Class 6 Science Chapter 3 Notes Mindful Eating: A Path to a Healthy Body
→ Food: The edible substances which we eat to obtain energy, materials required for growth and development of the body and to repair worn out tissues are called food.
→ Cultivation of food crops: The act of growing food crops is known as cultivation of food crops.
→ Culinary practice: The act of preparing something to eat by the application of heat is known as culinary practice.
→ Components of food: The main components of food are carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals. These are called nutrients.
→ Carbohydrate: The component of food which provides us energy to do work is called carbohydrate, e.g. sugar.
→ Starch: It is the major source of carbohydrate.
→ Glucose: Glucose is a type of carbohydrate that provides instant energy to our body.
→ Fats: The energy-providing substances in the food are called fats. They are the richest source of energy. Fats produce more energy than carbohydrates, e.g. ghee, oil.
→ Energy-gividg foods: Food items which are rich in carbohydrates and fats and provide us energy for performing various activities are called energy-giving foods.
→ Proteins: The food items which are needed for the growth and repair of our body are called proteins, e.g. egg, milk, pea, meat, etc.
![]()
→ Body-building foods: Protein-rich foods that help in growth and repair of our body are called body-building foods.
→ Vitamins: The substances which are required in very small quantities to protect our body against diseases and to keep our eyes, bones, teeth and gums healthy are called vitamins.
→ Minerals: The substances which are required in very small quantities to protect our body are called minerals, e.g., calcium and iron.
→ Protective Nutrients: Vitamins and minerals which protect our body from diseases and keep us healthy are called protective nutrients.
→ Deficiency: When a person eats a particular diet for a long time that does not contain a particular nutrient, the person may suffer from its deficiency.
→ Deficiency Diseases: Diseases that occur due to lack of carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins and minerals in the diet over a long period are called deficiency diseases.
→ Night Blindness (Loss of Vision): This is a type of disease caused due to lack of vitamin ‘A’.
→ Beriberi: It is a disease caused due to deficiency of vitamin B1. Weak muscles is the major symptom.
→ Scurvy: It is a type of disease that occurs due to the deprivation of vitamin ‘C’ for a long period from our diet. Mostly seen as bleeding gums.
→ Rickets: It is a type of disease caused due to deficiency of vitamin ‘D’. It causes soft and bent bones.
→ Goitre: It is a type of disease seen in the person having deficiency of “Iodine” in the body.
→ Anaemia: It is a disease due to lack of “Iron”.
→ Roughage: The fibrous substances in our food are called roughage. They do not provide any nutrient to our body. They add bulk to our body and help our body get rid of undigested food.
![]()
→ Balanced Diet: A diet which provides adequate amount of carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins and minerals along with roughage and water to maintain a healthy body is known as balanced diet.
→ Junk Food: Some foods have high calories due to high sugar and fat content but they contain very less amounts of proteins, mineralst vitamins, and dietary fibres. These foods are called junk foods.
→ Millets: Millets are highly nutritious grains, for example, jowar, bajra, ragi and sanwa.
→ Food Miles: The entire distance travelled by a bag of wheat or any other food item, from the producer to the consumer, is known as its food miles.
Introduction
Food gives life to living beings. Food supplies proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins and minerals all of which we require for body development, growth and health.
→ Carbohydrates : The compounds of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen which provides energy for our body are called carbohydrates.
→ Millets : Jawar, bajra, ragi and sanwa grains are called millets.
→ Analyse : Examining of something by examining its ports and their relationship.
→ Culinary practices : Cooking practices.
→ Minerals : Salts of certain metals and non-metals needed our body for its normal functioning are collectively called minerals.
→ Compare : To be like or equal.
![]()
→ Deficiency diseases : A disease caused due to lack of one or more nutrients in the diet is called deficiency disease.
→ Nutrients : A substance which is essential for maintaining life and for growth is called nutrient
→ Infer : Reach an opinion from facts or reasoning.
→ Fats : Energy giving compounds producing more energy than carbohydrates.
→ Proteins : Body-building compounds.
→ Interpret : Explain.
→ Food components : Any of the parts of which it is made.
→ Rickets : It is the deficiency disease of vitamins. Child suffering from rickets has bow legs and a pigeon-type chest.
→ Investigate : Inquire.
→ Food miles : The entire distance travelled by a bag of food items, from the producer to the consumer, is known as its food miles.
→ Roughage : It is the fibrous matter in food which cannot be digested.
→ Observe To notice.
→ Iodized salt : The common salt which contains adequate amount of iodine salts is known as iodised salt.
![]()
→ Scurvy : Deficiency of vitamin C causes a disease called scurvy. The symptom of this disease is bleeding gums.
→ Prediction : Forecast.
→ Vitamins : Protective compounds having no food value, important for proper-functioning.
→ Survey : Study
→ People across India eat diverse types of food, containing various food components.
→ Choice of food may vary according to the cultivation of food crops in a region teets preferences, culture and traditions and so on.
→ Culinary practices (cooking practices) have changed over time. There is a significant difference between traditional and modern methods of cooking food.
→ Food provides us energy, support growth repairs our bodies and protects us from diseases.
→ The major nutrients in our food are carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins and minerals. In addition, food also contains dietary fibres and water.
→ Carbohydrates and fats are primary energy sources, while proteins are body-building nutrients.
→ Vitamins and minerals strengthen our body, protect us from infections and keep us healthy.
→ Water is essential for life but has no food value in our body. A person can live without food for several ‘weeks but would die in a few days without water.
→ Roughage provides bulk to the food, keeps the food and waste matter i.e., faeces moving along the intestines and helps to present constipation.
![]()
→ A balance diet provides all the essencial nutrients in the right quantities, along with adequate roughage and water.
→ Deficiency of one or more nutrients in our diet for a long time can lead to deficiency diseases and disorder.
→ Junk foods are unhealthy because they contain high level of sugar and fats but little protein, minerals, vitamins and dietary fibres.
→ By eating too much, a person takes the more nutrients than the body requires. The body stores the excess amount of nutrients as fat and gains weight, overweight people are at risk of developing heart diseases and diabetes.
→ Eating two little means taking the fewer amounts of nutrients than the body requires. A person who eats less for a long period of time will be underweight and weak. Thus, being overweight or underweight harms the person health.
→ Millets are known as nutri-cereals as they provide most of the nutrients required for the normal functioning of our bodies. They can be easily cultivated in different climatic conditions.
→ Eating food that is locally grown and plant based, to the extent possible, is not only healthy four our bodies but is also good for our environment and our planet.
→ The distance travelled by a food item, from the place of its production to the consumer is called food miles. We must aim to minimise food miles.
→ We should never waste food and only take as much as we can consume.
→ The washing of fruits and vegetables after they have been peeled and out, removes the water soluble vitamins and some minerals from them. This lowers their nutritive value. To avoid the loss of vitamins and minerals, the fruits and vegetables should be first washed, and then peeled and out.
→ Vitamin C gets destroyed easily by heat during cooking. So when food is cooked at a high temperature, then the excessive heat destroyes a major portion of vitamin C.
→ Carbohydrates and fats provide us energy for performing various activities. Therefore, they are called energy giving foods.
![]()
→ Proteins : Proteins help the body to grow. They also help repair the injured and worm-out parts of the body. Sports-persons need proteins in larger quantities to build their muscles. We get proteins from the plants as well as animals.
→ Some plants sources of protein are pulses, beans, peas and nuts. Animal sources of protein are milk, paneer, egg, fish and meat.
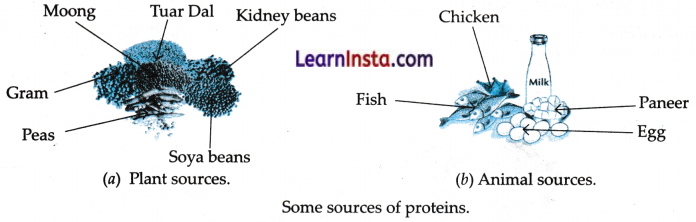
→ Protein-rich foods help in growth and repair of our body. These are, therefore, called bodybuilding foods.
→ The right amount of proteins must be added in the diet of growing children for their proper growth and development.
→ Vitamins (A, B, C and D) and minerals (Calcium, iodine and iron), are two groups of food components that protect our body from various diseases.
Our body needs vitamins and minerals in smell quantities to remain healthy.
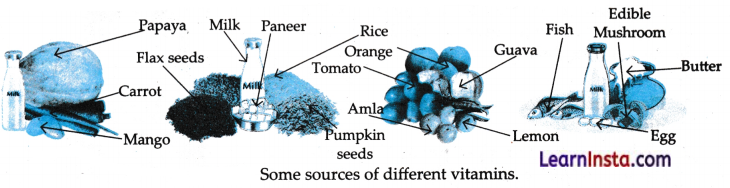
→ Nutrients : Food components that provide energy, support growth, help repair and protect our body from diseases and maintain various bodily functions are called nutrients. The major nutrients in our food include carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals. These nutrients protect our body from disease and keep us healthy.
→ Difference between raw and cooked vegetables: Vegetables sometimes lose their bright colour or become softer and less crisp when cooked. Some nutrients like vitamin ‘C’ and others are lost during cooking due to high heat. Washing cut or peeled vegetables and fruits may also result in the loss of some vitamins flowever, it is highly recommended that all fruits and vegetables be thoroughly washed before consumption.
→ Dietary Fibre (Roughage) : The fibrous indigestible material present in any food is termed as Dietary Fibre. It has no nutritive value. However, they are an essential components of our
![]()
food. They help our body get rid of undigested food and ensure smooth passage of stools. Roughage in our diet is provided mainly by suitable plant products. Green leafy vegetables, fresh fruits, whole grains, pulses and nuts are good source of roughage.
Water: It is an essential part of our diet. It helps the body absorb nutrients from food. It removes waste from the body through sweat and urine. Our body needs 2-3 litres of water every day.
Coluthur Gopalan (1918-2019) :
He initiated nutrient in India. He analysed more than 500 Indian foods for their nutritional value. He recommended our appropriate diet in the Indian context. He led surveys on the nutrients states of the Indian population, identifying wide spread deficiencies in protein, energy and other food components. This led to the implementation of the Mid-day Meal Programme in 2002,. now a “PM POSHAN” initiative, to provide balance food in the government-run and government aided schools of our country. This scheme has played an important role in improving the health and nutrition of millions of children nationwide.

Balance Of Diet
→ Requirements of the type and amount of nutrients in a diet may vary according to age, gender, physical activity, health status, life-style and so on.
→ A balanced diet varies with age health and occupation. A labourer doing manual work needs more carbohydrates and fats in his diet which could provide him more energy. A young child needs to take more proteins, they help in body-building.
→ Food Safety and Standard Authority of India (FSSAI) : FSSAI is a government food quality of India. Packaged food items must have information about the nutrients on their cover. The information should list the amount of each nutrient. Sometimes more nutrients are added to the food during processing (fortification) to improve its nutritional quality. Iodised salt and some baby foods are examples of fortified foods.
![]()
Millets : (nutrition-rich cereals)
Jawar, bajra, ragi and sanwa are native crops of India. These can be easily cultivated in different climatic conditions. These highly nutrious grains are also called millets. Millets are small-sized grains. They have been a necessary part of the Indian diet for centuries. They have regained popularity due to their many health benefits. They are good sources of vitamins, minerals (like iron and calcium) and also dietary fibres. They are also called nutricereals.

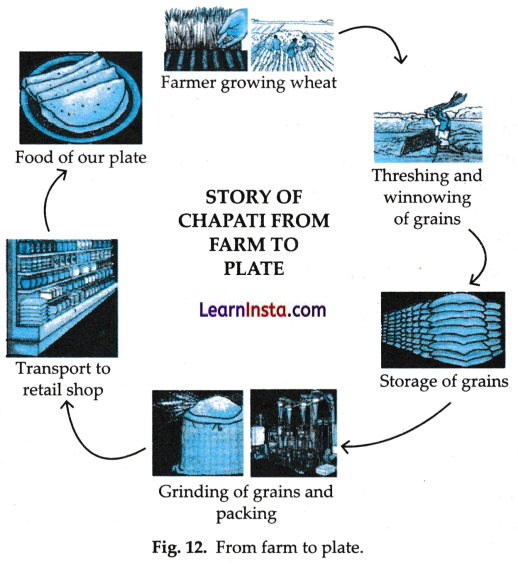
Food Miles : From Farm To Our Place
The entire distance travelled by a bag of wheat or any other food item, from the producer to the consumer, is known as its food miles.
Reducing food miles is important because it cuts down the cost and pollution during its transport. It helps support local farm rs and it also keeps our food fresher and healthier.
The various processes involved in getting to food from farm to plate is shown in Fig. 12.
Many people waste food, leaving it unconsumed on their plates. We must take only as much food as we can consume. It would reduce food wastage.