Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science with Solutions Set 4 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science Set 4 with Solutions
Time Allowed :3 Hours
Maximum Marks:80
General Instructions:
Read the following instructions carefully.
- This question paper consists of 39 questions in 5 sections.
- All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions. A student is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
- Section A consists of 20 objective-type questions carrying I mark each.
- Section B consists of 6 Very Short questions carrying 02 marks each, Answers to these questions should be in the range of 30 to 50 words.
- Section C consists of 7 Short Answer hipe questions carrying 03 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 50 to 80 words.
- Section D consists of 3 Long Answer type questions carrying 05 marks each. Answer to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
- Section E consists of 3 source-based/case-based units of assessment of 04 marks each with sub-parts.
Section – A
(Select and write the most appropriate option out of the four options given for each of the questions 1 – 20. There is no negative mark for incorrect response.)
Question 1.
Tina passes light beam through two liquid mixtures in separate glasses. The picture shows Tina’s observations.
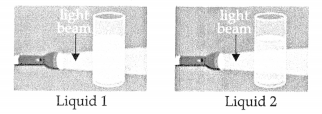
Based on the behaviour of the light beam what are liquids 1 and 2? [1]
| Liquid 1 | Liquid 2 |
| A. Solution | Colloid |
| B. Colloid | Suspension |
| C. Solution | Suspension |
| D. Suspension | Colloid |
Answer:
Option (C) is correct.
Explanation: Liquid 1 is solution as there are no partides visible and no scattering of light. liquid 2 is suspension as there is no scattering of light but small particles are visible in the liquid.
Question 2.
Which of the following is/are properties of gases? [1]
(A) Gases are compressible.
(B) Gases flow easily.
(C) Gases exert pressure on the walls of the gas containei:
(D) All of these.
Answer:
Option (D) is correct.
Explanation: Gases neither have a definite shape nor a definite volume. They are compressible. They exert pressure on the walls of the gas container due to the collision of molecules. They flow easily.
Question 3.
A mixture that has uniform composition throughout its mass is called: [1]
(A) heterogeneous
(B) homogeneous
(C) compound
(D) suspension
Answer:
Option(B)is correct.
Explanation: A mixture that has uniform composition throughout its mass is called a homogeneous mixture.
Question 4.
Which of the following correctly represents the electronic distribution in the Mg atom? [1]
(A) 3, 8, 1
(B) 2, 8, 2
(C) 1, 8, 3
(D) 8, 2, 2
Answer:
Option (B) is correct.
Explanation: Atomic number and the number of electrons in magnesium atom is 12. So, electronic configuration is 2, 8, 2 (because 12 = 2 + 8 + 2).
Question 5.
Ca(OH)2 is the formula for compound: [1]
(A) Calcium carbonate
(B) Calcium oxide
(C) Calcium hydroxide
(D) Carbon dioxide
Answer:
Option (C) is correct.
Explanation: Ca(OH)2 is the formula for calcium hydroxide.
Question 6.
The term used for heat absorbed during change of states is …………………. . [1]
(A) Heat of vaporization
(B) Heat of evaporation
(C) Heat of fusion
(D) Latent heat
Answer:
Option (D) is correct.
Explanation: Heat absorbed during a change of states is called latent heat.
Question 7.
Which of the following is suspension? [1]
(A) Milk
(B) Sugar in water
(C) Chalk powder in water
(D) Blood
Answer:
Option (C) is correct.
Explanation: Chalk powder in water is suspension, milk, and blood are colloids while sugar in water is a solution.
Question 8.
Name the plastid involved in conversion of a green brinjal to violet. [1]
(A) Leucoplast
(B) Chromoplast
(C) Chloroplast
(D) All of these
Answer:
Option (B) is correct.
Explanation: Chromoplast is involved in conversion of green brinjal to violet. Leucoplast is colourless while chloroplast gives green colour.
Question 9.
Which is not a function of epidermis?
(A) Protection from adverse condition
(B) Preventing entry of pathogen
(C) Conduction of water
(D) Transpiration
Answer:
Option (C) is correct.
Explanation: The main function of epidermis is to protect the plant from desiccation and infection. Stomata present in epidermis are the site for transpiration. Cuticle of epidermis helps to reduce water loss by evaporation from the plant surface and also helps in preventing the entry of pathogens.
Question 10.
Meristematic tissues in plants are: [1]
(A) Localised and permanent
(B) Not limited to certain regions
(C) Localised and dividing cells
(D) Growing in volume
Answer:
Option (C) is correct.
Explanation: Meristematic tissues consist of actively dividing cells and are present in the growing regions of plants, e.g., the tips of roots and stems.
Question 11.
Choose the wrong statement.[1]
(A) The nature of the matrix differs according to the function of the tissue.
(B) Fats are stored below the skin and in between the internal organs.
(C) Epithelial tissues have intercellular spaces between them.
(D) Cells of striated muscles are multinucleated and unbranched.
Answer:
Option (C) is correct.
Explanation: Epithelial tissues do not have intercellular spaces between them.
Question 12.
The muscles which perform voluntary action are [1]
(A) Skeletal muscles
(B) Smooth muscles
(C) Cardiac muscles
(D) All of these
Answer:
Option (A) is correct.
Explanation: Skeletal muscles consist of thousands of muscle fibers that are controlled by will i.e. they are voluntary in action.
Question 13.
A passenger in a moving train tosses a coin which falls behind him. It means that the motion of the train is: [1]
(A) Accelerated
(B) Uniform
(C) Retarded
(D) Along circular tracks.
Answer:
Option (A) is correct.
Explanation: If the coin falls behind the passenger that means the train is accelerated. When the coin is tossed it has same velocity as that of train but during the time it is in air its velocity becomes less than that of train (because the train is accelerated), so it falls behind the passenger.
Question 14.
The inertia of an object tends to cause the object: [1]
(A) To increase its speed
(B) To decrease its speed
(C) To resist any change in its state of motion
(D) To decelerate due to friction.
Answer:
Option (C) is correct.
Explanation: The inertia of an object tends to cause the object to resist any change in its state of rest or motion.
Question 15.
Which one of the following species of honey bee is an Italian species? [1]
(A) Apis dorsafa
(B) Apis florea
(C) Apis cerana indica
(D) Apis mellifera
Answer:
Option (D) is correct.
Explanation: Apis mellifera is an Italian honey bee.
Question 16.
The decomposition of organic matter using worms like earthworms to obtain manure is called [1]
(A) Green manure
(B) Fertilisers
(C) Vermicomposting
(D) Organic farming
Answer:
Option (C) is correct.
Explanation: Organic matter are decomposed by earthworms and converted into manure she help to increase the fertility of soil.
Assertion-Reason Based Questions
Question No. 17 to 20 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(A) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(B) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(C) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(D) (A) is false but (R) is true.
Question 17.
Assertion (A): Valency 0 fluorine is one. [1]
Reason (R): Fluorine atom contains seven valence electrons.
Answer:
Option (A) is correct
Explanation: Seven electrons are present in the outermost shell of fluorine atom. To attain stable configuration, fluorine atom gains one electron.
Question 18.
Assertion (A): Bark of trees are impervious to gases and water.
Reason (R): Cells of bark have suberin in their walls. [1]
Answer:
Option (A) is correct.
Explanation: Cells of bark are dead and compactly arranged without intercellular spaces. They have a chemical called suberin in their walls that make them impervious to gases and water.
Question 19.
Assertion (A): Sudden application of brakes in a moving car may cause injury.
Reason (R): Inertia is the tendency of an oblect to keep moving or being at rest when undisturbed. [1]
Answer:
Option (B) is correct
Explanation: When we are in a moving car, our body is also moving with the velocity of car. Sudden brake application stops the car as well as lower body portion while upper body portion is still in motion that causes injury.
Question 20.
Assertion (A): Layers are given more of vitamin A and vitamin K.
Reason (R): Layers are raised for eggs. [1]
Answer:
Option (A) is correct.
Explanation: [.ayers are given more vitamin A and K. Layer birds are raised for eggs.
Section – B
(Question No. 21 to 26 are very short answer questions)
Question 21.
Illustrate three states of matter with a schematic diagram. [2]
Answer:
The three states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas.
Question 22.
List two characteristics of cork. Name the chemical present in them and mention its role. [2]
Answer:
- Cells of cork are dead and compactly arranged without intercellular spaces.
- They also have a chemical called suberin in their walls which makes them impervious to gases and water.
Question 23.
What is the distinction of RBCs? What is the lifespan of human RBCs? [2]
OR
Identify the cell organelle which is known as the powerhouse of the cell. State reason.
Answer:
Transportation of oxygen and carbon dioxide and maintenance of pH constancy in blood are the functions of RBCs. Life span of human RBCs is about 120 days.
OR
Mitochondria are powerhouse of the cell. Energy is released by mitochondria in the form of ATP.
Question 24.
The distance moved by a student at different intervals of time, while walking to school, is given in the table below. A distance-time graph for the motion of the student is also shown. Study the table and the graph and choose correct option to answer questions given below:
| Time from the starting point (s) | 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 |
| Distance moved (m) | 0 | 15 | 30 | 45 | 30 | 60 |
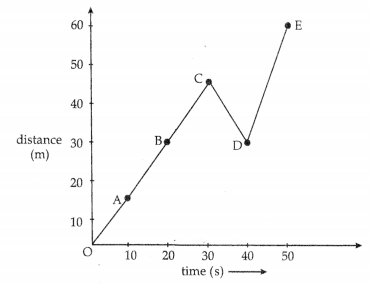
(a) Name the physical quantities denoted by the slope of the distance-time graph.
(b) What does the shape of the graph suggest about the tvp of motion? [2]
Answer:
(a) Speed
(b) The graph indicates non-uniform motion.
Question 25.
What type of motion is represented by each of the following graphs? [2]
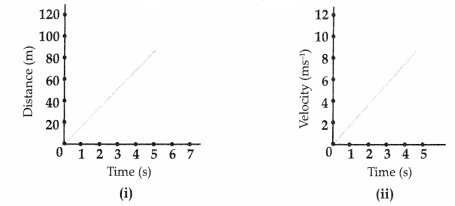
OR
What is the source of centripetal force that a planet requires to revolve around the Sun? On what factors does that force depend?
Answer:
- Uniform motion.
- Uniform accelerated motion.
OR
Gravitational force. This force depends on the product of the masses of the planet and the Sun and the inverse of the square of the distance between them.
Question 26.
Observe the diagram and answer the questions:
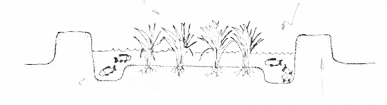
(a) What is shown in the picture?
(b) Where do we find such a kind of fish culture? [2]
Answer:
(a) Composite fish culture is a process of growing different types of fish in the same pond.
(b) It is done in combination with rice crops where the fish are grown in the water in paddy fields.
Section – C
(Question No. 27 to 33 are short answer questions)
Question 27.
(a) Define atomicity.
(b) Name the elements whose atomicity is:
(i) Tetra atomic
(ii) Monoatomic
(c) State the number of atoms present in each of the following chemical species:
(i) CO3-2
(ii) HNO3
Answer:
(a) The number of atoms constituting a molecule is known as atomicity.
(b) (i) P4 (ii) Ar
(c) (i) 4 (ii) 5
Question 28.
While boiling the water, a student observed that temperature remains constant at 100° C till whole of water vaporises. Explain. [3]
OR
Write the chemical formula of the following compounds:
(a) Iron (III) chloride
(b) Magnesium hydrogen carbonate
(c) Sodium phosphate
Answer:
This is because the heat supplied is absorbed by the water particles and this heat increases their kinetic energy Thus, because of an increase in kinetic energy, the bond between the water particles are cut down and they move more freely, compared to water.
Hence, they become gas. Thus, the temperature remains constant even though heat is supplied continuously to the water.
OR
(a) FeCl3
(b) Mg(HCO3)2
(c) Na3PO4
Question 29.
Give differences between cytoplasm and nucleoplasm. [3]
Answer:
Differencesbetweencytoplasm and nudeoplasm:
| Cytoplasm | Nucleoplasm |
| (i) Cytoplasm is the protoplasm which lies outside the nucleus. i.e., between the nudeus and the cell membrane. | It is the part of protoplasm that lies inside the nucleus. |
| (ii) It is a semi-fluid jelly-like substance. | It is transparent. |
| (iii) It contains various organdies and inclusions. | It is a colloidal substance having similar composition to cytoplasm but contains more of nucleotides. |
| (iv) It contains a number of inorganic substances forming clear true solution as well as organic substances lipids, protein, and carbohydrates. | It contains chromatin material. |
Question 30.
‘write two distinguishing features between the muscles present in the alimentary canal and limbs of man. Drai labelled diagrams of the two kinds of muscles. [3]
Answer:
Alimentary canal: smooth muscle-spindle shaped, long pointed ends, uninucleate, involuntary, etc.
Limbs: Striated-muscle, cylindrical, unbranched, voluntary, multinucleate.
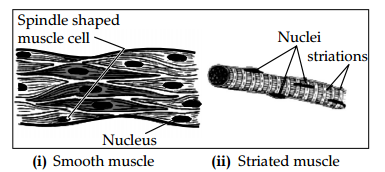
Question 31.
A ball thrown up vertically returns to the thrower after 6 seconds. Find:
(a) The velocity with which it was thrown up.
(b) The maximum height it reaches.
(c) Its position after 4 seconds. [3]
Answer:
(a) Time of ascent = Time of descent
So, to attain the maximum height ball takes 3
ν =0, g=-9.8m/s2
ν = u + gt
0 = u + (-9.8 × 3)
u = 9.8 × 3 = 29.4 m/s
The velocity with which it is thrown is 29.4 m/s.
(b) u = 29 m/s, v’ = 0, g = -9.8 m/s2, t = 3s
h = ut + 1/2gt2
=29.4 × 3 + 1/2 × (-9.8) × (3)2
= 88.2 – 44.1
=44.1 m
Maximum height it reaches is 44.1 meters.
(c) s = ut+1/2 gt2
= 29.4 × 4- 1.2 × 9.8 × (4)2
= 117.6 – 78.4 = 39.2 m
Ball is 39.2 m above the ground after 4 seconds.
Question 32.
State the universal law of gravitation. Mention four phenomena which can be explained by this law. [3]
Answer:
The universal law of gravitation states that the force of attraction between two objects is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Four phenomena which can be explained by this law are:
- The force that binds us to Earth.
- The motion of the Moon around the Earth.
- The motion of planets around the Sun.
- The tides due to the Moon and the Sun.
Question 33.
A person holds a bundle of hay over his head for 30 minutes and gets tired. Has he done some work or not? Justify your answer. [3]
Answer:
The force applied by the person on the bundle is zero, although the weight of the bundle is acting on the person. Here the person gets tired because of muscular fatigue. There is no displacement in the bundle of hay. So, work done by the person on the bundle is zero.
Section – D
(Question No. 34 to 36 are long answer questions)
Question 34.
(a) Write postulates of Thomson’s model of an atom with diagram.
(b) What were the limitations of this model? [5]
OR
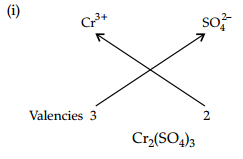
(a) Define the formula unit mass. Calculate the formula unit mass of NaCl, (Atomic mass or Na = 23 u, Li = 35.5 u)
(b) Write the formula of the compounds formed by the following ions.
(i) Cr3+ and SO42-
(ii) Pb2+ and NO3–
Answer:
(a) Postulates of Thomson’s model of an atom are:
- An atom is a uniform sphere of positive charges (due to presence of protons) as well as negative charges (due to presence of electrons), which are embedded in it. This model is called watermelon or plum pudding model’.
- An atom, as a whole, is electrically neutral because the negative and positive charges are equal in magnitude.
(b) limitations of Thomson’s model of the atom were:
- The model failed to explain how protons and electrons could be arranged in an atom so close to each other.
- It also failed to explain an atom’s stability.
- The theory did not mention anything about the nucleus of an atom.
OR
(a) The sum of the atomic masses of all atoms in a formula unit of a compound is called formula unit mass.
NaCl = (1 × 23) + (1 × 35.5)
=23 + 35.5
= 58.5u
(b)
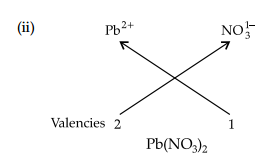
(i) Cr3+ and SO42-
(ii) Pb2+ and NO3–
Question 35.
Name the following tissues:
(a) The connective tissue found between the skin and muscles.
(b) The tissue which connects two hones.
(c) The epithelia! tissue which forms the lining of the kidney tubules.
(d) The tissue which is present in the veins of leaves.
(e) The simple permanent tissue which provides flexibility in plants. [5]
OR
(a) Why do sclerenchyma cells have a narrow lumen?
(b) Where are these tissues present and why?
(c) Explain the process of formation of cork.
Answer:
(a) Areolar,
(b) ligament,
(c) Cuboidal epithelium,
(d) Sderenchyma
(e) Collenchyma
OR
(a) Due to deposition of lignin.
(b) In stems around vascular bundles, in veins of leaves, and in hard coverings of seeds and nuts. It makes the plant hard, and stiff and provides strength.
(c) The strip of the secondary meristem replaces the epidermis of the stem. Cells are cut off on the outside from the cork.
Question 36.
(a) The following figure shows a wave of frequency 50 Hz. Find from graph:
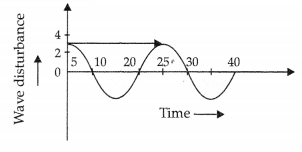
(i) The amplitude
(ii) The wavelength
(iii) The velocity of the wave
(b) Why human can not hear some sounds which are heard by other animals? [5]
OR
Four men lift a 250 kg box to a height of 1 m and hold it without raising or lowering it.
(a) How much work is done by the men in lifting the box?
(b) How much work do they do in just holding it?
(c) Why do they get tired while holding it? (g = 10 ms-2)
Answer:
(a)
(i) Amplitude is maximum displacement = 3 cm.
(ii) Wavelength (l) = Distance between two crests = 25-5 = 20 cm. = 0.2 m
(iii) Velocity = Frequency × wavelength = 50 × 0.2 = 10m/s
(b) There is a range of sound frequencies which can be heard by human ear. Such sounds are called audible sounds and the frequency range is 20 hz to 20 kHz. Sound waves with frequencies lower than 20 Hz are known as Infrasound. But sounds of such low frequency are too low for humans to hear, Animals such as whales, elephants and other animals can
detect infra sounds and use it to communicate.
Sounds having frequency more than 20,000 Hz or 20 kHz are called ultrasonic sound. As this is above the normal hearing range for humans, we cannot hear ultrasonic sound.
OR
(a) Mass, m = 250 kg Height, h = 1 m
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 10 m/s2
Work done by the man in lifting the box = Potential energy of box
W = nigh
Put the values, W = 250 × 1 × 10 = 2500 J
(b) Work done will be zero because the box does not move. So, the displacement is zero that’s why work done is zero.
(c) In holding the box, men are applying a force which is opposite and equal to the gravitational force acting on the box. While applying the force, muscular effort is involved. So, they feel tired.
Section – E
(Question No. 37 to 39 are case-based! data-based questions with 2 to 3 short sub-parts. Internal choice is provided in one of these sub-parts.)
Question 37.
The percentage of three elements-calcium, carbon, and oxygen in a sample of calcium carbonate is given as:
| Element | Percentage in calcium carbonate |
| Calcium | 40% |
| Carbon | 12% |
| Oxygen | 48% |
If the law of constant proportion is true,
(a) What weight of calcium will be present in 1.5 gm of another sample of calcium carbonate? (Atomic mass of Ca = 40u,C = 12u,O = 16u)
(b) What weight of carbon will be present in 1.5gm of another sample of calcium carbonate?
(c) What weight of oxygen will be present in 1.5gm of another sample of calcium carbonate? State the formula for calcium carbonate. [4]
OR
State law of constant proportion.
Answer:
(a) Mass of calcium in 1.5 gm of sample = \(\frac{40}{100}\) × 1.5 = 0.6 gm
(b) Mass of carbon in 1.5 gm of sample = \(\frac{12}{100}\) × 1.5 = 0.18 gm
(c) Mass of oxygen in 1.5 gm of sample = \(\frac{48}{100}\) × 1.5=0.72gm
Formula for calcium carbonate: CaCO3
OR
Law of constant proportion: In a chemical substance, the elements are always present in a definite proportion by mass.
Question 38.
The diagram of a cell with some of its organdies is given below.
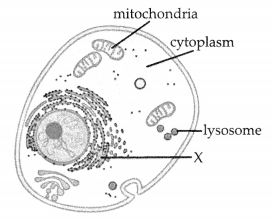
(a) What does X represent in the diagram?
(b) identify the type of cell shown in the diagram.
(c) Which cell organelles found only in a plant cell are not shown in the diagram?
OR
The inner membrane of the mitochondria is folded into many linger-like projections. Explain what would happen if the inner membrane was not folded? [4]
Answer:
(a) Endoplasmic reticulum
(b) Animal cell
(c) Cell wall and chioroplast.
OR
Surface area will decrease so less energy will be produced.
Question 39.
The figure below shows the motion of a car along a straight path. It then moves back to the school and stops. The car moves from house to school and school to library and then back to school from library.
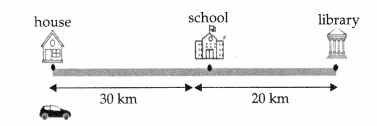
(a) What is the net displacement of the car?
(b) What is the total distance traveled by the car?
(c) The graph below shows how the car travelled from house to school.
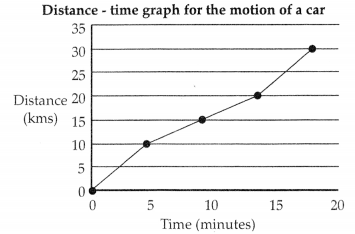
Did the car move with uniform motion from house to school? Explain your answer. [4]
OR
When is a both’ said to he in uniform motion?
Answer:
(a) Displacement = Distance between intial position (house) And final position (school) = 30 km
(b) Total distance travelled = Distance between home to school + Distance between school to library + Distance between library to school 30+20+20 = 70km
(c) The car did not travel in a uniform motion as it moved with a different speed between 10 km and 20 km of its path.
OR
A body is said to be in uniform motion if it travels equal distances in equal intervals of time.