Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science with Solutions and marking scheme Set 3 will help students understand the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set 3 with Solutions
Time Allowed: 3 hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
(i). This question paper consists of 39 questions in 5 sections.
(ii). All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions. A student is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
(iii). Section A consists of 20 Objective type questions carrying 1 mark each.
(iv). Section B consists of 6 Very Short questions carrying 02 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 30 to 50 words.
(v). Section C consists of 7 Short Answer type questions carrying 03 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 50 to 80 words.
(vi). Section D consists of 3 Long Answer type questions carrying 05 marks each. Answer to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
(vii). Section E consists of 3 source-based/case-based units of assessment of 04 marks each with sub-parts.
Section – A (20 Marks)
Select and write the most appropriate option out of the four options given for each of the questions 1 – 20. There is no negative mark for an incorrect response.
Question 1.
Identify gas A in the following experiment.
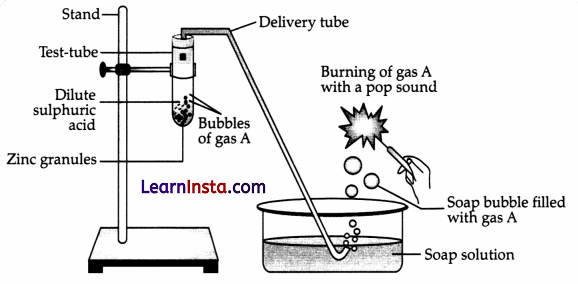
(A) Nitrogen
(B) Hydrogen
(B) Hydrogen
(D) Carbon dioxide
Answer:
(B) Hydrogen
Explanation: The gas A is hydrogen as hydrogen gas bums with a pop sound.
Question 2.
Which of the following will contain a covalent double bond between its atoms?
(a) H2
(b) O2
(c) NaCl
(d) Cl2
Answer:
(b) O2
The oxygen atom has six (6) valence electrons. Thus, to complete its octet, it forms a double bond with another oxygen atom to get an O2 molecule as
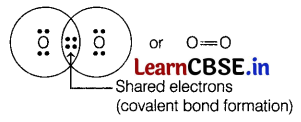
Question 3.
A metal ribbon ‘X’ burns in oxygen with a dazzling white flame forming a white ash ‘Y. The correct description of X, Y and the type of reaction is:
(A) X = Ca; Y = CaO; Type of reaction = Decomposition
(B) X = Mg; Y = MgO; Type of reaction = Combination
(C) X = Al; Y = Al2O3; Type of reaction = Thermal decomposition
(D) X = Zn; Y = ZnO; Type of reaction = Endothermic
Answer:
(B) X = Mg; Y = MgO; Type of reaction = Combination
Explanation: X is Mg, Y is MgO and the type of reaction is a combination reaction.
2Mg(X) + O2 → 2MgO(Y), This is an example of a combination reaction.
![]()
Question 4.
Which of the following is the correct representation of the electron dot structure of nitrogen?
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Answer:
![]()
The electronic configuration of N (atomic number 7) is K – 2, L – 5 Therefore, it needs three more electrons to complete its octet. Each nitrogen atom shares three electrons to form a molecule of N2 as

Question 5.
The correct electron dot structure of a water molecule is:
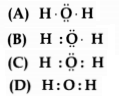
Answer:
![]()
Explanation: In the electron dot structure, oxygen has a complete octet, while each atom of hydrogen has two electrons in the outermost shell.
Question 6.
__________ is the first member of the alkyne homologous series.
(a) ethene
(b) propyne
(c) ethyne
(d) methane
Answer:
(c) The general formula of alkyne is CnH2n-2. Where n is the number of carbon atoms. The first member of the alkyne homologous series is ethyne (C2H2).
Question 7.
In which of the following, the identity of initial substance remains unchanged?
(A) Curdling of milk
(B) Formation of crystals by process of crystallisation
(C) Fermentation of grapes
(D) Digestion of food
Answer:
(B) Formation of crystals by process of crystallisation
Explanation: During the formation of crystals by the process of crystallisation, the identity of the initial substance remains unchanged. It merely gets crystallised. However, in the process of curdling of milk, the initial substance which is used gets changed as the milk gets converted into curd. In the fermentation of grapes process, the initial substance, grapes change into an alcoholicbeverage. In the process of digestion of food, the initial substance of food gets digested to give essential nutrition and energy to our body.
Question 8.
In the following given food chain, organisms are labelled as A to D. Match the labelling referred to in Column I with their most suitable feature in Column II.
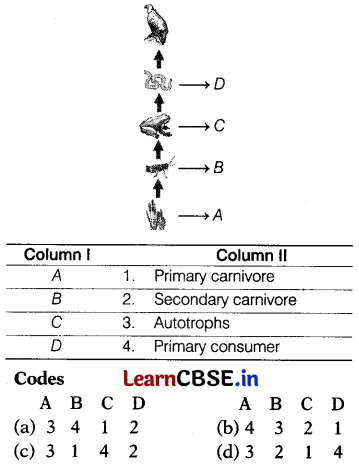
Answer:
(a) A – 3, 6 – 4, C – 1, D – 2
The given food chain is as follows.
Grass (A) → Grasshopper (B) → Frog (C) → Snake (D) → Hawk (E)
A. Grass acts as a producer in the given food chain. These are autotrophic. Thus, makes its food in the presence of sunlight. All living organisms depend upon plants directly or indirectly.
B. Grasshoppers are the primary consumers as they feed on plants (grass) directly.
C. Frogs are the primary carnivores as they feed on plant-eating animals (grasshoppers)
D. Snakes are the secondary carnivores as they eat the flesh of other animals and feed on primary carnivores majorly.
Question 9.
One of the events that do not occur during photosynthesis is:
(A) Chlorophyll absorbs solar energy.
(B) Carbon dioxide is released during the process.
(C) Oxygen is released during the process.
(D) Carbon dioxide is absorbed during the process.
Answer:
(B) Carbon dioxide is released during the process.
Explanation: During photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) from the air and soil. Within the plant cell, the water is oxidised, meaning it loses electrons, while the carbon dioxide is reduced, meaning it gains electrons. This transforms the water into oxygen and the carbon dioxide into glucose.
Question 10.
The following results were obtained by a scientist who crossed the F1 generation of pure breeding parents for round and wrinkled seeds.

From these results, it can be concluded that the actual number of round seeds he obtained was
(a) 1881
(b) 22572
(c) 2508
(d) 5643
Answer:
(d) When pure breeding parents for round and wrinkled seeds are crossed, the ratio of phenotype of F2-generation is 3 : 1.
In the given table,
Number of F2 offspring = 7524
Number of round seeds obtained = \(\frac{7524 \times 3}{4}\) = 5643 seeds
![]()
Question 11.
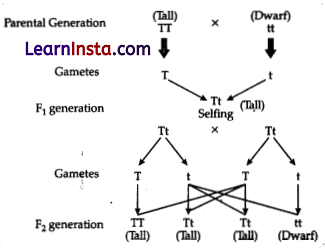
In an experiment with pea plants, a pure tall plant (TT) is crossed with a pure short plant (tt). The ratio of pure tall plant to pure short plants in F2 generation will be:
(A) 1 : 3
(B) 3 : 1
(C) 1 : 1
(D) 2 : 1
Answer:
(C) 1 : 1
Explanation: When a pure tall plant (TT) is crossed with the pure short plant (tt), then the progeny in the Fi generation will be hybrid (Tt). When the F1 generation is self-crossed (Tt), then in the F2 generation, the progeny produced will be tall homozygous (TT), Tall heterozygous (Tt), and dwarf homozygous (tt). Hence, the ratio of pure tall plants to pure short plants in F2 generation will be 1 :1 (TT : tt)
Question 12.
The figure given below shows a female reproductive system in humans with labels A to D.
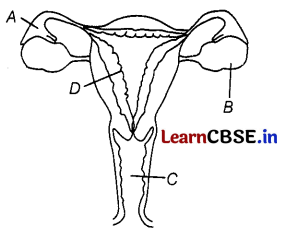
Match the labelling referred to in Column I and correlate with the function in Column II.
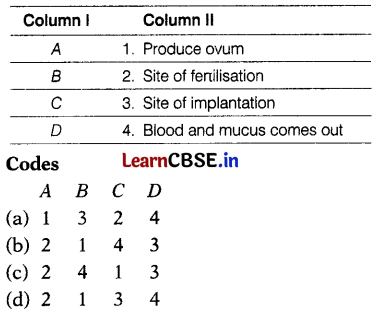
Answer:
(b) A – 2, B – 1, C – 4, D – 3
It can be explained as
A – Oviduct or Fallopian tube is the site ot fertilisation.
B – The ovary produces one mature egg (ovum) every month.
C – In the absence of fertilization, the lining of the uterus slowly breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucus.
D – The lining of the uterus is the site for the implantation of the embryo.
Thus, option (b) is correct.
Question 13.
In torch lights and head lights of vehicles, the bulb is placed:
(A) Between the pole and the focus of the reflector.
(B) Very near to the focus of the reflector.
(C) Between the focus and centre of curvature of the reflector.
(D) At the centre of curvature of the reflector.
Answer:
(B) Very near to the focus of the reflector.
Explanation: Inside a bulb there generally is a concave reflector. For a concave mirror, when an object is placed at its focus, after reflection from the mirror, it reflects a parallel beam of light that goes to infinity. Hence, in torches, searchlights and headlights of vehicles, the bulb is placed very near to the focus of the reflector.
Question 14.
If a beam of red light and a beam of violet light are incident at the same angle on the inclined surface of a prism from an air medium and produce angles of refraction r and v respectively, which of the following is correct?
(a) r = v
(b) r > v
(c) r = \(\frac{1}{v}\)
(d) r < v
Answer:
(d) r < v
Since red light deviates the least, therefore refracting angle for the red light will also be minimum. Hence, r < v.
![]()
Question 15.
Which group of organisms are not constituents of a food chain?
(i) Grass, lion, rabbit, wolf
(ii) Plankton, man, fish, grasshopper
(iii) Wolf, grass, snake, tiger
(iv) Frog, snake, eagle, grass, grasshopper
(A) (i) and (iii)
(B) (iii) and (iv)
(C) (ii) and (iii)
(D) (i) and (iv)
Answer:
(C) (ii) and (iii)
Explanation: Food chain (ii): It is an aquatic food chain so grasshopper cannot be a part of it. In food chain (iii): Wolf, snake and tiger, all are carnivores. There are no herbivores to eat grass; therefore grass cannot be a part of the food chain.
Question 16.
The maleness of a child is determined by
(a) X-chromosome in the zygote
(b) Y-chromosome in the zygote
(c) the cytoplasm of germ cells which determines the sex
(d) sex is determined by chance
Answer:
(b) Y-chromosome in the zygote
The maleness of a child is determined by the Y chromosome in the zygote inherited from the father.
Questions Nos. 17 to 20 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true but R is false.
(D) A is false but R is true.
Question 17.
Assertion (A): Sodium hydrogen carbonate is used as an ingredient in antacids.
Reason (R): NaHCO3 is a mild non-corrosive basic salt.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: Sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3) is used as an ingredient in antacids because being alkaline, it neutralizes excess acid in the stomach and provides relief. It is a mild, non-corrosive salt.
Question 18.
Assertion (A): In human beings, the respiratory pigment is haemoglobin.
Reason (R): It is a type of protein that has a high affinity for CO2.
Answer:
(c) A is true, but R is false.
R can be corrected as Haemoglobin has a high affinity for carbon monoxide.
Question 19.
Assertion (A): On freely suspending a current-carrying solenoid, it comes to rest in geographical N-S direction.
Reason (R): One end of current carrying straight solenoid behaves as a North pole and the other end as a South pole, just like a bar magnet.
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: A current carrying freely suspended solenoid behaves just like a bar magnet. Hence, it rests in the North-South direction exactly in the same manner as a bar magnet does.
![]()
Question 20.
Assertion (A): The magnetic field produced by a current-carrying solenoid is independent of its length and cross-sectional area.
Reason (R): The magnetic field inside the solenoid has a variable value.
Answer:
(c) A is true but R is false.
The magnetic field is independent of length and the area of the solenoid, it only depends on the number of turns and current flowing through the solenoid. It is uniform inside the solenoid.
Section – B (12 Marks)
Question 21.
The industrial process used for the manufacture of caustic soda involves electrolysis of an aqueous solution of compound ‘X’, In this process, two gases ‘Y and ‘Z’ are liberated. ‘Y’ is liberated at cathode and ‘Z’, which is liberated at anode, on treatment with dry slaked lime forms a compound ‘B’. Name X, Y, Z and B.
Answer:
Compound X is NaCl(aq), which is a concentrated aqueous solution of sodium chloride in water.
Compound Y is H2 (hydrogen gas), liberated at cathode.
Compound Z is Cl2 (chlorine gas), liberated at anode.
Treatment of gas Z (Cl2 with dry slaked lime, Ca(OH)2, gives bleaching powder (CaOCl2).
Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H2O
Hence, Compound B is CaOCl2
The overall balanced chemical equation is: 2NaCl(aq) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + Cl2(g) + H2(g)
Question 22.
Write a short note on male and female chromosomes.
Or
How is the sex of a child determined in human beings?
Answer:
(i) Autosomes: These chromosomes are responsible for the determination of physical characters. Both males and females contain the same types of autosomes. In both males and females, 22 pairs of autosomes are present. (1)
(ii) Sex chromosomes or Heterosomes: These are responsible for sex determination in human beings. These are also known as heterosomes. These are of different types male and female. This is the 23rd pair of chromosomes in humans. In females, this pair of chromosomes is represented as XX, and in males it is XY (1)
Or
A male gamete carries either one X or one Y chromosome, while a female gamete carries only X chromosomes. Therefore, the sex of the child depends upon what happens during fertilization.
(i) If a sperm carrying an X-chromosome fertilizes the egg, the child born will be a female (XX). (1)
(ii) If a sperm carrying a Y-chromosome fertilizes the egg, the child born will be a male (XY). (1)
Question 23.
Name the part of brain which is responsible for the following actions:
(a) Maintaining posture and balance
(b) Beating of heart
(c) Thinking
(d) Blood pressure
Answer:
(a) Cerebellum
(b) Medulla
(c) Cerebrum
(d) Medulla
OR
Where are auxins synthesised in a plant? Which organ of the plant shows:
(a) Positive phototropism
(b) Negative geotropism
(c) Positive hydrotropism
Answer:
Auxins are synthesised in the growing regions at the tip of the shoot and root in a plant.
(a) Positive phototropism- Shoot
(b) Negative geotropism- Shoot
(c) Positive hydrotropism- Root
![]()
Question 24.
A student focussed the image of a candle flame on a white screen by placing the flame at various distances from a convex lens. He noted his observation in the following table.
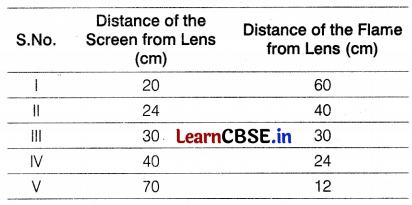
Analyze the above table and give the answers to the following questions.
(i) What is the focal length of a convex lens?
(ii) Which set of observations is incorrect and why?
Answer:
(i) We know that when the object is placed at 2F,
the distance of an object from the lens = distance of the image from the lens.
Therefore, from III observation, the radius of curvature R = 30 cm
Thus, focal length, f = \(\frac{R}{2}=\frac{30}{2}\) = 15 cm (1)
(ii) The last observation is incorrect because when an object is placed at a distance less than 15 cm away from a convex lens, we will have a virtual image, which cannot be taken on screen. (1)
Question 25.
A circuit contains a battery, a variable resistor and a solenoid. The figure shows the magnetic field pattern produced by the current in the solenoid.
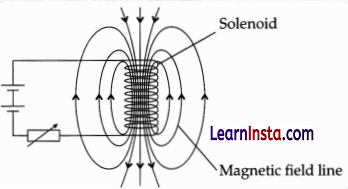
(a) State how the magnetic field pattern indicates regions where the magnetic field is stronger.
(b) What happens to the magnetic field when the current in the circuit is reversed?
Answer:
(a) Relative closeness of field lines indicates the strength of the magnetic field. Since field lines are crowded around the ends of the solenoid, hence these are the regions of strongest magnetism.
(b) The direction of the field will also be reversed
OR
State any two factors on which the magnetic field produced by a current carrying straight conductor depends. Mention the rule which helps to find the direction of its magnetic field.
Answer:
Factors on which the magnetic field produced by a current-carrying conductor depends:
(i) Strength of current passing through the conductor.
(ii) Distance of the point of measurement from the conductor.
Right-Hand Thumb rule gives the direction of the magnetic field
Question 26.
How are water and minerals transported in plants?
Answer:
Water and minerals are transported through the xylem in plants. The cells in roots that are in contact with soil actively take up ions, creating a difference in concentration of ions between the cells sap of roots and soil water. Water moves into the roots to eliminate this difference of concentration forming a steady movement of water in the root xylem. This creates a column of water that is steadily pushed upwards. Loss of water from leaves creates a suction that pulls water from the xylem of the roots to the aerial parts of the body.
Section – C (21 Marks)
Question 27.
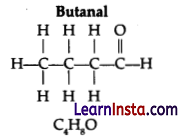
Consider the following organic compounds:

(a) Name the functional group present in these compounds.
(b) Write the general formula for the compounds of this functional group.
(c) State the relationship between these compounds and draw the structure of any other compound having similar functional group.
Answer:
(a) Functional group: Aldehyde
(b) General formula: CnH2nO
(c) It forms part of the homologous series of the aldehydes as these compounds differ from each other by -CH2 unit.
Structure of 4th member of this series is:
Question 28.
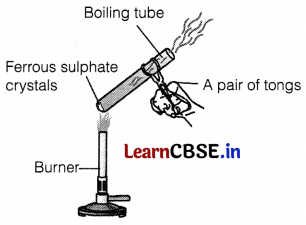
(a) Identify the gases that evolved.
(b) Name the type of reaction shown in the figure.
(c) What is the formula of crystalline ferrous sulphate? Write the equation involved.
Answer:
(a) SO2 and SO3 gases are evolved. (1)
(b) Thermal decomposition reaction occurs here. (1)
(c) The formula of crystalline ferrous sulphate is FeSO4. 7H2O.
Equation involved is
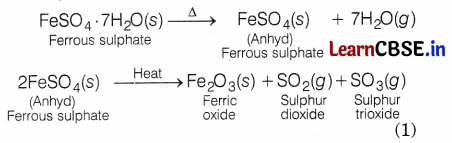
![]()
Question 29
(a) What is double circulation?
(b) Why is the separation of the right side and the left side of the heart useful?
(c) How does it help birds and mammals?
Answer:
(a) Double circulation is the process during which blood passes twice through the heart during one complete cycle. Blood is circulated to the body tissues through systemic circulation and to the lungs through pulmonary circulation.
(b) The separation of the right side and left side of the heart helps in the separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, which allows a more efficient supply of oxygen to the body cells.
(c) Birdsand mammals are warm blooded animals. Since they require more energy to maintain a constant body temperature; hence, the separation provides the availability of oxygen during respiration to generate more energy for thermoregulation.
Question 30.
Observe the following cross between tall plants having round seeds and dwarf plants having wrinkled seeds. The individuals obtained in the F1 generation were thereafter self-crossed.
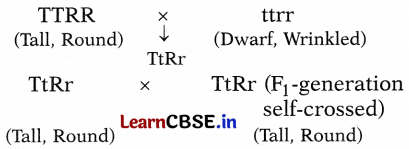
(i) What would be the phenotypes of the individuals obtained in the F2 generation? Give their ratios.
(ii) Why do you think all the individuals of the F1 generation were tall with round seeds?
Answer:
(i) Phenotypic ratio of the individuals in F2-generation.
Parents:
TtRr × TtRr (F1-generation self-crossing)
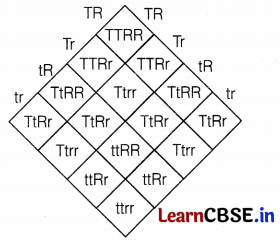
In F2-generation, the phenotypes of the individuals obtained would be
Tall and Round = 9;
Tall and Wrinkled = 3;
Dwarf and Round = 3;
Dwarf and Wrinkled = 1
Thus, the ratio is 9 : 3 : 3 : 1. (2)
(ii) The appearance of all tall plants with round seeds in the Frgeneration shows that the tallness and round-shaped seeds are dominant traits over the dwarfness and wrinkled shape of the seeds. (1)
Question 31.
(a) What is the visible spectrum?
(b) Why is red used as the stopping light at traffic signals?

(c) Two triangular glass prisms are kept together and connected through their rectangular side. A light beam is passed through one side of the combination. Will there be any dispersion? Justify your answer.
Answer:
(a) Visible |pectrum is the band of coloured components of a white light beam.
(b) Red light is scattered the leastby air molecules and has a longer wavelength. It travels the longest distance.
(c) The. given setup will behave like a glass dab, resulting in the recombination of the seven colours to produce white light.
Question 32.
An electric lamp of 100 Ω, a toaster of 50 Ω, and a water filter of resistance 500 Ω are connected in parallel to a 220 V source.
(a) What is the resistance of an electric iron connected to the same source that takes as much current as all three appliances?
(b) What is the current through it?
Answer:
Let resistance of lamp, R1 = 100 Ω
Resistance of toaster, R2 = 50 Ω
Resistance of filter, R3 = 500 Ω
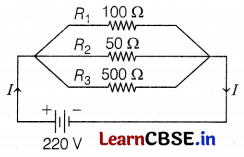
(a) Net resistance, \(\frac{1}{R}=\frac{1}{R_1}+\frac{1}{R_2}+\frac{1}{R_3}\)
[∵ R1, R2 and R3 are connected in parallel]
\(\frac{1}{R}=\frac{1}{100}+\frac{1}{50}+\frac{1}{500}=\frac{16}{500}\)
or R = \(\frac{500}{16}\) = 31.25 Ω
(b) The resistance of iron to take the same current as much current drawn by all the appliances should be 31.25 Ω.
Current through circuit, I = \(\frac{V}{R}=\frac{220}{31.25}\) = 7.04 A
Thus, the current through iron is 7.04 A. (3)
Question 33.
(a) A student wants to use an electric heater, an electric bulb and an electric fan simultaneously. How should these gadgets be connected with the mains? Justify your answer giving three reasons.
(b) What is an electric fuse? How is it connected in a circuit?
Answer:
(a) All these electrical gadgets can be connected in parallel. It is because:
(i) All appliances will get the same potential difference in parallel so the flow of any one appliance is not affected on switching on or off of other appliance.
(ii) In parallel arrangement if one appliance is switched off or fuses, other can effectively work.
(b) Electric fuse is a safety device that protects our electrical appliances in case of short circuit or overloading. It is made up of pure tin or an alloy of copper and tin. It is always connected in series with a live wire.
Section – D (15 marks)
Question 34.
Arshdeep took two iron salts. First iron salt A reacts with NaOH to form a green precipitate. Another iron salt B reacts with NaOH to form a brown precipitate. Identify the iron salts, A and B alongwith their colours, and write the reactions involved.
Or
(a) A student mixes sodium sulphate powder in barium chloride. What change would the student observe in mixing the two powders? Justify your answer and explain how he can obtain the desired change. (2)
(b) List two observations you would record in your 30 minutes after adding iron filings to copper sulphate solution.
Answer:
(a) Iron salts A and B are ferrous sulphate and ferric sulphate respectively. (1)
(b) The ferrous salt is generally green coloured, whereas ferric salts are brown. (1)
(c) When a ferrous salt solution is treated with a solution of sodium hydroxide, a greenish precipitate of ferrous hydroxide is obtained. Hence, salt A is FeSO4.
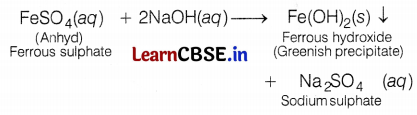
When a ferric salt solution is treated with a 1 solution of sodium hydroxide, a brown precipitate of ferric hydroxide is produced. Hence, salt B is Fe2(SO4)3.
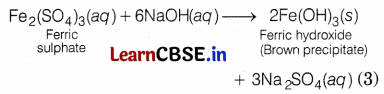
Or
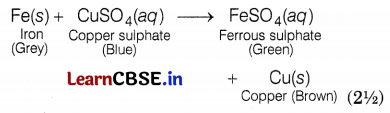
(a) When the student mixes sodium sulphate powder in barium chloride in a dry state, no change will be observed. But when he dissolved them in water, barium sulphate precipitated out and sodium chloride remained in the solution. This is called a double displacement reaction. (2\(\frac{1}{2}\))
(b) The colour of copper sulphate solution changes when an iron filling is dipped in it because iron being more reactive than copper, displaces copper metal from aqueous copper sulphate solution. Thus, the blue colour of copper sulphate fades away to give a green colour solution of ferrous sulphate.
Question 35.
(a) Name the two types of pollination and differentiate between them.
Answer:
The two types of pollination are self-pollination and cross pollination.
(i) Self pollination: When the pollen grains from the stamens of a flower fall on the stigma of the same flower, then self pollination occurs.
(ii) Cross pollination: When pollen grains from the stamens of a flower fall on the stigma of another flower, then cross pollination occurs
(b) Explain the post fertilisation changes that occur in the ovary of a flower.
Answer:
(b) Post-fertilisation changes that occur in the ovary of a flower are:
(i) The fertilised ovule forms a seed.
(ii) The seed contains an embryo, enclosed in a protective covering, called the seed coat.
(iii) As the seed grows further, other floral parts wither and fall off.
(iv) This leads to the growth of the ovary, which enlarges and ripens to become a fruit with a thick wall called the pericarp.
(c) Given below is a diagram of a germinating seed. Label the parts that:

(i) Gives rise to future shoot.
(ii) Gives rise to future root system.
(iii) Stores food.
Answer:
(i) The part labelled as A is plumule, which gives rise to future shoot.
(ii) The part labelled as B is radical, which gives rise to future root.
(iii) The part labelled as C is cotyledon, which stores food
OR
(i) Name and explain the two modes of asexual reproduction observed in Hydra.
Answer:
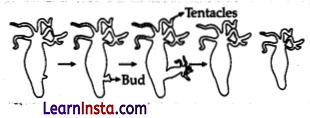
The two modes of asexual reproduction observed in Hydra are: Budding and regeneration.
Budding in Hydra: In budding, a small part of the body of the parents grows out as a ‘bud’ which then detaches and becomes a new organism. Hydra reproduces by budding using the regenerative cells. A bud develops as an outgrowth in Hydra due to repeated cell division at one specific site. When fully mature, the bud detaches itself from the parent body and develops into new independent individuals.
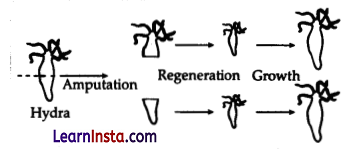
Regeneration in Hydra: In this method, small cut or broken parts of the organisms’ body grow or regenerate into separate individuals. Regeneration of Hydra from the body parts is carried out by specialised cells, which proliferate and make a large number of cells.
(ii) What is vegetative propagation? List two advantages of using this technique.
Answer:
Vegetative propagation is the development of a new plant from the vegetative parts (roots, stem and leaves) of a plant.
Advantages:
- Such plants can bear flowers and fruits earlier than those produced from seeds.
- Allows propagation of plants (banana, orange, etc) that have lost the capacity to produce seeds.
- All plants produced are genetically similar to the parent plant and hence have all its characteristics.
![]()
Question 36.
(a) Define the following terms in the context of spherical mirrors.
(i) Pole
(ii) Centre of curvature
(iii) Principal axis
(iv) Principal focus
(b) Draw a ray diagram to show the principal focus of a
(i) concave mirror and
(ii) convex mirror
(c) Consider the following diagram in which M is a mirror and P is an object 1 and Q is its magnified image formed by the mirror.
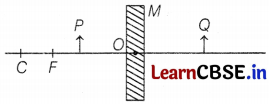
State the type of the mirror M and one characteristic property of the image Q.
Or
A 6 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 25 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 40 cm. By calculation determine
(a) the position and
(b) the size of the image formed.
(i) The pole of the spherical mirror is the mid-point of its reflecting surface.
(ii) Centre of Curvature of a spherical mirror is the center of the imaginary sphere of which, the mirror is a part,
(iii) Principal Axis of a spherical mirror is the line joining the pole and center of curvature.
(iv) The Principal Focus of a concave mirror is a point on the principal axis of the mirror at which the light rays coming parallel to the principal axis, after reflecting meet. (2)
(b)
(c) The given diagram in the question can be redrawn as
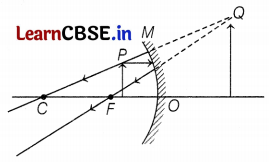
So, M is a concave mirror and the image Q formed is enlarged. (1)
Or
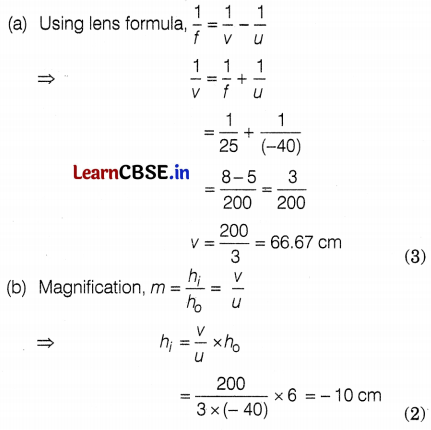
Given, the height of the object, h0 = 6 cm
The focal length of the lens, f = 25 cm
Distance of object, u = -40 cm
Section – E (12 Marks)
Question 37.
The melting points and boiling points of some ionic compounds are given below:
| Compound | Melting Point(K) | Boiling Point (K) |
| NaCl | 1074 | 1686 |
| LiCl | 887 | 1600 |
| CaCl2 | 1045 | 1900 |
| CaO | 2850 | 3120 |
| MgCl2 | 981 | 1685 |
These compounds are termed ionic because they are formed by the transfer of electrons from a metal to a nonmetal. The electron transfer in such compounds is controlled by the electronic configuration of the elements involved. Every element tends to attain a filled valence shell of its nearest noble gas or a stable octet.
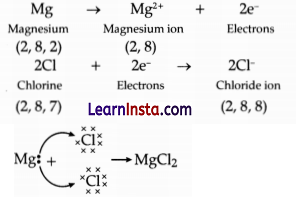
(a) Show the electron transfer in the formation of magnesium chloride.
Answer:
Electron transferin the formation of magnesium chloride:
(b) List two properties of ionic compounds other than their high melting and boiling points.
Answer:
Two properties of ionic compounds are:
(i) They conduct electricity in a solution or molten state.
(ii) They are hard and brittle crystalline solids.
(c) While forming an ionic compound say sodium chloride how does the sodium atom attain its stable configuration?
Answer:
Sodium chloride is formed by the combination of sodium and chloride ions. Sodium loses one electron from the valence shell to attain a stable noble gas configuration.
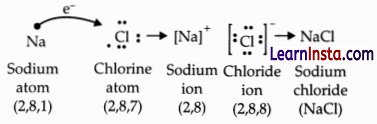
OR
(c) Give reasons:
(i) Why do ionic compounds in the solid state not conduct electricity?
(ii) What happens at the cathode when electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of sodium chloride?
Answer:
(i) Ionic compounds do not conduct electricity in a solid state due to the absence of free ions but they conduct electricity in a molten and aqueous state
due to the presence of free ions.
(ii) Reduction takes place at cathode. Therefore, during electrolysis of an aqueous solution of sodium chloride, hydrogen gas is evolved at cathode due to the reduction of H+ ions.
2H+ + 2e– → H2 ↑
![]()
Question 38.
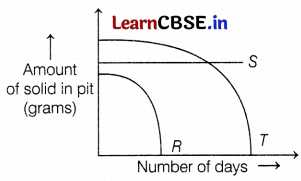
Sheenu took three different types of solid wastes R, S, and T. She buried them under the soil in a pit, as she wanted to study their rate of decomposition. Her findings are shown in the given graph.
(a) Among R, S, and T, which of the following wastes will not decompose at all?
(b) What are the safe methods of disposal of the non-biodegradable waste?
(c) What type of solid waste comes under the category of R?
Or
What are the other artificial methods of waste disposal?
Answer:
(a) S is the solid waste that will not decompose at all. According to the graph, there is no change in the amount of S waste. So, no decomposition takes place in any number of days. Hence, it is a non-biodegradable waste. (1)
(b) Non-biodegradable waste can be decomposed by recycling or by dumping it underground into landfills. (1)
(c) Solid waste R completely decomposes in very few days which means it is an easily decomposable biodegradable waste.
e.g. Cow dung, fruit pulp, etc., comes under this category. (2)
Or
Incineration is a method of waste disposal in which the burning of substances takes place at high temperatures to form ash. It is used to dispose of hospital or harmful wastes of biomedical industries. (2)
Question 39.
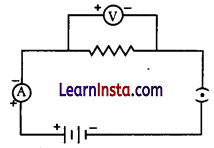
The picture shows an electric circuit.
(a) Which of these is true about the circuit? Circle ‘Yes’ or ‘No’ for the correct response.
| Is this true for the circuit | Yes or No |
| The circuit is open. | Yes/No |
| The circuit has double batteries. | Yes/No |
| The circuit has an ammeter and a voltmeter parallel to each other. | Yes/No |
(b) Will there be any change in the ammeter reading if the length of the wire in the circuit is doubled? Explain your answer.
(c) How is ammeter connected in the circuit to measure electric current?
Answer:
(a)
| Is this true for the circuit | Yes or No |
| The circuit is open. | No |
| The circuit has double batteries. | Yes |
| The circuit has an ammeter and a voltmeter parallel to each other. | No |
(b) The ammeter’s reading will be decreased by one-half.
When the length of the wire is doubled, the resistance is also doubled, because resistance is directly proportional to the length of the wire. Hence according to Ohm’s law, for a given potential difference, the current reduces to half.
(c) Ammeter is connected in series in an electric circuit.
OR
(c) What is the shape of the graph obtained by plotting the potential difference applied across a conductor against the current flowing through it?
Answer:
A straight line is passing through the origin and has a constant slope.