Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Entrepreneurship with Solutions and marking scheme Set 5 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Entrepreneurship Set 5 with Solutions
Time Allowed: 3 hours
Maximum Marks: 70
General Instructions:
- This question paper contains 34 questions.
- The question paper contains 4 sections – A, B, C and D.
- Part A contains multiple-choice questions.
- Part B – 2 marks; Answers to these questions may be from 30 – 40 words.
- Part C – 3 marks; Answers to these questions may be from 50 – 75 words.
- Part D – 5 marks; Answers to these questions may be from 120 – 150.
- Internal choice is given in the paper, there is no overall choice.
Part – A(18 Marks)
Question 1.
In which of the following form of merger, two entities combine together and form a new entity, extinguishing both the existing entities:
(A) Absorption
(B) Amalgamation
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) None of these
Answer:
(B) Amalgamation
Question 2.
V.M. Ltd is a leading mobile phones manufacturer in India. The company decided to launch a new model which will have in-built software for hands-free use and enhance the customer experience through 3D photos. They are also looking into ideas to use eco-friendly recyclable materials for the body of the phones that may cause negligible damage to the environment. Identify the factor of the PESTEL model discussed here.
(A) Social and Political
(B) Ecological and Technological
(C) Economic and Social
(D) Legal and Economic
Answer:
(B) Ecological and Technological
Explanation: Technological- “the company decided to launch……………………. 3D photos.” Ecological- “they are looking into ideas to use ecofriendly……………………………negligible damage to environment”
Question 3.
Shoes and Socks Ltd. is a leading shoes and socks manufacturing company. It decided to join its operations together with Drink Up Ltd., which is an energy drink company especially for sportsmen and women. After this merger, Shoes and Socks Up would help the existing companies to extend their markets as both of these firms will share the goodwill. Identify the type of merger relationship they are in.
(A) Product Extension Merger
(B) Vertical Merger
(C) Horizontal Merger
(D) Market Extension Merger
Answer:
(A) Product Extension Merger
![]()
Question 4.
Sohan started a small-scale business of manufacturing and marketing pickles and named the same as ‘Desi Achar’. He supplied the pickle in the whole city. Now he wants to expand his business in other cities. He discussed the same with his father, who suggested to Sohan to properly look into those conditions and forces which are external to a business under which it operates. On his father’s suggestion Sohan carefully monitored the internal and external environment for detailing early signs of opportunities and threats that may influence its current and future plans. Sohan’s father suggested to him about:
(A) Problem solving
(B) Image budding
(C) Environment scanning
(D) Tapping useful resources
Answer:
(C) Environment scanning
Explanation: Business environment may be defined as all those conditions and forces external to a business unit under which it operates. Entrepreneurship does not emerge and grow spontaneously. Rather, it is dependent upon several economic, social, political, legal and other factors.
Question 5.
Which of the following types of franchises provide an organization with the right to manufacture a product and sell it to the public, using the franchisor’s name and trademark:
(A) Product franchise business opportunity
(B) Manufacturing franchise opportunity
(C) Business franchise opportunity ventures
(D) Business format franchise opportunity
Answer:
(B) Manufacturing franchise opportunity
Explanation: This type of franchise is found most often in the food and beverage industry. Most bottlers of soft drinks receive a franchise from a company and must use its ingredients to produce, bottle and distribute the soft drinks.
Question 6.
Assertion (A): The net result of external expansion is the increase in business activities and broadening the present capital structure.
Reason (R): In the process of external expansion combination, two or more units engage in similar business or related process or stages.
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Answer:
(D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Explanation: Internal expansion results from the gradual increase in the activities of the concern. The concern may expand its present production capacity by adding more machines or by replacing old machines with the new machines with higher productive capacity. The net result of internal expansion is the increase in business activities and broadening the present capital structure. External expansion refers to business combination where two or more concerns combine and expand their business activities. In the process of combination, two or more units engage in similar business or related process or stages. Sometimes stages of the same business join with a view to carry on their activities or shape their polices on common basis or in coordination for mutual benefit or maximum profits.
Question 7.
Rashmi, a teacher of Entrepreneurship, was teaching the steps in the creative process. By the time she was able to explain the first two steps of the process with a number of examples from day-to day life, the period was over. She asked the students to read the sequence of the remaining steps to be discussed in the next period. The remaining steps and their correct sequencing is:
(A) Verification, Illumination and Incubation
(B) Incubation, Verification and Illumination
(C) Illumination, Incubation and Verification
(D) Incubation, Illuminations and Verification
Answer:
(D) Incubation, Illuminations and Verification
Explanation: The steps involved in creative process are:
(i) Idea germination
(ii) Preparation
(iii) Incubation
(iv) Illumination
(v) Verification
![]()
Question 8.
Assertion (A): The design of the product contributes to making the product attractive to the target customers.
Reason (R): A good design can improve performance of a product and also give it a competitive advantage in the market.
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Answer:
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Question 9.
An economic idea which can be implemented to create a business enterprise and earn profits must be possessed with:
(i) Practicability of the idea
(ii) Competence of the entrepreneur to encash it
(iii) Potential for future growth
(A) Only (i)
(B) (i) and (ii) only
(C) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(D) (ii) and (iii) only
Answer:
(C) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Explanation: An economic idea to create an enterprise and increase the profits must be practical, competent and should have the potential for future growth.
Question 10.
Raghav is a very creative person and has always been working on innovating products and services that can make living healthy and hygienic. He developed a design of an air conditioner with an inbuilt air purifier as well. Since he did not get any financial support from any bank, he approached Nirvana Vent (VC), a venture capitalist firm. Though VC liked the idea but it refused to help Raghav at the seeding stage and asked him to come again if needed during second round financing. Why was seed capital not given by VC when it was ready to fund the second round financing?
(A) They did not like the idea.
(B) They did not have enough funds for the innovation.
(C) They doubt on the potential for rapid growth.
(D) They do not give preference to new businesses.
Answer:
(C) They doubt on the potential for rapid growth.
Question 11.
At what stage of the creative process is Fit Ltd., a renowned fitness brand, currently engaged in as they conduct a market survey among individuals of different age groups to gauge the potential acceptance of their new product, which they anticipate will be a groundbreaking innovation in the industry?
(A) Idea germination
(B) Preparation
(C) Incubation
(D) Illumination
Answer:
(B) Preparation
Question 12.
SPS Ltd. is planning to expand their business and they have decided to merge with ARX Ltd. After the merger is completed and all the formalities have been performed, SPS Ltd. will need some additional funds to expand and meet the manufacturing costs. In order the meet the needs for these additional funds, the management has decided to offer its securities to their existing shareholders on a pro-rata basis. Keeping in mind the above step taken by the management, this step of raising funds with shareholders is known as
(A) Public Issue
(B) Private Placement
(C) Offer to Employees
(D) Rights Issue
Answer:
(D) Rights Issue
Explanation: Rights issue is a method of raising additional finance from existing shareholders by offering securities to them on pro-rata basis i.e., giving them a right to a certain number of shares in proportion to the shares they are holding.
Question 13.
Ganga Dhar was working as the production manager in a German company. The company was producing remote operated high-end kitchen equipment. He resigned from his job and returned to his hometown, Patna. In Patna, he met his old friend Aditya, who had been managing his factory producing steel utensils with old technology. Ganga Dhar encouraged Aditya for the production of high-end kitchen equipment. He also promised to help Aditya by providing funds and expertise so that the production unit run by Aditya can develop into a big production house and its investors may get high returns on investment. Ganga Dhar is:
(A) Angel investor
(B) Venture capitalist
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer:
(A) Angel investor
![]()
Explanation: Business angel or informal investor or an angel investor, is an affluent individual who provides capital for a business start-up and early stage companies having a high-risk, high-return matrix usually in exchange for convertible debt or ownership equity. They fill the gap in start-up or early stage financing between “friends and family”, by providing seed funding and formal venture capital.
Question 14.
A factory is engaged in manufacturing plastic buckets of all sizes. The following information is available to you?
Sales = ₹1,00,000
Direct labour cost (1,000 units) = ₹10,000
Direct material cost (1,000 units) = ₹25,000
Direct expenses (1,000 units) = ₹5,000
Fixed cost = ₹30,000
What will be the variable cost per unit of the factory?
(A) ₹40
(B) ₹60
(C) ₹55
(D) ₹45
Answer:
(A) ₹40
Explanation: Variable cost = Direct labour cost + Direct material cost + Direct expenses
= ₹10,000 + ₹25,000 + ₹5,000
= ₹40,000
Variable cost per unit = ₹ 40 000/1000
= ₹40 per unit
Question 15.
Assertion (A): At the break-even level, total revenue is equal to total expenses.
Reason (R): Usefulness of break-even analysis continues to be the same whether you are operating a single product or multiple product business.
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Answer:
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Explanation: Break-even point is the level of sales (or revenue generated) that equals all the expenses required for generating that revenue. It is not more than the expenses (i.e. no profit) nor is it less than the expenses (i.e. no loss). In other words, there is neither loss nor profit. Usefulness of break–even analysis continues to be the same whether you are operating a single product or multiple product business. It helps in setting profit goal and sales target. In a manufacturing environment, it helps in determining the products that are not contributing to meet the fixed expenses and thus brings up the item for discussion in management meetings about its continuity.
Question 16.
Identify the micro-environmental factors from the following:
(i) General public
(ii) Competitors
(iii) Economic
(iv) Intermediaries
(v) Legal
(A) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(B) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(C) (iii), (iv) and (v)
(D) (i), (ii) and (iv)
Answer:
(D) (i), (ii) and (iv)
Explanation: General public, competitors and intermediaries are micro-environmental factor whereas legal and economic are macroenvironmental factor.
Question 17.
Rishabh lives in Vijay Nagar, a residential colony near Delhi University (DU). Being close to DU this area is a hub for students who come from outside Delhi to study here as they find good accommodation with tiffin service readily available. Rishabh has a vacant residential building there. He found it to be an attractive economic idea to start a paying Guest House. He knows that he has a good market because of the location of his building. Identify the other requirement that he has to ensure before opting for this opportunity.
(A) The rate of return on the investment has to be attractive
(B) Assured market scope
(C) Practicality of idea
(D) None of these
Answer:
(A) The rate of return on the investment has to be attractive
Question 18.
The founder of Domino’s Pizza had a tough childhood, was raised in orphanages and hostel homes. In 1960 he and his brother borrowed $900 and bought a pizzeria. His brother left within a year, but he hung on, surviving bankruptcy and fire. He worked 18 hours a day seven days a week whole heartedly making Domino’s Pizza. today it is one of the biggest MNC in the world and a household name. What type of business was Domino’s when it was started initially?
(A) Partnership
(B) Joint stock company
(C) Sole proprietorship
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(A) Partnership
Explanation: A partnership is an association of two or more persons to carry on, as co-owners, a business and to share its profits and losses. Thus, two or more persons may form a partnership by making a written or oral agreement to carry a business jointly and share its proceeds. The objective of the business is to make profits and distribute the same amongst partners.
![]()
Part – B (12 Marks)
Question 19.
“Human life is built around works”. Identify the form of business organisation being talked about in the following sentences:
(i) “The one-man control is the best in the world if that man is big enough to manage everything.”
(ii) “Two heads being better than one.”
(iii) “Self-help as well as mutual help system.”
(iv) “The birth of this legal person is by law and can be put to death by law only.”
Answer:
(i) Sole proprietorship
(ii) Partnership
(iii) Co-operative society
(iv) Company
Question 20.
State two basic qualities of a successful entrepreneur.
Answer:
(i) Identification of business opportunity in the environment.
(ii) Initiating steps to produce and sell goods and services to the best use of that opportunity. (In case the examinee has mentioned any other suitable quality, he/she should be awarded full marks)
OR
What is meant by ‘Strategic Positioning’?
Answer:
Strategic Positioning means that knowledge, skills, competencies and creative thinking needed to develop an idea, are backed by factors critical for market success.
Question 21.
With it’s help the consumers are able to identify the products of a firm and are also able to differentiate them from those of the competitors. Identify the concept and state its components.
Answer:
(i) Brand
(ii) It has the following components: brand name; brand mark; trade mark.
OR
Evaluate the two approaches used in sales strategy by a company while retaining its present customers and when attracting new customers.
Answer:
Potential customers need communication that introduces the brand and product or service in ways that show how it can solve his or her problems. Current customers require more personal communication about new features or benefits to keep them engaged. Promotions and referral discounts work to motivate current customers to spend their money and to spread the word to others.
Question 22.
Shahida, a student of school of Rug Weaving Institute, Turkey, visited her grandparents in Kashmir for the first time. Breathtaking mountain scenery, clear lakes, lush vegetation and magnificent forests mesmerized her. The valley is home to a rich biodiversity including a large number of bird species, many of which are unique to Kashmir. It is home to Yak and sheep that are taken care of by nomads. Kashmiri lifestyle is essentially slow paced, and reflects religious diversity. Kashmiris are known to enjoy their music in its various local forms and the traditional dress of both genders is often quite colourful. Tulip, saffron, dry fruits and artistic wood workare its hallmark. She also observed that the government was stable and all the tourist places were well guarded by the army. She found it to be an ideal place to start a unit for carpet weaving and employ local people to preserve the ethnic touch. After the devastating floods, a considerable population was rendered jobless; her unit would help to revive their economic condition. She started scanning and screening the environment and collected the information.
Identify and explain any two elements in the PESTEL model which is present in this passage.
Answer:
(i) Political: The political environment includes taxation policy, government stability and foreign trade regulations.
(ii) Economic: The economic environment includes interest rates, inflation, business cycles, unemployment, disposable income, energy, availability and cost.
(iii) Social: The social/cultural environment includes population demographics, social mobility, income distribution, lifestyle changes, attitudes to work and leisure, levels of education and consumerism.
(iv) Ecological: It considers the ways in which the organization can produce its goods or services with minimum environmental damage.
![]()
Question 23.
‘The Shop’ a ready-made garments retail shop sold 5,000 shirts at ₹200 per shirt during the year ended 31st March, 2014. Cost of placing an order and receiving goods is ₹1,000 per order. Inventory holding cost is ₹250 per year. What will be the ‘Economic Ordering Quantity’ of ‘The Shop’?
OR
A grocery owner has an equity stake of ₹80,000/- in the business. He has borrowed ₹1,20,000/- at the interest rate.of 10% per annum. He made a net profit of ₹40,000/- in one year. What will be the Return on Equity for the grocery owner?
Answer:
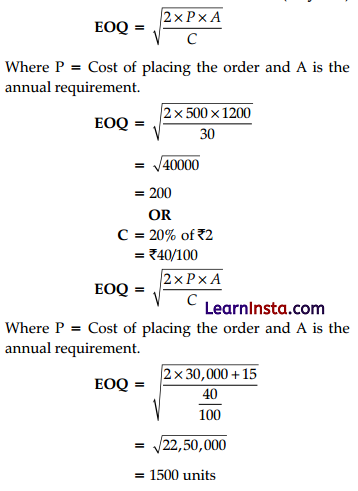
Question 24.
“Unique Motors Ltd.” was a car dealer. It took over a car manufacturing plant “Speed Cart & Co.” and started a new business in the name of “Unique Cart Ltd.” To synergise and capture a major share of the market like other competitors, they decided to sell their cars through company appointed dealers (retailers) in various parts of the country. This would relieve the company from the burden ofselling the cars while at the same time giving them control over the distribution process. Identify and explain the “Enterprise growth strategy”.
Answer:
Merger: A merger is a combination of two companies into one larger company. In merger, the acquiring company takes over the assets and liabilities of the merged company. All the combining companies are dissolved and only the new entity continues to operate.
Part – C (15 Marks)
Question 25.
Aditi started her boutique business near an industrial area and she was not getting clients as she had expected before starting the boutique? Suggest any six factors that she has to look into before venturing into business.
Answer:
She has ignored the following factors:
(i) Whether there is a good market for the product that she is going to produce.
(ii) The rate of return on the investment is attractive or not.
(iii) Assured market scope.
(iv) Practicability of the idea.
(v) Competence of the entrepreneur to encash it.
(vi) Potential of future growth.
Question 26.
“Personal selling is a better method of sales promotion than advertising”. How? Explain with the help of any three points.
Answer:
(i) Effective Promotional Tool: Personal selling is a very effective promotional tool, which helps in influencing the prospective buyers about the merits of a product and thereby increasing its sales.
(ii) Two-way communication: Salesman functions as the “eyes and ears” of the producers. He helps in improving the products and sales policies by passing on the information about the liking and disliking of customers.
(iii) Consumer Attention: Through personal selling it is easy to get the attention of customer as there is face to face interaction between salesman and customers.
Question 27.
Purem Minds Ltd. was a company into manufacturing of water purifiers, water dispensers, packaged driving water and hand sanitizer. They do a lot of research and development and would update their product on a regular basis. They also encouraged feedback and suggestions from the customers. Acting on one suggestion, they decided to manufacture a water bottle with a built-in water purifier called “Wonder pure”. They spent a lot of money on promoting the product with the tag line “Your child is secure with wonder pure.” The target segment was quality conscious consumers. It was priced in such a way that the cost of investment of the original research gets recovered from the customer. The product was an instant hit.
(i) Identify and explain the pricing strategy to be used by Purem Minds Ltd.
(ii) State any one advantage of the pricing strategy identified in part (i).
Answer:
(i) Price skimming method: In this technique the company charges a higher price for their products so that the initial cost spent on research and development can be recovered. This strategy is often used to target “early adopters” of a product or service. Early adopters generally have a relatively lower price-sensitivity. This can be attributed to their need for the product outweighing their need to economics, a greater understanding of the product’s value, or simply having a higher disposable income. This strategy is employed only for a limited duration to recover most of the investment made to build the product.
(ii) Advantages of skimming price:
(a) Price skimming helps the company in recovering the research and development costs which are associated with the development of a new product.
(b) If the company caters to consumers who are quality conscious rather than price conscious, then this type of strategy can work in a great way for a company.
![]()
Question 28.
A business plan is a comprehensive project report which helps to understand the feasibility and viability of the proposed venture. In the light of the given statement, examine the relevance of the business plan.
Answer:
The business plan is valuable to the entrepreneur, potential investors, venture capitalists, banks, financial institutions, new personnel’s suppliers, customers, advisors and others who are trying to familiarize themselves with the venture, its goals, and objectives. The business plan –
(i) Helps in determining the viability of the venture in a designated market.
(ii) Helps in providing guidance to the entrepreneur in organizing his/her planning activities as such:
(a) identifying the resources required,
(b) enabling obtaining of licenses if required, etc.,
(c) working out with legal requirements as desired by the government.
(iii) Helps in satisfying the concerns, queries, and issues of each group of people interested in the venture.
(iv) Provides room for self-assessment and selfevaluation, requiring entrepreneur to think through various scenarios and plan ways to avoid obstacles.
(v) Though not desirable, at times, business plan helps to realize the obstacles which cannot be avoided or overcome, suggesting to terminate the venture while still on paper without investing further time and money.
(vi) As the investors/lenders focus on the four Cs of credit: character, cash flow, collateral and equity contribution, it is the business plan which reflects the entrepreneur’s credit history, the ability to meet debt and interest payments, and the amount of personal equity invested thus serving as an important tool in funds procurement.
OR
What information is provided to the potential investor in organisational plant with a clear understanding of who controls the organisation and how other members will interact in performing their management functions?
Answer:
The organisational plan is that part of the business plan that describes the proposed venture’s form of ownership.
(i) The terms and conditions associated with the selected form.
(ii) Lines of authority and responsibility of members of the new venture.
(iii) The names, designation, addresses and resumes of the members.
(iv) Stake of members in the organisation.
(v) Roles and responsibilities of each member.
(vi) Procedure for solving conflicts/disputes amongst members.
(vii) Forms of payment for the members of the organisation.
(viii) Voting rights, managerial and controlling rights of the members.
All this information provides the potential investor with a clear understanding of who controls the organisation and how other members will interact in performing their management functions.
Question 29.
“While one needs a good idea and a well laid out implementation plan, for the business to run successfully it needs adequate capital.” Justify.
Answer:
Need for capital:
(i) For procuring or investing in longer term assets – land, building, machinery, equipment, etc. These are typically known as Fixed Assets. Once pressed in to service, they last over a reasonably longer period. These are placed in service for carrying out the main activity of the business – production and sales or service, etc. and are not traded or sold to receive money (except when they have outlived their life). In other words, money invested on these items does not result in direct cash inflow for the business.
(ii) For buying raw materials, packing materials, paying rent, insurance premium, utility bills, wages and salaries and for many other services and/or materials used in the production or service. In other words, this is the money needed for the day-to-day operations of the business.
OR
How does capital market satisfy firstly savers and at the same time investors?
Answer:
Capital market is a place where savers as well as investors get maximum satisfaction. The capital market functions as a link between savers and investors. It plays an important role in mobilising the savings and diverting them in productive investment. In this way, capital market plays a vital role in transferring the financial resources from surplus and wasteful areas to deficit and productive areas.
Part-D (25 Marks)
Question 30.
What is acquisition? Explain the types of acquisitions.
Answer:
Acquisition: A corporate action in which a company buys most, if not all, of the target company’s ownership stakes in order to assume control of the target firm. Acquisitions are often made as part of a company’s growth strategy whereby it is more beneficial to take over an existing firm’s operations and niche compared to expanding on its own. Acquisitions are often paid in cash, the acquiring company’s stock or a combination of both. An acquisition, also known as a takeover, is the buying of one company (the target) by another.
There are four types of acquisitions:
(i) Friendly acquisition: Both the companies approve of the acquisition under friendly terms. There is no forceful acquisition and the entire process is cordial.
(ii) Reverse acquisition: A private company takes over a public company.
(iii) Back flip acquisition: A very rare case of acquisition in which the purchasing company becomes a subsidiary of the purchased company.
(iv) Hostile acquisition: Here, as the name suggests, the entire process is done by force. The smaller company is either driven to such a condition that it has no option but to say yes to the acquisition to save its skin or the bigger company just buys off all its share, thereby establishing majority and hence initiating the acquisition.
OR
What is the purpose of designing a Logo for a product or a business?
Answer:
Logo gives an identity to a product or business. Its purposes are:
(i) Logos are a critical aspect of business marketing. As the company’s major graphical representation, a logo anchors company’s brand.
(ii) Corporate logos are intended to be the identity of an enterprise because of displaying graphically enterprise’s uniqueness.
(iii) Through a set colour combination, fonts, images, impression and/or pattern, logos provide essential information about a company that allows customers to relate with the enterprise’s core brand.
(iv) Enterprises normally resort to logos as a short path for advertising and other marketing materials.
(v) Logos act as the key visual component of an enterprise’s overall brand identity.
![]()
Question 31.
Analyse and provide justification for the statement that angel investors play a crucial role in bridging the funding gap for start-ups or early-stage ventures, providing both seed funding and formal venture capital.
Answer:
The job of an angel investor is invaluable. They fill the gap in start-up or early-stage financing between “friends and family”, by providing seed funding and formal venture capital. Although it is usually difficult to raise more than a few thousands from friends and family, even the venture capitalist is least interested to make investments. Thus, angel investments are a common second round of financing for high-growth start-ups or early-stage companies.
(i) Most angel investors are current or retired executives, business owners or high net worth individuals who have the knowledge, expertise, and funds that help start-ups match up to industry standards.
(ii) As angel investors bear extremely high risk and are usually subject to dilution from future investment rounds. They expect a very high return on investment.
(iii) Apart from investing funds, most angels provide proactive advice, guidance, industry connections and mentoring start-ups in its early days.
(iv) Their objective is to create great companies by providing value creation, and simultaneously helping investors realize a high return on investments.
(v) They have a sharp inclination to keep abreast of current developments in a particular business arena, mentoring another generation of entrepreneurs by making use of their vast experience.
Question 32.
“Sensitivity to environmental factors is crucial for an entrepreneur.” In the light of the given statement, examine the relevance of an environment of business.
Answer:
Sensitivity to environmental factors is crucial for an entrepreneur. If a company is able to adapt to its environment, it would succeed in the long run. For example, Sony is failing to understand the changing trends in mobile phones and therefore losing its market share.
The benefits of understanding the relevant environment of business are:
(i) Identification of opportunities to get first mover advantage: By keeping in touch with the changes in the external environment, an enterprise can identify opportunities and find strategies to capitalise on the opportunities at the earliest. For example, Volvo, the Swedish brand, has 74% share in the luxury bus segment as it had entered India earlier.
(ii) Formulation of strategies and policies: It helps in identifying threats and opportunities in the market. These can serve as the basis of formulation of strategies to counter threats and capitalise on opportunities in the market.
(iii) Tapping useful resources: If the company has a thorough knowledge of the external environment, it can tap raw materials, technology and even financial resources from the market at economical prices, at the right time.
(iv) Better performance: Proper understanding of the various elements of the external environment is necessary to take timely action to deal with threats and avail opportunities for the purpose of improvement in the performance of the firm.
(v) Sensitisation of entrepreneurs to cope up with rapid changes: A keen watch on the trends in the environment would help sensitise the entrepreneur to changing technology, competition, government policies and changing needs of the customers. For example, trends in clothing.
(vi) Image building: If a company is sensitive to the external environment, it will come out with new products and services to meet the requirements of the customers. This would build the image or reputation of the firm in the eyes of the general public. For example, call–radio taxis with additional features like GPS systems, online booking, etc.
OR
How many choices an entrepreneur has under ‘company’ form of organization to incorporate an enterprise?
Answer:
An entrepreneur, under the ‘Company’ form of organisation has a further choice to incorporate an enterprise either as a:
(i) Private company
A private company:
(a) Has a minimum of two and a maximum of fifty members excluding its past and present employees.
(b) Restricts the right of its members to transfer shares.
(c) Prohibits an invitation to the public to subscribe for any shares or debentures of the company, or accept any deposits from persons other than its directors, members or relatives.
(d) Has a minimum paid up capital of one lakh rupees (subject to change)
(e) Uses the word ‘Pvt. Ltd.’ at the end of its name.
(ii) Public company: Under Section 3(i) (ii) of the Companies Act, a public company is a company which is not a private company. By implication, a public company:
(a) Has minimum seven people to commence with no upper limit to membership.
(b) Does not restrict any transfer of shares.
(c) Invites public to subscribe for its shares, debentures and public deposits.
(d) Has a minimum paid up capital of five lakh rupees.
(e) Uses the word ‘Ltd.’ at the end of its name.
![]()
Question 33.
Dr. Bhim is a senior cardiologist and is concerned about the depleting health index. He researched and found that proper eating habits can improve the quality of life. He initiated ‘Medi Bytes’, a unique canteen, where the food is provided as per one’s health needs. The food served at ‘Medi Bytes’ has no fast food and no aerated drinks. It provides zero oil food with all the basic nutrients required for the body. Initially health conscious, ‘Medi Bytes’ is planning to open their branches in other locations also.
(i) Identify and explain the idea field that was explored by Dr. Bhim.
(ii) State any three idea fields with examples other than the one identified in (i) above.
Answer:
(i) Service Sector Ideas: Entrepreneurial opportunities are not only restricted to the manufacturer. Service sector is the most growing field these days, the world over, thanks to emerging knowledge societies and advancements in Information and Technology. So, new opportunities can be identified by understanding the linkages to different business activities.
OR
Market driven or demand driven ideas: Market research yields valuable data about trends of supply, demand and consumer preferences.
Market research is a key factor to maintain competitiveness over competitors.
OR
Creative efforts: Apart from applying creativity to spot and harness opportunities, it can also be applied to develop new products and services.
There are basically five ways in which creative ideas can be generated:
(a) Develop a new product or service.
(b) Improve an existing product or service
(c) Find a new process or resource for manufacturing a product.
(d) Find new markets for existing products or services.
(e) Find a new use of an existing product or service.
A very useful concept to bear in mind is that, most often creative products and services are born as results of problem solving.
(ii) (a) Natural resources: Ideas can be generated based on natural resources. A product or service may be desired from forest resources, agriculture, horticulture, etc.
(b) Existing products or services: A great business idea combines skills with imagination and market demand.
(c) Trading related ideas: Trading these days is not limited to ordinary grocer or distributor outlets. With increasing consumerism, the scope and nature of trade has enlarged; local trade, import and export, e-commerce are all making trading a very wide area of enterprise.
Question 34.
The United Company manufactures three products Lipsticks, Eyeliners, Nail paints. The variable expenses and sales price of all these products are given below:
| Lipsticks | Eyeliners | Nail Paints | |
| Sales price per unit | ₹200 | ₹100 | ₹50 |
| Variable cost per unit | ₹100 | ₹75 | ₹25 |
The total fixed expenses of the company are ₹50,000 per month. For the coming month, it expects the sale of three
products in the following ratio:
Product X: 20%
Product Y: 50%
Product Z: 70%
Compute the break-even point of the company in units and rupees for the coming months.
Answer:
Contribution per unit for each product:
| Product | Lipsticks | Eyeliners | Nail paints |
| Sale price p.u. | ₹200 | ₹100 | ₹50 |
| Variable cost price p.u | ₹100 | ₹75 | ₹25 |
| Contribution | ₹100 | ₹25 | ₹25 |
Calculation of weighted average contribution p.u.:
| Product | Contribution(₹) | Weight (%) | Weighted Avg. Cont. p.u. (₹) |
| Lipstick | 100 | 20 | 20.00 |
| Eyeliner | 25 | 50 | 12.50 |
| Nail paint | 25 | 70 | 17.50 |
| Total | 50.00 | ||
Break-even of sales mix (in units)
\(\begin{aligned}
& =\frac{\text { Total fixed cost }}{\text { Weighted Average Cont. p.u. }} \\
& =\frac{₹ 50,000}{₹ 50}=1,000 \text { units }
\end{aligned}\)
Products break-even points in units:
Lipsticks = 1,000 units × 20% = 200 units
Eyeliner = 1,000 units × 50% = 500 units
Sakil points = 1,000 units × 70% = 700 units
Break-even point in rupees:
Lipsticks = 200 units × ₹200 = ₹40,000
Eyeliner = 500 units × ₹100 = ₹50,000
Nail paints = 700 units × ₹50 = ₹35,000