Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science with Solutions and marking scheme Set 5 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set 5 with Solutions
Time Allowed: 3 hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
(i) This question paper consists of 39 questions in 5 sections.
(ii) All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions. A student is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
(iii) Section A consists of 20 Objective-type questions carrying 1 mark each.
(iv) Section B consists of 6 Very Short questions carrying 02 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 30 to 50 words.
(v) Section C consists of 7 Short Answer type questions carrying 03 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 50 to 80 words.
(vi) Section D consists of 3 Long Answer type questions carrying 05 marks each. Answer to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
(vii) Section E consists of 3 source-based/case-based units of assessment of 04 marks each with sub-parts.
Section – A (20 Marks)
Select and termite the most appropriate option out of the four options given for each of the questions 1 – 20. There is no negative mark for an incorrect response.
Question 1.
The graph given below depicts a neutralization reaction (acid + alkali → salt + water).
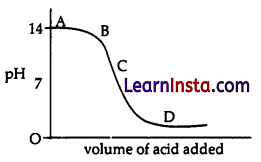
The pH of a solution changes as we add excess of acid to an alkali.
Which letter denotes the area of the graph where both acid and salt are present?
(A) A
(B) B
(C) C
(D) D
Answer:
(D) D
Explanation: When both add and salt are present, the pH of the solution becomes less than 7. Since, from the graph, the pH is less than 7 at only part D.
Question 2.
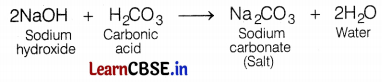
___________ is a basic salt because it is a salt of weak acid and strong base.
(a) Sodium bicarbonate
(b) Sodium carbonate
(c) Sodium hydroxide
(d) Sodium chloride
Answer:
(b) Sodium carbonate
Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) is the salt of a weak acid (carbonic acid) and a strong base (sodium hydroxide).
![]()
Question 3.
Sodium hydroxide is termed an alkali while Ferric hydroxide is not because:
(A) sodium hydroxide is a strong base, while Ferric hydroxide is a weak base.
(B) sodium hydroxide is a base which is soluble in water while Ferric hydroxide is also a base but it is not soluble in water.
(C) sodium hydroxide is a strong base while Ferric hydroxide is a strong acid.
(D) sodium hydroxide and Ferric hydroxide both are strong bases but the solubility of sodium hydroxide in water is comparatively higher than that of Ferric hydroxide.
Answer:
(B) sodium hydroxide is a base that is soluble in water while Ferric hydroxide is also a base but it is not soluble in water.
Explanation: An alkali is a base that dissolves in water hence, all alkalis are bases but all bases are not alkalis.
Sodium hydroxide is termed an alkali as it is a strong base as well as highly soluble in water. Ferric hydroxide is also a base, but it is not an alkali as it is not soluble in water.
Question 4.
Select the acid which contains four hydrogen atoms in it.
(a) Formic acid
(b) Sulphuric acid
(c) Nitric acid
(d) Acetic acid
Answer:
(d) Acetic acid
Acetic acid also known as carboxylic acid has the chemical formula CH3COOH. It has four hydrogen atoms.
Question 5.
The name of the salt used to remove the permanent hardness of water is:
(A) Sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3)
(B) Sodium chloride (NaCl)
(C) Sodium carbonate decahydrate (Na2CO3.10H2O)
(D) Calcium sulphate hemihydrate (CaSO4.12H2O)
Answer:
(C) Sodium carbonate decahydrate (Na2CO3.1OH2O)
Explanation: Sodium carbonate decahydrate (washing soda: Na2CO3.10H2O) is used to remove the permanent hardness of water.
Question 6.
Which of the following is the mineral acid?
(a) Hydrochloric acid
(b) Citric acid
(c) Acetic acid
(d) Lactic acid
Answer:
(a) Hydrochloric acid
The mineral acids are those which are obtained from minerals and do not contain carbon.
e.g. HCl, H2SO4, HNO3, etc.
Question 7.
How will you protect yourself from the heat generated while diluting a concentrated acid?
(A) By adding acid to water with constant stirring.
(B) By adding water to acid with constant stirring.
(C) By adding water to acid followed by base.
(D) By adding base to acid with constant stirring.
Answer:
(A) By adding acid to water with constant stirring.
Explanation: The mixing of water with add is highly exothermic. So, if water is added to an add, it produces a very large amount of heat. This can break the container and sometimes even causes burning. Hence, it is advised to add concentrated add to water with constant stirring.
Question 8.
In a food chain, the snake predated a rabbit which fed on fresh green bushes. What percentage amount of the energy accumulated by rabbits, would be acquired by snakes?
(a) 90%
(b) 10%
(c) 50%
(d) 25%
Answer:
(b) 10%
According to Lindemann’s 10% energy law, in a food chain, only around 10% of the available energy is passed on to the next trophic level. The rest of the energy is lost to the ecosystem in the form of heat.
Question 9.
The sensory nerve of a reflex arc carries information from the receptor cells to the:
(A) Spinal cord
(B) Brain
(C) Muscles of the effector organ
(D) Bones of the receptor organ
Answer:
(A) Spinal cord
Explanation: The sensory nerve of a reflex arc carries information from the receptor cells to the spinal cord. It is also called an afferent neuron.
![]()
Question 10.
In human males, all the chromosomes are paired perfectly, except one. These unpaired chromosomes are
(i) large chromosome
(ii) small chromosome
(iii) Y-chromosome
(iv) X-chromosome
Which of the following options is correct regarding the same?
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (iii) only
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer:
(b) (iii) and (iv)
In human males, all chromosomes are paired perfectly, except one. These unpaired chromosomes are the Y-chromosome and X-chromosome. In human males, one pair called the sex chromosomes are unpaired. Here, one is of normal size (X-chromosome) while the other is shorter (Y-chromosome)
Question 11.
In a person, the tubule part of the nephron is not functioning at all. What will its effect be on urine formation?
(A) The urine will not be formed.
(B) Quality and quantity of urine is unaffected.
(C) Urine is more concentrated.
(D) Urine is more diluted.
Answer:
(D) Urine is more diluted.
Explanation: The function of a tubule is the re¬ absorption of useful substances such as glucose and amino acids, salts, and a major amount of water into the blood capillaries. Therefore, if the tubule part of the nephron is not functioning, the urine is more diluted since it contains both useful and waste substances.
Question 12.
A Planaria worm is cut horizontally from the middle into two halves P and Q. Another Planaria worm is cut vertically into two halves R and S. Which of the cut pieces of the two Planaria worms could regenerate to form the complete worm?
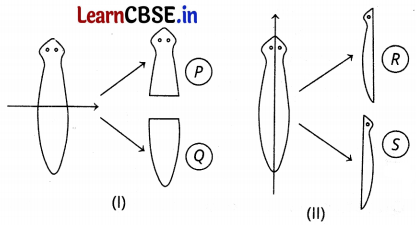
(a) Only P
(b) R and S
(c) P and Q
(d) P, Q, R, and S
Answer:
(d) P, Q, R, and S
The Planaria reproduces through the regeneration method, therefore all the cut parts (i.e. P, Q, R, and S) of the Planaria will regenerate to form complete worms.
Question 13.
Consider the following properties of virtual images:
(i) Cannot be obtained on the screen.
(ii) Are formed by both concave and convex lens.
(iii) Are always erect.
(iv) Are always inverted.
The correct properties are:
(A) (i) and (iv)
(B) (i) and (ii)
(C) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(D) (i), (ii) and (iv)
Answer:
(C) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Explanation: A virtual image is formed when reflected rays appear to meet. Such images cannot be obtained on screen. Plane mirrors, convex mirror and concave lens always form a virtual image. They are always erect.
Question 14.
The size of the pupil of the eye is adjusted by
(a) cornea
(b) retina
(c) iris
(d) blind spot
Answer:
(c) iris
Iris is a dark muscular diaphragm that controls the size of the pupil.
Question 15.
The pyramid of energy is the:
(A) total energy in an ecosystem.
(B) net energy in an ecosystem.
(C) energy consumed by various organisms.
(D) graphic representation of energy levels at each trophic level.
Answer:
(D) graphic representation of energy levels at each trophic level.
Explanation: When the energy level is represented in the form of a pyramid, it is known as a pyramid of energy.
![]()
Question 16.
Which of the listed tools was used to study the law of inheritance in pea plants by Gregor Johann Mendel?
(a) Family tree
(b) Pedigree tree
(c) Punnett square
(d) Herbarium sheet
Answer:
(c) Punnett square
Punnett square was used by Gregor Johann Mendel to determine the low of inheritance in his experiments with pea plants.
Questions Nos. 17 to 20 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true but R is false.
(D) A is false but R is true.
Question 17.
Assertion (A): The melting point and boiling point of ethanol are lower than that of sodium chloride.
Reason (R): The forces of attraction between the molecules of ionic compounds are very strong.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: The melting point and boiling point of ethanol are indeed lower than that of sodium chloride. This is because ethanol is a covalent compound, while sodium chloride is an ionic compound. Covalent compounds have weaker intermolecular forces than ionic compounds, which means less energy is required to break the bonds holding the molecules together. Therefore, covalent compounds tend to have lower melting and boiling points than ionic compounds.
Question 18.
Assertion (A): Lymph also known as colourless tissue.
Reason (R): It lacks erythrocytes.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Lymph is similar to the plasma of blood but is colorless due to a lack of erythrocytes. Erythrocytes contain hemoglobin, which provides red colour to blood. Due to its absence, lymph is colorless.
![]()
Question 19.
Assertion (A): AC load line is used for long-distance transmission.
Reason (R): It has very less loss of energy in long-distance transmission.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: AC load line can be easily transmitted over long distances without much loss in energy.
Question 20.
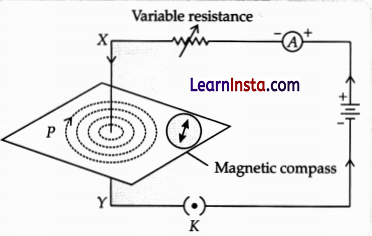
Assertion (A): A current-carrying solenoid, always comes to rest in a geographical N-S direction, when suspended freely.
Reason (R): One end of the current carrying a straight solenoid behaves as a North pole and the other end as a South pole, just like a bar magnet.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
When a current is flowing through a solenoid, then according to the “clock face rule” one end of the solenoid behaves as the North pole and the other end behaves as the South Pole. Hence, a current-carrying solenoid behaves as a bar magnet. On freely suspending, it comes to rest in the geographical N-S direction. Therefore, both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Section – B (12 Marks)
(Q. no. 21 to 26 are very short answer questions.)
Question 21.
State whether the given chemical reaction is a redox reaction or not. Justify your answer
MnO2 + 4HC1 → MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2
Answer:
The given reaction is an example of a redox reaction because the oxidation and reduction take place simultaneously in the reaction.
(i) MnO2 + 4H+ + 2e– → Mn2+ + 2H2O
As you can see in this reaction, Mn02 is converted to Mn2+ because the addition of electrons takes place in this reaction, hence we can say that MnO2 is the compound which is reduced.
(ii) 2Cl– → Cl2 + 2e–
In this reaction, Cl– is oxidised to Cl2 because the removal of electrons takes place. Hence, we can say that the oxidised compound is HCl.
Question 22.
Outline a project, which aims to find the dominant coat colour in dogs.
Answer:
Select a homozygous black (BB) male dog and a homozygous white (bb) female dog and cross-breed them. The resultant offspring (F1-generation) will be
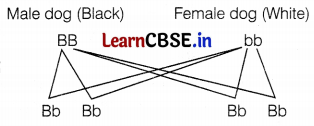
If all the offspring of the F1 generation are black, we can conclude that black colour is dominant over white coat colour in dogs and if all the offsprings are white, the dominant colour will be white. (2)
Question 23.
How is an electric impulse created in the human nervous system? Identify the parts of a neuron which help the nerve impulse to travel:
(a) Towards the cell body
(b) Away from the cell body
Answer:
A nerve impulse is generated when the stimulus is strong. This stimulus triggers the electrical and chemical changes in the neuron.
- Dendrites are the part of neurons where information is acquired. It receives impulses and transmits impulses toward the cell body.
- Axon is the part of the neuron through which information travels as an electric impulse. It helps in transmitting impulses away from the cell body.
OR
With the help of an example, explain how the feedback mechanism regulates hormone secretion.
Answer:
Feedback mechanism is the mechanism in our body to maintain the hormonal levels in the body in a desirable amount. An increase or decrease in the hormonal level in our body triggers the feedback mechanism.
For example, The increase in the blood sugar level stimulates the secretion of insulin so that the sugar level is maintained. If the blood sugar level falls below normal, then it stimulates the secretion of glucagon. Glucagon stimulates the breakdown of glycogen to glucose, and thus, the normal sugar level is maintained.
Question 24.
The refractive indices of the three media are given below.
| Medium | Refractive Index |
| A | 1.6 |
| B | 1.8 |
| C | 1.5 |
A ray of light is traveling from A to B and another ray is traveling from B to C.
(a) In which of the two cases the refracted ray bends towards the normal?
(b) In which case does the speed of light increase in the second medium? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer:
(a) When light travels from an optically rarer medium to an optically denser medium it moves towards the normal. Then, nB > nA. The light ray will bend towards the normal on passing from medium A to B.
(b) The speed of light will increase when the light travels from B to C, since nC < nB and v = (c/n), the speed of light ray will increase in the second medium. (1)
Question 25.
The figure shows two magnets X and Y kept near each other. Their poles are not marked, but the magnetic field lines are shown in the figure.

If magnet X is moved towards magnet Y as indicated by the arrow, will the two magnets attract or repel each other? Justify your answer by describing how you interpret the field lines.
Answer:
They will repel each other.
The right end of magnet X and the left end of magnet Y are both north poles since field lines start from there.
OR
What are the three types of wires used in household circuits? Pick out the wire used as a safety measure for an electrical appliance with a metallic body.
Answer:
(a) Live wire
(b) Neutral wire
(c) Earth wire
![]()
Question 26.
(a) Describe the role of Fallopian tubes in the female reproductive system.
(b) Placenta.
Answer:
(a) Fertilisation of ovum by sperm occurs in Fallopian tubes. It acts as a site of fertilization in human females. (1)
(b) The placenta is an organ that develops in the uterus during pregnancy. It provides oxygen and nutrients to the mother. It also removes waste produced by the baby. (1)
Section – C (21 Marks)
(Q.no. 27 to 33 are short answer questions.)
Question 27.
(a) While electrolyzing water before passing the current some drops of an acid are added. Why? Name the gases liberated at cathode and anode. Write the relationship between the volume of gas collected at the anode and the volume of gas collected at the cathode.
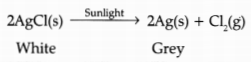
(b) What is observed when silver chloride is exposed to sunlight? Give the type of reaction involved.
Answer:
(a) Water is a non-electrolyte. So, the addition of acid will make it a good conductor of electricity. By this action, ions will be produced due to the dissociation of acidified water that acts as a charge carrier for the faster conduction of electricity.
The gas liberated at the cathode is hydrogen gas.
The gas liberated at the anode is oxygen gas. y In the electrolysis of water, the ratio of volumes of hydrogen and oxygen obtained is 2:1, 2 volumes of hydrogen and volume of oxygen combine to form water
(b) When silver chloride is exposed to light, it decomposes to form silver metal and chlorine gas.
The type of reaction is photolytic decomposition.
Question 28.
During the reaction of some metals with dilute hydrochloric acid, the following observations were made.
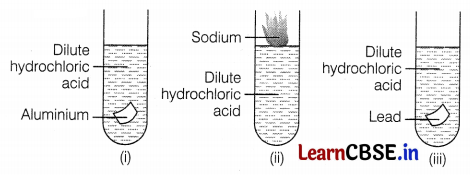
(a) The temperature of the reaction mixture rises when aluminium (Al) is added.
(b) The reaction of sodium metal is found to be highly explosive.
(c) Some bubbles of gas are seen when lead (Pb) is reacted with the acid. Explain these observations with suitable reasons.
Answer:
(a) The temperature of the reaction mixture rises when aluminium is added because it is an exothermic reaction and thus, heat gets liberated in these reactions. (1)
(b) Reaction of sodium metal is found to be highly explosive because it is an exothermic reaction. (1)
(c) When lead is treated with hydrochloric acid, bubbles of hydrogen gas are evolved.

Question 29.
What is geotropism? Draw a labelled diagram of a potted plant showing positive geotropism and negative geotropism.
Answer:
The upward growth of shoots and the downward growth of roots in response to the pull of the earth’s gravity is called geotropism.

Question 30.
‘In humans, there is a 50% probability that a boy will be born and 50% probability that a girl will be born’. Justify the statement based on the mechanism of sex determination in human beings.
Answer:
All children will inherit an X chromosome from their mother regardless of whether he is a boy or a girl. Thus, the sex of the child will be determined by what they inherit from their father. A child who inherits an X-chromosome from her father will be a girl and one who inherits a Y-chromosome will be a boy. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes. Both males and females carry two sets of sex chromosomes. Male (XY) has one X and one Y sex chromosome. Female (XX) has both X sex chromosomes. (3)
Question 31.
A student observes the above phenomenon in the lab as a white light passes through a prism. Among many other colors, he observed the position of the two colors: Red and Violet.
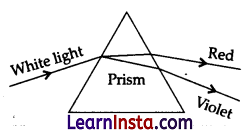
(a) What is the phenomenon called?
(b) What is the reason for the violet light to bend more than the red light?
(c) Draw a ray diagram to show the path of light when two identical
glass prisms are arranged together in an inverted position concerning each other and a narrow beam of white light is allowed to fall obliquely on one of the focus of the first prism.
Answer:
(a) The phenomenon is called dispersion.
(b) Speed of violet light inside the prism is slowest and that of red is highest. Hence, the deviation of violet light is maximum and that of red is minimum.
(c) Ray diagram:
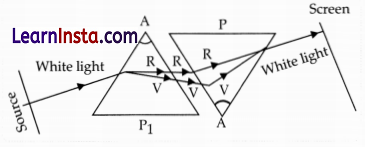
Question 32.
An object of height 5 cm is placed on the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm. If the virtual image is formed by the concave mirror at a distance of 10 cm from its pole, then find
(a) the size of the image.
(b) magnification produced by the mirror.
Answer:
(a) Given, height of an object, h1 = 5 cm, f = -20 cm and v = 10 cm
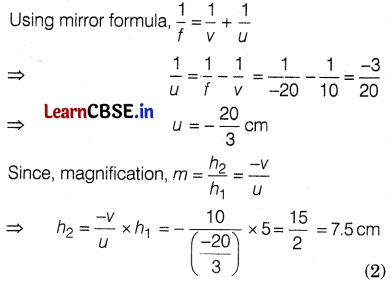
Alternate solution
Given, height of an object, h1 = 5 cm, f = -20 cm and v = 10 cm
Linear magnification of concave mirror, m = \(\frac{f-v}{f}\)
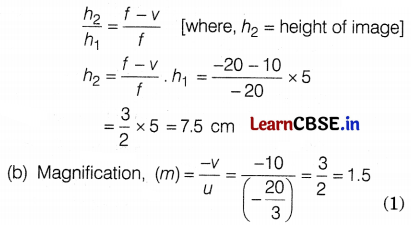
![]()
Question 33.
Suppose your parents have constructed a two-room house and you want in the living room there be a provision of one electric bulb, one electric fan, a refrigerator and a plug point for appliances of power up to 2 kilowatts. Draw a circuit diagram showing the electric fuse and earthing as safety devices.
Answer:
(i) Four components should be labelled.
(ii) All of them should be in parallel and there should be a fuse for safety.
(iii) Live and earth wires should be there.
Section – D (15 marks)
(Qzno. 34 to 36 are long answer questions.)
Question 34.
Kamini was studying the compound C6H14. She wondered about its different structure with the same formula. Give the name of the compound. Also, write the structural formulae of all the isomers of an alkane with six C-atoms (C6H14).
Or
(a) Calcium reacting with water starts floating. Give the reason behind this and write the balanced chemical equation of the reaction.
(b) Rashmi was studying about CH3Cl compound. Show the bond formation in this compound.
Answer:
The name of the compound is hexane and it has the following five isomers.
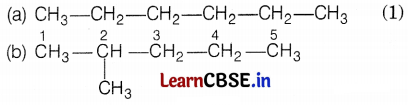
[Here, 5 carbon atoms are arranged in a straight I line, one is branched at 2 C-atoms] (1)
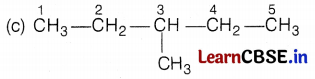
[Here, the branch is at 3C-atom] (1)
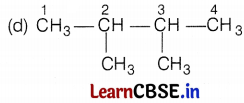
[Here, branches are at C-2 and C-3 atoms] (1)
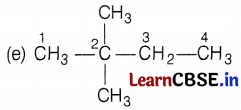
[Here, branches are at C-2 carbon atom only] (1)
Or
(a) Calcium reacts with cold water to form calcium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. (2)

The bubbles of hydrogen gas produced stick to the surface of calcium and hence, it starts floating on the surface of water. (1)
(b) Electronic configuration of carbon, 6 = 2, 4 (K = 2, L = 4)
Electronic configuration of hydrogen, 1 = 1 (K = 1)
Electronic configuration of chlorine, 17 = 2, 8, 7 (K = 2, L = 8, M = 7)
The carbon atom has four outermost electrons, each hydrogen atom has one electron and chlorine has seven outermost electrons. Carbon shares its four outermost electrons with 3 hydrogen atoms and 1 chlorine atom to form CH3Cl as follows.
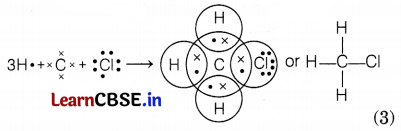
Question 35.
Different organisms reproduce by different methods suitable to their body designs.
(a) Justify the above statement using examples of three different organisms that reproduce by different methods of asexual reproduction.
(b) Differentiate between sexual and asexual modes of reproduction.
Answer:
(a) Amoeba: Binary fission
Plasmodium: Multiple fission
Hydra: Budding
Planaria: Regeneration (Any three + Explain)
(b) Sexual: two parents; Asexual: single parent.
Detailed Answer:
(a) (i) Binary Fission in Amoeba: In this method, the nucleus first divides mitotically into two, followed by the division of the cytoplasm. The cell finally splits into two daughter cells. So, from one Amoeba parent, two daughter Amoebae are formed.
(ii) Budding in Hydra: In budding, a small part of the body of the parents grows out as a ‘bud’, which then detaches and becomes a new organism. Hydra reproduces by budding using regenerative cells. A bud develops as an outgrowth in Hydra due to repeated cell division at one specific site. When fully mature, the bud detaches itself from the parent body and develops into new independent individuals.
(iii) Regeneration in Planaria: In this method, small cut or broken parts of an organism’s body grow or regenerate into separate individuals. Planaria can be cut into any number of pieces and each piece grows into a complete organism.
(b) Differences between sexual and asexual reproduction:
| S.No | Sexual Reproduction | Asexual Reproduction |
| (i) | Two parents are required | Only one parent is required |
| (ii) | Offsprings are genetically dissimilar from parents | Offsprings are identical to parents |
OR
Give one example each of unisexual and bisexual flowers. Differentiate between the two types of pollination that occur in flowers. What happens when pollen lands on a suitable stigma? Write about the events that occur till the seed formation in the ovary.
Answer:
Unisexual flower: Papaya/watermelon/any other. (Anyone)
Bisexual flower: Hibiscus/Rose/any other.
Self-pollination: The pollen grains are transferred from the anther to the stigma of the same flower or to the flower of the same plant.
Cross-pollination: The pollen grains are transferred from the anther to the stigma of a flower of a different plant.
After pollen lands on a suitable stigma, a pollen tube grows out of the pollen grain and travels through the style to reach the ovary. The male germ cell fuses with the female germ cell to form a zygote. Zygote divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule. The ovule develops tough coat and gradually gets converted into a seed.
![]()
Question 36.
It is desired to obtain an erect image of an object, using a concave mirror of a focal length of 12 cm.
(a) What should be the range of distance of an object placed in front of the mirror?
(b) Will the image be smaller or larger than the object? Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image in this case.
(c) Where will the image of this object be, if it is placed 24 cm in front of the mirror? Draw a ray diagram for this situation to justify your answer. Show the positions of the pole, principal focus, and the center of curvature in the above ray diagrams.
Or
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on the walls of a school laboratory by using a lens.
(a) Which type of lens should he use and why?
(b) At what distance in terms of focal length F of the lens should he place the candle flame, to get
(i) a magnified and
(ii) a diminished image respectively, on the wall?
(c) Draw ray diagrams to show the formation of the image in each case.
Answer:
(a) f = -12 cm
Thus, range to obtain an erect image
⇒ 0 < u < 12 (1)
(b) the Image will be larger than the object (2)
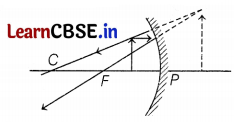
(c) Position of image
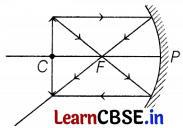
Here, f = -12 cm, u = -24 cm, v = ?
By using the mirror formula,
\(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{u}\)
⇒ \(\frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{-12}-\frac{1}{(-24)}\)
⇒ v = -24 cm (2)
Or
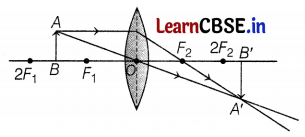
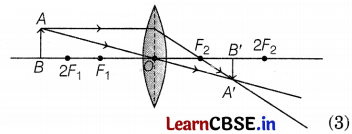
(a) He should use a convex lens as real images are formed by it.
(b) (i) For a magnified image, he should place the candle flame between the focus (F) and the center of curvature (2F) of the lens.
(ii) To get the diminished image, he should place the candle flame beyond the center of curvature (2F) of the lens. (2)
(c) (i) For magnified image
(ii) For diminished image
Section – E (12 Marks)
Question 37.
Based on reactivity metals are grouped into three categories:
(a) Metals of low reactivity
(b) Metal of medium reactivity
(c) Metals of high reactivity
Therefore, metals are extracted in pure form from their ores based on their chemical properties. Metals of high reactivity are extracted from their ores by electrolysis of the molten ore. Metals of low reactivity are extracted from their sulphide ores, which are converted into their oxides. The oxides
of these metals are reduced to metals by simple heating.
(a) Name the process of reduction used for a metal that gives a vigorous reaction with air and water both.
(b) Carbon cannot be used as a reducing agent to obtain aluminium from its oxide? Why?
(c) Describe briefly the method to obtain mercury from cinnabar. Write the chemical equation for the reactions involved in the process.
Answer:
(a) Electrolytic reduction: The metal is likely to be sodium (Na). It has a very much affinity to oxygen. So, reducing agents like carbon and aluminium can’t be used.
(b) Because aluminium has a greater affinity for oxygen than for carbon, therefore carbon cannot reduce alumina (Al2O3) to aluminium.
(c) Cinnabar (HgS-mercury (II) sulphide or mercury sulphide) is an ore of mercury. It is heated in air to give mercuric oxide (HgO). Mercuric oxide is further heated to get mercury.
The reaction involved are: \(\begin{aligned}
& 2 \mathrm{HgS}(s)+3 \mathrm{O}_2(g) \stackrel{\Delta}{\longrightarrow} 2 \mathrm{HgO}(s)+2 \mathrm{SO}_2(g) \\
& 2 \mathrm{HgO}(s) \stackrel{\Delta}{\longrightarrow} 2 \mathrm{Hg}(l)+\mathrm{O}_2(g)
\end{aligned}\)
OR
(c) Differentiate between roasting and calcination giving a chemical equation for each.
Answer:
Calcination is defined as the process of converting ore into an oxide by heating it strongly. The ore is heated below its melting point either in the absence of air or in limited supply.
e.g., ZnCO3 → ZnO + CO2
Roasting is a process of metallurgy where ore is converted into its oxide by heating it below its melting point in the presence of excess air. An example of roasting is when Zinc sulphide is converted into zinc oxide.
2ZnS + 3O2 → 2ZnO + 2SO2
![]()
Question 38.
To study the ozone layer depletion, Mrs. Sharma, a science teacher drew the given flow chart on the blackboard. After completing this topic she asked some questions from students. Help them by answering the following questions.
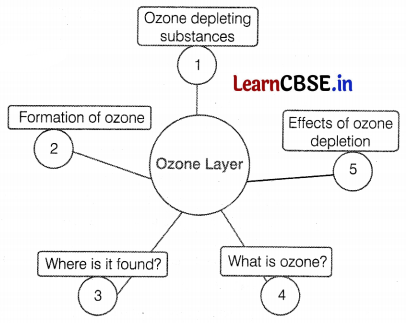
(a) What are ozone-depleting substances?
(b) Ravi wants to draw the ozone layer in a diagram showing different layers of the atmosphere, where does he label it?
(c) How is ozone formed?
Or
What could be the effect of ozone depletion?
Answer:
(a) Substances that are responsible for the depletion of the ozone layer or breakdown of ozone molecules are known as ozone-depleting substances, e.g. CFCs, halogens, nitrous oxide, CCl4, and CH4 are ozone-depleting substances responsible for ozone layer depletion. (1)
(b) The ozone layer is found in the stratosphere around 15-30 km above the earth’s surface. (1)
(c) Atomic oxygen is highly reactive. It combines with molecular oxygen under the action of UV radiations to form ozone.
O2 \(\stackrel{\mathrm{UV}}{\longrightarrow}\) [O] + [O]
2O2 + 2 [O] → 2O3 (Ozone) (2)
Or
Cancers, mutations, effects on eyesight, global warming, weakening of the immune system, etc. are some adverse effects of ozone depletion. (2)
Question 39.
A student was asked to experiment to study the force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field. He took a small aluminium rod AB, a strong horseshoe magnet, some connecting wires, a battery, and a switch and connected them as shown. He observed that on passing the current, the rod gets displaced. On reversing the direction of the current, the direction of displacement also gets reversed. Based on your understanding of this phenomenon, answer the following questions:
(a) Why does the rod get displaced on passing a current through it?
(b) State the rule that determines the direction of the force on the conductor AB.
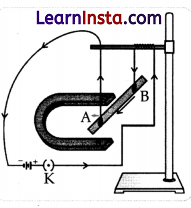
(c) (i) If the U-shaped magnet is held vertically and the aluminium rod is
suspended horizontally with its end B towards due north, then on
passing current through the rod from B to A as shown, in which direction will the rod be displaced?
(ii) Name any two devices that use current-carrying conductors and magnetic fields.
Answer:
(a) When a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a force, due to which the rod gets displaced.
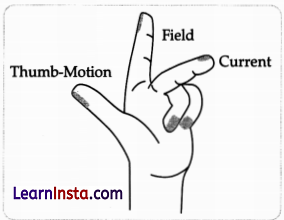
(b) The rule that determines the direction of the force on the conductor AB is Fleming’s Left-Hand rule. According to this rule, if the direction of electric current is perpendicular to the magnetic field, the direction of force is also perpendicular to both of them. Stretch the thumb, forefinger, and middle finger of your left hand such that they are mutually perpendicular. If forefinger points in the direction of the magnetic field, the middle finger in the direction of current, then the thumb will point in the direction of motion of force.
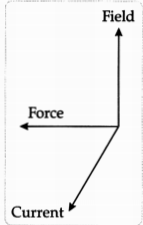
(c) (i) According to Fleming’s Left-Hand rule, the rod will get displaced upwards.
(ii) Devices that use current-carrying conductors and magnetic fields are electric motor, electric generator, loudspeaker, microphones, etc.
OR
(c) Draw the pattern of magnetic field lines produced around a current-carrying straight conductor held vertically on a horizontal cardboard. Indicate the direction of the field lines as well as the direction of the current flowing through the conductor.
Answer:
(c) The magnetic field lines around a current-carrying conductor can be represented by concentric circles.
The direction of the magnetic field can be determined by using the Right-Hand Thumb rule.