Materials Around Us Class 6 Extra Questions and Answers Science Chapter 6
Materials Around Us Class 6 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why do we need to group materials? Give one reason.
Answer:
We often group materials for our convenience. It makes our study systematic. It helps to describe their properties.
Question 2.
Suggest two bases on which,we can group objects.
Answer:
(i) Material used in making the object, e.g. wood or metal or plastic.
(ii) Material of the object is soft or hard, or substance is soluble or insoluble in water.
Question 3.
Is a substance which can be compressed soft or hard?
Answer:
Substance that can be compressed are called soft substance.
Question 4.
Select a lustrous material out of the following substances:
Wood, aluminium, plastic, cotton
Answer:
Aluminium
Question 5.
Which material is generally used for making pens?
Answer:
Plastic or metal.
![]()
Question 6.
Is oil soluble in water?
Answer:
Oil does not dissolve in water so it is insoluble in water and floats on the surface of water.
Question 7.
Name two objects which are made from opaQuestion ue materials.
Answer:
Wooden doors, blackboard/steel plate.
Question 8.
What is common between salt and sand?
Answer:
Both have mass and are in solid state.
Question 9.
List three liQuestion uids which are transparent.
Answer:
Water, alcohol and acetone/benzene.
Question 10.
Write two substances which are made from leather.
Answer:
Belt and shoes.
Question 11.
Name some substances which are made from plastics.
Answer:
Toys, plates, tumblers, buckets, baskets.
Question 12.
Which is hard—sponge or iron?
Answer:
Iron is hard while sponge is soft.
Question 13.
Write two gases which are soluble in water.
Answer:
Oxygen, Carbon dioxide.
Question 14.
The tumbler can be made of which type of materials?
Answer:
Plastic, glass, steel, etc.
Question 15.
What are translucent objects ?
Answer:
The materials through which we can see but not clearly.
Question 16.
Give two examples of translucent objects.
Answer:
Frosted glass, oily paper, X-ray film, etc.
Question 17.
Write two examples of transparent objects.
Answer:
Water and glass
Question 18.
Name two opaQuestion ue materials.
Answer:
Leather and Wood
Question 19.
What is the shape ofjiill moon.
Answer:
Round
![]()
Question 20.
Are all lustrous materials metals?
Answer:
No, other than metals some materials are polished or coated with shiny plastic wax.
Question 21.
Name one liquid which is soluble in water.
Answer:
Honey
Materials Around Us Class 6 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write any four properties of materials.
Answer:
(a) Appearance
(b) Hardness
(c) Solubility
(d) Transparency
Question 2.
Why is a tumbler not made with a piece of cloth?
Answer:
We use tumblers made of glass, plastic and metal to keep a liquid as these substances can hold a liquid.
A tumbler made of cloth cannot hold a liquid because:
(i) Cloth piece is not hard enough to hold liquids and
(ii) Cloth piece has very minute pores through which the liquid oozes out.
Question 3.
What are the similarities between iron, copper and aluminium?
Answer:
(a) They all have lustre.
(b) They are all metals.
(c) They are hard.
Question 4.
Mention some materials which are made up of paper.
Answer:
Books, notebooks, newspapers, calendars, etc.
Question 5.
Classify the following materials into lustrous or non-lustrous material.
Gold, Sulphur, Steel, Jute, Bronze.
Answer:
Lustrous material: Gold, Steel, Bronze Non-lustrous material: Sulphur, Jute
Question 6.
What is the basis for sorting materials?
Answer:
Materials are grouped on the basis of similarities or dissimilarities in their properties.
Question 7.
What is the reason for grouping materials?
Answer:
Materials are grouped for our convenience to study their properties and also observe any patterns in these properties.
Question 8.
Make a table of objects and the materials they are made of.
Answer:
| Objects | Materials they are made of |
| Plate (thali) | Steel, glass, plastic |
| Pen | Plastic, metal |
| Bucket | Plastic, metal |
| Knife | Steel/metal with handles of wood/plastic |
Question 9.
Make a table of different types of objects that are made from the same material.
Answer:
| Materials | Objects that are made from same material |
| Wood | Chair, table, plough, bullock cart and its wheels |
| Paper | Books, notebooks, newspaper, calendars |
| Leather | Shoes, belts, purses, jackets, suitcase, bags |
| Plastics | Buckets, chairs, tables, bags, briefcase, lunch box |
| Cotton | Clothes, bandage, bedsheets, cushions, bags |
| Iron | Chairs, tables, doors, bathroom fittings, mesh, wheels and other railway goods. |
Question 10.
Make a table and find out whether the following liquids mix with water: Vinegar, Lemon juice, Mustard oil, Coconut oil, Kerosene.
Answer:
| Liquid | Mixes well/ Does not mix |
| Vinegar | Mixes well” |
| Lemon juice | Mixes well |
| Mustard oil | Does not mix |
| Coconut oil | Does not mix |
| Kerosene | Does not mix |
![]()
Question 11.
Metals have lustre (shine). Give reason why some metal articles become dull and loose their shine.
Answer:
Metals when exposed to air react with moisture and gases present in it, thereby forming a dull layer of some other compound on it.
Question 12.
Kerosene, coconut oil, mustard oil do not dissolve in water, even on shaking. They separate after sometime forming two different layer. Explain why.
Answer:
The molecules of water do not intermingle (mix) with the molecules of oil. The space between the molecules of water is not taken by oil, so they are immiscible in water.
Question 13.
What do you mean by volume and write the SI unit of it.
Answer:
Volume is the amount of space that a three-dimensional object occupies and its SI unit is cubic metre (m3).
Question 14.
Is air matter, explain. Is air transparent?
Answer:
Air is a matter as it occupies space and has mass. Yes, air is transparent as we can see through it clearly.
Question 15.
Can we fill 600 mL of water in a bottle labelled as capacity of 500 mL? Justify your answer.
Answer:
No, we cannot fill 600 mL of water in a bottle labelled as capacity of 500 mL because bottle has only volume to fill 500 mL and extra 100 mL of water gets spilled off the bottle.
Question 16.
Find the odd one out from the following:
(a) Chair, Bed, Table, Baby, Cupboard
(b) Rose, Jasmine, Boat, Marigold, Lotus
(c) Aluminium, Iron, Copper, Silver, Sand
(d) Sugar, Salt, Sand, Copper sulphate
Answer:
(a) Baby (all others are non-living)
(b) Boat (all others are flowers)
(c) Sand (all others are metals)
(d) Sand (all others are soluble in water)
Question 17.
Write two advantages of grouping materials.
Answer:
(i) It helps to locate the objects easily.
(ii) It makes easy to study the properties of materials.
Question 18.
Define the term classification.
Answer:
The method of arranging objecs into groups is called classification.
Question 19.
Match the following items:
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) Surgical instruments | (i) Plastic |
| (b) Newspaper | (ii) Animal product |
| (c) Electrical switches | (iii) Steel |
| (d) Wool | (iv) Plant product |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) Surgical instruments | (iii) Steel |
| (b) Newspaper | (iv) Plant product |
| (c) Electrical switches | (i) Plastic |
| (d) Wool | (ii) Animal product |
![]()
Question 20.
Given below are the names of some objects and materials:
Water, basket ball, orange, sugar, globe, apple and earthen pitcher Group them as:
(a) Round shaped and other shapes
(b) Eatables and non-eatables
Answer:
(a) (i) Round shaped: Basket ball, apple, orange, globe and earthen pitcher.
(ii) Other shapes: Water and sugar.
(b) (i) Eatables: Water, orange, sugar and apple.
(ii) Non-eatables: Basket ball, globe and earthen pitcher.
Materials Around Us Class 6 Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
‘Grouping of objects helps the shopkeeper. ’ Justify the statement.
Answer:
Proper grouping of objects helps shopkeeper in.tiie following ways:
– (i) He can locate the required object easily and Quickly.
(ii) He can easily come to knojv what stocks are going to finish and he should purchase them for his customers.
Question 2.
Describe an experiment to prove that water is transparent.
Answer:
Take a beaker half-filled with clean water. Put a coin in the beaker of water.
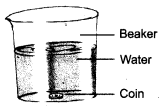
Place the beaker undisturbed for a few minutes where enough light is present. Now, observe the coin immersed in water from the top of the beaker. Are you able to see the coin? You — Beaker can clearly see the coin immersed in water. This proves that water is a transparent liquid.
Question 3.
Write an experiment to show that our palm is translucent.
Answer:
Cover the glass of a torch with your palm at a dark place. Switch on the torch and observe from the other side of palm. We see that the light of torch passes through palm but not clearly. This experiment shows that our palm becomes translucent when a strong beam of light passes through it.
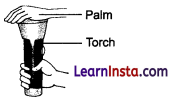
Experiment to show that our palm becomes translucent when light is passed.
Question 4.
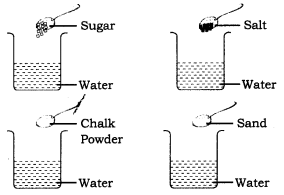
How can you show that some solids like sugar and salt are soluble in water whereas solids like chalk powder and sand are not soluble in water?
Answer:
Collect samples of sugar, salt, chalk powder and sand. Take four beakers. Fill each one of them about two-third with water. Add a teaspoonful of sugar to the first beaker, salt to the second, chalk powder to the third and sand to the fourth. Stir the contents of each beaker with a spoon/stirrer.
Wait for a few minutes and observe what happens to the substances added to the water.
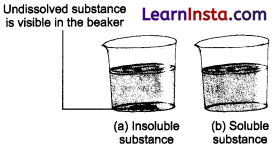
(a) The solid substance is visible in water and hence insoluble (chalk powder and sand),
(b) The solid is not visible in water and hence soluble (sugar and salt). Note down your observations in the following table.
Table: Mixing different solid materials in water
| Substance | Disappears in water/does not disappear in water |
| 1. Sugar | Disappears completely in water |
| 2. Salt | Disappears completely in water |
| 3. Chalk powder | Does not disappear in water |
| 4. Sand | Does not disappear in water |
Inference:
(i) Sugar and salt are soluble in water.
(i) Chalk powder and sand are insoluble in water.
Materials Around Us Class 6 Skill-Based Questions
Question 1.
Observe the following figure and answer the Questions.
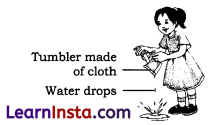
(i) Why should we not use a tumbler made of cloth?
(ii) What inference can we draw from it?
Answer:
(i) Tumbler made of cloth cannot hold water.
(ii) We should choose a material to make an object depending on its properties and the purpose for which the object is to be used.
Question 2.
Find out whether the following objects are transparent, translucent or opaque material. Write your observations in the tabular form. Spoon, glass, water, mirror, butter paper, CD, ceramic, plastic bottle, air, sand, rock, sugar solution.
Answer:
| Objects | Material |
| Spoon | Opaque |
| Glass | Transparent |
| Water | Transparent |
| Mirror | Opaque |
| Butter paper | Translucent |
| CD | Opaque |
| Ceramic | Opaque |
| Plastic bottle | Transparent |
| Air | Transparent |
| Sand | Opaque |
| Rock | Opaque |
| Sugar solution | Transparent |
![]()
Question 3.
Hold the listed objects with your hands.
Feel whether the objects are hard or soft. Find out the materials they are made up of. ‘ Write your observations in Table. Pillow, Cup, Stone, Chair, Sweater, Moistened clay
Answer:
| Object | Hard/Soft | Material |
| Pillow | Soft | Cotton, cloth |
| Cup | Hard | Ceramic |
| Stone | Hard | Mineral rock |
| Chair | Hard | Wood/Plastic |
| Sweater | Soft | Wool |
| Moistened clay | Soft | Wet clay |
Materials Around Us Class 6 Case-Based Questions
Question 1.
Collect samples of some solid substances such as sugar, salt, chalk powder, sand and sawdust. Take five glasses or beakers. Fill each one of them about two-third with water. Add a small amount (spoonful) of sugar to the first glass, salt to the second and similarly, add small amounts of the other substances into separate glasses. Stir the contents of each of them with a spoon. Wait for a few minutes. Observe what happens to the substances added to water. Note down your observations in the form of table.
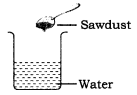
Answer:
Mixing different solid substances in water:
| Substance | Disappears in water/does not disappear in water |
| Salt | Disappears completely in water |
| Sugar | Disappears completely in water |
| Sand | Does not disappear |
| Chalk powder | Does not disappear |
| Sawdust | Does not disappear |
Question 2.
A Science teacher labelled three glass slides as P, Question and R. She painted slide Question with light blue colour, slide R with black colour and slide P was left as such.
Then she asked students to put the slide on a white paper having (X) mark on it.
(a) Through which slide students will not be able to see mark (X) ‘
(b) Identify the properties of slides P, Question and R.
Answer:
(a) As slide R was painted with black colour, it is opaque and students will not be able to see mark (X) through it.
(b) Slide P is transparent, Slide Q is translucent and slide R is opaque.