In this page, we are providing Reproduction in Animals Class 8 Extra Questions and Answers Science Chapter 9 pdf download. NCERT Extra Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals with Answers will help to score more marks in your CBSE Board Exams.
Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Extra Questions and Answers Reproduction in Animals
Extra Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals with Answers Solutions
Reproduction in Animals Class 8 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
What is reproduction?
Answer:
Reproduction is the biological process by which new individual organisms are produced from their parents.
Question 2.
What is sexual reproduction?
Answer:
Reproduction which involves the fusion of male and female gametes is known as sexual reproduction.
Question 3.
What is fertilisation?
Answer:
The fusion of ova and sperm is called fertilisation.
Question 4.
What is a fertilised egg called?
Answer:
Zygote
Question 5.
What is asexual reproduction?
Answer:
The mode of reproduction in which only a single parent is involved.
Question 6.
Which mode of reproduction does take place in human beings?
Answer:
Sexual reproduction
Question 7.
How many partners involve in sexual reproduction?
Answer:
Two (Parents)
Question 8.
Name two animals in which asexual reproduction takes place.
Answer:
Hydra and yeast
Question 9.
Name the reproductive organs of male.
Answer:
A pair of testes, two spermducts and a penis.
Question 10.
Name the reproductive organs of female.
Answer:
A pair of ovaries, oviducts and uterus.
Question 11.
Name the modes of reproduction.
Answer:
- Sexual reproduction
- Asexual reproduction.
Question 12.
What is male gamete or sperm?
Answer:
The reproductive cell produced by male reproductive organs is called male gamete or sperm.
Question 13.
What is female gamete or ova?
Answer:
The reproductive cell produced by female reproductive organs is called female gamete or ova.
Question 14.
Which organ produces eggs or ovum?
Answer:
A pair of ovary.
Question 15.
Name the male gamete.
Answer:
Sperm
Question 16.
Name the female gamete.
Answer:
Ova or egg
Question 17.
Which male reproductive organ produces sperm?
Answer:
A pair of testes.
Question 18.
In which organ fertilisation take place in female?
Answer:
Fallopian tube
Question 19.
What are the two methods of asexual reproduction?
Answer:
- Budding
- Binary fission
Question 20.
Name two animals which undergo external fertilisation.
Answer:
Frog and fish
Question 21.
Name two animals which undergo internal fertilisation.
Answer:
Human being and cow
Question 22.
Which type of reproduction takes place in Amoeba?
Answer:
Asexual reproduction through binary fission.
Question 23.
What type of reproduction is cloning?
Answer:
Asexual reproduction
Question 24.
What is foetus?
Answer:
Foetus is a well developed embryo.
Question 25.
What is IVF technique of reproduction?
Answer:
It is fertilisation outside the body.
Question 26.
Give the full form of IVF.
Answer:
In vitro Fertilisation.
Question 27.
How are test tube babies born?
Answer:
Test tube babies are born through IVF technique.
Question 28.
What is cloning?
Answer:
Cloning is the production of exact copy of a part of or whole living body.
Reproduction in Animals Class 8 Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Explain two modes of reproduction with examples.
Answer:
There are two modes of reproduction:
- Sexual reproduction: This type of reproduction takes place by fusion of male and female gametes e.g., Human beings, mammals like cow, buffalo, etc.
- Asexual reproduction: This mode of reproduction involves only a single parent e.g., Hydra, Amoeba, yeast, etc.
Question 2.
Explain the process of fertilisation in brief.
Answer:
Fusion of the male and female gamete, i.e., sperm and egg is called fertilisation. During fertilisation, the nuclei of the sperm and the egg fuse to form a single nucleus resulting in the formation of a fertilised egg or zygote.
Question 3.
What is internal fertilisation? Explain briefly.
Answer:
Fertilisation which takes place inside the female body is called internal fertilisation. In this a smaller number of ova or eggs are produced. Offsprings have high chance of survival. It occurs mostly in mammals; e.g., in human being, cow, buffalo, etc.
Question 4.
Explain briefly the external fertilisation.
Answer:
In external fertilisation, fusion of male and female gametes take place outside the female body. The female discharge many eggs in the water and the male discharge sperms. The sperms swim to the eggs and fertilise them. It occurs in most of the aquatic animals like frog, fish, starfish, etc.
Question 5.
How is an embryo developed?
Answer:
Fertilisation results in the formation of zygote. The zygote divides repeatedly to give rise to a ball of cells which then begin to form groups that develop into different tissues and organs of the body. This developing structure is called an embryo. It gets embedded in the wall of the uterus for further development.
Question 6.
Explain what is foetus.
Answer:
The embryo continues to develop in the uterus. It gradually develops different body parts such as hands, legs, head, eyes, etc. The stage of the embryo in which all the body parts can be identified is called a foetus. After its development is complete, the mother gives birth to the baby.
Question 7.
What are viviparous and oviparous animals?
Answer:
The animals which give birth to young ones are called viviparous animals and those which lay eggs are called oviparous animals. For example, Mammals including human beings are viviparous animals and hen, lizards, all birds, etc., are oviparous animals.
Question 8.
What are sperm and ovum? Explain.
Answer:
The male gamete is called sperm. It is produced by male reproductive organ, testes. Structurally, it consists of a head attached to a long tail. The tail helps the sperm to move around. The head bears the small nucleus.
Ovum are the female gamete. They are also called egg. They are produced by the female reproductive organ. They consist of larger nucleus. Both sperm and ovum are reproductive cells and contain single cell.
Question 9.
Explain briefly the life cycle of a frog.
Answer:
There are mainly three distinct stages in the life cycle of a frog, i.e., egg tadpole (larva) → adult. Tadpoles look different from the adults. After sometime tadpoles are converted into an adult frog.
Question 10.
Explain in short life cycle of silkworm.
Answer:
The life cycle of silkworm is completed in four stages.
Egg → Larva or Caterpillar→ Pupa → Adult
In silkworm the caterpillar or pupa looks very different from the adult moth.
Reproduction in Animals Class 8 Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
What do you mean by reproduction? Describe various modes of reproduction.
Answer:
Reproduction is an important process which is responsible for the continuity of life on the planet earth. In this process, an individual produces young ones of the same species. It helps in increasing the population of the same species on the earth, generation after generation. This is the fundamental feature which ensures the existence of all life forms on the earth. There are two modes of reproduction:
(i) Sexual reproduction: In this type of reproduction, both male and female parents are involved and they produce different gametes called male gametes or sperms and female gametes or ova (egg) respectively. Both fuse to form zygote which finally develops into foetus. For example, mammals including human beings higher invertebrates and all vertebrates undergo sexual reproduction.
(ii) Asexual reproduction: In this type of reproduction, only single parent is involved and gametes or sex cells are not produced. Budding, binary fission, etc., are different methods of asexual reproduction. Lower organisms like Hydra, Amoeba, yeast, etc., undergo asexual reproduction.
Question 2.
What do you mean by metamorphosis? How does metamorphosis take place in frog? Explain with a diagram.
Answer:
The transformation of the larva into an adult through drastic (sudden or abrupt) changes is called metamorphosis. For example, a moth emerging out of the cocoon, an adult frog from a tadpole, etc., undergo metamorphosis.
Frog undergoes through three stages during its life cycle in which eggs laid down by frogs transform into tadpoles (larva) and finally into an adult following the process of metamorphosis.
The following diagram clearly shows this process.
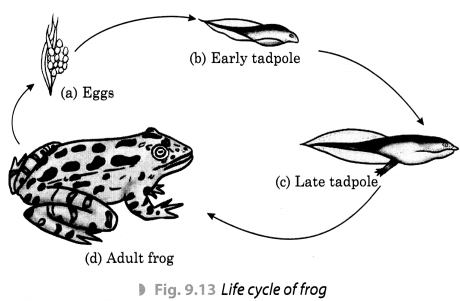
Question 3.
Describe the male reproductive organs with the help of a labelled diagram.
Answer:
The male reproductive organs mainly consist of a pair of testes, two sperm ducts (vas deferens) and a penis. Male gametes called sperms are produced by the testes. Though the sperms are very small in size, each has a head, a middle piece and a tail. It is unicelled with all the usual cell components. Figure 9.14 shows the male reproductive organs in humans.
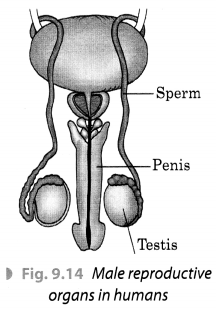
Question 4.
Describe female reproductive organs with the help of a labelled diagram.
Answer:
The female reproductive organs mainly consist of a pair of ovaries, oviducts or fallopian tubes, uterus and vagina. The female gametes called ova or eggs are produced by ovary. In human beings, a single matured egg is released into the oviduct by one of the ovaries every month. Uterus is the part inside which the embryo grows and develops finally into a baby. An egg or ovum is a single cell. Vagina is the part which receives the penis during copulation. The following diagram shows these organs clearly.
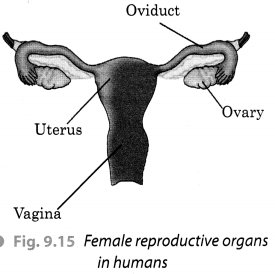
Question 5.
Explain with a diagram the development of an embryo.
Answer:
An embryo is developed in the process of fertilisation. Fertilisation results in the formation of zygote which begins to develop into an embryo [Refer Fig. 9.7(a)].
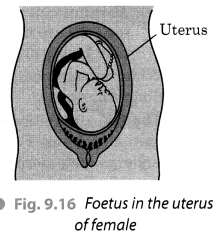
The zygote divides repeatedly to give rise to a ball of cell (Refer Fig. 9.7(b)) which further begin to form groups that develop into different tissues and organs of the body. This developing structure is called an embryo. The embryo gets embedded in the wall of the uterus for further development [Refer Fig. 9.7(c)]. The embryo continues to develop in the uterus. It gradually develops different body parts. This developing stage of embryo is called foetu (Fig. 9.16).
Question 6.
What is cloning? Explain how first cloned mammal was born.
Answer:
Cloning is the production of an exact or a true copy of a cell, any other living part, or a complete organ¬ism by asexual reproduction. Cloning of an animal was successfully performed for the first time by Ian Wilmut and his colleagues at the Roslin Institute in Edinburgh, Scotland. They cloned the sheep named Dolly on July 5,
In the process of cloning Dolly, a cell was collected from the mammary gland of a female Finn Dorsett sheep [Fig. 9.17(a)]. Meanwhile, an egg was obtained from a Scottish blackface ewe [Fig. 9.17(b)].
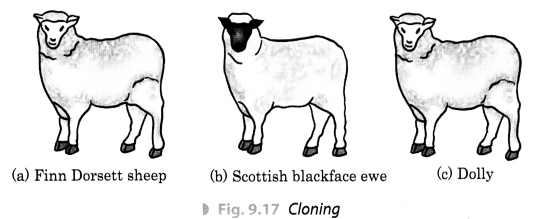
The nucleus was removed from the egg. Then, the nucleus of the mammary gland cell from the Finn Dorsett sheep was inserted into the egg of the Scottish blackface ewe whose nucleus had been removed. This egg was implanted into the Scottish blackface ewe. The egg developed normally and finally Dolly was born. Cloning of Dolly was a successful attempt.
However, many clones often die soon after birth. Sometimes cloning also leads to certain abnormalities among clones. Unfortunately, Dolly died on 14th February, 2003 due to a certain lung disease.
Question 7.
What is budding? Explain.
Answer:
Budding is type of asexual reproduction in which an organism or new individual develops from an outgrowth from a single parent. This outgrowth is called bud. On maturation this bud get separated from the parent’s body to grow into new individual. This process of reproduction is known as budding. For example, Hydra, yeast and sponges produce their young ones through the process of budding. In some organisms, like sponges, buds are not separated from their parent’s body and form a colony. They remain attached to parent’s body.
Question 8.
Explain how Amoeba reproduce?
or
Explain in brief the process of binary fission.
Answer:
Amoeba reproduces through the process of binary fission. Binary fission is another method of asexual reproduction. Amoeba is a single-celled organism. It begins the process of reproduction by the division of its nucleus into two nuclei followed by division of its body into two, each part receiving a nucleus. Finally two daughter cells are produced from one parent Amoeba. This type of asexual reproduction in which an animal reproduces by dividing into two individuals is known as binary fission.
Question 9.
What is metamorphosis? Explain.
Answer:
Some insects and animals undergo a series of changes after birth. Their young ones look quite different from them. The features of these young ones are completely different from the adults. A biological process in which larva transforms into an adult through drastic changes (sudden and abrupt changes) in the body of the animal during the life cycle of an invertebrate or amphibian is called metamorphosis. For example, frog, butterfly, etc., undergo metamorphosis.
Question 10.
How are babies produced through IVF technique? What are such babies called?
Answer:
IVF (In Vitro Fertilisation), is an artificial type of fertilisation. Some women’s oviducts are blocked and so they cannot bear babies because sperms cannot reach the egg for fertilisation. In such cases, freshly released eggs and sperms are kept together for a few hours for IVF (fertilisation outside the body). In case fertilisation occurs, zygote thus formed is allowed to develop for a week and then it is placed in the mother’s uterus. Complete development of baby occurs in uterus and is born like any other baby. Babies born through this technique are called test tube babies.
Reproduction in Animals Class 8 Extra Questions HOTS
Question 1.
Although two cells called gamete fuse, the product formed is a single cell called zygote. Justify.
Answer:
During fertilisation, only the male nucleus moves into the egg cell and fuses to the egg nucleus to form zygote which is thus a single cell. The sperm remain outside the egg cell and degenerates after some time.
Question 2.
The eggs of frogs do not have shells for protection, yet they are safe in water. How?
Answer:
A layer of jelly covers the eggs of frog and provides protection. Water help them to float and retain moisture. If eggs are laid in land then they will dry up and die.
Question 3.
Mother gives birth to a baby but the baby has characters of both parents. How?
Answer:
Human beings show sexual reproduction. During fertilisation, two gametes, one from the mother and the other from father, fuse together to form zygote. Therefore baby developed from zygote has characters of both parents though mother gives birth to a baby.
Question 4.
Why do only male gametes have a tail?
Answer:
Male gametes have to reach non-motile female gamete in oviduct from the vagina. So they have a tail to reach the egg cell.
Question 5.
Though hen and frog both are oviparous but they have different types of fertilisation. Justify.
Answer:
In hen, internal fertilisation takes place. The fertilised egg develops into an embryo inside the body. But development of chick from the embryo takes place outside the body. On the other hand, frog shows external fertilisation. The female frog discharge many eggs in the water and the male frog discharge sperms. The sperms swim to the eggs and fertilise them.
Question 6.
How does twinning occurs during sexual reproduction?
Answer:
Twins are two offspring produced by same pregnancy. Non-identical twins results from two fertilised eggs when get implanted in the uterus wall at the same time. Identical twins occur when a single egg is fertilised to form one zygote which then divides into two separate embryos.
Reproduction in Animals Class 8 Extra Questions Value Based (VBQs)
Question 1.
Ram with his family went to a picnic spot near a pond. He saw some jelly-like mass floating on the sides of the pond. He asked about this to his father. His father explained him that these are frog’s egg and are millions in number. Ram wondered if all of them get hatched, what will happen to other aquatic animals?
(a) What type of fertilisation is shown by frog?
(b) Why do frog lay eggs in large amount?
(c) Is Ram’s concern about hatching of too many eggs at a time will affect the aquatic animals correct? Why?
(d) What Value of Ram is shown here?
Answer:
(a) Frog shows external fertilisation.
(b) Mortality rate is very high for tadpoles as their predators are more. Many of the eggs do not develop due to being not get fertilised. So for continuation of their species, they lay egg in large amount.
(c) No, his concern is not correct because most of the eggs either never develops or are preyed by other animals. So survival chance of a frog from its egg to an adult frog is very low.
(d) Ram is inquisitive, future thinker and eco-concerned.