is CnH2n+2
OR
1. Propene: C3H6
2. Butene: C4H8
Question 3.
A house has main fuse rating 5 A. Three lamps each of 100 W and three CFL’s each of 40 W are used simultaneously. Find: (2)
(a) the current drawn from the main of 220 V, and
(b) the number of additional CFL’s each of 40 W which can also be lighted?
Answer:
(a) Total power of appliances used simultaneously
P = (3 × 100) + (3 × 40)
= 420 W
Voltage of mains, V = 220 V
Current drawn from the mains, I = \(\frac{P}{V}=\frac{420}{220}\) = 1.91 A
(b) Excess current available which can be safely used
= 5 A – 1.91 A
= 3.09 A
∴ Current drawn by each CFL of 40 W at 220 V,
I = \(\frac{P}{V}=\frac{40}{220}\) = 0.18 A
∴Number of additional CFL’s of 40 W each which can be lighted.
n = \(\frac{Excess current available}{Current drawn by each tube light}\)
= \(\frac{3.09}{0.18}\)
= 17.2
∴ Seventeen additional CFL’s can be lighted.
Question 4.
What is the significance of testes being located in scrotal sacs outside abdomen? (2)
OR
List two functions performed by testes in human males.
Answer:
The testes are located in scrotal sacs outside abdomen because sperms requires a minimum temperature of 2°C-3°C lower than body temperature for their development. So, testes are located in a sac like structures called scrotum outside the abdomen.
OR
In human male testes perform the following functions:
1. Sperms are produced by the process of spermatogenesis.
2. Interstitial cells present in testes produce the male hormone called as testosterone.
Question 5.
(a) Are binary fission and budding faster processes of reproduction when compared to sexual reproduction? Justify.
(b) Name the type of asexual reproduction in which two individuals are formed from a single parent and the parental identity is lost. State the event with which this reproduction starts. (2)
Answer:
(a) Yes, binary fission and budding are faster processes of reproduction when compared to sexual reproduction because in sexual reproduction there are lot of events like formation of gametes, fusion of gametes, development of a zygote to a young one etc.
(b) Binary fission is the type of asexual reproduction in which two individuals are formed from a single parent and the parental identity is lost. This reproduction starts with elongation of Nucleus.
Question 6.
Flow can you help in reducing the problem of waste disposal? Give any two methods. (2)
OR
Why biogas is considered an excellent fuel?
Answer:
We can help in reducing the problem of waste disposal by the following two methods:
1. By separating biodegradable wastes from the non-biodegradable wastes.
2. By putting the biodegradable organic waste into compost pits dug in the ground and preparing compost.
OR
Biogas is considered as an excellent fuel because:
1. It is environmental friendly as it does not leads to air pollution since combustion of biogas is smoke free.
2. It is economical and serves as an excellent way of waste disposal.
3. It produces a large amount of heat per unit mass and therefore, has high calorific value.
Question 7.
What will be the correct order of decreasing metallic character of elements Na, Si, Cl, Mg, Al? (2)
Answer:
The metallic character is the tendency of an element to lose electrons and form positive ions or cations. The non-metallic character is the tendency of an element to accept electrons and form negative ions or anions. Sodium has 1, Mg has 2, Al has 3, and Si has 4 electrons in their outermost shells. But Cl has 7 electrons in its outermost shell. Hence, sodium shows the maximum character of metallic elements followed by magnesium, aluminium, silicon and chlorine which shows non-metallic properties. Metallic characteristic decreases across a period on moving right. Therefore, the correct order will be Na > Mg > A1 > Si > Cl.
Section – B
Question 8.
Briefly describe different methods of wastes disposal? (3)
Answer:
The various methods of waste disposal are:
1. Land-fills: In urban areas wastes, are filled or deposited in low lying areas. These are also known as dumping grounds where wastes are buried.
2. Recycling of wastes: Some wastes like papers, plastics, metals etc., which can be recycled are send to special recycling treatment plants so that new substances can be made from them.
3. Preparation of compost: Biodegradable wastes like kitchen wastes, peels of fruits and vegetables etc., can be used to prepare compost which serves as a good manure to the plants.
4. Incineration: Some wastes like medical wastes, chemical wastes are burnt at very high temperature in an incinerator and the ashes left behind are disposed by landfills.
5. Production of biogas: Biodegradable wastes can be used in biogas plants to produce biogas which is used for several purposes like as a fuel.
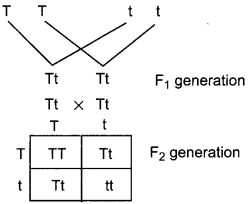
Question 9.
Name the plant Mendel used for his experiment. What type of progeny was obtained by Mendel in F1 and F2 generations when he crossed the tall and short plants? Write the ratio he obtained in F2 generation plants. (3)
Answer:
Mendel used pea plant (Pisum sativum) when he crossed tall and short plants the progeny obtained in Fa generation were tall. When the Fj plants were selfed the F<sub>1</sub> generations showed three tall and one dwarf plant. The genotypic ratio of F<sub>2</sub> generation is 1 : 2 :1.
(TT : Tt: Tt: tt)
The Phenotypic ratio 3 :1 (Tall: Dwarf)
Question 10.
A student wound an insulated copper wire around a soft iron rod. Fie then connected one end to the rheostat and the other free end to the battery via a key. He closed the key and observes the deflection in the magnetic needle placed nearby. Now he altered the current by reversing the connections of the battery and again noted the change in the deflection of the needle. (3)
(a) Why do the student perform this activity?
(b) What did the student observe?
(c) Comment on the statement “a material in the middle of a current carrying coil gets magnetised”.
OR
Answer the following question:
(a) What type of magnetic field is produced due to a straight current carrying conductor?
(b) The magnetic field lines produced by a straight solenoid resemble the magnetic field lines produced by another object. Identify that object.
(c) Why does it become more difficult to move a magnet towards a coil when the number of turns in a coil have been increased?
Answer:
(a) The student conducted this activity to make an electromagnet.
(b) The electrical current flowing through a coil will create a uniform magnetic field. This magnetic field causes the needle to turn. Reversing, the connections to the battery, reverses the direction of the current flow and the needle will point in the opposite direction.
(c) When an iron rod is placed along the axis of a current carrying coil, it gets magnetised under the influence of the magnetic field produced by the coil through induction. But this magnetism lasts as long as the current supply is not withdrawn.
OR
(a) Magnetic field lines are concentric circular loops in a plane perpendicular to the straight conductor. The centres of the circular lines lie on the conductor.
(b) The magnetic field produced due to a straight solenoid is similar to that produced by a bar magnet.
(c) It becomes more difficult to move a magnet towards a coil when the number of turns in the coil is increased because the induced current in the coil due to electromagnetic induction increases and the induced current opposes the motion of the magnet towards the coil.
Question 11.
State the reason why carbon can neither form \(C^{4+}\) cations nor \(C^{4+}\) anions, but forms covalent compounds. Also state reasons to explain why covalent compounds: (3)
(a) Are bad conductors of electricity?
(b) Have low melting and boiling point?
OR
Why certain compounds are called hydrocarbons? Write the general formula for homologous series of alkanes, alkenes and alkynes and also draw the structure of the first member of each series. Write the name of the reaction that converts alkenes into alkanes and also write chemical equations to show the necessary conditions for the reaction to occur.
Answer:
Carbon has 4 electrons in its valence shell and it needs 4 more electrons to complete its octet. Thus, carbon can either gain or lose 4 electrons. But due to energy consideration, it is not possible. Therefore, in place of gaining or losing 4 electrons, carbon does sharing of these 4 electrons to form covalent bonds. Therefore, can neither form C4+ cations nor C4- anions but forms covalent compounds only by sharing of electrons.
(a) Covalent compounds are bad conductors of electricity because they do not contain ions.
(b) Covalent compounds have usually low melting and boiling point because the force of attraction between the molecules of covalent bond is very weak.
OR
Compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons.
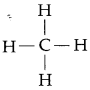
General formula for the homologous series of alkanes is CnH2n+2 First member of the alkane family is methane.
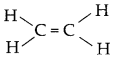
General formula for the homologous series of alkenes is CnH2n. First member of the alkene family is ethene.
General formula for the homologous series of alkynes = CnH2n-2. First member of the alkyne family is ethyne.
H – C ≡C – H
Catalytic hydrogenation is the reaction used to convert alkenes to alkanes.
\(CH2 = CH2 + H2\frac{\text { Nicke }}{300^{\circ} \mathrm{C}} CH6\)
Question 12.
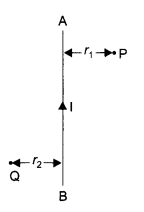
AB is a current carrying conductor in the plane of the paper as shown in figure. What are the directions of magnetic fields produced by it at points P and Q? Given \(r_{1}>r_{2}\), where will the strength of the magnetic field be larger? (3)
Answer:
Since the direction of the current in the current carrying conductor AB is upwards, the direction of the magnetic field would be anti-clockwise as deduced by applying right hand thumb rule. Consequently, the magnetic field at point P would be towards the plane and, at point Q, the direction of the magnetic field would be away from the plane. Since the strength of the magnetic field is inversely proportional to the distance (r), the field at P would be weaker as compared to Q [∵ r1 > r2].
Question 13.
The electrons in the atoms of four elements A, B, C and D are distributed in three shells having 1,3,5 and 7, electrons respectively in their outermost shells. Write the group numbers in which these elements are placed in the Modem Periodic Table. Write the electronic configuration of the atoms of B and D, and the molecular formula of the compound formed when B and D combine. (3)
Answer:
A → 1st group.
B → 13thth group.
C → 15th group.
D → 17th group.
Electronic configuration
B → Atomic number = 13
K L M
2 8 3
D → Atomic number = 17
K L M
2 9 7
The molecular formula of the compound when B and D combine is BD3.
Section – C
This section has 02 case-based questions (14 and 15). Each case is followed by 03 sub-questions (a, b and c). Parts a and b are compulsory. However, an internal choice has been provided in part c.
Question 14.
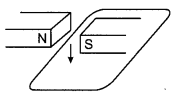
The wire in the figure below is being moved downwards through the magnetic field, so as to produce induced current. (4)
What would be the effect of :
(a) moving the wire at a higher speed?
(b) moving the wire upwards rather than downwards?
(c) using a stronger magnet?
Draw the pattern of magnetic field lines produced around a current carrying straight conductor passing perpendicular through a horizontal cardboard. State and apply right-hand thumb rule to mark the direction of the field lines. How will the strength of the magnetic field change when the point where magnetic field is to be determined is moved away from the straight conductor? Give reason to justify your answer.
Answer:
(a) The induced current increases at a higher speed.
(b) The induced current is reversed.
(c) The induced current increases.
OR
Maxwell’s Right Hand Thumb rule states that if current carrying wire is imagined to be held in the right hand so that thumb points in the direction of current, then the direction in which fingers encircle the wire will give the direction of magnetic field lines around the wire. If we hold the current carrying straight wire so that thumbs in upward direction points the direction of current, the direction of magnetic field lines will be anticlockwise. The strength of magnetic field is inversely proportional to the distance of the point of observation from the wire. So, as we move away from the wire the strength of magnet decreases.
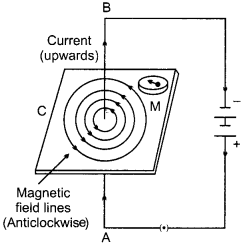
Magnetic field pattern due to a straight current-carrying wire
Question 15.
The sexual act always has the potential to lead to pregnancy. Pregnancy will make major demands on the body and the mind of the woman, and if she is not ready for it, her health will be adversely affected. Therefore, many ways have been devised to avoid pregnancy. (4)
(a) Name any two bacterial diseases that are caused due to unprotected sex.
(b) How a pill helps in preventing pregnancy?
(c) What is vasectomy?
OR
What are the common side-effects of using contraceptive pills?
Answer:
(a) The two bacterial diseases that are caused due to unprotected sex are gonorrhea and syphilis.
(b) The pill helps in preventing pregnancy as it prevents the release of the ovum, by changing the hormonal balance.
(c) Vasectomy is the surgical process by which the vas deferens is cut. This prevents the sperms from reaching the ejaculatory duct.
OR
The common side-effects of using contraceptive pills are irritation, nausea, and mood swings.