Class 6 Science Chapter 9 Notes Methods of Separation in Everyday Life
Mixture: A mixture is a material made by mixing two or more substances which can be easily separated.
Characteristics of a mixture:
- The components of a mixture have no fixed ratio by weight.
- The components of a mixture retain their original characteristics.
- The components of a mixture can be separated easily.
Purposes of Separation of Substances:
- To remove an undesirable thing, e.g. removing pebbles from wheat and peeling banana skin.
- To obtain a desirable component, e.g. purifying water to make it free from germs by boiling.
- To obtain a useful component, e.g. separation of healthy eggs from a lot.
- To obtain a pure product, e.g. sugar from sugarcane juice.
![]()
→ Principle of Separation: The constituents of a mixture do not lose their original properties such as particle’s size, density, melting point, boiling point, etc.
Methods of Separation:
There are several methods of separation. The choice of the method used depends upon the nature or the properties of the constituent substances present in the mixture. However, various methods used in separating materials are handpicking, winnowing, sieving, magnetic separation, sedimentation, decantation, loading, filteration, evaporation, sublimation, distillation, churning, etc.
Separation of Solids from Solids: Solids are separated from solids, according to the size, weight and magnetic properties of their particles. Following are some common methods:
Handpicking: This is the simplest of all methods. Small pebbles are picked up from rice or wheat. Cotton is separated from its seeds by hands. Flowers and fruits are plucked from plants. Handpicking is very slow and has a limited use. It can be used only when one of the component is present in small quantity and component is easily picked up by hand. It is done on the basis of differences in size, colour and shape of the components.
Threshing: The process used to separate grains from stalks is called threshing. In the process of threshing, the stalks are beaten to free grain seeds. This process of threshing can be done with the help of bullock. Machines are generally used to thresh large quantities of grain.
Winnowing: This is used by farmers for separating lighter husk particles (bhoosa) from heavier grains of wheat. The farmer takes the mixture in a winnow (also called bamboo trayor soop) (chhaj) and drops it from a height. He also shakes the winnow. The husk being lighter flies away with the wind and the wheat being heavier falls near his feet.

The separation of grains and husk is more conveniently and quickly done by a farm combine-harvester. It automatically harvests the crop, threshes it and then separates the husk from the grains.

![]()
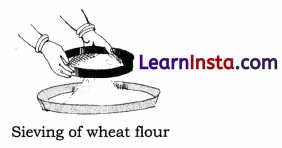
Sieving: A sieve (chhalni) has a fine net or gauze fixed on a wooden or metal frame. It is used for separating fine particles from the bigger ones. The mixture is put in the sieve and shaken by hand or by machine. The finer particles pass through the sieve and drop down. The bigger ones remain behind.

Separation of Soluble Solids from Liquids:
Evaporation: The process of conversion of water into vapour form is called evaporation. Evaporation can also take place at the ordinary temperature in the open. Thus, common salt is made from sea water or the water from salt lakes (such as Sambhar lake in Rajasthan), by evaporation in large shallow fields. The sun’s heat helps in accelerating the process.
Condensation: The process of conversion of vapour of a liquid (say water vapour) to its liquid form (water) is called condensation. Water can be obtained from salty water by the process of evaporation, followed by condensation by putting a cold steel plate over boiling salt solution.
Purification of Substances by Combination of Different Methods of Separation:
A substance is said to be pure, when it is all alone. If other things are mixed with it, the substance is called impure. The undesirable materials present are called impurities. The process of removing impurities and obtaining a pure,- substance is called purification or refining.
Suppose you are given a mixture of sand, iron filings, common salt, solid salt and naphthalene. You can separate its components as follows:
Iron filings—by magnetic separation
Naphthalene—by sublimation
Common salt and sand are dissolved in water. Salt is soluble but sand being insoluble, settles and can be separated by sedimentation, decantation followed by evaporation of salt water.
![]()
Separation of Insoluble Solids from Liquids:
Solids which do not dissolve in a liquid can be separated by the following methods:
Step 1. Sedimentation: When the heavier component of a mixture settle down in the container, it is called sedimentation.
Step 2. Decantation: Sedimentation is followed by decantation. In this process the water is separated from the settled sand.
Step 3. Filtration: To obtain clear water, the loaded water is allowed to pass through a filter paper.
Sedimentation: Mix up sand and water in a beaker. Stir it with your pencil and wait for some time. What do you see? You will see that the sand lies at the bottom and clear water stands on it. This process is called sedimentation. The solid below is termed as sediment and the clear liquid above it is known as supernatant layer.
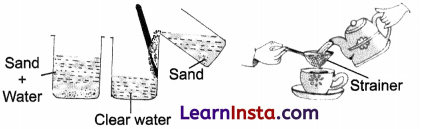
Decantation: It is the process by which water of the supernatant is removed from v. the mixture of sand and water. Decantation is used for purifying river water containing sand. This is also used for the separation of mud or sludge from sewage (waste water of cities).
Filtration: Decantation is not enough for complete separation of a solid-liquid mixture. This can be done better by filtration, in which the mixture is dropped on a porous material known as filter. The liquid passes through the filter and comes down as filtrate. The insoluble solid left behind is known as residue.
When you make tea, you filter it through a strainer having a wire gauze. The tea extract comes down as the filtrate and the boiled tea leaves are left behind as the residue!
Filters may be a wide variety of materials like fine cloth, plastic gauze, cotton wool, filter paper, glass wool, sand, etc. They are used for different solids according to the size of their particles.
![]()
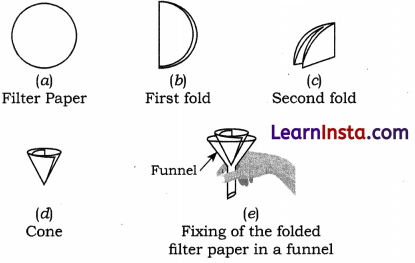
For the filtration, we need a clean funnel made of glass, plastic, or metal. Take a round filter paper, fold it and place in a funnel, as shown in the given figure.
→ Churning: The method by which milk or curd is churned by the mathni to separate cream.
→ Magnetic Separation: In this method a magnet is used for picking up iron pieces, nails, pins, etc., from grains or any other commodity. On a larger scale, a powerful magnet is employed for separating scrap iron from non-magnetic waste materials.


→ Churning : The process of separation of light particles of a solid suspended in a liquid is called churning.
→ Mixture : A mixture is a material which consists of two or more pure substances which are physically mixed in any proportion.
→ Create : Make or produce.
![]()
→ Decantation : The process of separating clear liquid without disturbing the settled solid particles is called decantation.
→ Sedimentation : The process of settling down of heavier insoluble particles in a mixture of water and insoluble substances is called sedimentation.
→ Design : Drawing or outline.
→ Evaporation : The phenomenon of change of a liquid into vapours at any temperature is called evaporation.
→ Sieving : The method of separating a mixture by using a sieve is called sieving.
→ Experiment : Test or trial done carefully.
→ Filtration : The process of separating the insoluble suspended solids of various sizes from a suspension by using a filter.
→ Threshing : It is a process in which stalks are beaten to separate grains from the stalks, and from the chaff that covers the grains.
→ Explore : To travel into, in order to learn about it.
→ Handpicking : The process of removing unwanted components such as pebbles stop from rice and pulses by hand is called handpicking.
→ Winnowing : It is the method of separating husk from grains with the help of wind.
→ Magnetic Separation : Separation of a mixture by using a magnet is called magnetic separation.
→ Investigate : Inquire.
![]()
→ Observe : To see or notice.
→ Handpicking is used for separating solid materials on the basis of differences in size, colour and shape from a mixture.
→ The process in which the stacks are beaten to separate grains from them is called threshing.
→ The method of separating lighter husk from heavier grains by wind or blowing air is called winnowing!
→ The process of separating solids from a mixture based on variations in particle size using a sieve is called sieving.
→ Evaporation is a process in which a liquid gets converter into its vapour. It can be used to separate a solid dissolved in a liquid.
→ The process of settling down of heavier insoluble components at the bottom of a liquid is called sedimentation. When the liquid is removed by tilting the container, the process is called decantation.
![]()
→ The process of separating the insoluble suspended solids of various size from a suspension by using a filter is called filtration.
→ Filtration can be used to separate insoluble solid components from a liquid.
→ The process of separation of lighter particles of a solid suspended in a liquid is called churning.
→ Churning is used to extract butter from curd.
→ Separation of magnetic and non-magnetic substances by using a magnet is called magnetic separation.
Introduction
We buy rice, wheat and pulses from the market. These food grains usually contain small pieces of stones. These pieces of stones are harmful to us. Hence, we separate the small pieces of stones from wheat, rice and pulses before using them.
The mixture are separated with their components for various purposes, such as
- To remove undesirable substances
- To remove harmful substances
- To separate useful substances
- To obtain pure sample of a substances.
![]()
Separation Of Solids
→ Handpicking : In our day-to-day life, unwanted materials mixed in food grains, pulses and food items are separated by handpicking.
Handpicking is done on the basis of difference in size, colour and shape of the particles to be removed are present in small quantities, can easily be picked up by hand.

→ Threshing : Threshing is the process in which stalks of wheat, paddy, etc. are beaten separate grains from the stalks and from the chaff that cover the grains. The method of separation is based on the fact that the stalks of the crop plants and the chaff are soft whereas the grains are very hard. In this process, the stalks are beaten against any hard surface such as a stone slab to free the grains. Threshing is also done with the help of animals, nowadays, machines called threshers are used to separate grains from the stalk.

→ Winnowing: The method of separating heavier and lighter components of a mixture by wind or by blowing air is called Win nowing. Farmers drop its mixture of wheat and husk and hay from a height. The lighter husk and hay are carried by the wind and form a heap at a small distance away. The wheat grains from a separate heap nearby. Nowaday, winnowing is done by machines.

→ Sieving: Sieving is used to separate solid substances that differ in size. In this method, a sieve heaving holes of proper size is used. The bigger particles are retained by the sieve whereas small ones pass through etc. Sieves are mostly made from a wire mesh or metals plate with holes on it. The size of the mesh or the holes depend on the size of the substance, it used to separate. The cashewnuts of different size are separated in a cashew- nuts factories by the process of the sieving. Similarly, Jewellers separate the pearls of different size by the method of sieving.

![]()
→ Obtaining common salt from Sea Water: To obtain common salt, the Sea-Water is kept in shallow pits and exposed in sunlight and air. In a few days. The water evaporates completely, leaving behind the solid mixture by further purification and salt gets ready.

→ Sedimentation: The process of settling down of heavier in soluble component at the bottom of a liquid is called Sedimentation.
Sedimentation allows the separation of undissolved solid particles from a liquid. It stand is added to a beaker contains water and left undisturbed for sometime Stand being heavier than water settles at the bottom of the beaker. This undissolved part which settles at the bottom of the liquid is called the Sediment.
→ Decantation: The process of transforming the clear liquid (after sedimentation) without disturbing the insoluble heavy particles (sediment) is called decantation.

If we do not have a strainer, we can still remove most of the tea leaves. Leave the saucepan (container) containing tea undisturbed for sometime and gently pour the tea in a cup. The tea leaves will be settled at the bottom.
→ Filtration : Filtration is used to separate insoluble particles from liquids using a porus device called filter.
A filtering device can be a four piece of cloth that is used to filter water or a special paper used to filter liquids in a laboratory. A filter paper is one such filter that has very fine pores in it.
![]()
→ Folding of filter paper : Filter paper is folded properly to make a hollow. The filter paper is folded in the following steps:
- The round piece of filter paper is taken and folded in half.
- The half folded paper is folded again.
- The twice folded paper is opened to form a hollow cone by keeping three layers of the filter paper on one side and one layer on the other side.

→ Churning : The process of separation of lighter particles of a solid suspended in a liquid is called Churning. Butter can be obtained by churning curd. Cream can be obtained from unboiled milk by churning.
When the milk is churned for some time in a mixer grinder, the lighter cream particles float to its top surface from where they are ladled out.
Similarly, the butter separates out of curd when curd with water is churned for some time, either by hand churner or in a mixer grinder. The butter being lighter floats up the heavier butter milk and is then ladled out.

→ Magnetic Separation: The materials which are attracted towards a magnet are called magnetic materials. Materials made from iron, steel (except stainless steel), cobalt and nickel are magnetic in nature.
![]()
‘The materials which are not attracted towards a magnet are called non-magnetic materials. Wood, plastic, cotton, etc are non magnetic. In order to separate iron nails from sawdust, a magnet is moved on the surface of the mixture. The iron nails are attracted by the magnet, they cling to the poles of the magnet and get separated. The process has to be repeated a number of times to achieve complete separation of non magnetic nails. Saw-dust is not attracted by magnet, so it remains behind. In many industries, the waste material often contains scrap iron. This is separated from the hip of waste materials using magnets filled to a crane.
