Class 6 Science Chapter 8 Notes A Journey through States of Water
→ Water Vapour: It is the gaseous state of water.
Evaporation:
- The process of conversion of water into water vapour is called evaporation.
- Evaporation takes place from open surfaces of water all the time-day and night and at all temperatures.
- Evaporation of water takes place continuously from oceans, rivers, lakes, wells and seas which are called water bodies.
- Evaporation causes cooling because liquid molecules absorb heat from water or surrounding to be converted into vapour.
![]()
Evaporation depends upon the following factors:
(a) Temperature
(b) Surface area of water
(c) Speed of air over the exposed surface of water
(d) Humidity
Large surface area, high the temperature and high speed of air increases the rate of evaporation. Evaporation causes cooling effect. Lesser/the humidity faster will be the evaporation.

→ Condensation: The process of conversion of water vapour into liquid form of water is called condensation. For example, formation of tiny water droplets on the surface of leaves/flower petals. Formation of water droplets on the outside surface of glass containing ice-cold water.
Different States of Water:
Water is found in nature in all the three physical states of matter: solid (ice), liquid (water) and gas (water vapour).
I. Liquid state: The water that we use every day is a liquid. It is called liquid state of water.
II. Gaseous state: Water evaporates on heating. Water vapour is the gaseous state of water.
III. Solid state: On cooling the water turns into ice. Ice is solid form of water.
Differences between Different states of water:
| Property | Solid (Ice) | Liquid (Water) | Gas (Water vapour) |
| Shape | Retain its shape (fixed shape) | Does not have fixed shape(Takes shape of container) | Does not possess a fixed shape (Takes shape of container) |
| Volume | Fixed volume | Fixed volume | No fixed volume |
| Flow or Spread | Does not flow | Flows | Flows |
→ The different physical forms of water are inter-convertible. The easy inter-convertibility of water from one form to other form, makes its availability in all parts of the earth and throughout the year.
→ The different physical forms of water are inter convertible. The easy inter-convertibility of water from one form to other form, makes its availability in all parts of the earth and throughout the year.
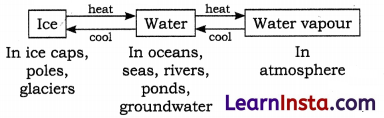
→ Melting: The process of conversion of a solid into liquid state on heating is called melting.
→ Freezing: The process of conversion of liquid into solid state on cooling is called freezing.
![]()
→ Clouds formation: The water vapour in the air condenses to form tiny droplets of water, which appear as clouds.
→ Many small water droplets come together and fall as rain, hail or snow. The earth’s surface is hotter but as we go up in atmosphere the temperature gradually decreases. At the upper layer of atmosphere, where the temperature is very low, the vapour gets condensed into tiny water droplets and forms clouds.

→ Humidity: The amount of water vapour in the air is known as humidity. If the amount of water in the air is already high (more humidity), water evaporates slowly.
→ Groundwater: The water that seeps into the ground accumulates under the ground is known as groundwater. Groundwater is the source of wells and lakes. Groundwater is withdrawn through handpumps and tubewells.
→ Rain: If water droplets fall in the form of liquid on the surface of the earth it is called as rain.
→ Hail/Snow: If the size of frozen water drops is large, the solid form is called as hail. If solidification is in the form of light flakes, it is called snow.
![]()
→ Dew: Water droplets, especially during winter nights, formed by water vapour present in the air, are called as dew.
→ Water Cycle: The circulation of water between the earth surface and atmosphere is known as the water cycle. Water cycle helps in regulating weather on the earth. Water cycle is like a ring. In nature, the water cycle takes place from sea to land and back to sea again.

→ Conservation of Water: Water is abundant on Earth, but the usable supply is limited and is decreasing due to over-usage. With a growing population, the demand for water for drinking, food preparation, and industry is increasing. Conservation involves using water carefully, and efficiently, and avoiding waste. Successful conservation programs require everyone’s faithful participation.
→ How to Conserve Water: In the first place, make it a habit to close a water tap, immediately, after taking the required amount of water from it. Minimum quantity of water should be used for bathing, washing and cleaning purposes.
→ Condensation : The changing of water vapour into liquid water on cooling, is called condensation.
→ Experiment : Test or trial done carefully in order to study what happens and gain new knowledge.
→ Evaporation : The changing of water into water vapour is called evaporation.
![]()
→ Investigate : To inquire
→ Freezing : The process by which a liquid (water) changes into solid (ice) state.
→ Observe : To see or notice.
→ Gas : It is a form of matter which has neither shape nor definite volume.
→ Predict : Forecast
→ Humidity : Humidity is a measure of water vapour (or moisture) in air.
→ Question : Querry
→ Liquid : It is a form of matter which has no fixed shape but have a fixed volume
→ The process of conversion of water into its vapour state is called evaporation.
→ The process of conversion of water vapour into its liquid State is called condensation.
![]()
→ The loss of water from plants as water vapour through the pores of their leaves is called transpiration.
→ Solids have definite shape, distinct bundaries and fixed volumes.
→ Liquids have no fixed shape but have a fixed volume.
→ Gases have neither definite shape nor definite volume but have definite mass.
→ Water is found in different states – Solid, liquid and gas.
→ Water changes its state on heating or cooling.
→ Conditions which make the evaporation faster or slower are exposed area, humidity, air movement etc.
→ Evaporation causes cooling effect.
→ The water vapour in the air condenses to form tiny droplets of water, which appear as clouds. Many tiny droplets come together and fall down as rain, hail or snow.
→ The circulation of water between the Earth surface and atmosphere is known as the water cycle.
→ Tiny drops of water floating in air are called droplets.
→ The process by which a liquid changes into solid state.
![]()
→ The temperature at which a liquid changes into solid State is called its freezing point.
Introduction
Depending upon the conditions of temperature and pressure, the same substance exist in any one of the three states (solid, liquid, gas) of matter. Water can exist as solid (as in ice), as liquid (as in water) and a gas (as in water vapours or steam). Ice and water are two forms of the substance. These forms are also called states. These different states of water show many differences in their behaviour. Water flows but ice does not. Water splashes but ice does not.
Investigating Water’s Disappearing Act
You must have seen your day-to-day life that where water is left uncovered in a dish, it slowly disappears. When wet clothes are spread in air, they get dried up, water present in wet clothes evaporate by receiving heat from the sun or surrounding air to form water vapours. This water vapours goes into air. Gradually, all the water present in wet clothes evaporates and the clothes become dry.
![]()
The changing of water into water vapours is called evaporation. The water spilled on the floor dries up and disappears due to evaporation. If we wipe a black-board with wet cloth, it dries up after a while. The wet black-board dries up after wiping it due to evaporation of water from its surface.
What Are The Different States Of Water?
Water is a substance that can be observed in three states in our daily life. In the solid state, if exists as ice. On heating, the ice melts and gets converted into its liquid state. On further heating, water gets converted into its gaseous state.
- Ice (Solid State) : It retains its shape, irrespective of the container in which it is placed while water takes the shape of the container. Ice does not flow or spread.
- Water (Liquid State) : Water does not have a fixed shape. It flows and changes its shape. . It takes up the shape of the container in which it is kept, but the volume of water remains constant. Water also has its property to spread while keeping the volume constant.
- Water vapour (Gaseous State) : Exhibits a property of spreading out in the entire available space. Gases do not possess a fixed shape. Gases acquire the shape of the container in which they are placed. Water vapour exists even at room temperature, though it is invisible to us. It is present in the air around us. You can smell the food being cooked even without entering the kitchen. It is because the smell of food from cooking spreads through the air and reaches our nostrils, even if we are not in the kitchen.
How Can We Change The States Of Water?
If we have to change ice into water, and water into water vapour, we have to supply heat to it. When heat is supplied to a solid, its temperature increases and hence the kinetic energy of particles increases. Due to increase in kinetic energy, the particles start vibrating with greater speed. As the temperature is further increased, heat overcomes the forces of attraction between the particles. At this stage, the particles leave their fixed position and the solid (ice) is converted into liquid (water).
If we want to change water into ice, it can be done by placing water in a cold environment such as freezer. Water freezes and is converted into ice. If we take the ice out of the freezer, it melts and is converted into water. We can change the liquid wax back into the solid state. We should cool the liquid wax to change it into a solid. The process of conversion of a solid into liquid state is called melting. The process of conversion of a liquid into solid state is called freezing.
![]()
How Can Water Be Evaporated Faster Or Slower?
Greater is the surface area, more is rate of evaporation. For example, we often spread the wet clothes in order to dry them in air. By doing so, the surface area available for evaporation of water increases and hence the clothes get dried up soon.
Other conditions affecting evaporation of water (liquid)
- Temperature: The rate of evaporation increase with increase in temperature.
- Humidity : The rate of evaporation decreases with increase in humidity.
- Wind speed: The rate of evaporation increases with increase in wind speed.
- Nature of liquid: The volatile liquids evaporates faster than less volatile liquids.
Cooling Effect : Evaporation produces cooling as the particles at the surface of the liquid gain energy from the surroundings and change into vapour thereby producing a cooling effect. Water kept in an earthen pot (matka) becomes cool during summer. Water seeps through the surface of the earthen pot and evaporates, which imparts a cooling effect on the water.
![]()
How Do Clouds Give Us Rain?
When air moves higher above the Earth’s surface, it becomes cooler and cooler. At certain heights, the air gets so cool that the water vapour in it turns into droplets which are generally formed around dust particles. These small droplets float in the air and form clouds. Many droplets join together to form bigger drops of water. Some drops get so heavy that they start falling. These falling water drops are called rain. During winter in very cold regions, the water drops in the sky freeze to form snow (ice). Water also falls down is earth in the frozen state called snow. This is called Snowfall.