Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science with Solutions and marking scheme Set 4 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set 4 with Solutions
Time Allowed: 3 hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- This question paper consists of 39 questions in 5 sections.
- All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions. A student is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
- Section A consists of 20 Objective type questions carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B consists of 6 Very Short questions carrying 02 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 30 to 50 words.
- Section C consists of 7 Short Answer type questions carrying 03 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 50 to 80 words.
- Section D consists of 3 Long Answer type questions carrying 05 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
- Section E consists of 3 source-based/case-based units of assessment of 04 marks each with sub-parts.
Section – A (20 Marks)
Select and write the most appropriate option out of the four options given for each of the questions 1 – 20. There is no negative mark for incorrect response.
Question 1.
Identify the correct option from the given table which represents the type of reactions occurring in step 1 and step 2.
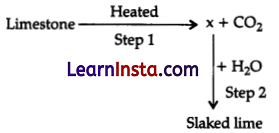
| Option | Endothermic | Exothermic |
| (A) | ✘ | ✔ |
| (B) | ✔ | ✘ |
| (C) | ✔ | ✔ |
| (D) | ✘ | ✘ |
Answer:
| (C) | ✔ | ✔ |
Explanation: When limestone is heated, it absorbs heat (endothermic) and decomposes to form calcium oxide. When water is added to this calcium oxide (lime), calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2, ie., slaked lime is formed. This is an exothermic reaction.
![]()
Question 2.
Carbon can use four hydrogen atoms to form methane (CH4), because
(a) valency of carbon is four
(b) valency of hydrogen is one
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) carbon gets noble gas configuration by making four covalent bonds with hydrogen
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
Carbon has 4 electrons in its valence shell, while hydrogen has one electron in its valence shell. To complete their octet and duplet respectively, they form covalent bonds. Carbon utilizes its 4 valence electrons and forms 4 covalent bonds with 4 hydrogen atoms, using one valence electron with each hydrogen atom.
Question 3.
Ethane, with the molecular formula C2H4 has:
(A) 6 covalent bonds
(B) 7 covalent bonds
(C) 8 covalent bonds
(D) 9 covalent bonds
Answer:
(B) 7 covalent bonds
Explanation: Ethane has 7 covalent bonds. One bond is between two carbon atoms and the rest of the six is between hydrogen atoms.
Question 4.
With the reference to four given oxides, which one of the options in the table is correct?
| Oxide | Nature of Oxide |
| (a) SO2 | Basic |
| (b) H2O | Acidic |
| (c) Al2O3 | Amphoteric |
| (d) CaO | Neutral |
Answer:
(c) Al2O3 – Amphoteric
(a) SO2 is acidic oxide because S is non-metal and non-metals form acidic oxide.
(b) H2O is a neutral oxide.
(c) Al2O3 is an amphoteric oxide that behaves as an acid as well as a base.
(d) CaO is basic oxide because Ca is a metal and metals form basic oxide.
Question 5.
When aqueous solutions of potassium iodide and lead nitrate are mixed, an insoluble substance separates.
The chemical equation for the reaction involved is:
(A) KI + PbNO3 → PbI + KNO3
(B) 2KI + Pb(NO2)2 → PbI2 + 2KNO3
(C) KI + Pb(NO2)2 → PbI + KNO3
(D) KI + PbNO3 → PbI2 + KNO3
Answer:
(B) 2KI + Pb(NO2)2 → PbI2 + 2KNO3
Explanation: When an aqueous solution of potassium iodine and lead nitrate is mixed, an insoluble yellowish lead iodide is formed along with potassium nitrate.
The chemical reaction involved is:
Pb(NO3)2 + 2KI → PbI2 + 2KNO3
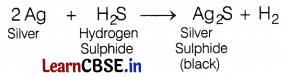
Question 6.
Due to the formation of ________, silver articles become black on prolonged exposure to air.
(a) Ag3N
(b) Ag3O
(c) Ag2S
(d) Ag2S and Ag3N
Answer:
(c) Ag2S
Silver articles become black because silver reacts with the gas present in the air to form a black coating of Ag2S. The reaction is as follows.
![]()
Question 7.
Bronze is an alloy of:
(A) copper and zinc
(B) aluminium and tin
(C) copper, tin and zinc
(D) copper and tin
Answer:
(D) copper and tin
Explanation: Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin.
Question 8.
Which of the following statement(s) is (are) true about the heart?
(i) The Left atrium receives oxygenated blood from different parts of the body while the right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the lungs.
(ii) The left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to different body parts while the right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
(iii) The left atrium transfers oxygenated blood to the right ventricle which sends it to different body parts.
(a) Only (i)
(b) Only (ii)
(c) Only (ii)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Answer:
(c) Only (ii)
Statement (ii) is correct about the heart.
The route of blood circulation in the heart is as follows.
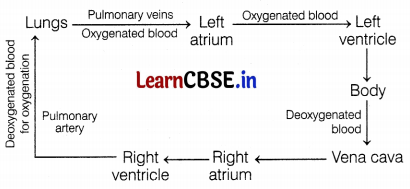
Question 9.
Adolescence is a unique stage of human development and an important time for laying the foundations of good health. During adolescence, the reproductive phase starts and:
(A) general growth rate begins to slow down.
(B) height becomes less.
(C) the body weight is reduced.
(D) hair growth decreases.
Answer:
(C) the body weight is reduced.
Explanation: Sexual maturation of reproductive tissues is a necessary link for reproduction because of the need for germ-cells to participate in sexual reproduction. The body of the individual organism has to grow toits adult size, the rate of general body growth begins to slow down and reproductive tissues begin to mature during adolescence.
Question 10.
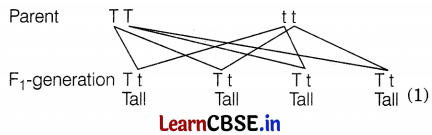
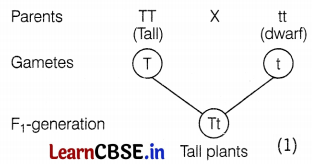
A cross between a tall pea plant (TT) and a short pea plant (tt) resulted in progeny that were all tall plants because
(a) tallness is the dominant trait
(b) shortness is the dominant trait
(c) tallness is the recessive trait
(d) height of the pea plant is not governed by gene ‘T’ or ‘t’.
Answer:
(a) tallness is the dominant trait
In the F1 generation, the cross between TT and tt will result in all tall plants as shown in the figure given below. Thus, tallness is the dominant trait that expresses itself regardless of its presence in the homozygous or heterozygous state.
Question 11.
Water in the root enters due to:
(A) the function of the root to absorb water
(B) difference in the concentration of ions between the root and the soil.
(C) excess water present in the soil
(D) diffusion of water in the roots
Answer:
(B) difference in the concentration of ions between the root and the soil.
Explanation: Water in the root enters due to difference in the concentration of ions between the root and the soil.
![]()
Question 12.
Consider the following figure concerning the brain.
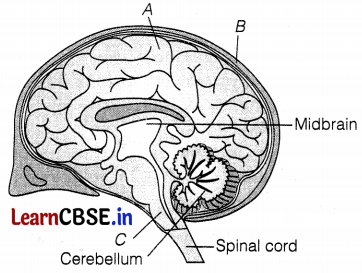
Identify the unlabelled parts (A, B, and C) by choosing the correct option below.
| A | B | C | |
| (a) | Medulla | Cerebrum | Skull |
| (b) | Skull | Medulla | Cerebrum |
| (c) | Cranium | Cerebrum | Medulla |
| (d) | Cerebrum | Cranium | Medulla Oblongata |
Answer:
(d) A – Cerebrum, B – Cranium, C – Medulla Oblongata
A is the cerebrum, which is responsible for reasoning, speech, hearing, intelligence, and usage of information.
B is the cranium, which protects the brain, while C is the medulla oblongata which controls involuntary actions, such as breathing, blood pressure (BP), etc.
Question 13.
To obtain a magnification of + 2 with a concave mirror of radius of curvature 60 cm, the object distance must be.
(A) -90cm.
(B) -45cm
(C) -30cm
(D) -15cm
Answer:
(D) -15cm
Explanation: Given: Concave mirror has a radius
of curvature = 60cm
So, Focal length = 60/2 = -30cm
‘ve is taken because the focus of the mirror is behind the pole.
Given: Magnification = 2
Also, v is image distance, u is object distance and f is focal length.
As magnification = -v/u
Hence on putting the values we get, -v/u = 2
v = -2u
Now, putting the value of v and f we get,
u = -15cm
Question 14.
The bluish colour of water in the deep sea is due to
(a) the presence of algae and other plants found in water
(b) reflection of the sky in the water
(c) scattering of light
(d) absorption of light by the sea
Answer:
(c) scattering of light
The bluish colour of water in the deep sea is due to the scattering of light as the very fine particles of H2 and O2 molecules present in water are scattered mainly blue light.
Question 15.
Study the given figure of a food web and identify the primary consumer in the food web:
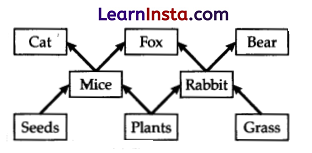
(A) Mice and Bear :
(B) Rabbit and Cat
(C) Rabbit and Fox
(D) Mice and Rabbit
Answer:
(B) Rabbit and Cat
Explanation: Primary consumers make up the second trophic level. They are also called herbivores. They eat producers. In the given food web, mice and rabbit are primary consumers.
![]()
Question 16.
The development of a seedling from an embryo under appropriate conditions is called
(a) regeneration
(b) germination
(c) vegetative propagation
(d) pollination
Answer:
(b) germination
Germination is a process occurring in plants in which the embryo develops into a seedling under appropriate conditions. (1)
Questions Nos. 17 to 20 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true but R is false.
(D) A is false but R is true.
Question 17.
Assertion (A): It is advised that while diluting an acid one should add water to acid and not acid to water keeping, the solution continuously stirred.
Reason (R): The process of dissolving an acid into water is highly exothermic.
Answer:
(D) A is false but R is true.
Explanation: We should add acid to water and not water to acid. It is highly exothermic and may cause burns. Hence, the assertion is false but the reason is true.
Question 18.
Assertion (A): Plants lack the nervous system, but they do coordinate.
Reason (R): It is so because of hormones.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Plants lack the nervous system but coordinate via hormones like auxin, gibberellins, cytokinins, etc.
Question 19.
Assertion (A): In Fleming’s Left-Hand rule, the direction of magnetic field, force and current are mutually perpendicular.
Reason (R): Fleming’s Left-Hand rule is applied to measure the induced current.
Answer:
(C) A is true but R is false.
Explanation: Fleming’s Left-Hand rule is used to find the direction of force in a current-carrying conductor in the presence of a magnetic field.
Question 20.
Assertion (A): The magnetic field produced by a current-carrying solenoid is independent of its length and cross-sectional area.
Reason (R): The magnetic field inside the solenoid has a variable value.
Answer:
(c) A is true but R is false.
The magnetic field produced by a current-carrying solenoid is independent of its length and area of cross-section. It only depends on the number of turns and current flowing through the solenoid. So, Assertion is true. The magnetic field produced inside a current-carrying solenoid is uniform. So, the Reason is false. (1)
![]()
Section – B (12 Marks)
(Q. no. 21 to 26 are very short answer questions.)
Question 21.
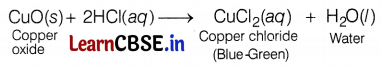
A student took a small amount of copper oxide in a conical flask and added dilute hydrochloric acid to it with constant stirring. He observed a change in the colour of the solution.
(a) Write the name of the compound formed and its colour.
(b) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction involved.
Answer:
(a) The compound formed is copper(II) chloride or cupric chloride (CuCl2).
The colour of CuCl2 is blue-green.
(b) The balanced chemical equation is:
CuO (s) + 2HCl (aq) → CuCl (aq) + H2O (l)
Question 22.
Explain how the movement of leaves of a sensitive plant is different from the movements of shoots towards light.
Answer:
Movements in Mimosa pudica (sensitive plant) occur in response to touch. In such movements, plant cells change shape by changing the amount of water in them resulting in folding up and drooping of leaves. This movement is independent of growth. (1)
Plants respond to a stimulus by growing in a particular direction and the movement is due to growth. This growth is directional. Movement of shoots towards light indicates phototropism, i.e. movement occurs in response to light. (1)
Question 23.
List two differences between the movement of leaves of a sensitive plant and the movement of a shoot towards light.
Answer:
The type of movement of leaves of the sensitive plant is known as a nastic movement. This type of movement does not depend on the direction of stimuli.
The movement of shoot towards light is known as a tropic movement. This movement depends on the direction of light. This type of movement is directional and promotes growth development.
OR
What happens at the synapse between two neurons? State briefly.
Answer:
Transmission of nerve impulses between two neurons takes place through the synapse. At the end of the axon, the electrical impulse sets off the release of some chemicals called neurotransmitters. These chemicals cross the gap or synapse and start a similar electrical impulse in the dendrite of the next neuron.
Question 24.
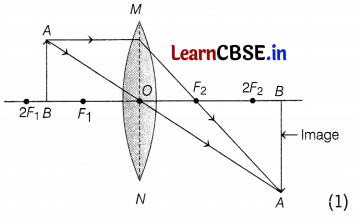
Observe the following incomplete ray diagram of an object where the image A’B’ is formed after refraction from a convex lens.
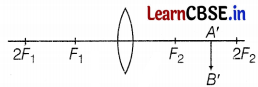
Based on the above information fill in the blanks.
(a) The position of object AB would have been ________
(b) The size of the object would have been ________ than the size of the image.
Answer:
(a) The position of object AB would have been beyond 2F1.
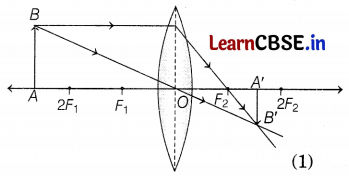
(b) The size of the object would have been bigger than the size of the image. (1)
Question 25.
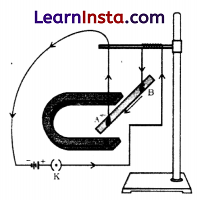
As shown in the diagram an aluminium rod ‘AB’ is suspended horizontally between the two poles of a strong horseshoe magnet in such a way that the axis of the rod is horizontal and the direction of the magnetic field is vertically upward. The rod is connected in series with a battery and a key.
State giving reason:
(a) What is observed when a current is passed through the aluminium rod from end B to end A?
(b) What change is observed in a situation in which the axis of the rod ‘AB’ is moved and aligned parallel to the magnetic field and current is passed in the rod in the same direction?
Answer:
(a) It is observed that the rod is displaced towards the left as force is exerted on the current-carrying aluminium rod when it is placed in a magnetic field.
(b) No displacement will be observed as the rod will not experience any force because the angle between the magnetic field and the current-carrying conductor is zero.
![]()
OR
When is the force experienced by a current-carrying straight conductor placed in a uniform magnetic field:
(a) Maximum
(b) Minimum
Answer:
(a) The force experienced by a current-carrying straight conductor placed in a uniform magnetic field is maxinium when the conductor carrying current is perpendicular to the direction of a uniform magnetic field.
(b) The force experienced by a current-carrying straight conductor placed in a uniform magnetic field is minimum when the conductor-carrying current is parallel or anti-parallel to the direction of a uniform magnetic field.
Question 26.
Vegetarian food habits can sustain a larger number of people. Justify the statement in terms of the food chain.
Answer:
In a food chain, about 90% of the energy gets lost at each trophic level. This means that in long food chains, very little energy from the producer is available to the top carnivores. For example,

But in shorter food chains, more energy will be available to man.
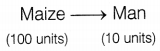
Hence, vegetarian food habits, where nutrition is derived directly from producers, can sustain a large number of people. (2)
Section – C (21 Marks)
(Q.no. 27 to 33 are short answer questions.)
Question 27.
A substance X is used as a building material and is insoluble in water. When it reacts with dil. HCL it produces a gas that turns lime water milky.
(a) Write the chemical name and formula of ‘X’.
(b) Write chemical equations for the chemical reactions involved in the above statements.
Answer:
(a) Substance X is calcium carbonate.
Chemical formula: CaCO3
(b) In the reaction between calcium carbonate and dilute hydrochloric acid (HCI), calcium chloride (CaCl2), carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O)
are produced.
CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl (aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
The carbon dioxide evolved reacts with limewater (Ca(OH)2 to form calcium carbonate and water.
Ca(OH)2(s) + CO2(g) → CaCO3(s) + H2O(l)
The production of calcium carbonate is responsible for the milky white colour.
Question 28.
What are soaps chemically? How do they differ from synthetic detergents? Also, mention their uses.
Or
An organic compound A is a constituent of many medicines is used as an antifreeze and has the molecular formula C2H6O. Upon reaction with alk.KMnO4, the compound A is oxidized to another compound B with the formula C2H4O2. Identify the compounds A and B. Write the chemical equation for the reaction that leads to the formation of B.
Answer:
Soaps are chemically sodium or potassium salts of long-chain carboxylic acids. In contrast, detergents are ammonium or sulphonate salts of long-chain carboxylic acids. Both soaps and detergents are used as cleansing agents. Soaps are used for washing clothes only in soft water, i.e. water which does not contain Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions, while detergents are used to make shampoos and products for cleaning clothes even in hard water. (3)
Or
The organic compound A which is a constituent of many medicines and act as antifreeze with the molecular formula C2H6O is ethanol (CH3CH2OH). Ethanol is oxidized to ethanoic acid (B) upon reaction with alk. KMnO4.

![]()
Question 29.
(a) How does Paramecium obtain its food?
Answer:
Paramecium takes its food at a specific spot by endocytosis. Food is moved to this spot by the movement of cilia which cover the entire surface of the cell.
(b) List the role of each of the following in our digestive system:
(i) Hydrochloric acid
(ii) Trypsin
(iii) Muscular walls of stomach
(iv) Salivary amylase
Answer:
(i) Hydrochloric acid: The hydrochloric acid creates an acidic medium which facilitates the action of enzyme pepsin and it also kills the germs in the food.
(ii) Trypsin: Trypsin helps in the digestion of proteins into smaller peptides.
(iii) Muscular wall of stomach: The muscular wall of the stomach help in mixing the food thoroughly with more digestive juices.
(iv) Salivary amylase: Saliva contains an enzyme called salivary enzyme which breaks down starch to give simple sugar.
Question 30.
Explain, how pesticides accumulate in the environment.
Answer:
Pesticides are poisonous chemical substances, which are sprayed over crop plants to protect them from pests and diseases. These pesticides mix up with soil and water. From here they are absorbed by the growing plants along with water. These chemicals enter the environment through the food chains, in the following manner. (1)
When herbivorous animals eat plants, these poisonous chemical pesticides enter into their bodies through the food chain. When the carnivorous animals eat herbivores, then the pesticides get transferred to their bodies. In this process of transfer of food through food chains, these harmful chemicals get concentrated at each subsequent trophic level. This is known as biomagnification or bio-concentration. (2)
Question 31.
In the figure given below, a narrow beam of white light is shown to pass through a triangular glass prism. After passing through the prism, it produces a spectrum XY on the screen.
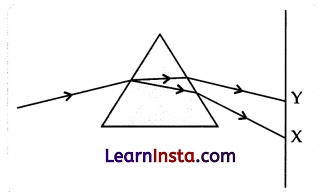
(a) Name the phenomenon.
(b) State the colours seen at X and Y.
(c) Why do different colours of white light bend at different angles through a prism?
Answer:
(a) The phenomenon is called dispersion,
(b) X; Violet, Y; Red
(c) Different colours of white light bend through different angles concerning the incident beam of light due to differences in the speed of light of different wavelengths.
Question 32.
What is meant by the “electrical resistance” of a conductor? State how the resistance of a conductor is affected when
(a) a low current passes through it for a short duration.
(b) a heavy current passes through it for about 30 seconds.
Answer:
The electrical resistance of a conductor may be defined as the property of any substance to oppose the flow of current through it.
(a) The resistance of the conductor will increase when a low current passes through it for a short duration. (2)
(b) The resistance of the conductor will decrease when a heavy current passes through it. (1)
![]()
Question 33.
For the current-carrying solenoid as shown, draw magnetic field lines and give a reason to explain that out of the three points A, B and C, at which point the field strength is maximum and at which point is it minimum?
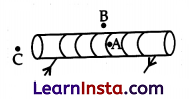
Answer:
(i) The field strength will be maximum at point A as A is inside the solenoid where the field lines have the highest density.
(ii) The field strength will be minimum at point B as field lines have the least density.
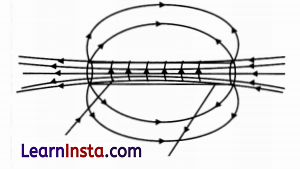
Section – D (15 marks)
(Q.no. 34 to 36 are long answer questions.)
Question 34.
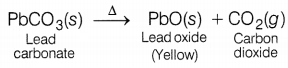
(a) The carbonate of metal X is a white solid. It decomposes when heated to form carbon dioxide and yellow solid oxide. What is metal X?
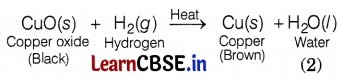
(b) What happens when Rakesh passes hydrogen gas over the heated copper oxide? Write the chemical equation involved in this reaction.
Or
Write three physical properties of each of the acids and bases. How will you show with an example that metal oxides are basic? Give chemical equation also.
Answer:
(a) Metal X is lead (Pb). Metal carbonate, i.e. Lead carbonate is a white solid amorphous powder.
When lead carbonate is heated CO2 gas is evolved along with the formation of lead oxide. (3)
(b) When hydrogen gas is passed over heated copper oxide (CuO) the black coating on the surface turns brown and copper is obtained.
Or
(i) Properties of Acids
(a) Acids are sour.
(b) Acids turn blue litmus to red.
(c) Acids are corrosive.
Properties of Bases
(a) Bases have a bitter taste.
(b) Bases feel soapy to touch.
(c) Bases turn red litmus to blue. (2)
(ii) The reaction between copper oxide and dil. hydrochloric acid:
The colour of the solution becomes blue-green due to the formation of copper (II) chloride. Metallic oxide, i.e. CuO behaves as a base and forms salt and water when it reacts with an acid like HCl. Hence, metallic oxides are basic. (3)
![]()
Question 35.
(a) “Use of a condom is beneficial for both the sexes involved in a sexual act.” Justify this statement by giving two reasons.
(b) How do oral contraceptives help in avoiding pregnancies?
(c) What is sex-selective abortion? How does it affect a healthy society? (State any one consequence)
Answer:
(a) Two reasons:
(i) Avoids unwanted/undesirable pregnancies / STDs.
(ii) Use of condoms prevents the transmission of infections from one person to another.
(b) Oral contraceptives change the hormonal balance of the body so that the eggs are not released.
(c) Sex-selective abortion is a procedure that is done for female fetuses/female foeticide. It adversely affects the male-female sex ratio.
OR
(a) Draw the diagram of the female reproductive system and match and mark the part(s):
(i) Where the block is created surgically to prevent fertilization.
(ii) Where is CuT inserted?
(iii) Inside which condom can be placed.
Answer:
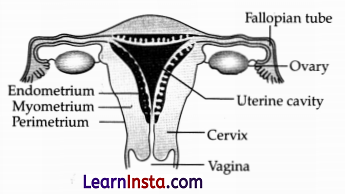
Correct diagram with correct labelling, correctly matched with the following parts:
(i) Fallopian Tube/oviduct
(ii) Uterus
(iii) Vagina
(b) Why do more and more people prefer to use condoms? What is the principle behind the use of condoms?
Answer:
People prefer the use of condoms as it prevents STDs/gives privacy to the user. Condoms help create a mechanical barrier preventing the meeting of sperm and ovum.
Question 36.
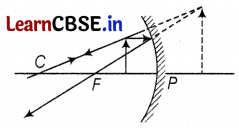
It is desired to obtain an erect image of an object, using a concave mirror of a focal length of 12 cm.
(a) What should be the range of distance of an object placed in front of the mirror?
(b) Will the image be smaller or larger than the object? Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image in this case.
(c) Where will the image of this object be, if it is placed 24 cm in front of the mirror? Draw a ray diagram for this situation and also justify your answer.
Show the positions of the pole, principal focus, and the center of curvature in the above ray diagrams.
Or
A thin converging lens forms a real magnified image and a virtual magnified image of an object in front of it.
(a) Write the positions of the objects in each case.
(b) Draw ray diagrams to show the image formation in each part.
(c) How will the following be affected by cutting this lens into two halves along the principal axis?
(i) Focal length
(ii) Intensity of the image formed by the half lens.
Answer:
(a) Given, focal length, f = -12 cm, Thus, range to obtained erect image
⇒ 0 < u < 12 (1)
(b) The image will be larger than the object
(c) Position of image
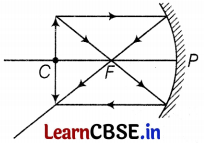
Here, f = -12 cm, u = -24 cm, v = ?
By using the mirror formula,
\(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{u}\)
⇒ \(\frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{-12}-\frac{1}{(-24)}\)
⇒ v = -24 cm (3)
Or
(a) (i) Object is placed between F and 2F.
(ii) The object is placed between the optical centre and F.
(b) The ray diagrams are as follows.
Part (a)
Part (b)
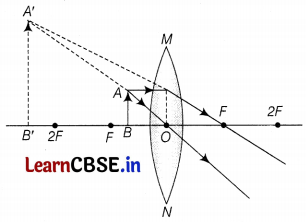
(c) (i) There will be no change in focal length.
(ii) Intensity will become one-fourth. (1)
Section – E (12 Marks)
(Q.no. 37 to 39 are case-based/data-based questions with 2 to 3 short sub-parts.)
(Internal choice is provided in one of these sub-parts.)
Question 37.
Two students decided to investigate the effect of water and air on iron objects under identical experimental conditions. They measured the mass of each object before placing it partially immersed in 10 mL of water. After a few days, the objects were removed, and dried and their masses were measured. The table shows their results.
| Student | Object | Mass of object before rusting in g |
Mass of the coated object in g |
| A | Nail | 3.0 | 3.15 |
| B | Thin plate | 6.0 | 6.33 |
(a) What might be the reason for the varied observations of the two students?
(b) In another setup the students coated iron nails with zinc metal and noted that iron nails coated with zinc prevent rusting. They also observed that zinc initially acts as a physical barrier, but an extra advantage of using zinc is that it continues to prevent rusting even if the layer of zinc is damaged. Name this process of rust prevention and give any two other methods to prevent rusting.
Answer:
(a) Rusting occurs in both A and B so there is an increase in mass.
As the surface area of B is greater, the extent of rusting is greater.
(b) Galvanisation
Oiling/greasing/painting/alloying/chromium plating or any other. (any two 1/2 mark each)
OR
(b) In which of the following applications of iron, rusting will occur most? Support your answer with a valid reason.
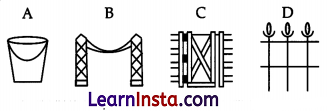
Answer:
Iron hinges on a gate.
Tron is in contact with atmospheric oxygen and moisture/water vapour.
Question 38.
If we cross pure-breed tall (dominant) pea plants with pure-breed dwarf (recessive) pea plants, we get pea plants of F1 generation. If we now self-cross the pea plant of the F1 generation, then we obtain the pea plant of the F2 generation.
(i) What do the plants of the F1 generation look like?
(ii) What is the ratio of tall plants to dwarf plants in F2-generation?
(iii) Statement type of plants not found in F1-generation but appeared in F2-generation mentioning the reason for the same.
Or
Write the phenotypic and genotypic ratio of plants in F2-generation.
Answer:
(i) The plants produced in the F1 generation are all tall.
(ii) The ratio of tall plants to dwarf plants in F2-generation
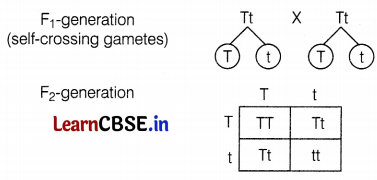
TT and Tt are phenotypically tall plants and tt is a dwarf plant ratio of tall plants in F2 generation = 3 : 1.
(iii) Dwarf pea plants are not found in F1-generation but appeared in F2-generation. This observation indicates that both the traits of shortness and tallness are inherited in the F1 generation. But only the tallness tract is expressed in the F1 generation. Because for a plant to be tall, a single copy of ‘T’ is enough. But dwarfness in pea plants is a successive trait and it requires a homozygous condition (tt) to express itself. (2)
Or
The phenotypic ratio of pea plants in F2-generation is 3 : 1. (1)
The genotypic ratio of pea plants in F2-generation is 1 : 2 : 1. (1TT : 2Tt : 1tt). (2)
![]()
Question 39.
Electrical resistivity is the electrical resistance of a specific specimen of the material of unit length and unit cross-sectional area. The electrical resistivity shows the current opposing property of a conductor. The table shows four different materials and their resistivity.
| Material | Resistivity |
| Material 1 | 1.62 × 10-8 |
| Material 2 | 100 × 10-6 |
| Material 3 | 6.84 × 10-8 |
| Material 4 | 44 × 10-6 |
(a) Name the material, which is the best conductor of electricity?
(b) What is the SI unit of resistivity?
(c) Why is nichrome wire used in many electrical heating devices? Give two reasons.
Answer:
(a) Material 1 is the best conductor of electricity. Good conductors have high conductivity and low resistivity.
(b) The SI unit of resistivity is ohm-meter (Ω m).
(c) Nichrome wire is generally used as a heating element in heating appliances as:
(i) It offers a very large resistance. So a large amount of electric energy is converted into a large amount of heat energy.
(ii) It has a high melting point such that it can be heated till red hot without melting.
OR
(c) Name the element, which can be used for electrical transmission lines. Give reason.
Answer:
Copper, because it is economical, less oxidative than other metals and has low resistivity.