CBSE Class 6 Social Science Sample Papers
CBSE Class 6 Social Science Sample Paper Set 1
Time : 3 hrs
Maximum Marks. : 80
General Instructions :
1 All questions are compulsory.
2 Marks for each question are indicated against the questio
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) :
Question 1.
Which statement about the Earth’s shape is correct? (1)
(a) It is a perfect sphere.
(b) It is slightly flattened at the poles.
(c) It is completely flat.
(d) It is shaped like a cube.
Answer:
(b) It is slightly flattened at the poles.
Question 2.
The International Date Line Is located approximately along which longltude? (1)
(a) 90° E
(b) 0°
(c) 180°
(d) 90° W
Answer:
(c) 180°
![]()
Question 3.
Which ocean lies to the East of India? (1)
(a) Atlantic Ocean
(b) Pacific Ocean
(c) Arabian Sea
(d) Bay of Bengal
Answer:
(d) Bay of Bengal
Question 4.
Which of the following rivers originates from the Vindhya Range? (1)
(i) Ganga
(ii) Yamuna
(iii) Ghagara
(iv) Son
Codes :
(a) Both (i) and (ii)
(b) Only (iv)
(c) Both (iii) and (iv)
(d) Only (iii)
Answer:
(b) Only (iv)
Question 5.
Match the elements in column I with their correct description In column II. (1)
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Geologists | 1. Study the remains of plants, animals and humans from millions of years ago |
| B. Palaeontologists | 2. Study the physical features of the Earth |
| C. Archaeologists | 3. Study human societies and cultures |
| D. Anthropologists | 4. Study past remains left by humans, plants and animals |
Codes
A B C D
(a) 2 1 4 3
(b) 1 2 3 4
(c) 4 3 2 1
(d) 3 2 1 4
Answer:
(a) 2 1 4 3
Question 6.
Which of the following was an important crop grown by the Harappans? (1)
(a) Rice
(b) Tea
(c) Coffee
(d) Cocoa
Answer:
(a) Rice
![]()
Question 7.
What is a characteristic of a nuclear family? (1)
(a) Includes grandparents, parents and children
(b) Includes only a couple and their children
(c) Includes uncles, aunts and cousins
(d) Includes multiple generations living together
Answer:
(b) Includes only a couple and their children
Question 8.
What does the term ‘grassroots democracy’ refer to?
(a) Rule by a single leader
(b) Involvement of ordinary citizens in decision-making
(c) Avoiding elections
(d) Eliminating local governments
Answer:
(b) Involvement of ordinary citizens in decision-making
Question 9.
In the context of Indlan governance, what does a Municlpal Corporation handle?
(a) National Defense
(b) City infrastructure and services
(c) International Relations
(d) State Education Policies
Answer:
(b) City infrastructure and services
Question 10.
What is the primary role of the legislature in a government?
(a) Implementing laws
(b) Making new laws
(c) Deciding whether laws are fair
(d) Enforcing laws
Answer:
(b) Making new laws
![]()
Question 11.
Assertion (A) The Equator is the largest circle that can be drawn on the Earth’s surface.
Reason (R) The Equator is located at 90° latitude.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of $A$.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of $A$.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Answer:
(c) A is true, but R is false.
Question 12.
What is the name of India’s first scientific base station in Antarctica?
(a) Dakshin Bharat
(b) Dakshin Gangotri
(c) Northern Star
(d) Sagar Mata
Answer:
(b) Dakshin Gangotri
Question 13.
Which of the following was not a characteristic of Harappan cities?
(a) Wide streets oriented to cardinal directions
(b) Houses with individual bathrooms
(c) Large, open marketplaces
(d) Fortifications around the city
Answer:
(c) Large, open marketplaces
![]()
Question 14.
What does the term ‘ atman’ refer to In Vedic culture?
(a) The world
(b) The self
(c) The cosmos
(d) The divine essence of nature
Answer:
(b) The self
Fill in the Blanks :
1. Jainism emphasises the idea of __________ , which means non-attachment to material possessions.
Answer:
aparigraha
2. The process of taking decisions, organising society’s life with different sets of rules, and ensuring they are followed is called __________ (1)
Answer:
governance
![]()
3. The __________ branch of government implements laws and includes the head of state and ministers.
Answer:
executive
True or False :
1. The Ganga is the largest river originating in the Himalayas.
Answer:
True
2. Jambudvipa is derived from a tree native to India.
Answer:
True
3. The Harappans were the first in Eurasia to grow cotton.
Answer:
True
Very Short Answer Type Questions :
Question 1.
Which mountain is known as the highest in South India?
Question 2.
What is a significant feature of the Harappan reservoir at Dholavira?
Or
What was a major feature of Harappan town-planning?
![]()
Question 3.
Which Indian plain supports a large population and agriculture?
Question 4.
Suppose a historian finds conflicting accounts about a historical event in two different sources. How should they proceed?
Question 5.
What did the ‘People of India’ project reveal about the linguistic diversity in India?
Or
What is one feature of Indian literature that illustrates unity in diversity?
Short Answer Type Questions :
Question 1.
Evaluate the importance of Harappan seals and their inscriptions in understanding trade and communication in the Indus-Sarasvati civilisation. (3)
Or
Examine the significance of agricultural practices in sustaining Harappan cities.
Question 2.
Discuss the reasons for the decline of the Indus-Sarasvati civilisation around 1900 BCE.
Or
Describe the types of artifacts found in Harappan cities and what they reveal about daily life and social organisation.
Question 3.
Evaluate the role of community support as illustrated by the Bhil community’s response to the water crisis and Kamal Parmar’s initiative for underprivileged children.
Question 4.
Discuss the concept of ‘Participatory Democracy’ and provide examples of how citizens can engage in governance at the local level.
Question 5.
Explain how rivers contribute to the formation of floodplains and how these areas become ideal for agriculture.
![]()
Question 6.
Discuss the environmental threats oceans facing today.
Long Answer Type Questions :
Question 1.
Explain the differences between joint and nuclear families, and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each type.
Or
Discuss the concept of ‘dharma’ in the context of family life. How does the principle of dharma influence the roles and responsibilities of family members?
Question 2.
Discuss the importance of the separation of powers in government. How does this separation prevent abuse of power and ensure fairness in governance? (5)
Or
Describe the roles and responsibilities of the three branches of government: legislature, executive and judiciary, and explain how they interact with each other to maintain governance.
![]()
Question 3.
Compare and contrast the teachings of Buddhism and Jainism, focusing on their core principles and how they address the concept of suffering and enlightenment.
Or
What are the main features of Vedic society as described in the Rig Veda? How were the different janas or clans organised and governed?
Case Based Questions :
1. Any government operates at two levels at the least – local and national. In many countries, including India, it functions at three levels or tiers – local, state or regional and national. Each level deals with different matters. To use a comparison, if a bulb in your home is not lighting up, you will first check the bulb, switch, fuse, etc. If that does not work, you may call an electrician, and if it is found that the problem is not within your home, you may need to go to the Electricity Board and file a complaint. These are also three levels of dealing with a problem.
(I) Discuss why it is important for a country to have multiple tiers of government?
(II) In what ways does the presence of local governments enhance decision-making and problem-solving at the grassroots level? (1)
(III) Analyse how the Interaction between local, state and national governments in India can lead to more effective governance, particularly in resolving complex problems. (2)
2. Today, there are diverse economic activities such as manufacturing computers, mobile phones and drones; working in banks, schools and hotels; driving various types of vehicles for transportation; making furniture; tailoring clothes using machines; creating software; repairing refrigerators and washing machines; etc. Classifying all these activities helps us to understand how they function and the links they have with each other.
(I) Discuss how different sectors of the economy, such as manufacturing, services and transportation, contribute to the overall functioning of society. Provide examples.
(II) Analyse the interdependence of various economic actlvities mentioned in the passage, such as manufacturing, transportation and services.
(III) How has the rise of technology-based actlvitles, such as creating software and repairing electronic appliances, transformed the traditional economic landscape?
![]()
3. Year after year, the reglon around the town of Jhabua, in Madhya Pradesh, suffered from an acute water crisis. Following their halma (see facing page) tradition of coming together to support any individual or family in times of crisis, the Bhil community decided to plant thousands of trees in hundreds of villages. The Bhils also dug many trenches to conserve rainwater and created other water harvesting structures. They did not get paid for thls work but did it as their duty towards their community and the environment.
(I) Analyse the role of community-based Initiatlves, like the one taken by the Bhil community, in solving environmental challenges such as water scarcity. (1)
(II) Why do you think the Bhil community chose not to accept payment for their work in water conservation? What does this reveal about their values? (1)
(III) Why is it important for communities to take proactive steps in conserving natural resources? (2)
Map Based Questions :
Question 1.
Locate the following on a worid map. (3)
(i) Largest ocean in the world
(ii) The smallest ocean
(iii) Largest island in the world
Question 2.
On the given map of India, identify and label the following. (2)
(i) Identify and label the continents on the map that are generally considered to be two continents but if seen as a single landmass, they can also be considered as one.
(ii) Island group of India.
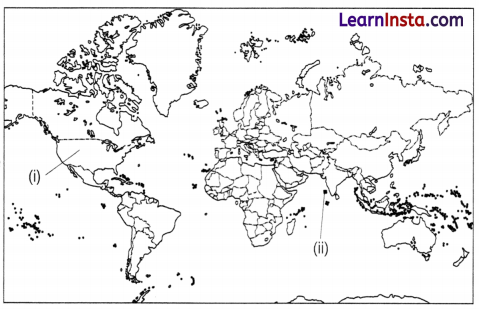
Answer:
(i) North America and South America
(ii) Lakshadweep Islands
CBSE Class 6 Social Science Sample Paper Set 2
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) :
Question 1.
India’s Standard Time is ahead of Greenwich Mean TIme (GMT) by (1)
(a) 4 hours
(b) 5 hours
(c) 5 hours 30 minutes
(d) 6 hours
Answer:
(c) 5 hours 30 minutes
![]()
Question 2.
What is the latitude of the Equator?
(a) 0°
(b) 90° N
(c) 45° S
(d) 180°
Answer:
(a) 0°
Question 3.
How did anclent Greeks refer to the reglon we now call India?
(a) Hind
(b) Yindu
(c) Indoi
(d) Sindhu
Answer:
(c) Indoi
Question 4.
What does ‘dharma’ represent In the context of family llfe?
(a) Duty and responsibilities.
(b) Entertainment and leisure.
(c) Financial status.
(d) Educational qualifications.
Answer:
(a) Duty and responsibilities.
![]()
Question 5.
What is the main role of a Residents’ Welfare Association in urban communities? (1)
(a) To manage agricultural practices
(b) To create new job opportunities
(c) To make rules about waste management and cleanliness
(d) To provide financial assistance
Answer:
(c) To make rules about waste management and cleanliness
Question 6.
Which of the following is a key feature of a democracy? (1)
(a) Direct rule by all citizens
(b) Representation through elected officials
(c) No laws or rules
(d) Control by a single leader
Answer:
(b) Representation through elected officials
Question 7.
In which sector does transportation of goods fall? (1)
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Tertiary
(d) Quaternary
Answer:
(c) Tertiary
![]()
Question 8.
Assertion (A) Oceans are vital for the survival of life on Earth.
Reason (R) Oceans provide rain and more than half of the oxygen we breathe.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 9.
Match the elements in Column I with their correct description in column II. (1)
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Common Era (CE) | 1. Period of 1000 years |
| B. Before Common Era (BCE) | 2. Years counted forward from Jesus Christ’s birth |
| C. Century | 3. Period of 100 years |
| D. Millennium | 4. Years counted backward from Jesus Christ’s birth |
Codes :
A B C D
(a) 4 1 3 2
(b) 1 2 3 4
(c) 3 4 2 1
(d) 2 4 3 1
Answer:
(d) 2 4 3 1
![]()
Question 10.
Which activity would fall under non-economic activities? (1)
(a) A person running a small business.
(b) A mother helping her children with schoolwork.
(c) A truck driver transporting goods for a company.
(d) A technician operating machines at a construction site.
Answer:
(b) A mother helping her children with schoolwork.
Question 11.
What type of payment is described as “payment in kind”? (1)
(a) Payment made through money
(b) Payment made through credit
(c) Payment received in the form of goods instead of cash
(d) Payment received for non-economic activities
Answer:
(c) Payment received in the form of goods instead of cash
Question 12.
Which of the following is a characteristic of primary sector actlvities? (1)
(a) They involve service provision
(b) They require the processing of raw materials
(c) They directly depend on nature
(d) They focus on the management of businesses
Answer:
(c) They directly depend on nature
Question 13.
Which of the following activities belongs to the tertiary sector? (1)
(a) Coal mining
(b) Manufacturing of textiles
(c) Software development
(d) Crop cultivation
Answer:
(c) Software development
![]()
Question 14.
In the context of urban governance, what does a Ward Committee typically do? (1)
(a) Create national policies
(b) Manage city infrastructure
(c) Report local issues like water leaks
(d) Implement foreign policies
Answer:
(c) Report local issues like water leaks
Fill in the Blanks :
1. Harappan cities often had wide streets oriented to the _______ directions. (1)
Answer:
1. Cardinal
2. The ancient text Rig Veda first mentions the _______ river. (1)
Answer:
Sarasvati
3. The Nohkalikai Falls are located on the _______ plateau. (1)
Answer:
Cherrapunji
True or False :
1. Mountains like the Aravalli Range are relatively younger than the Himalayas.
Answer:
False
2. The Ujiayini prime meridian was used in ancient Indian astronomy.
Answer:
True
![]()
3. The Equator divides the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres.
Answer:
False
Very Short Answer Type Questions :
Question 1.
What do we call land surrounded by water on all sides?
Question 2.
List any one feature of Indian literature that illustrates unity in diversity.
Or
How has the sari been used creatively beyond just a dress?
Question 3.
Imagine an archaeologist discovers a set of ancient tools buried under a city. What could this tell us about the civilisation that used them?
Question 4.
What evidence shows that Harappans engaged in long-distance trade?
Or
What type of structures were commonly used in Harappan cities for water management?
![]()
Question 5.
What is the primary economic activity on plateaus due to their mineral deposits?
Short Answer Type Questions :
Question 1.
Describe the three main components of a map and explain why each is important.
Question 2.
There is a connection between latitude and climate. Explain.
Or
The Greenwich Meridian is not the first prime meridian. Justify the statement.
Question 3.
Compare and contrast young mountains like the Himalayas with order mountain ranges such as the Aravalli range.
Question 4.
Discuss the importance of oceans in regulating the Earth’s climate and how they contribute to life on the planet.
Question 5.
Describe the secondary sector and its significance in the transformation of raw materials from the primary sector into finished products.
Or
Examine the role of the tertiary sector in supporting both the primary and secondary sectors.
![]()
Question 6.
Evaluate the significance of sacred mountains in different cultures.
Long Answer Type Questions :
Question 1.
Explain the classification of economic activities into the primary, secondary and tertiary sectors. How do these sectors interrelate in the process of economic production? (5)
Or
Discuss the role of the primary sector in economic development. Provide examples of different primary sector activities and how they contribute to the economy.
Question 2.
Describe the evolution of human societies from hunter-gatherers to agricultural communities. How did the shift to settled farming communities influence social structures and the development of villages? (5)
Or
Analyse how different sources of history contribute to our knowledge of the past. Why is it important to use multiple sources when studying history?
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the differences between economic and non-economic activities. Provide examples of each and discuss how these activities impact both individuals and society. (5)
Or
What are non-econorlic activities and why are they considered valuable despite not generating income? Explain with the help of examples.
Case Based Questions :
1. Altogether, urban local bodies are responsible for a range of functions – helping take care of the infrastructure, maintaining the burial ground, garbage collection and disposal, checking the implementation of government schemes, collecting local taxes and fines and so on. They also have some role in planning for the area’s economic and social development. However, for these bodies to be able to perform their functions efficiently, people living in the city must also perform their duties, which means that they must show care and concern for their area (remember, this is a participatory democracy).
(I) How do urban local bodies ensure the Implementation of government schemes and the collection of local taxes? Discuss the significance of these functions for city management. (1)
(II) Explain the relationship between participatory democracy and the efficient functioning of urban local bodies. How does citizen Involvement influence governance? (1)
(III) How do urban local bodies contribute to grassroots democracy? (2)
2. Over the decades, the number of economic activities has increased tremendously. For example, earlier most people were invoived in activities such as agriculture, livestock rearing. production of tools, pottery and weaving cloth. As societies progressed, the number of economic activities through which people earn their livelihoods increased vastly.
(I) Compare the types of economic activities people were traditionally engaged in with the modern economic activities that exist today. (1)
(II) How do technological advancements contribute to the increase in economic activities over time? (1)
(III) How do modern economic activities differ from traditional ones in terms of skilis and resources required? (2)
![]()
3. Around 1900 BCE, this Sindhu-Sarasvati civilisation, despite all its achievements, began to fall apart. The cities were abandoned one by one. If any inhabitants remained, they adopted a rural lifestyle in the changed environment – it appears that the earlier government or administration no longer existed. Gradually the Harappans scattered over hundreds, if not thousands, of small rural settlements.
(l) Discuss the possible reasons for the decline and abandonment of citles in the Sindhu-Sarasvati civillsation around 1900 BCE. (1)
(II) How did the lifestyle of the Harappans change after the cities were abandoned? (1)
(III) Discuss how the abandonment of cities in the Sindhu-Sarasvati civilisation might have, affected trade, economy and soclal organisation. (2)
Map Based Questions :
Question 1.
On the political map of Indla, locate the following. (3)
(i) State in which the site of Kalibangan is located.
(ii) First site in the Indus Valley Civilisation to be excavated.
(iii) State in which the site of Dholavira is located.
Question 2.
On the given map of India, identify and label the following.
(i) Identify the first city of the Indus-Sarasvati civilisation to be discovered.
(ii) The site which is believed to have been an ancient dockyard.
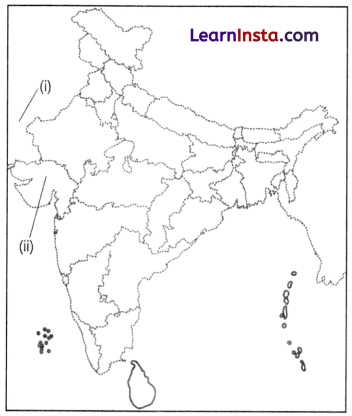
Answer:
(i) Mohenjo-daro
(ii) Lothal
CBSE Class 6 Social Science Sample Paper Set 3
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) :
Question 1.
Which Vedic delty Is assoclated with the oceans in Indian mythology?
(a) Indra
(b) Agni
(c) Varuna
(d) Surya
Answer:
(c) Varuna
![]()
Question 2.
What is the primpry source of the world’s oxygen production?
(a) Forests
(b) Oceans
(c) Ponds
(d) Deserts
Answer:
(b) Oceans
Question 3.
Assertion (A) Plateaus are less faovrable to farming than plains.
Reason (R) Most plateaus have rocky soil, making them less fertile than plains.
Codes :
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Question 4.
What term is used to refer to the years before the conventional date of Jesus’ birth? (1)
(a) AD
(b) CE
(c) BCE
(d) BC
Answer:
(c) BCE
Question 5.
What is the focus of anthropology as a discipline?
(a) The study of physical features of the Earth.
(b) The study of human societies and cultures.
(c) The study of fossils and ancient remains.
(d) The study of ancient inscriptions.
Answer:
(b) The study of human societies and cultures.
![]()
Question 6.
Which term from the Mahabharata refers to the Indian subcontinent?
(a) Bharatavarsha
(b) Sapta Sindhava
(c) Jambudvipa
(d) Hind
Answer:
(a) Bharatavarsha
Question 7.
Which of the following is not a characteristic of Harappan cIvillsation?
(a) Development of writing systems
(b) Formation of complex government and administration
(c) Development of advanced metallurgy techniques
(d) Exclusive reliance on hunting and gathering
Answer:
(d) Exclusive reliance on hunting and gathering
Question 8.
What type of objects were commonly exported by the Harappans?
(a) Precious stones and metals
(b) Agricultural tools and clothing
(c) Ornaments, beads and possibly cotton
(d) Military weapons and armor
Answer:
(c) Ornaments, beads and possibly cotton
![]()
Question 9.
Match the Harappan cItles from Column I with their corresponding modern states or reglons from column II. (1)
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Harappa | 1. Punjab |
| B. Mohenjo-daro | 2. Sindh |
| C. Dholavira | 3. Rajasthan |
| D. Kalibangan | 4. Gujarat |
Codes :
A B C D
(a) 1 2 4 3
(b) 2 3 4 1
(c) 4 1 2 4
(d) 1 2 3 4
Answer:
(a) 1 2 4 3
Question 10.
Which organ of government is responsible for enforcing laws?
(a) Judiciary
(b) Legislature
(c) Executive
(d) Parliament
Answer:
(c) Executive
Question 11.
What is the main purpose of rules and laws in soclety?
(a) To restrict freedom
(b) To maintain order and harmony
(c) To increase confusion
(d) To eliminate jobs
Answer:
(b) To maintain order and harmony
![]()
Question 12.
What is the primary role of the Gram Panchayat in the Panchayati Raj system?
(i) Overseeing district-level administrative functions
(ii) Implementing national policies
(iii) Addressing local Issues and promoting development
(iv) Conducting state elections
Codes :
(a) Only (i) and (iii)
(b) Only (iii)
(c) Only (iv)
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Only (iii)
Question 13.
In the context of economic activities, what is ‘value addition’? (1)
(a) Adding more time to complete a task.
(b) Transforming something into another form that has monetary value.
(c) Increasing the number of people involved in an activity.
(d) Reducing the cost of production.
Answer:
(b) Transforming something into another form that has monetary value.
Question 14.
Which of the following is an example of an economic activity? (1)
(a) Volunteering to teach computer skills
(b) Cooking food for family
(c) Selling furniture made from wood
(d) Taking care of grandparents
Answer:
(c) Selling furniture made from wood
Fill in the Blanks :
1. The term ‘millennium’ refers to a period of _____ years. (1)
Answer:
1,000
2. The Mahabharata uses the terms ‘Bharatavarsha’ and ‘ _____ ‘ to describe the Indian subcontinent.
Answer:
Jambudvipa
![]()
3. The word “Veda” comes from the Sanskrit word _____ ‘ which means ‘knowledge.’
Answer:
Vid
True or False :
1. Panchangas are still widely used in India to list days of the month and related astronomical data.
Answer:
True
2. The term ‘Hindustan’ was first used by the ancient Greeks to refer to India.
Answer:
False
3. The Vedas were originally written down in text form.
Answer:
False
Very Short Answer Type Questions :
Question 1.
A new tourist destination is being developed in a mountainous region. What measures should be taken to protect the fragile mountain environment?
Question 2.
Which Indian plateau is known for having huge reserves of iron coal and manganese?
Or
What term is used to describe water falling from the sky in solid form?
Question 3.
What is the term used in the Rig Veda to describe the North-West region of the Indian subcontinent?
Or
What does the term ‘Bharatavarsha’ mean?
![]()
Question 4.
Which natural disaster can originate in the ocean and cause widespread damage to coastal areas? (2)
Question 5.
Which continents are symbolised by the five rings in the Olympic Games?
Short Answer Type Questions :
Question 1.
Explain the challenges and opportunities associated with living in mountainous regions. Provide examples.
Question 2.
What is the Gregorian calendar, and how is it commonly used today?
Question 3.
Describe the agricultural practices of the Harappans and their importance to the civilisation.
Question 4.
Using the example of AMUL, describe how a cooperative model can impact economic activities in rural areas.
Or
Analyse the interdependence among the primary, secondary and tertiary sectors using a detailed example.
Question 5.
Discuss the life and teachings of Siddhartha Gautama.
Or
Describe the key principles of Jainism as taught by Mahavira.
![]()
Question 6.
How do oceans contribute to the cultural, economic, and historical development of human societies? Provide examples of how oceans have shaped human migration, trade and expansion.
Long Answer Questions :
Question 1.
Describe the three-tier structure of the Panchayati Raj system in India. Discuss the key functions and responsibilities of each tier in the governance and development of rural areas. (5)
Or
Discuss the importance of the Panchayati Raj system in strengthening democracy at the grassroots level. How does it facilitate local participation in decision-making processes?
Question 2.
Discuss the various theories proposed to explain the decline of the Indus-Sarasvati civilisation. Which factors are most widely accepted by archaeologists (5)
Or
The term ‘civilisation’ is used for an advanced stage of human societies.Discuss the essential characteristics of a civilisation.
![]()
Question 3.
Evaluate the role of textiles and clothing, specifically the sari, in representing the unity and diversity of Indian culture. (5)
Or
Analyse the impact of Indian epics, such as the Ramayana and the Mahabharata, on the cultural unity and diversity across different communities in India. How have these ejics been adapted and interpreted in various regional and tribal contexts?
Case Based Questions :
1. The Harappans were engaged in active trade, not only within their own civilisation (other cities nearby or far away), but with other civilisations and cultures within and outside India. They exported ornaments, timber, and some objects of daily use, probably also gold and cotton, and possibly some food items. The most favoured ornaments were beads of carnelian, a reddish semi precious stone found mostly in Gujarat. Harappan craftspeople developed special techniques to drill them, so a string could pass through them, and to decorate them in various ways. They also worked conch shells into beautiful shell bangles, which requires sophisticated techniques as shell is a hard material.
(I) What was one of the main reasons Harappan craftspeople were able to work with carnellan beads? (1)
(II) Describe the types of goods that the Harappans likely exported and the possible benefits they derived from this trade. (1)
(III) What can be Inferred about the Harappans’ trade practices based on the types of goods they exported and imported? (2)
2. The strength of community participation The Swachh Bharat Abhlyan is based on the collective efforts of all Indian citizens to keep our surroundings clean. Individually, we keep our homes and surroundings clean. People have also come together to clean up streets, roads, parks and other public places or community areas. Together, these efforts lead to a clean home, neighbourhood, society and nation. Another example of collective community participation is the celebration of Van Mahotsav (the festival of forests) in India to promote awareness about the value of trees and the conservation of forests. The initiative brings together members of the community for tree plantation drives.
(I) Describe how non-economic activities, such as volunteering and community service, contribute to societal development. (1)
(II) Evaluate the Impact of the Swachh Bharat Abhlyan on community cleanliness. (1)
(III) How do these initiatives demonstrate the strength of community involvement in addressing environmental issues? (2)
![]()
3. Hiware Bazar, a village in Ahmednagar district of Maharashtra, used to be affected by frequent droughts and poor agricultural yield. After Popatrao Baguji Pawar became its Sarpanch, he started applying Anna Hazare’s model of rainwater harvesting, watershed conservation and massive tree planting of lakhs of trees, all of which contributed to the recharge of groundwater. With the collaboration of the villagers, Hiware Bazar became a green and prosperous village in a few years. Shri Popatrao Pawar was awarded the Padma Shri in 2020.
(I) List three key measures taken by Popatrao Pawar to address the problems in Hiware Bazar. (1)
(II) How did the collectlive efforts of the villagers contribute to transforming Hiware Bazar Into a prosperous village? (1)
(III) What was the impact of massive tree planting on the village of Hiware Bazar? How did It contribute to its prosperity? (2)
Map Based Questions :
Question 1.
On the political map of India, locate the following.
(i) Highest mountain in South India
(ii) 2 highest peaks of the Himalayan range
(iii) Mountain ranges which are much older and have been rounded by erosion
Question 2.
On the given map of India, identify and label the following.
(i) Anaimudi is located in this region.
(ii) The largest and highest plateau in the world.
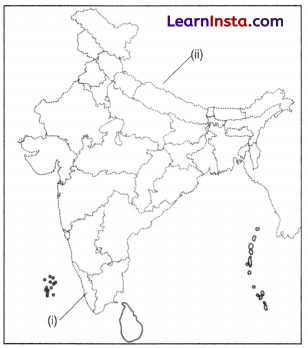
Answer:
(i) Kerala
(ii) Tibetan plateau
Also Read
- Class 6 SST Extra Questions
- Exploring Society India and Beyond Class 6 Solutions
- Class 6 Social Science MCQ
- Class 6 Social Science Notes (SST)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 6